1、主要参考
(1)官网的地址
Global registration — Open3D 0.16.0 documentation
2、作用和原理
2.1个人理解
PS理解:(1)ICP的作用是,2个点云数据在初步转换关系(已知不精确)的情况下进行精细调整。(2)Global registration是不知道2个点云数据的初始关系,直接来一波计算,得到初步转换关系,接下来给ICP计算用。
2.2 介绍
ICP配准和彩色点云配准都被称为本地配准方法,因为它们依赖于粗略对齐作为初始化。本教程展示了另一类注册方法,称为全局注册。这一系列算法不需要对初始化进行对齐。它们通常产生不太紧密的对齐结果,并被用作局部方法的初始化。
2.3 例子中封装的可视化函数
下面的辅助函数将转换后的源点云与目标点云一起可视化:
def draw_registration_result(source, target, transformation):
source_temp = copy.deepcopy(source)
target_temp = copy.deepcopy(target)
source_temp.paint_uniform_color([1, 0.706, 0])
target_temp.paint_uniform_color([0, 0.651, 0.929])
source_temp.transform(transformation)
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([source_temp, target_temp],
zoom=0.4559,
front=[0.6452, -0.3036, -0.7011],
lookat=[1.9892, 2.0208, 1.8945],
up=[-0.2779, -0.9482, 0.1556])2.4 提取几何特征
我们对点云进行下采样,估计法线,然后为每个点计算一个FPFH特征。FPFH特征是描述点的局部几何性质的33维向量。在33维空间中的最近邻查询可以返回具有相似局部几何结构的点。详见[Rasu2009]。
def preprocess_point_cloud(pcd, voxel_size):
print(":: Downsample with a voxel size %.3f." % voxel_size)
pcd_down = pcd.voxel_down_sample(voxel_size)
radius_normal = voxel_size * 2
print(":: Estimate normal with search radius %.3f." % radius_normal)
pcd_down.estimate_normals(
o3d.geometry.KDTreeSearchParamHybrid(radius=radius_normal, max_nn=30))
radius_feature = voxel_size * 5
print(":: Compute FPFH feature with search radius %.3f." % radius_feature)
pcd_fpfh = o3d.pipelines.registration.compute_fpfh_feature(
pcd_down,
o3d.geometry.KDTreeSearchParamHybrid(radius=radius_feature, max_nn=100))
return pcd_down, pcd_fpfh3、测试的例子
3.1 读取输入的两个点云文件
下面的代码从两个文件读取一个源点云和一个目标点云。它们与单位矩阵的变换不对齐。
(1)注意:下面代码中的np.identity(4),相当于没有进行平移和旋转
import open3d as o3d
import numpy as np
from copy import deepcopy
def draw_registration_result(source, target, transformation):
# source_temp = copy.deepcopy(source)
# target_temp = copy.deepcopy(target)
source_temp = deepcopy(source)
target_temp = deepcopy(target)
source_temp.paint_uniform_color([1, 0.706, 0])
target_temp.paint_uniform_color([0, 0.651, 0.929])
source_temp.transform(transformation)
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([source_temp, target_temp],
zoom=0.4559,
front=[0.6452, -0.3036, -0.7011],
lookat=[1.9892, 2.0208, 1.8945],
up=[-0.2779, -0.9482, 0.1556])
def preprocess_point_cloud(pcd, voxel_size):
print(":: Downsample with a voxel size %.3f." % voxel_size)
pcd_down = pcd.voxel_down_sample(voxel_size)
radius_normal = voxel_size * 2
print(":: Estimate normal with search radius %.3f." % radius_normal)
pcd_down.estimate_normals(
o3d.geometry.KDTreeSearchParamHybrid(radius=radius_normal, max_nn=30))
radius_feature = voxel_size * 5
print(":: Compute FPFH feature with search radius %.3f." % radius_feature)
pcd_fpfh = o3d.pipelines.registration.compute_fpfh_feature(
pcd_down,
o3d.geometry.KDTreeSearchParamHybrid(radius=radius_feature, max_nn=100))
return pcd_down, pcd_fpfh
def prepare_dataset(voxel_size):
print(":: Load two point clouds and disturb initial pose.")
