概述
这是一个基于MTCNN(Multi-task Cascaded Convolutional Networks)算法的人脸捕获程序,用于收集训练人脸识别模型所需的人脸图像数据。程序使用facenet-pytorch库实现的MTCNN检测器。
思维导图
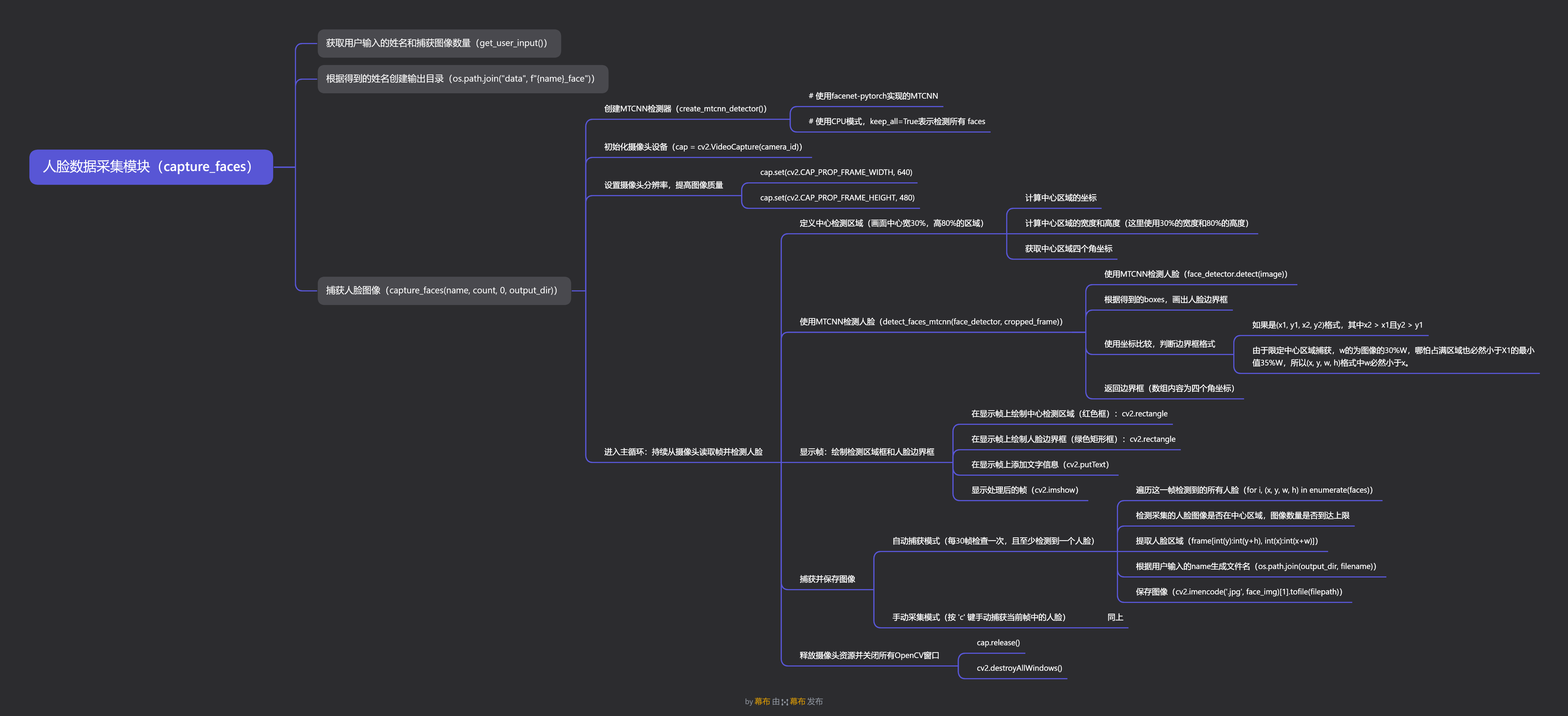
核心功能
1. **人脸检测**:使用MTCNN算法检测图像中的人脸
2. **图像捕获**:自动或手动捕获人脸图像
3. **中心区域限制**:限定人脸检测在画面中心区域,提高检测准确性
4. **中文路径支持**:使用imencode方法解决OpenCV对中文路径的支持问题
5. **交互式操作**:通过键盘控制图像捕获过程
技术要点
1.MTCNN人脸检测
MTCNN是一种多任务级联卷积神经网络,包含三个阶段:
1. P-Net(Proposal Network):快速生成人脸候选区域
2. R-Net(Refine Network):过滤掉大量非人脸区域
3. O-Net(Output Network):输出人脸关键点和更精确的人脸边界框
def create_mtcnn_detector():
"""
创建MTCNN人脸检测器,使用facenet-pytorch实现
Returns:
MTCNN检测器对象或None(如果无法创建)
"""
try:
# 使用facenet-pytorch实现的MTCNN
from facenet_pytorch import MTCNN
# 使用CPU模式,keep_all=True表示检测所有 faces
mtcnn = MTCNN(keep_all=True, device='cpu')
print("使用facenet-pytorch的MTCNN实现")
return mtcnn
except ImportError:
print("错误: 未找到facenet-pytorch库,请安装:")
print(" pip install facenet-pytorch")
return None
'''
'''
# 使用MTCNN检测人脸
# 返回boxes, probs
boxes, probs = face_detector.detect(image)
2.中文路径处理
为了解决OpenCV对中文路径支持不佳的问题,程序使用以下方法:
