本文节选自吴恩达老师《深度学习专项课程》编程作业,在此表示感谢。
课程链接:https://www.deeplearning.ai/deep-learning-specialization/
After this assignment you will be able to:
- Build and apply a deep neural network to supervised learning.
目录
3 - Architecture of your model
3.2 - L-layer deep neural network
7) Test with your own image (optional/ungraded exercise)
1 - Packages
Let's first import all the packages that you will need during this assignment.
- numpy is the fundamental package for scientific computing with Python.
- matplotlib is a library to plot graphs in Python.
- h5py is a common package to interact with a dataset that is stored on an H5 file.
- PIL and scipy are used here to test your model with your own picture at the end.
- dnn_app_utils provides the functions implemented in the "Building your Deep Neural Network: Step by Step" assignment to this notebook.
import time
import numpy as np
import h5py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scipy
from PIL import Image
from scipy import ndimage
from dnn_app_utils_v2 import *
%matplotlib inline
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (5.0, 4.0) # set default size of plots
plt.rcParams['image.interpolation'] = 'nearest'
plt.rcParams['image.cmap'] = 'gray'
%load_ext autoreload
%autoreload 2
np.random.seed(1)2 - Dataset
You will use the same "Cat vs non-Cat" dataset as in "Logistic Regression as a Neural Network" (Assignment 2). The model you had built had 70% test accuracy on classifying cats vs non-cats images. Hopefully, your new model will perform a better!
Problem Statement: You are given a dataset ("data.h5") containing:
- a training set of m_train images labelled as cat (1) or non-cat (0)
- a test set of m_test images labelled as cat and non-cat
- each image is of shape (num_px, num_px, 3) where 3 is for the 3 channels (RGB).Let's get more familiar with the dataset. Load the data by running the cell belo
train_x_orig, train_y, test_x_orig, test_y, classes = load_data()
# Example of a picture
index = 9
plt.imshow(train_x_orig[index])
print ("y = " + str(train_y[0,index]) + ". It's a " + classes[train_y[0,index]].decode("utf-8") + " picture.")
print(train_x_orig.shape)
As usual, you reshape and standardize the images before feeding them to the network. The code is given in the cell below.

# Reshape the training and test examples
train_x_flatten = train_x_orig.reshape(train_x_orig.shape[0], -1).T # The "-1" makes reshape flatten the remaining dimensions
test_x_flatten = test_x_orig.reshape(test_x_orig.shape[0], -1).T
# Standardize data to have feature values between 0 and 1.
train_x = train_x_flatten/255.
test_x = test_x_flatten/255.
print ("train_x's shape: " + str(train_x.shape))
print ("test_x's shape: " + str(test_x.shape))3 - Architecture of your model
Now that you are familiar with the dataset, it is time to build a deep neural network to distinguish cat images from non-cat images.
You will build two different models:
- A 2-layer neural network
- An L-layer deep neural network
You will then compare the performance of these models, and also try out different values for ?L.
Let's look at the two architectures.
3.1 - 2-layer neural network

