🌞欢迎来到深度学习实战的世界
🌈博客主页:卿云阁💌欢迎关注🎉点赞👍收藏⭐️留言📝
🌟本文由卿云阁原创!
📆首发时间:🌹2025年2月7日🌹
✉️希望可以和大家一起完成进阶之路!
🙏作者水平很有限,如果发现错误,请留言轰炸哦!万分感谢!
目录

RNN
介绍
RNN(Recurrent Neural Network) 是一种用于处理序列数据的神经网络模型,特别适用于处理时间序列、语音、文本等具有顺序关系的数据。
简单的神经网络都是水平方向的延申,RNN可以关联不同的时刻,RNN的输出不仅取决于当前时刻的输出还取决于上一时刻隐藏层的输出。(神经网络具有某种记忆的能力)

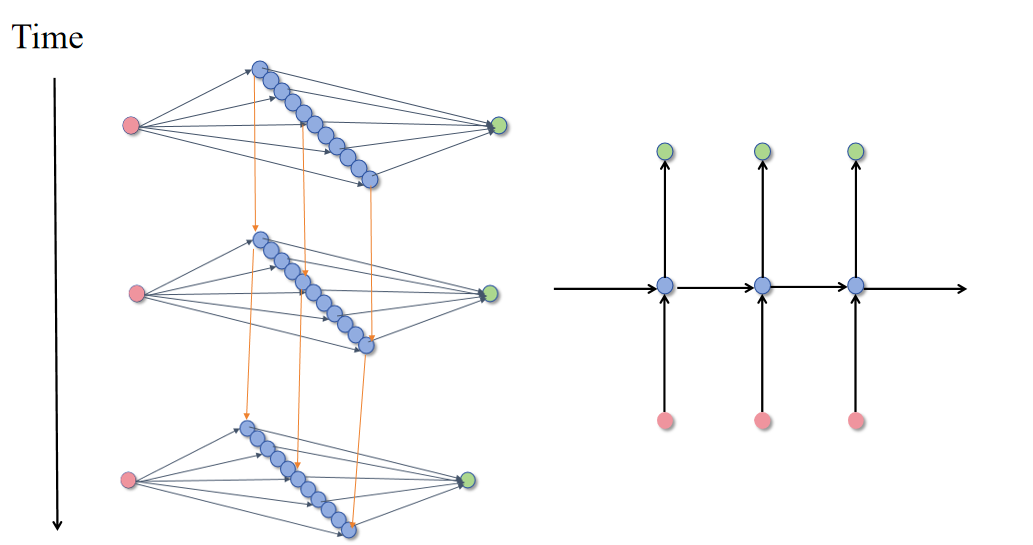

举个例子(使用RNN进行情感分类)


手算模拟

代码实现
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
# 设置随机种子保证结果可复现
torch.manual_seed(42)
# 定义超参数
input_size = 1 # 输入特征数 (单个数)
hidden_size = 2 # 隐藏层大小 (两个神经元)
num_layers = 1 # RNN 层数
seq_length = 3 # 序列长度 (3 个时间步)
batch_size = 1 # 只有 1 个样本
# 创建 RNN
rnn = nn.RNN(input_size, hidden_size, num_layers, batch_first=True)
# 人工设定权重和偏置(方便计算)
with torch.no_grad():
rnn.weight_ih_l0.copy_(torch.tensor([[0.5], [-0.5]], dtype=torch.float32)) # 输入到隐藏层的权重
rnn.weight_hh_l0.copy_(torch.tensor([[0.3, -0.3], [0.6, -0.6]], dtype=torch.float32)) # 隐藏层到隐藏层
rnn.bias_ih_l0.zero_() # 输入层偏置设为 0
rnn.bias_hh_l0.zero_() # 隐藏层偏置设为 0
# 输入数据 (时间步数为 3)
X = torch.tensor([[[1.0], [2.0], [3.0]]]) # 形状 (batch_size, seq_length, input_size)
# 初始化隐藏状态 (全零)
h0 = torch.zeros(num_layers, batch_size, hidden_size)
# 进行前向传播
out, hn = rnn(X, h0)
# 打印输出
print("隐藏状态 Ht (每个时间步):\n", out.detach().numpy()) # 所有时间步的隐藏状态
print("\n最终隐藏状态 hn:\n", hn.detach().numpy()) # 最后一个时间步的隐藏状态