# 使用imencode和tofile方法保存包含中文的路径
# cv2.imencode(保存格式, 保存图片)[1].tofile(保存路径)
cv2.imencode('.jpg', face_img)[1].tofile(filepath)
# 使用isfile方法获取保存文件状态是否成功
success = os.path.isfile(filepath)
另注:关于在cv2的putText方法中使用中文会出现乱码的问题,可以通过以下方法解决
# 安装这个扩展之后puttext的中文显示问题就解决啦
# 但是文件中文名写入不使用上面的imencode方法还是会显示乱码
pip install opencv-python-rolling
3.边界框格式处理
MTCNN返回的边界框可能有两种格式:
1. `(x1, y1, x2, y2)`:矩形对角点坐标
2. `(x, y, w, h)`:左上角坐标和宽高
# 使用坐标比较判断边界框格式
# 如果是(x1, y1, x2, y2)格式,其中x2 > x1且y2 > y1
if box[2] > box[0] and box[3] > box[1]:
x1, y1, x2, y2 = box
w, h = x2 - x1, y2 - y1
faces.append((int(x1), int(y1), int(w), int(h)))
else:
# 可能已经是(x, y, w, h)格式
faces.append((int(box[0]), int(box[1]), int(box[2]), int(box[3])))
思路:
实际上,很难通过返回的boxes的长度来判断格式,因为不同的库和版本可能返回不同的格式。
理想的方法是明确知道所使用的库和版本,并参考其文档来确定返回的边界框格式,但程序运行在不同的环境中,一般难以确定使用的库和版本。
根据坐标值的大小来判断?
如果boxes的长度为4且所有值均为正数且x2 > x1且y2 > y1,
不能判断为(x1, y1, x2, y2)格式的主要原因是(x, y, w, h)格式也可能满足这些条件。
比如:人脸贴摄像头比较近的时候,w和h可能会比较大,此时w和h的值可能会大于x1和y1。
探究靠得太近的本质,在于x,y的坐标,也就是左上角的坐标,距离边界的距离太小。
那么该如何控制人脸框和边界的距离大小呢?
