The Multilingual Mind: A Survey of Multilingual Reasoning in Language Models
链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2502.09457
1. Motivation
近年来,大型语言模型(LLMs)在自然语言处理领域取得了显著进展,尤其在语言生成、翻译和总结方面表现出色。然而,这些模型在处理多语言推理任务时仍面临诸多挑战,如跨语言对齐问题、训练数据中的偏差以及低资源语言的资源匮乏。
文章提供了对LMs多语言推理的首次深入讨论,提供了一个系统的概述,概述了将语言模型应用于跨不同语言推理的挑战,动机和基础方面内容。
2. Contribution
1) Comprehensive Overview: We systematically review existing methods that leverage LLMs for multilingual reasoning, outlining challenges, motivations, and foundational aspects of applying reasoning to diverse languages.
2) Training Corpora and Evaluation Benchmarks: We analyze the strengths, limitations, and suitability of existing multilingual corpora and evaluation benchmarks in assessing the reasoning capabilities of LLMs for diverse linguistic tasks.
3) Analysis of State-of-the-Art Methods: We evaluate the performance of various state-of-the-art (SOTA)techniques, including CoT prompting, instruction tuning, and cross-lingual adaptations, on multilingual reasoning benchmark tasks.
4) Future Research Directions: We identify key challenges and provide actionable insights for advancing multilingual reasoning, focusing on adaptive alignment strategies, culturally aware benchmarks, and methods for low-resource languages.
3. Multilingual Reasoning in LLMs
3.1. Preliminaries
- Large Language Models (LLMs):概率预测
- Reasoning:推理策略
-
- a) Deductive Reasoning 演绎推理
- b) Inductive Reasoning 归纳推理
- c) Abductive Reasoning 溯因推理
- d) Analogical Reasoning 类比推理
- e) Commonsense Reasoning 常识推理
3.2. Desiderata(期望) in Multilingual Reasoning
1. Consistency :结论一致性
2. Adaptability :对于低资源语言,模型应能够通过跨语言迁移从高资源语言中学习,并进行稳健的推理
3. Cultural Contextualization:推理应考虑每种语言固有的文化背景和语境差异
4. Cross-Lingual Alignment:模型需要在不同语言之间对齐推理过程,确保推理结果的一致性和连贯性。
4. Multilingual Reasoning Datasets
4.1. Training Corpus
- 数学推理:如GSM8K和OpenMathQA,用于提升数学推理能力。
- 微调:sPhinX (translate instruction-response pairs into 50 languages for fine-tuning.)
- 逻辑和编码推理:如XCSQA和MultiNLI。
- 多语言翻译:如OPUS、FLORES-200和LegoMT,用于将多语言表示映射到模型的表示空间。
- 跨语言迁移:如XCOPA,展示了多语言预训练和零样本微调的不足。
4.2. Evaluation Benchmark
- 领域和任务覆盖:多语言推理涉及多个领域,每个领域都有其复杂性和需求。当前的基准主要集中在数学、逻辑和常识推理领域,而科学、视觉、表格推理等领域则相对较少。
- 语言覆盖:当前的基准主要覆盖高资源语言,如中文、英语、法语和德语。低资源语言和语言类型学上差异较大的语言(如卡纳达语、古吉拉特语和克丘亚语)的代表性不足。基于语言,当前的基准可以主要分为
-
- 人类语言:Flores-200的数据集尝试平衡高资源和低资源语言,但无法实现全面的覆盖范围
- 编码语言:BBH-Hard, CRUXEval, and TCC
5. Methods
5.1. Representation Alignment
确保不同语言的语义表示在嵌入空间(Embedding)中保持一致,从而减少跨语言推理中的不一致性。Representation alignment ensures that equivalent concepts share similar embeddings, reducing inconsistencies in cross-lingual inference, essential for reasoning and multilingual generalization
- 多语言对比学习(Multilingual Contrastive Learning):通过将翻译对作为正样本,拉近它们的嵌入向量,从而弥合不同语言之间的表示差距。
- 多语言对齐学习(Multilingual Alignment Learning):通过外部多语言模型增强推理能力,将多语言编码器与LLMs对齐。
- 多语言组合学习(Multilingual Compositional Learning):通过组合多种语言中等价的词嵌入来构建组合表示。constructs compositional representations by combining equivalent token embeddings across multiple languages
5.2. Finetuning
利用cross-lingual数据和任务来微调模型,以增强推理和理解。
- 代码切换微调(Code-Switched Fine-tuning):LinguaLIFT:code-switched fine-tuning along with language alignment layers.
- 问题对齐微调(QuestionAlign):QuestionAlign takes a step further by aligning questions and responses in multiple languages, thereby enhancing cross-lingual understanding and consistency in reasoning.通过在多种语言中对齐问题和回答,增强跨语言推理的一致性。
- 选择性微调:仅微调对多语言理解至关重要的特定层,降低计算需求。SLAM [Fan et al., 2025] introduces a more parameterefficient strategy, which selectively tunes only layers critical for multilingual comprehension, significantly lowering the computational demands while still maintaining or even enhancing the model’s reasoning capabilities.
- 翻译感知微调(Translation-Aware Fine-tuning):通过翻译对齐不同语言,提升模型在跨语言任务中的表现。TransLLM, for instance, focuses on translation-aware fine-tuning to align different languages, thereby improving the model’s ability to perform reasoning across languages. This method not only enhances language understanding but also adapts the model for various cross-lingual tasks.