The model can be summarized as: ***INPUT -> LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID -> OUTPUT***.
3.2 - L-layer deep neural network
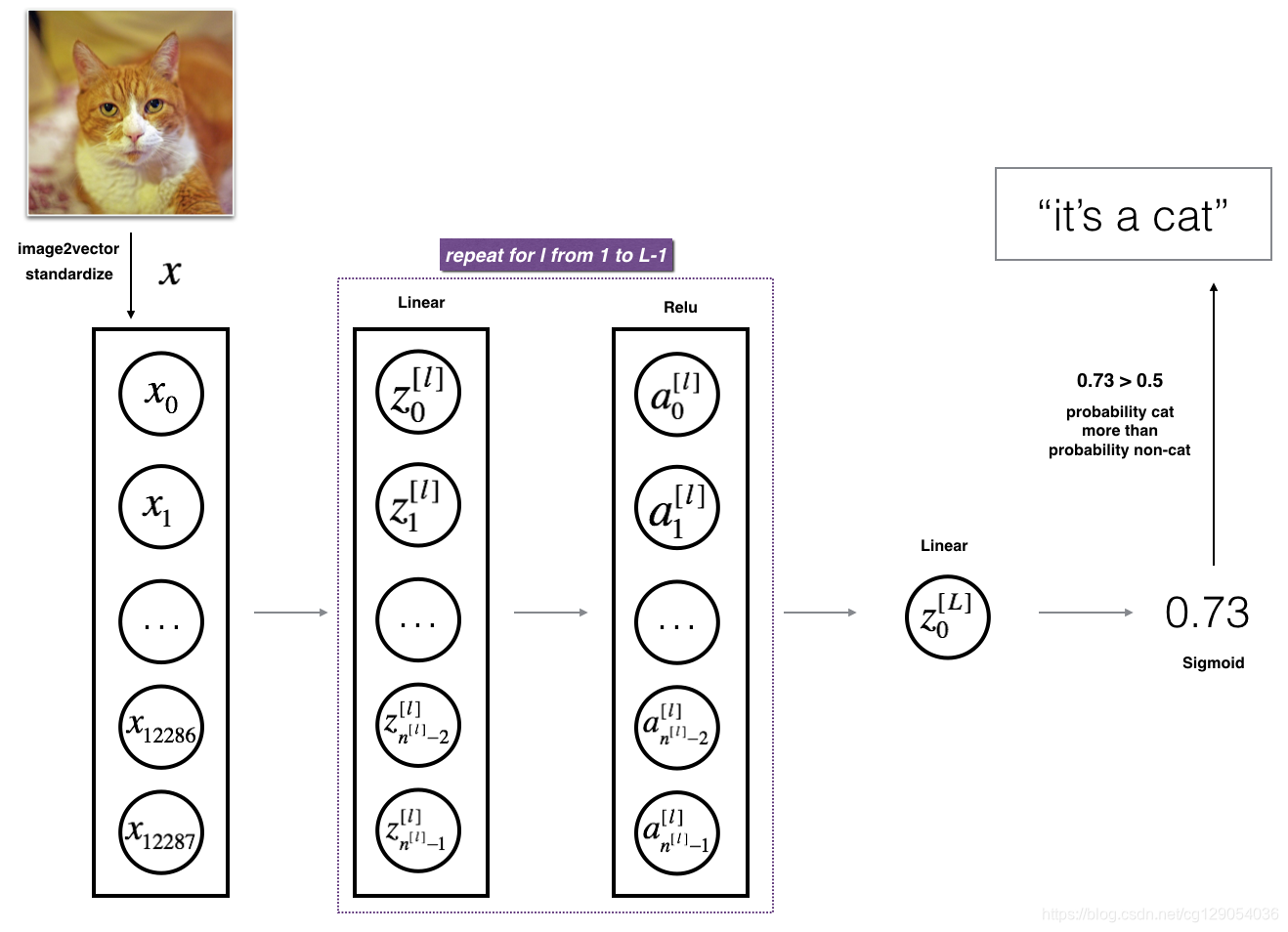
The model can be summarized as: ***[LINEAR -> RELU] ×× (L-1) -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID***
3.3 - General methodology
As usual you will follow the Deep Learning methodology to build the model:
1. Initialize parameters / Define hyperparameters
2. Loop for num_iterations:
a. Forward propagation
b. Compute cost function
c. Backward propagation
d. Update parameters (using parameters, and grads from backprop)
4. Use trained parameters to predict labels4 - Two-layer neural network
Question: Use the helper functions you have implemented in the previous assignment to build a 2-layer neural network with the following structure: LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID. The functions you may need and their inputs are:
def initialize_parameters(n_x, n_h, n_y):
...
return parameters
def linear_activation_forward(A_prev, W, b, activation):
...
return A, cache
def compute_cost(AL, Y):
...
return cost
def linear_activation_backward(dA, cache, activation):
...
return dA_prev, dW, db
def update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate):
...
return parameters### CONSTANTS DEFINING THE MODEL ####
n_x = 12288 # num_px * num_px * 3
n_h = 7
n_y = 1
layers_dims = (n_x, n_h, n_y)
def two_layer_model(X, Y, layers_dims, learning_rate = 0.0075, num_iterations = 3000, print_cost=False):
"""
Implements a two-layer neural network: LINEAR->RELU->LINEAR->SIGMOID.
Arguments:
X -- input data, of shape (n_x, number of examples)
Y -- true "label" vector (containing 0 if cat, 1 if non-cat), of shape (1, number of examples)
layers_dims -- dimensions of the layers (n_x, n_h, n_y)
num_iterations -- number of iterations of the optimization loop
learning_rate -- learning rate of the gradient descent update rule
print_cost -- If set to True, this will print the cost every 100 iterations
Returns:
parameters -- a dictionary containing W1, W2, b1, and b2
"""
np.random.seed(1)
grads = {}
costs = [] # to keep track of the cost
m = X.shape[1] # number of examples
(n_x, n_h, n_y) = layers_dims
# Initialize parameters dictionary, by calling one of the functions you'd previously implemented
parameters = initialize_parameters(n_x, n_h, n_y)
# Get W1, b1, W2 and b2 from the dictionary parameters.
W1 = parameters["W1"]
b1 = parameters["b1"]
W2 = parameters["W2"]
b2 = parameters["b2"]
# Loop (gradient descent)
for i in range(0, num_iterations):
# Forward propagation: LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID. Inputs: "X, W1, b1". Output: "A1, cache1, A2, cache2".
A1, cache1 = linear_activation_forward(X, W1, b1, 'relu')
A2, cache2 = linear_activation_forward(A1, W2, b2, 'sigmoid')
cost = compute_cost(A2, Y)
# Initializing backward propagation
dA2 = - (np.divide(Y, A2) - np.divide(1 - Y, 1 - A2))
# Backward propagation. Inputs: "dA2, cache2, cache1". Outputs: "dA1, dW2, db2; also dA0 (not used), dW1, db1".
dA1, dW2, db2 = linear_activation_backward(dA2, cache2, 'sigmoid')
dA0, dW1, db1 = linear_activation_backward(dA1, cache1, 'relu')
# Set grads['dWl'] to dW1, grads['db1'] to db1, grads['dW2'] to dW2, grads['db2'] to db2
grads['dW1'] = dW1
grads['db1'] = db1
grads['dW2'] = dW2
grads['db2'] = db2
parameters = update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate = 0.0075)
# Retrieve W1, b1, W2, b2 from parameters
W1 = parameters["W1"]
b1 = parameters["b1"]
W2 = parameters["W2"]
b2 = parameters["b2"]
# Print the cost every 100 training example
if print_cost and i % 100 == 0:
print("Cost after iteration {}: {}".format(i, np.squeeze(cost)))
if print_cost and i % 100 == 0:
costs.append(cost)
# plot the cost
plt.plot(np.squeeze(costs))
plt.ylabel('cost')
