1、CNN example
代码来自here
class CIFARModule(pl.LightningModule):
def __init__(self, model_name, model_hparams, optimizer_name, optimizer_hparams):
"""
Inputs:
model_name - Name of the model/CNN to run. Used for creating the model (see function below)
model_hparams - Hyperparameters for the model, as dictionary.
optimizer_name - Name of the optimizer to use. Currently supported: Adam, SGD
optimizer_hparams - Hyperparameters for the optimizer, as dictionary. This includes learning rate, weight decay, etc.
"""
super().__init__()
# Exports the hyperparameters to a YAML file, and create "self.hparams" namespace
self.save_hyperparameters()
# Create model
self.model = create_model(model_name, model_hparams)
# Create loss module
self.loss_module = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# Example input for visualizing the graph in Tensorboard
self.example_input_array = torch.zeros((1, 3, 32, 32), dtype=torch.float32)
def forward(self, imgs):
# Forward function that is run when visualizing the graph
return self.model(imgs)
def configure_optimizers(self):
# We will support Adam or SGD as optimizers.
if self.hparams.optimizer_name == "Adam":
# AdamW is Adam with a correct implementation of weight decay (see here for details: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1711.05101.pdf)
optimizer = optim.AdamW(
self.parameters(), **self.hparams.optimizer_hparams)
elif self.hparams.optimizer_name == "SGD":
optimizer = optim.SGD(self.parameters(), **self.hparams.optimizer_hparams)
else:
assert False, f"Unknown optimizer: \"{self.hparams.optimizer_name}\""
# We will reduce the learning rate by 0.1 after 100 and 150 epochs
scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.MultiStepLR(
optimizer, milestones=[100, 150], gamma=0.1)
return [optimizer], [scheduler]
def training_step(self, batch, batch_idx):
# "batch" is the output of the training data loader.
imgs, labels = batch
preds = self.model(imgs)
loss = self.loss_module(preds, labels)
acc = (preds.argmax(dim=-1) == labels).float().mean()
# Logs the accuracy per epoch to tensorboard (weighted average over batches)
self.log('train_acc', acc, on_step=False, on_epoch=True)
self.log('train_loss', loss)
return loss # Return tensor to call ".backward" on
def validation_step(self, batch, batch_idx):
imgs, labels = batch
preds = self.model(imgs).argmax(dim=-1)
acc = (labels == preds).float().mean()
# By default logs it per epoch (weighted average over batches)
self.log('val_acc', acc)
def test_step(self, batch, batch_idx):
imgs, labels = batch
preds = self.model(imgs).argmax(dim=-1)
acc = (labels == preds).float().mean()
# By default logs it per epoch (weighted average over batches), and returns it afterwards
self.log('test_acc', acc)
model_dict = {}
def create_model(model_name, model_hparams):
if model_name in model_dict:
return model_dict[model_name](**model_hparams)
else:
assert False, f"Unknown model name \"{model_name}\". Available models are: {str(model_dict.keys())}"
act_fn_by_name = {
"tanh": nn.Tanh,
"relu": nn.ReLU,
"leakyrelu": nn.LeakyReLU,
"gelu": nn.GELU
}
def train_model(model_name, save_name=None, **kwargs):
"""
Inputs:
model_name - Name of the model you want to run. Is used to look up the class in "model_dict"
save_name (optional) - If specified, this name will be used for creating the checkpoint and logging directory.
"""
if save_name is None:
save_name = model_name
# Create a PyTorch Lightning trainer with the generation callback
trainer = pl.Trainer(default_root_dir=os.path.join(CHECKPOINT_PATH, save_name), # Where to save models
accelerator="gpu" if str(device).startswith("cuda") else "cpu", # We run on a GPU (if possible)
devices=1, # How many GPUs/CPUs we want to use (1 is enough for the notebooks)
max_epochs=180, # How many epochs to train for if no patience is set
callbacks=[ModelCheckpoint(save_weights_only=True, mode="max", monitor="val_acc"), # Save the best checkpoint based on the maximum val_acc recorded. Saves only weights and not optimizer
LearningRateMonitor("epoch")], # Log learning rate every epoch
enable_progress_bar=True) # Set to False if you do not want a progress bar
trainer.logger._log_graph = True # If True, we plot the computation graph in tensorboard
trainer.logger._default_hp_metric = None # Optional logging argument that we don't need
# Check whether pretrained model exists. If yes, load it and skip training
pretrained_filename = os.path.join(CHECKPOINT_PATH, save_name + ".ckpt")
if os.path.isfile(pretrained_filename):
print(f"Found pretrained model at {pretrained_filename}, loading...")
