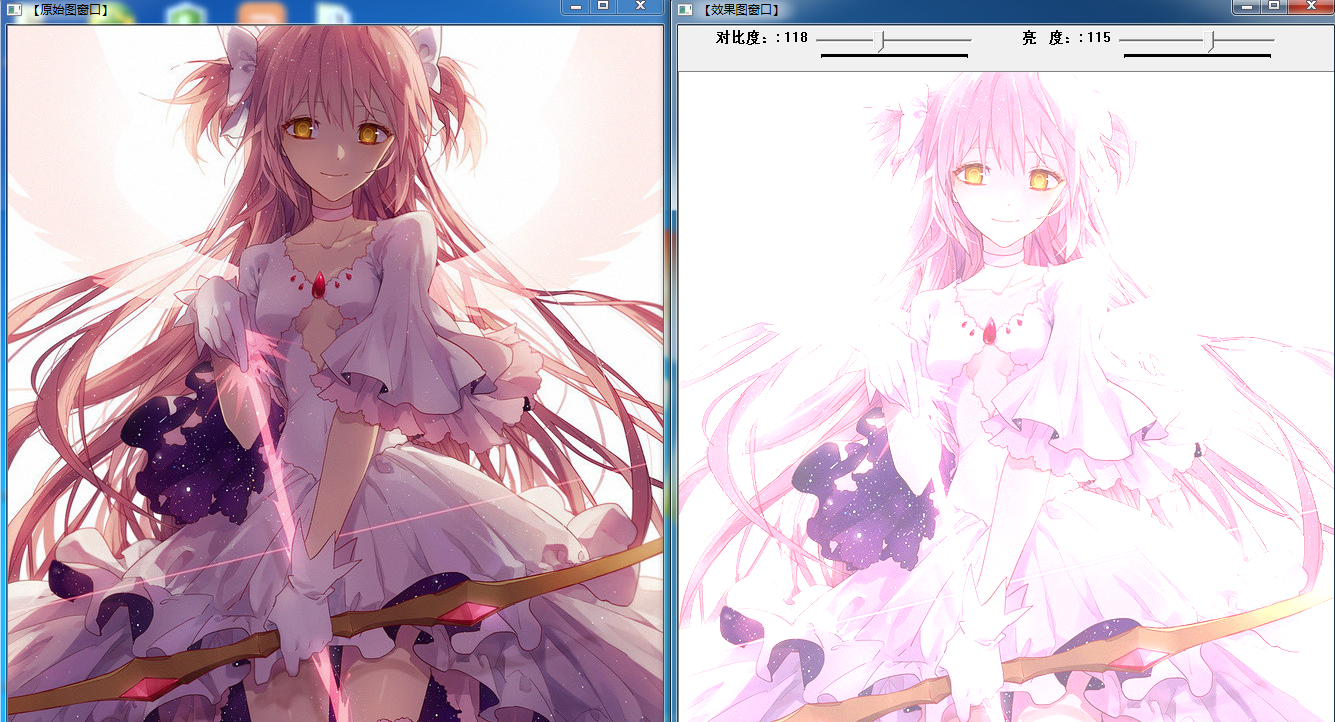
6.图像对比度,亮度调整
理论公式:g(i,j) = a*f(i,j) + b;
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include <iostream>
//-----------------------------------【命名空间声明部分】---------------------------------------
// 描述:包含程序所使用的命名空间
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
//-----------------------------------【全局函数声明部分】--------------------------------------
// 描述:全局函数声明
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
static void ContrastAndBright(int, void *);
//-----------------------------------【全局变量声明部分】--------------------------------------
// 描述:全局变量声明
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
int g_nContrastValue; //对比度值
int g_nBrightValue; //亮度值
Mat g_srcImage,g_dstImage;
//-----------------------------------【main( )函数】--------------------------------------------
// 描述:控制台应用程序的入口函数,我们的程序从这里开始
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
int main( )
{
//改变控制台前景色和背景色
system("color 2F");
ShowHelpText();
// 读入用户提供的图像
g_srcImage = imread( "1.jpg");
if( !g_srcImage.data ) { printf("读取g_srcImage图片错误~! \n"); return false; }
g_dstImage = Mat::zeros( g_srcImage.size(), g_srcImage.type() );
//设定对比度和亮度的初值
g_nContrastValue=80;
g_nBrightValue=80;
//创建窗口
namedWindow("【效果图窗口】", 1);
//创建轨迹条
createTrackbar("对比度:", "【效果图窗口】",&g_nContrastValue, 300,ContrastAndBright );
createTrackbar("亮 度:", "【效果图窗口】",&g_nBrightValue, 200,ContrastAndBright );
//调用回调函数
ContrastAndBright(g_nContrastValue,0);
ContrastAndBright(g_nBrightValue,0);
//输出一些帮助信息
cout<<endl<<"\t运行成功,请调整滚动条观察图像效果\n\n"
<<"\t按下“q”键时,程序退出\n";
//按下“q”键时,程序退出
while(char(waitKey(1)) != 'q') {}
return 0;
}
//-----------------------------【ContrastAndBright( )函数】------------------------------------
// 描述:改变图像对比度和亮度值的回调函数
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
static void ContrastAndBright(int, void *)
{
// 创建窗口
namedWindow("【原始图窗口】", 1);
// 三个for循环,执行运算 g_dstImage(i,j) = a*g_srcImage(i,j) + b
for( int y = 0; y < g_srcImage.rows; y++ )
{
for( int x = 0; x < g_srcImage.cols; x++ )
{
for( int c = 0; c < 3; c++ )
{
g_dstImage.at<Vec3b>(y,x)[c] = saturate_cast<uchar>( (g_nContrastValue*0.01)*( g_srcImage.at<Vec3b>(y,x)[c] ) + g_nBrightValue );
}
}
}
// 显示图像
imshow("【原始图窗口】", g_srcImage);
imshow("【效果图窗口】", g_dstImage);
imwrite("效果图.jpg",g_dstImage);