- 推理聚焦微调(Reasoning-Focused Fine-tuning):使用专门针对推理任务的数据集(如mCoT-MATH)进行微调,提升多语言逻辑推理能力。The Multilingual Chain-of-Thought (mCoT) Instruction Tuning method utilizes a dataset specifically curated for reasoning across languages (mCoT-MATH) and combines CoT reasoning with instruction tuning to boost consistency and logical problem-solving
- preference-based techniques to align reasoning outputs across languages emphasizes the use of language imbalance as a reward signal in models like DPO (Direct Preference Optimization) and PPO (Proximal Policy Optimization).
- curriculum-based and retriever-based fine-tuning techniques to enhance multilingual reasoning
5.3. Prompting
通过特定的提示策略,引导模型动态适应不同语言,解决数据不平衡问题,增强推理的跨语言一致性。
- Direct Multilingual Input Prompting:模型直接处理多种语言的输入,保留原始语言的细微差别。
- Translation-Based Prompting:将多语言输入翻译成一种枢纽语言(如英语)进行处理,然后将结果翻译回目标语言。
- diverse CoT with Negative Rationales (d-CoT-nR):通过引入正确和错误的推理路径来优化多语言推理能力。
5.4. Model Editing
通过修改模型存储的信息,实现对特定输入输出对的更新,而不影响模型在其他输入上的性能。model editing strategies update pre-trained models for specific input-output pairs without retraining them and impacting the baseline model performance on other inputs.
- 多语言精确编辑(Multilingual Precision Editing):对模型知识进行高度特定的更新,确保对不相关信息的影响最小化。Multilingual knowledge Editing with neuronMasked Low-Rank Adaptation (MEMLA) [Xie et al., 2024] enhances multilingual reasoning by leveraging neuron-masked LoRA-based edits to integrate knowledge across languages and improve multi-hop reasoning capabilities.
- 多语言翻译后编辑(Multilingual Translation Post-editing):通过纠正多语言输出中的错误,提升语义对齐和翻译质量。where we can enhance multilingual reasoning by incorporating auxiliary translations into the post-editing process, enabling LLMs to improve semantic alignment and translation quality across languages
6. Evaluation Metrics and Benchmarks
6.1. Metrics
- Accuracy-Based Metrics
-
- General Accuracy:衡量模型在所有样本上输出正确的比例。
- Zero-Shot Accuracy:评估模型在未见过的任务或类别上的表现,不进行微调。
- Reasoning and Consistency Metrics
-
- Reasoning Accuracy:评估模型在逻辑和多步推理任务中的正确性。
- Path Consistency:衡量链式思考(CoT)提示中推理步骤之间的连贯性。
- Translation and Cross-Lingual Metrics
-
- Translation Success Rate, TSR:衡量翻译的准确性和语义保持,计算准确翻译与总翻译的比例。
- Cross-Lingual Consistency:评估逻辑等价的陈述在不同语言中是否产生一致的推理输出。
- Perplexity and Alignment Metrics
-
- Perplexity-Based Alignment, Palign:where P (xi) is the model’s probability of predicting token xi. Lower perplexity indicates better alignment
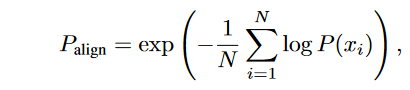
-
- Semantic Alignment Score (Salign):measures the cosine similarity between multilingual sentence embeddings
Salign=El⋅Et/∥El∥∥Et∥
6.2. Performance on Benchmarks
四个基准测试:
- MGSM:包含250个翻译成十种不同语言的数学问题,用于测试多语言算术推理能力。
- MSVAMP:包含10,000个跨十种语言的数学问题,用于评估模型在多语言数学推理中的泛化能力。
- xCSQA:包含12,247个翻译成15种语言的多项选择题,用于评估模型的跨语言常识推理能力。
- xNLI:包含15种语言(包括低资源语言)的句子推理任务,用于评估跨语言句子推理能力。
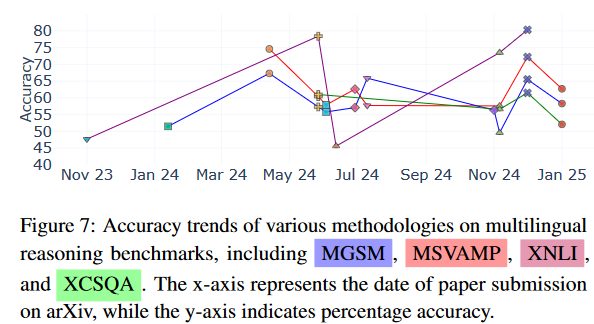
We find that advanced preference optimization (MAPO) achieves much stronger performance than CoT-based fine-tuning, suggesting advanced fine-tuning techniques are a better direction to beat the current best in this benchmark.
7. Take-aways:
- 了解了multilingual reasoning的概念,基本方法,挑战,数据集,benchmark等。
- 总结了一些sota方法的论文,可以方便查阅。
- 对方法分析提出了发现了RL的效果较好。 reward signals can be effectively transferred across languages, paving the way for post-training RL methods that improve reasoning in low-resource languages.






















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