LSTM
介绍

LSTM(Long Short-Term Memory) 是一种特殊类型的循环神经网络(RNN),旨在解决传统 RNN 在处理长序列时面临的梯度消失问题。LSTM 引入了特殊的结构(称为“门”)来控制信息的流动,能够更好地捕捉长期依赖关系。(简单的RNN在信息记忆方面效果不好)
与RNN相比,除了输入和前一时刻还要包括当前时刻(日记的信息Ct),包含了,两个更细致的操作,删除旧日记,增添新日记,f1函数就像是一个橡皮擦,根据昨天的记忆ht-1和今天的输入Xt,决定要修改日记中的那些记录。 f2函数就像是一个铅笔,根据昨天的记忆ht-1和今天的输入Xt,增加日记中的那些记录。f1和 f2进行运算得到新的日记啦。LSTM 就像延缓记忆衰退的良药, 可以带来更好的结果。
输入门(Input Gate):决定当前输入的哪部分信息应该被存储到“记忆单元”(Cell State)中。
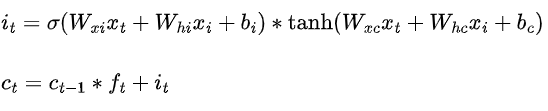
遗忘门(Forget Gate):决定前一时刻的“记忆单元”中哪些信息应该被遗忘。
![]()
输出门(Output Gate):决定记忆单元中的信息在当前时间步输出时的贡献。
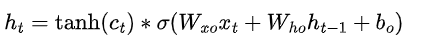
手动模拟
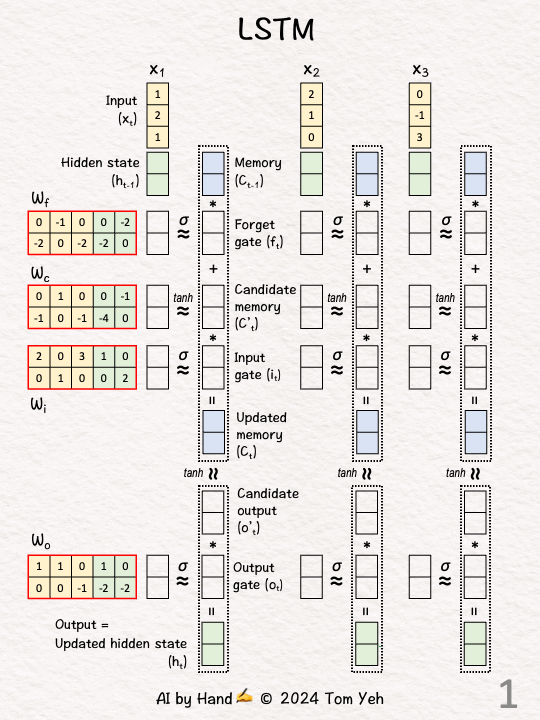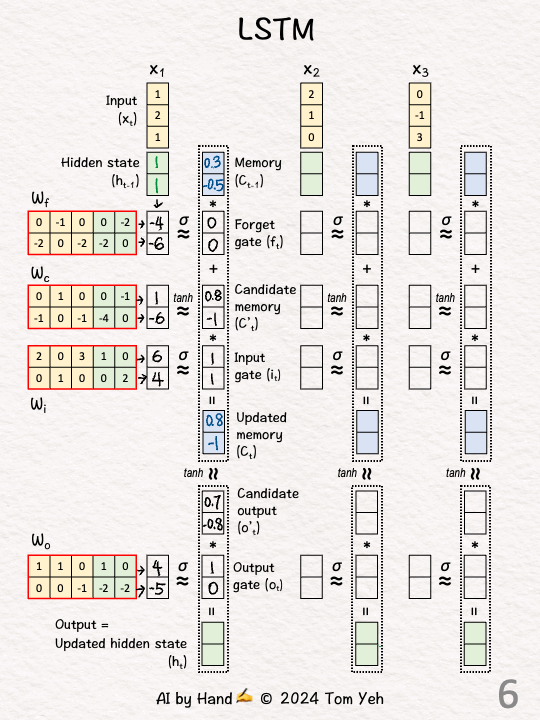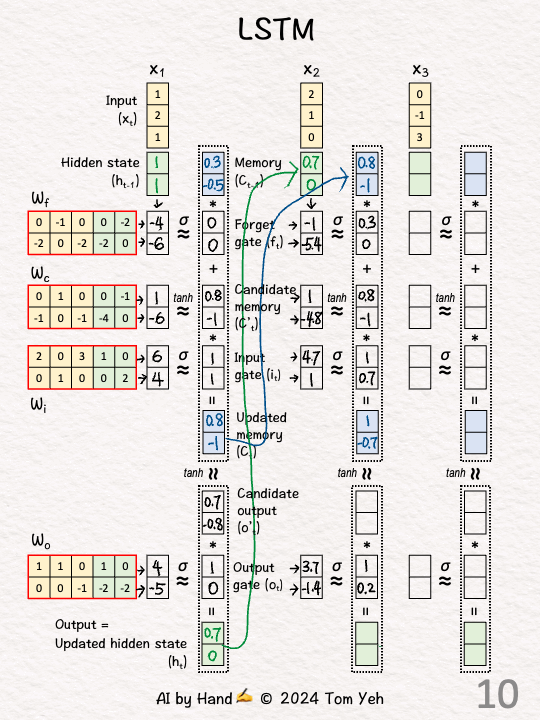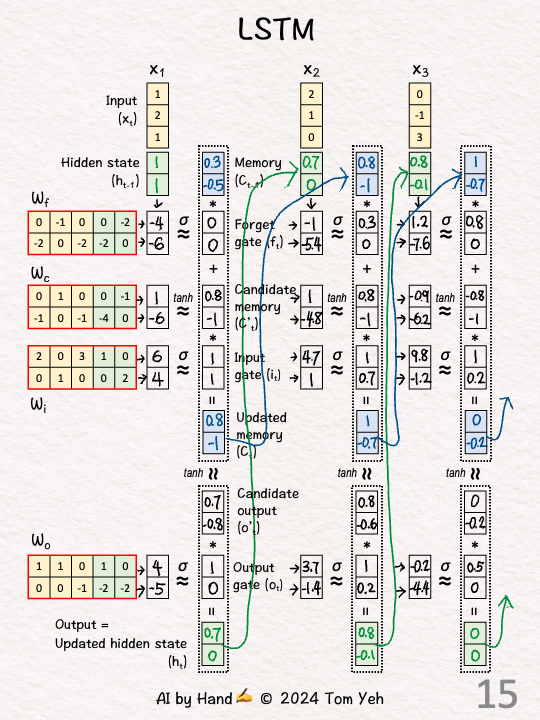
代码实现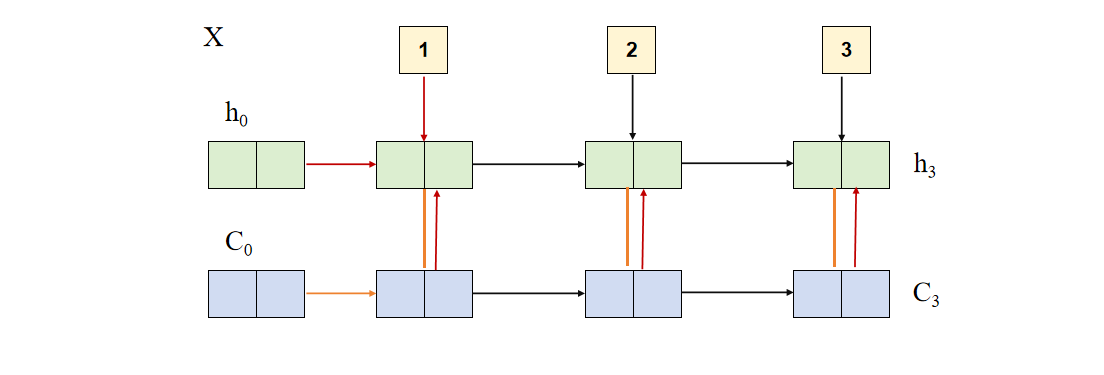
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
# 设置随机种子保证结果可复现
torch.manual_seed(42)
# 定义超参数
input_size = 1 # 输入特征数 (每个时间步只有 1 个输入)
hidden_size = 2 # 隐藏层大小 (两个神经元)
num_layers = 1 # LSTM 层数
seq_length = 3 # 序列长度 (3 个时间步)
batch_size = 1 # 只有 1 个样本
# 创建 LSTM
lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size, hidden_size, num_layers, batch_first=True)
# 输入数据 (时间步数为 3)
X = torch.tensor([[[1.0], [2.0], [3.0]]]) # 形状 (batch_size, seq_length, input_size)
# 初始化隐藏状态和细胞状态
h0 = torch.zeros(num_layers, batch_size, hidden_size) # 隐藏状态
c0 = torch.zeros(num_layers, batch_size, hidden_size) # 细胞状态
# 进行前向传播
out, (hn, cn) = lstm(X, (h0, c0))
# 打印输出
print("隐藏状态 Ht (每个时间步):\n", out.detach().numpy()) # 所有时间步的隐藏状态
print("\n最终隐藏状态 hn:\n", hn.detach().numpy()) # 最后一个时间步的隐藏状态
print("\n最终细胞状态 cn:\n", cn.detach().numpy()) # 最后一个时间步的细胞状态
实战
本项目的目标是实现一个基于 Seq2Seq(Sequence-to-Sequence) 和 LSTM(Long Short-Term Memory) 的机器翻译模型。它的功能是将 中文句子 转换为 英文句子,类似于翻译任务的基本实现。例如:
- 输入(中文):"我 很 好"
- 输出(英文):"I am fine"
-
数据预处理
- 构建 中英词典(词汇表),将汉字和单词转换为 索引 形式。
- 句子用 数值索引 表示
-
构建 Seq2Seq 模型
- Encoder(编码器):采用 双层 LSTM,用于读取输入句子,并将其转换为一个 上下文向量。
- Decoder(解码器):另一组 LSTM,接收编码器的输出,并逐步 生成目标句子。
- 注意力机制(可选):可以加入 Attention 机制,让解码器在翻译时关注不同的输入单词。
-
模型训练
- 采用 交叉熵损失(CrossEntropyLoss) 作为损失函数。
- 使用 Adam 优化器 进行梯度更新。