}
7.离散傅里叶变换
暂时理解不了理论部分,先把代码贴上来,以后有用到再好好研究
//---------------------------------【头文件、命名空间包含部分】-----------------------------
// 描述:包含程序所使用的头文件和命名空间
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include <iostream>
using namespace cv;
//--------------------------------------【main( )函数】-----------------------------------------
// 描述:控制台应用程序的入口函数,我们的程序从这里开始执行
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
int main()
{
//【1】以灰度模式读取原始图像并显示
Mat srcImage = imread("1.jpg", 0);
if (!srcImage.data) { printf("读取图片错误,请确定目录下是否有imread函数指定图片存在~! \n"); return false; }
imshow("原始图像", srcImage);
//【2】将输入图像延扩到最佳的尺寸,边界用0补充
int m = getOptimalDFTSize(srcImage.rows);
int n = getOptimalDFTSize(srcImage.cols);
//将添加的像素初始化为0.
Mat padded;
copyMakeBorder(srcImage, padded, 0, m - srcImage.rows, 0, n - srcImage.cols, BORDER_CONSTANT, Scalar::all(0));
//【3】为傅立叶变换的结果(实部和虚部)分配存储空间。
//将planes数组组合合并成一个多通道的数组complexI
Mat planes[] = { Mat_<float>(padded), Mat::zeros(padded.size(), CV_32F) };
Mat complexI;
merge(planes, 2, complexI);
//【4】进行就地离散傅里叶变换
dft(complexI, complexI);
//【5】将复数转换为幅值,即=> log(1 + sqrt(Re(DFT(I))^2 + Im(DFT(I))^2))
split(complexI, planes); // 将多通道数组complexI分离成几个单通道数组,planes[0] = Re(DFT(I), planes[1] = Im(DFT(I))
magnitude(planes[0], planes[1], planes[0]);// planes[0] = magnitude
Mat magnitudeImage = planes[0];
//【6】进行对数尺度(logarithmic scale)缩放
magnitudeImage += Scalar::all(1);
log(magnitudeImage, magnitudeImage);//求自然对数
//【7】剪切和重分布幅度图象限
//若有奇数行或奇数列,进行频谱裁剪
magnitudeImage = magnitudeImage(Rect(0, 0, magnitudeImage.cols & -2, magnitudeImage.rows & -2));
//重新排列傅立叶图像中的象限,使得原点位于图像中心
int cx = magnitudeImage.cols / 2;
int cy = magnitudeImage.rows / 2;
Mat q0(magnitudeImage, Rect(0, 0, cx, cy)); // ROI区域的左上
Mat q1(magnitudeImage, Rect(cx, 0, cx, cy)); // ROI区域的右上
Mat q2(magnitudeImage, Rect(0, cy, cx, cy)); // ROI区域的左下
Mat q3(magnitudeImage, Rect(cx, cy, cx, cy)); // ROI区域的右下
//交换象限(左上与右下进行交换)
Mat tmp;
q0.copyTo(tmp);
q3.copyTo(q0);
tmp.copyTo(q3);
//交换象限(右上与左下进行交换)
q1.copyTo(tmp);
q2.copyTo(q1);
tmp.copyTo(q2);
//【8】归一化,用0到1之间的浮点值将矩阵变换为可视的图像格式
//此句代码的OpenCV2版为:
//normalize(magnitudeImage, magnitudeImage, 0, 1, CV_MINMAX);
//此句代码的OpenCV3版为:
normalize(magnitudeImage, magnitudeImage, 0, 1, NORM_MINMAX);
//【9】显示效果图
imshow("频谱幅值", magnitudeImage);
imwrite("效果图.jpg", magnitudeImage);