model = CIFARModule.load_from_checkpoint(pretrained_filename) # Automatically loads the model with the saved hyperparameters
else:
pl.seed_everything(42) # To be reproducable
model = CIFARModule(model_name=model_name, **kwargs)
trainer.fit(model, train_loader, val_loader)
model = CIFARModule.load_from_checkpoint(trainer.checkpoint_callback.best_model_path) # Load best checkpoint after training
# Test best model on validation and test set
val_result = trainer.test(model, val_loader, verbose=False)
test_result = trainer.test(model, test_loader, verbose=False)
result = {"test": test_result[0]["test_acc"], "val": val_result[0]["test_acc"]}
return model, result
2、Inception
最初的inception block

figure credit - Szegedy et al
3、ResNet
前向传播:
x
l
+
1
=
x
l
+
F
(
x
l
)
x_{l+1}=x_l+F(x_l)
xl+1=xl+F(xl)
反向传播:
∂
x
l
+
1
∂
x
l
=
I
+
∂
F
(
x
l
)
∂
x
l
\frac {\partial x_{l+1}} {\partial x_l}=I+\frac {\partial F(x_l)} {\partial x_l}
∂xl∂xl+1=I+∂xl∂F(xl)
主要介绍两种ResNet Block,the original ResNet block, and the Pre-Activation ResNet block

figure credit - He et al
对于原始版本的ResNet,要注意通过F的输出要与输入维度相同,通常使用卷积核为1、步幅为2的卷积层,例子如下
class ResNetBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, c_in, act_fn, subsample=False, c_out=-1):
"""
Inputs:
c_in - Number of input features
act_fn - Activation class constructor (e.g. nn.ReLU)
subsample - If True, we want to apply a stride inside the block and reduce the output shape by 2 in height and width
c_out - Number of output features. Note that this is only relevant if subsample is True, as otherwise, c_out = c_in
"""
super().__init__()
if not subsample:
c_out = c_in
# Network representing F
self.net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(c_in, c_out, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=1 if not subsample else 2, bias=False), # No bias needed as the Batch Norm handles it
nn.BatchNorm2d(c_out),
act_fn(),
nn.Conv2d(c_out, c_out, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(c_out)
)
# 1x1 convolution with stride 2 means we take the upper left value, and transform it to new output size
self.downsample = nn.Conv2d(c_in, c_out, kernel_size=1, stride=2) if subsample else None
self.act_fn = act_fn()
def forward(self, x):
z = self.net(x)
if self.downsample is not None:
x = self.downsample(x)
out = z + x
out = self.act_fn(out)
return out
对于Pre-activition的ResNet block,代码如下
class PreActResNetBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, c_in, act_fn, subsample=False, c_out=-1):
"""
Inputs:
c_in - Number of input features
act_fn - Activation class constructor (e.g. nn.ReLU)
subsample - If True, we want to apply a stride inside the block and reduce the output shape by 2 in height and width
c_out - Number of output features. Note that this is only relevant if subsample is True, as otherwise, c_out = c_in
"""
super().__init__()
if not subsample:
c_out = c_in
# Network representing F
self.net = nn.Sequential(