-
推理(Inference)
- 给定一个新的中文输入句子,编码器提取语义信息,解码器逐步生成英文单词,最终得到翻译结果。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import torch.nn.functional as F
source_vocab = {"我": 0, "很": 1, "好": 2, "不": 3, "你": 4}
target_vocab = {"Bos": 0, "I": 1, "am": 2, "fine": 3, "you": 4, "very": 5, "Eos": 6}
class Encoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, emb_dim, hidden_dim, num_layers):
super(Encoder, self).__init__()
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(input_dim, emb_dim)
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(emb_dim, hidden_dim, num_layers, batch_first=True)
def forward(self, src):
embedded = self.embedding(src) # (batch_size, seq_length, emb_dim)
outputs, (hidden, cell) = self.lstm(embedded) # (batch_size, seq_length, hidden_dim)
return hidden, cell # 返回最终的隐藏状态和细胞状态
class Decoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, output_dim, emb_dim, hidden_dim, num_layers):
super(Decoder, self).__init__()
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(output_dim, emb_dim)
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(emb_dim, hidden_dim, num_layers, batch_first=True)
self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, output_dim) # 预测下一个词的全连接层
def forward(self, input, hidden, cell):
input = input.unsqueeze(1) # (batch_size, 1) → (batch_size, 1, emb_dim)
embedded = self.embedding(input)
output, (hidden, cell) = self.lstm(embedded, (hidden, cell))
prediction = self.fc(output.squeeze(1)) # (batch_size, output_dim)
return prediction, hidden, cell
class Seq2Seq(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, encoder, decoder, device):
super(Seq2Seq, self).__init__()
self.encoder = encoder
self.decoder = decoder
self.device = device
def forward(self, src, trg, teacher_forcing_ratio=0.5):
batch_size = src.shape[0]
trg_len = trg.shape[1]
trg_vocab_size = len(target_vocab)
outputs = torch.zeros(batch_size, trg_len, trg_vocab_size).to(self.device)
hidden, cell = self.encoder(src)
input = trg[:, 0] # 解码器的第一个输入是 <Bos>
for t in range(1, trg_len):
