成员对象和封闭类
成员对象:一个类的成员变量是另一个类的对象
封闭类:包含成员对象的类是封闭类
class CTyre{
public:
CTyre(int a,int b):radius(a),width(b){}
protected:
private:
int radius;
int width;
};
class CEngine{
public:
protected:
private:
};
class CCar{
public:
CCar(int a,int b,int c);
protected:
private:
int price;
CTyre tyre;CEngine engine;
};
CCar::CCar(int a,int b,int c):price(a),tyre(b,c){};
int main(){
CCar a(1,2,3);
return 0;
}封闭类构造函数的初始化列表
类名:构造函数(参数表):成员变量1(参数表),成员变量2(参数表)……{}
调用顺序
封闭类对象生成时:
– 1.执行所有成员对象构造函数
– 2.执行封闭类的构造函数
成员对象构造函数
–和成员对象在类中说明顺序一致
–与成员初始化列表中出现顺序无关
封闭类对象消亡时
–先执行封闭类的析构函数
–再执行成员对象的析构函数
构造函数调用顺序与析构函数调用顺序想反
对比分析
class CTyre{
private:
int radius, width;
public:
CTyre() {
cout << "CTyre constructor called" << endl;
}
~CTyre() {
cout << "CTyre deconstructor called" << endl;
}
};
class CEngine{
private:
public:
CEngine() {
cout << "CEngine constructor called" << endl;
}
~CEngine() {
cout << "CEngine deconstructor called" << endl;
}
};
class CCar{
private:
CTyre tyre; CEngine engine;
public:
CCar() {
cout << "CCar constructor called" << endl;
}
~CCar() {
cout << "CCar deconstructor called" << endl;
}
};
如果类CCar变成
class CCar{
private:
CEngine engine;CTyre tyre;
public:
CCar() {
cout << "CCar constructor called" << endl;
}
~CCar() {
cout << "CCar deconstructor called" << endl;
}
};
友元
- 友元函数
一个类的友元函数(包括构造、解析函数)
可以访问该类的私有成员
class CCar;
class CDriver{
private:
public:
void modify(CCar &p);
};
class CCar{
private:
int price;
public:
CCar(int x):price(x){}
friend void CDriver::modify(CCar& p);
void print() {
cout << price << endl;
}
};
void CDriver::modify(CCar& p) {
p.price += 100;
}
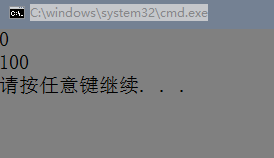
int main() {
CCar a(0);
CDriver b;
a.print();
b.modify(a);
a.print();
return 0;
注意:
modify函数不能写在前面
- 友元类
A是B的友元类,A可以访问B的私有成员
友元函数博客总结
class ccar{
public:
protected:
private:
int price;
friend class cd;
};
class cd{
public:
ccar my;
void modify(){
my.price+=1000;
}
protected:
private:
};
int main(){
return 0;
}友元类之间的关系不是传递,不是继承的。
this 指针
c++到c程序的翻译
class a{
public:
void set(int b){
price=b;
}
protected:
private:
int price;
};
int main(){
a cc;
cc.set(2);
return 0;
}对应c语言版本
struct CCar {
int price;
};
void SetPrice(struct CCar * this,int p){
this->price = p;
}
int main() {
struct CCar car;
SetPrice( & car, 20000);
return 0;//编译不能通过
}其作用就是指向成员函数所作用的对象
class Complex{
public:
double real,imag;
void print(){
cout<<real<<","<<imag<<endl;
}
Complex(double r,double i):real(r),imag(i){}
Complex AddOne(){
this->real++;
this->print();
return *this;
}
protected:
private:
};
int main(){
Complex a(4,5),b(1,2);
b=a.AddOne();
cout<<"学习c++"<<endl;
return 0;
}具体实例
class this_pointer{
public:
void hello(){
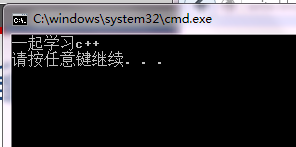