有丰富生活经验的朋友应该已经想到了,就是人脸识别的时候经常会出现的人脸框。
在反馈的图像中标划出一个人脸区域,然后让用户调整摄像头位置,使得人脸框和边界的距离适中。这样就可以避免人脸框过大或过小的问题,同时也能确保人脸框的格式正确。
4.中心区域检测
# 定义中心检测区域(画面中心宽30%,高80%的区域)
# 计算中心区域的坐标
center_x, center_y = frame_width // 2, frame_height // 2
# 计算中心区域的宽度和高度
# 这里使用30%的宽度和80%的高度
crop_width, crop_height = int(frame_width * 0.3), int(frame_height * 0.8)
# 获取中心区域四个角坐标
crop_x1 = center_x - crop_width // 2
crop_y1 = center_y - crop_height // 2
crop_x2 = crop_x1 + crop_width
crop_y2 = crop_y1 + crop_height
这里使用30%的宽度和80%的高度的主要原因
1.人脸是个竖立的椭圆,需要的人脸框width小height大。
2.想要区分(x1, y1, x2, y2)和(x, y, w, h)格式,实际上只需要保证w总小于x1就够了。
因此,高度的限制可以放宽成80%H,宽度则严格设定为30%W,以此保证它始终小于x1的min值35%W。
项目流程图

项目代码
由于是学习代码,注释写得比较细琐,跟着debug一遍基本上都能理解了,大概。
import cv2
import os
import sys
import numpy as np
def create_mtcnn_detector():
"""
创建MTCNN人脸检测器,使用facenet-pytorch实现
Returns:
MTCNN检测器对象或None(如果无法创建)
"""
try:
# 使用facenet-pytorch实现的MTCNN
from facenet_pytorch import MTCNN
# 使用CPU模式,keep_all=True表示检测所有 faces
mtcnn = MTCNN(keep_all=True, device='cpu')
print("使用facenet-pytorch的MTCNN实现")
return mtcnn
except ImportError:
print("错误: 未找到facenet-pytorch库,请安装:")
print(" pip install facenet-pytorch")
return None
def capture_faces(name, num_images=50, camera_id=0, output_dir="known_faces"):
"""
使用MTCNN捕获人脸图像用于训练人脸识别模型,在画面中心区域检测人脸
Args:
name (str): 人员姓名,将用作保存图像文件名的前缀
num_images (int): 要捕获的图像数量,默认为50张
camera_id (int): 摄像头设备ID,默认为0(第一个摄像头)
output_dir (str): 图像保存的目录路径,默认为"known_faces"
"""
# 创建MTCNN检测器
face_detector = create_mtcnn_detector()
if face_detector is None:
return
print(f"开始捕获人脸图像: {name}")
print(f"目标数量: {num_images} 张")
print(f"输出目录: {output_dir}")
print("=" * 50)
# 初始化摄像头设备
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(camera_id)
if not cap.isOpened():
print(f"错误: 无法打开摄像头 {camera_id}")
# 尝试其他设备ID (1-4),在某些系统中摄像头可能分配了不同的ID
for i in range(1, 5):
print(f"尝试摄像头 {i}...")
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(i)
if cap.isOpened():
print(f"成功打开摄像头 {i}")
camera_id = i
break
if not cap.isOpened():
print("无法打开任何摄像头")
return
# 设置摄像头分辨率,提高图像质量
cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH, 640)
cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT, 480)
# 初始化计数器
# captured_count: 已成功捕获并保存的图像数量
# frame_count: 处理的视频帧总数,用于控制自动捕获频率
captured_count = 0
frame_count = 0
print("\n操作说明:")
print("- 确保人脸正对摄像头")
print("- 保持不同角度和表情")
print("- 确保光线充足且均匀")
print("- 按 'q' 或 'ESC' 键退出")
print("- 按 'c' 键捕获当前帧中的人脸")
print("- 自动捕获模式下会自动保存检测到的人脸")
print("- 人脸应出现在画面中心区域(红色框内)")
print("\n准备开始...")