plt.xlabel('iterations (per tens)')
plt.title("Learning rate =" + str(learning_rate))
plt.show()
return parametersparameters = two_layer_model(train_x, train_y, layers_dims = (n_x, n_h, n_y), num_iterations = 2500, print_cost=True)
predictions_train = predict(train_x, train_y, parameters)5 - L-layer Neural Network
Question: Use the helper functions you have implemented previously to build an ?L-layer neural network with the following structure: [LINEAR -> RELU]××(L-1) -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID. The functions you may need and their inputs are:
def initialize_parameters_deep(layer_dims):
...
return parameters
def L_model_forward(X, parameters):
...
return AL, caches
def compute_cost(AL, Y):
...
return cost
def L_model_backward(AL, Y, caches):
...
return grads
def update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate):
...
return parameterslayers_dims = [12288, 20, 7, 5, 1] # 5-layer model
def L_layer_model(X, Y, layers_dims, learning_rate = 0.0075, num_iterations = 3000, print_cost=False):#lr was 0.009
"""
Implements a L-layer neural network: [LINEAR->RELU]*(L-1)->LINEAR->SIGMOID.
Arguments:
X -- data, numpy array of shape (number of examples, num_px * num_px * 3)
Y -- true "label" vector (containing 0 if cat, 1 if non-cat), of shape (1, number of examples)
layers_dims -- list containing the input size and each layer size, of length (number of layers + 1).
learning_rate -- learning rate of the gradient descent update rule
num_iterations -- number of iterations of the optimization loop
print_cost -- if True, it prints the cost every 100 steps
Returns:
parameters -- parameters learnt by the model. They can then be used to predict.
"""
np.random.seed(1)
costs = [] # keep track of cost
parameters = initialize_parameters_deep(layers_dims)
# Loop (gradient descent)
for i in range(0, num_iterations):
# Forward propagation: [LINEAR -> RELU]*(L-1) -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID.
AL, caches = L_model_forward(X, parameters)
# Compute cost.
cost = compute_cost(AL, Y)
# Backward propagation.
grads = L_model_backward(AL, Y, caches)
# Update parameters.
parameters = update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate = 0.0075)
# Print the cost every 100 training example
if print_cost and i % 100 == 0:
print ("Cost after iteration %i: %f" %(i, cost))
if print_cost and i % 100 == 0:
costs.append(cost)
# plot the cost
plt.plot(np.squeeze(costs))
plt.ylabel('cost')
plt.xlabel('iterations (per tens)')
plt.title("Learning rate =" + str(learning_rate))
plt.show()
return parameters6) Results Analysis
First, let's take a look at some images the L-layer model labeled incorrectly. This will show a few mislabeled images.

A few type of images the model tends to do poorly on include:
- Cat body in an unusual position
- Cat appears against a background of a similar color
- Unusual cat color and species
- Camera Angle
- Brightness of the picture
- Scale variation (cat is very large or small in image)
7) Test with your own image (optional/ungraded exercise)
Congratulations on finishing this assignment. You can use your own image and see the output of your model. To do that:
my_image = "my_image.jpg" # change this to the name of your image file
my_label_y = [] # the true class of your image (1 -> cat, 0 -> non-cat)
fname = "images/" + my_image
image = np.array(ndimage.imread(fname, flatten=False))
my_image = scipy.misc.imresize(image, size=(num_px,num_px)).reshape((num_px*num_px*3,1))
my_predicted_image = predict(my_image, my_label_y, parameters)
plt.imshow(image)
print ("y = " + str(np.squeeze(my_predicted_image)) + ", your L-layer model predicts a \"" + classes[int(np.squeeze(my_predicted_image)),].decode("utf-8") + "\" picture.")





















 1275
1275











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