cout<<"一起学习c++"<<endl;
}
protected:
private:
int i;
};
int main(){
this_pointer *p=NULL;
p->hello();
}输出
class this_pointer{
public:
void hello(){
cout<<"一起学习c++"<<i<<endl;
}
protected:
private:
int i;
};
int main(){
this_pointer *p=NULL;
p->hello();
}程序出错
注意:静态成员函数不能使用this指针,因为静态函数不具体作用于某个对象。
因此静态成员函数中参数的个数,就是程序中写出的参数的个数
常量对象
- 常量对象
如果不希望某个对象的值被改变,则定义该对象的时候在前面加上const 关键字
class Demo{
public:
void SetValue(){}
protected:
private:
int value;
};
const Demo obj;- 常量成员函数
在类的成员函数后面加上const关键字,即成为常量成员函数
常量成员函数在执行期间不修改其所作用对象,因此,常量成员函数中不能修改成员变量(静态成员变量除外),也不能调用非常量成员函数(静态成员函数除外)。
class Sample{
public:
int value;
void GetValue() const;
void func(){};
Sample(){};
protected:
private:
};
void Sample::GetValue() const{
value=0;//wrong
}- 常量成员函数的重载
两个成员函数,名字和参数表一样,但一个是const,一个不是,算函数重载
public:
CTest(int i=1):n(i){}
int getValue(){
return n;
}
int getValue() const{
return 2*n;
}
protected:
private:
int n;
};
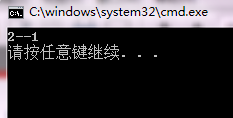
int main(){
const CTest a;CTest b;
cout<<a.getValue()<<"--"<<b.getValue()<<endl;
}- 常引用
例1:
class Time{
public:
Time(int,int ,int);
void print();
void reset(Time t);
protected:
private:
int year;int month;int day;
};
Time::Time(int a,int b,int c){
year=a;month=b;day=c;
}
void Time::print(){
cout<<year<<"/"<<month<<"/"<<day<<endl;
}
void Time::reset(Time t){
t.year=0;t.month=0;t.day=0;
}
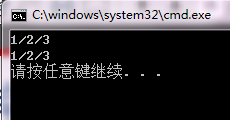
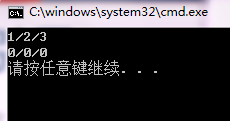
int main(){
Time t1(1,2,3);
t1.print();
t1.reset(t1);
t1.print();
}例2:
class Time{
public:
Time(int,int ,int);
void print();
void reset(Time &t);
protected:
private:
int year;int month;int day;
};
Time::Time(int a,int b,int c){
year=a;month=b;day=c;
}
void Time::print(){
cout<<year<<"/"<<month<<"/"<<day<<endl;
}
void Time::reset(Time &t){
t.year=0;t.month=0;t.day=0;
}
int main(){
Time t1(1,2,3);
t1.print();
t1.reset(t1);
t1.print();
}例:3:
class Time{
public:
Time(int,int ,int);
void print();
void reset(const Time &t);
protected:
private:
int year;int month;int day;
};
Time::Time(int a,int b,int c){
year=a;month=b;day=c;
}
void Time::print(){
cout<<year<<"/"<<month<<"/"<<day<<endl;
}
void Time::reset(const Time &t){
t.year=0;t.month=0;t.day=0;
}
int main(){
Time t1(1,2,3);
t1.print();
t1.reset(t1);
t1.print();
}编译出错
因为const长引用,不允许修改其变量
1>e:\学校\找工作\leetcode\leetcode\leetcode\leetcode.cpp(36): error C3490: 由于正在通过常量对象访问“year”,因此无法对其进行修改
1>e:\学校\找工作\leetcode\leetcode\leetcode\leetcode.cpp(36): error C3490: 由于正在通过常量对象访问“month”,因此无法对其进行修改
1>e:\学校\找工作\leetcode\leetcode\leetcode\leetcode.cpp(36): error C3490: 由于正在通过常量对象访问“day”,因此无法对其进行修改























 299
299

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