# 等待2秒让用户准备
cv2.waitKey(2000)
try:
# 主循环:持续从摄像头读取帧并检测人脸
while True:
# 从摄像头读取一帧图像
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
print("无法获取摄像头画面")
break
# 帧计数器递增
frame_count += 1
# 获取帧的尺寸
frame_height, frame_width = frame.shape[:2]
# 定义中心检测区域(画面中心宽30%,高80%的区域)
# 计算中心区域的坐标
center_x, center_y = frame_width // 2, frame_height // 2
# 计算中心区域的宽度和高度
# 这里使用30%的宽度和80%的高度
crop_width, crop_height = int(frame_width * 0.3), int(frame_height * 0.8)
# 获取中心区域四个角坐标
crop_x1 = center_x - crop_width // 2
crop_y1 = center_y - crop_height // 2
crop_x2 = crop_x1 + crop_width
crop_y2 = crop_y1 + crop_height
# 使用MTCNN检测人脸(仅在中心区域)
faces = detect_faces_mtcnn(face_detector, frame)
# 在显示帧上绘制中心检测区域(红色框)
display_frame = frame.copy()
cv2.rectangle(display_frame, (crop_x1, crop_y1), (crop_x2, crop_y2), (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.putText(display_frame, "人脸检测区域", (crop_x1, crop_y1 - 10),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 255), 1)
# 在显示帧上绘制绿色矩形框标记检测到的人脸
for (x, y, w, h) in faces:
cv2.rectangle(display_frame, (int(x), int(y)), (int(x+w), int(y+h)), (0, 255, 0), 2)
# 在显示帧上添加文字信息
cv2.putText(display_frame, f"已捕获: {captured_count}/{num_images}",
(10, 30), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.putText(display_frame, f"按 'c' 捕获, 'q' 退出",
(10, 60), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (0, 255, 0), 2)
# 显示处理后的帧
cv2.imshow('人脸捕获 (MTCNN-中心区域)', display_frame)
# 自动捕获模式(每30帧检查一次,且至少检测到一个人脸)
# 这样可以避免保存过多重复的人脸图像
if frame_count % 30 == 0 and len(faces) > 0 and captured_count < num_images:
# 遍历这一帧中的所有检测到的人脸
for i, (x, y, w, h) in enumerate(faces):
# 如果已达到目标数量则停止捕获
if captured_count >= num_images:
break
#检测采集的人脸图像是否在中心区域
if not (crop_x1 <= x <= crop_x2 and crop_y1 <= y <= crop_y2):
print(f"人脸不在中心区域内,跳过保存")
break
# 提取人脸区域(裁剪出人脸部分)
face_img = frame[int(y):int(y+h), int(x):int(x+w)]
# 生成文件名,格式为姓名+编号,如GUO01.jpg, GUO02.jpg
filename = f"{name.upper()}{captured_count+1:02d}.jpg"
filepath = os.path.join(output_dir, filename)
# 保存图像到指定目录
#success = cv2.imwrite(filepath, face_img)
cv2.imencode('.jpg', face_img)[1].tofile(filepath)
success = os.path.isfile(filepath)
if success:
captured_count += 1
print(f"已保存: {filename} (共{captured_count}张)")
else:
print(f"保存失败: {filename}")
# 等待按键输入(1毫秒)
key = cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF
# 按 'q' 或 ESC 键退出程序
if key == ord('q') or key == 27: # 27 is ESC key
break
# 按 'c' 键手动捕获当前帧中的人脸(立即保存当前检测到的人脸)
elif key == ord('c') and len(faces) > 0:
# 遍历这一帧中的所有检测到的人脸
for i, (x, y, w, h) in enumerate(faces):
# 如果已达到目标数量则停止捕获
if captured_count >= num_images:
break
#检测采集的人脸图像是否在中心区域
if not (crop_x1 <= x <= crop_x2 and crop_y1 <= y <= crop_y2):
print(f"人脸不在中心区域内,跳过保存")
break
# 提取人脸区域
face_img = frame[int(y):int(y+h), int(x):int(x+w)]
# 生成文件名
filename = f"{name.upper()}{captured_count+1:02d}.jpg"
filepath = os.path.join(output_dir, filename)
# 保存图像
#success = cv2.imwrite(filepath, face_img)
cv2.imencode('.jpg', face_img)[1].tofile(filepath)
success = os.path.isfile(filepath)
# 检查保存是否成功
if success:
captured_count += 1
print(f"已保存: {filename} (共{captured_count}张)")
else:
print(f"保存失败: {filename}")
# 检查是否达到目标数量
if captured_count >= num_images:
print(f"\n已完成! 成功捕获 {captured_count} 张人脸图像")
break
except KeyboardInterrupt:
# 处理用户按Ctrl+C中断程序的情况
print("\n用户中断程序")
finally:
# 释放摄像头资源并关闭所有OpenCV窗口
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
# 输出最终统计信息
print(f"\n捕获完成!")