waitKey();
return 0;
}
效果图
8.XML与YAML文件的写入和读取
//XML与YAML文件的写入
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include<time.h>
using namespace cv;
int main(){
//初始化
FileStorage fs("test.yaml", FileStorage::WRITE);
//开始文件写入
fs << "frameCount" << 5;
time_t rawtime; time(&rawtime);
fs << "calibrationDate" << asctime(localtime(&rawtime));
Mat cameraMatrix = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 1000, 0, 320, 0, 1000, 240, 0, 0, 1);
Mat distCoeffs = (Mat_<double>(5, 1) << 0.1, 0.01, -0.001, 0, 0);
fs << "cameraMatrix" << cameraMatrix << "distCoeffs" << distCoeffs;
fs << "features" << "[";
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
int x = rand() % 640;
int y = rand() % 480;
uchar lbp = rand() % 256;
fs << "{:" << "x" << x << "y" << y << "lbp" << "[:";
for (int j = 0; j < 8; j++){
fs << ((lbp >> j) & 1);
}
fs << "]" << "}";
}
fs << "]";
fs.release();
printf("文件读写完毕,请在工程目录下查看生成的文件~");
getchar();
return 0;
}
#include "opencv2/opencv.hpp"
#include <time.h>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
//XML与YAML文件的读取
int main()
{
//改变console字体颜色
system("color 6F");
//初始化
FileStorage fs2("test.yaml", FileStorage::READ);
// 第一种方法,对FileNode操作
int frameCount = (int)fs2["frameCount"];
std::string date;
// 第二种方法,使用FileNode运算符> >
fs2["calibrationDate"] >> date;
Mat cameraMatrix2, distCoeffs2;
fs2["cameraMatrix"] >> cameraMatrix2;
fs2["distCoeffs"] >> distCoeffs2;
cout << "frameCount: " << frameCount << endl
<< "calibration date: " << date << endl
<< "camera matrix: " << cameraMatrix2 << endl
<< "distortion coeffs: " << distCoeffs2 << endl;
FileNode features = fs2["features"];
FileNodeIterator it = features.begin(), it_end = features.end();
int idx = 0;
std::vector<uchar> lbpval;
//使用FileNodeIterator遍历序列
for (; it != it_end; ++it, idx++)
{
cout << "feature #" << idx << ": ";
cout << "x=" << (int)(*it)["x"] << ", y=" << (int)(*it)["y"] << ", lbp: (";
// 我们也可以使用使用filenode > > std::vector操作符很容易的读数值阵列
(*it)["lbp"] >> lbpval;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)lbpval.size(); i++)
cout << " " << (int)lbpval[i];
cout << ")" << endl;
}
fs2.release();
//程序结束,输出一些帮助文字
printf("\n文件读取完毕,请输入任意键结束程序~");
getchar();
return 0;
}

























 1853
1853

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