output, hidden, cell = self.decoder(input, hidden, cell)
outputs[:, t] = output
top1 = output.argmax(1) # 选择最高概率的词
input = trg[:, t] if torch.rand(1).item() < teacher_forcing_ratio else top1
return outputs
# 词表大小
input_dim = len(source_vocab)
output_dim = len(target_vocab)
# 超参数
emb_dim = 8
hidden_dim = 16
num_layers = 1
learning_rate = 0.01
num_epochs = 1000
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
# 初始化模型
encoder = Encoder(input_dim, emb_dim, hidden_dim, num_layers).to(device)
decoder = Decoder(output_dim, emb_dim, hidden_dim, num_layers).to(device)
model = Seq2Seq(encoder, decoder, device).to(device)
# 损失函数 & 优化器
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
# 训练数据 (假设只有一对句子)
source_sentence = torch.tensor([[0, 1, 2]]).to(device) # "我 很 好"
target_sentence = torch.tensor([[0, 1, 2, 3, 6]]).to(device) # "Bos I am fine Eos"
# 训练
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = model(source_sentence, target_sentence)
output = output[:, 1:].reshape(-1, output_dim) # 计算损失,跳过 <Bos>
target = target_sentence[:, 1:].reshape(-1)
loss = criterion(output, target)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if epoch % 100 == 0:
print(f"Epoch [{epoch}/{num_epochs}], Loss: {loss.item():.4f}")
def translate_sentence(model, sentence):
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
src_tensor = torch.tensor([sentence]).to(device)
hidden, cell = model.encoder(src_tensor)
trg_indexes = [0] # "<Bos>"
for _ in range(10): # 限制最大翻译长度
trg_tensor = torch.tensor([trg_indexes[-1]]).to(device)
output, hidden, cell = model.decoder(trg_tensor, hidden, cell)
pred_token = output.argmax(1).item()
trg_indexes.append(pred_token)
if pred_token == 6: # "<Eos>"
break
return [list(target_vocab.keys())[list(target_vocab.values()).index(i)] for i in trg_indexes]
# 测试翻译
test_sentence = [0, 1, 2] # "我 很 好"
translation = translate_sentence(model, test_sentence)
print("翻译结果:", translation) # 预期: ['Bos', 'I', 'am', 'fine', 'Eos']



























 1354
1354

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