print(f"目标数量: {num_images}")
print(f"实际捕获: {captured_count}")
print(f"保存位置: {os.path.abspath(output_dir)}")
def detect_faces_mtcnn(face_detector, image):
"""
使用MTCNN检测图像中的人脸
Args:
face_detector: MTCNN人脸检测器对象
image: 要检测的图像
Returns:
list: 人脸边界框列表,每个元素为(x, y, w, h)格式
"""
try:
# 使用MTCNN检测人脸
# 返回boxes, probs
boxes, probs = face_detector.detect(image)
# 如果没有检测到人脸
if boxes is None or len(boxes) == 0:
return []
# 确保boxes是numpy数组
if not isinstance(boxes, np.ndarray):
boxes = np.array(boxes)
# 如果是三维数组,取第一个元素
if boxes.ndim == 3:
boxes = boxes[0]
# 转换边界框格式为(x, y, w, h)
faces = []
for box in boxes:
if len(box) == 4:
# 使用坐标比较判断边界框格式
# 如果是(x1, y1, x2, y2)格式,其中x2 > x1且y2 > y1
if box[2] > box[0] and box[3] > box[1]:
x1, y1, x2, y2 = box
w, h = x2 - x1, y2 - y1
faces.append((int(x1), int(y1), int(w), int(h)))
else:
# 可能已经是(x, y, w, h)格式
faces.append((int(box[0]), int(box[1]), int(box[2]), int(box[3])))
elif len(box) == 5:
# 有些版本可能返回5个值,前4个是边界框
x1, y1, x2_or_w, y2_or_h = box[:4]
# 使用同样的判断逻辑
if x2_or_w > x1 and y2_or_h > y1:
w, h = x2_or_w - x1, y2_or_h - y1
faces.append((int(x1), int(y1), int(w), int(h)))
else:
faces.append((int(x1), int(y1), int(x2_or_w), int(y2_or_h)))
return faces
except Exception as e:
print(f"人脸检测出错: {e}")
return []
def get_user_input():
"""
获取用户输入的姓名和捕获数量
Returns:
tuple: (姓名, 数量) 或 (None, None)(输入格式错误时)
"""
# 提示用户输入姓名和数量
user_input = input("请输入姓名,并指定捕获数量。示例格式:GUO+50\n")
try:
# 解析用户输入,按"+"分割姓名和数量
name, count_str = user_input.split('+')
count = int(count_str)
return name.strip(), count
except ValueError:
# 处理输入格式错误的情况
print("输入格式错误,请使用格式:姓名+数量,例如:GUO+50")
return None, None
def main():
"""
主函数:获取用户输入并调用捕获人脸图像功能
"""
print("人脸图像捕获工具 (MTCNN版本-中心区域检测)")
print("=" * 40)
# 获取用户输入的姓名和数量
name, count = get_user_input()
if name is None or count is None:
return
# 设置输出目录为 data/name_face 格式,如 data/GUO_face/
output_dir = os.path.join("data", f"{name}_face")
# 创建输出目录,如果目录不存在则创建
if not os.path.exists(output_dir):
os.makedirs(output_dir)
print(f"创建目录: {output_dir}")
# 调用捕获人脸图像的函数
capture_faces(name, count, 0, output_dir)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 程序入口点
main()




















 815
815

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