nn.BatchNorm2d(c_in),
act_fn(),
nn.Conv2d(c_in, c_out, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=1 if not subsample else 2, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(c_out),
act_fn(),
nn.Conv2d(c_out, c_out, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False)
)
# 1x1 convolution can apply non-linearity as well, but not strictly necessary
self.downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.BatchNorm2d(c_in),
act_fn(),
nn.Conv2d(c_in, c_out, kernel_size=1, stride=2, bias=False)
) if subsample else None
def forward(self, x):
z = self.net(x)
if self.downsample is not None:
x = self.downsample(x)
out = z + x
return out
DenseNet
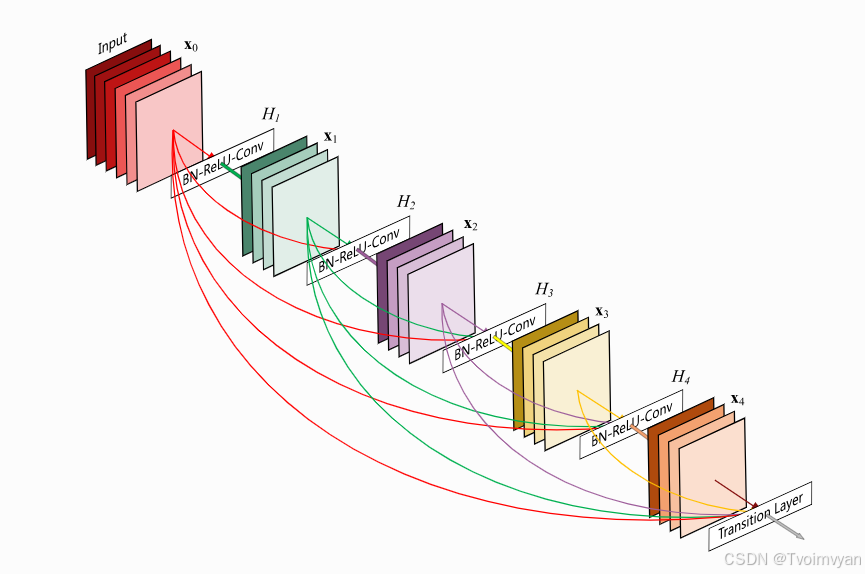
figure credit - Hu et al.
class DenseNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=10, num_layers=[6,6,6,6], bn_size=2, growth_rate=16, act_fn_name="relu", **kwargs):
super().__init__()
self.hparams = SimpleNamespace(num_classes=num_classes,
num_layers=num_layers,
bn_size=bn_size,
growth_rate=growth_rate,
act_fn_name=act_fn_name,
act_fn=act_fn_by_name[act_fn_name])
self._create_network()
self._init_params()
def _create_network(self):
c_hidden = self.hparams.growth_rate * self.hparams.bn_size # The start number of hidden channels
# A first convolution on the original image to scale up the channel size
self.input_net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, c_hidden, kernel_size=3, padding=1) # No batch norm or activation function as done inside the Dense layers
)
# Creating the dense blocks, eventually including transition layers
blocks = []
for block_idx, num_layers in enumerate(self.hparams.num_layers):
blocks.append(
DenseBlock(c_in=c_hidden,
num_layers=num_layers,
bn_size=self.hparams.bn_size,
growth_rate=self.hparams.growth_rate,
act_fn=self.hparams.act_fn)
)
c_hidden = c_hidden + num_layers * self.hparams.growth_rate # Overall output of the dense block
if block_idx < len(self.hparams.num_layers)-1: # Don't apply transition layer on last block
blocks.append(
TransitionLayer(c_in=c_hidden,
c_out=c_hidden // 2,
act_fn=self.hparams.act_fn))
c_hidden = c_hidden // 2
self.blocks = nn.Sequential(*blocks)
# Mapping to classification output
self.output_net = nn.Sequential(
nn.BatchNorm2d(c_hidden), # The features have not passed a non-linearity until here.
self.hparams.act_fn(),
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1,1)),
nn.Flatten(),
nn.Linear(c_hidden, self.hparams.num_classes)
)
def _init_params(self):
# Based on our discussion in Tutorial 4, we should initialize the convolutions according to the activation function
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, nonlinearity=self.hparams.act_fn_name)
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.input_net(x)
x = self.blocks(x)
x = self.output_net(x)
return x























 101
101

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