demo_icp_pcds = o3d.data.DemoICPPointClouds()
source = o3d.io.read_point_cloud(demo_icp_pcds.paths[0])
target = o3d.io.read_point_cloud(demo_icp_pcds.paths[1])
trans_init = np.asarray([[0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0], [1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0],
[0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0], [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0]])
source.transform(trans_init)
draw_registration_result(source, target, np.identity(4))
source_down, source_fpfh = preprocess_point_cloud(source, voxel_size)
target_down, target_fpfh = preprocess_point_cloud(target, voxel_size)
return source, target, source_down, target_down, source_fpfh, target_fpfh
if __name__ == "__main__":
voxel_size = 0.05 # means 5cm for this dataset
source, target, source_down, target_down, source_fpfh, target_fpfh = prepare_dataset(
voxel_size)
(2)下载后应该用了下面的这个文件

(3)显示的两个点云初始关系如下

(4)操作流程
3.2 RANSAC算法和测试
3.2.1原理
我们使用RANSAC进行全局注册。在每次RANSAC迭代中,从源点云中选取ransac_n个随机点。通过在33维FPFH特征空间中查询最近的邻居来检测它们在目标点云中的对应点。修剪步骤需要快速的修剪算法来快速地在早期拒绝错误匹配。
Open3D提供以下剪枝算法:
- CorrespondenceCheckerBasedOnDistance 检查对齐点云是否接近(小于指定的阈值)。
- CorrespondenceCheckerBasedOnEdgeLength检查从源和目标匹配分别绘制的任意两条边(由两个顶点组成的线)的长度是否相似。本教程检查||edgesource||>0.9带||edgetarget||和||edgetarget||>0.9带||edgesource||是否为真。
- CorrespondenceCheckerBasedOnNormal考虑任何匹配的顶点法线亲和。它计算两个法向量的点积。它取一个弧度值作为阈值。
只有通过修剪步骤的匹配才被用于计算转换,并在整个点云上进行验证。核心函数是registration_ransac_based_on_feature_matching。该函数最重要的超参数是RANSACConvergenceCriteria。它定义了RANSAC迭代的最大次数和置信概率。这两个数字越大,结果越准确,但算法花费的时间也越多。
我们根据[[Choi2015]](../reference.html# Choi2015)提供的经验值设置RANSAC参数。
3.2.2测试代码
(1)代码
import open3d as o3d
import numpy as np
from copy import deepcopy
def draw_registration_result(source, target, transformation):
# source_temp = copy.deepcopy(source)
# target_temp = copy.deepcopy(target)
source_temp = deepcopy(source)
target_temp = deepcopy(target)
source_temp.paint_uniform_color([1, 0.706, 0])
target_temp.paint_uniform_color([0, 0.651, 0.929])
source_temp.transform(transformation)
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([source_temp, target_temp],
zoom=0.4559,
front=[0.6452, -0.3036, -0.7011],
lookat=[1.9892, 2.0208, 1.8945],
up=[-0.2779, -0.9482, 0.1556])
def preprocess_point_cloud(pcd, voxel_size):
print(":: Downsample with a voxel size %.3f." % voxel_size)
pcd_down = pcd.voxel_down_sample(voxel_size)
radius_normal = voxel_size * 2
print(":: Estimate normal with search radius %.3f." % radius_normal)
pcd_down.estimate_normals(
o3d.geometry.KDTreeSearchParamHybrid(radius=radius_normal, max_nn=30))
radius_feature = voxel_size * 5
print(":: Compute FPFH feature with search radius %.3f." % radius_feature)
pcd_fpfh = o3d.pipelines.registration.compute_fpfh_feature(
pcd_down,
o3d.geometry.KDTreeSearchParamHybrid(radius=radius_feature, max_nn=100))
return pcd_down, pcd_fpfh
def prepare_dataset(voxel_size):
print(":: Load two point clouds and disturb initial pose.")
demo_icp_pcds = o3d.data.DemoICPPointClouds()
source = o3d.io.read_point_cloud(demo_icp_pcds.paths[0])
target = o3d.io.read_point_cloud(demo_icp_pcds.paths[1])
trans_init = np.asarray([[0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0], [1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0],
[0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0], [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0]])
source.transform(trans_init)
draw_registration_result(source, target, np.identity(4))
source_down, source_fpfh = preprocess_point_cloud(source, voxel_size)
target_down, target_fpfh = preprocess_point_cloud(target, voxel_size)
return source, target, source_down, target_down, source_fpfh, target_fpfh
def execute_global_registration(source_down, target_down, source_fpfh,
target_fpfh, voxel_size):
distance_threshold = voxel_size * 1.5
print(":: RANSAC registration on downsampled point clouds.")
print(" Since the downsampling voxel size is %.3f," % voxel_size)
print(" we use a liberal distance threshold %.3f." % distance_threshold)
result = o3d.pipelines.registration.registration_ransac_based_on_feature_matching(
source_down, target_down, source_fpfh, target_fpfh, True,
distance_threshold,
o3d.pipelines.registration.TransformationEstimationPointToPoint(False),
3, [
o3d.pipelines.registration.CorrespondenceCheckerBasedOnEdgeLength(
0.9),
o3d.pipelines.registration.CorrespondenceCheckerBasedOnDistance(
distance_threshold)
], o3d.pipelines.registration.RANSACConvergenceCriteria(100000, 0.999))
return result
if __name__ == "__main__":
#(1)原始,下采样,查看
voxel_size = 0.05 # means 5cm for this dataset
source, target, source_down, target_down, source_fpfh, target_fpfh = prepare_dataset(
voxel_size)
#(2)ransac全局注册
result_ransac = execute_global_registration(source_down, target_down,
source_fpfh, target_fpfh,
voxel_size)
print(result_ransac)
draw_registration_result(source_down, target_down, result_ransac.transformation)
(2)结果
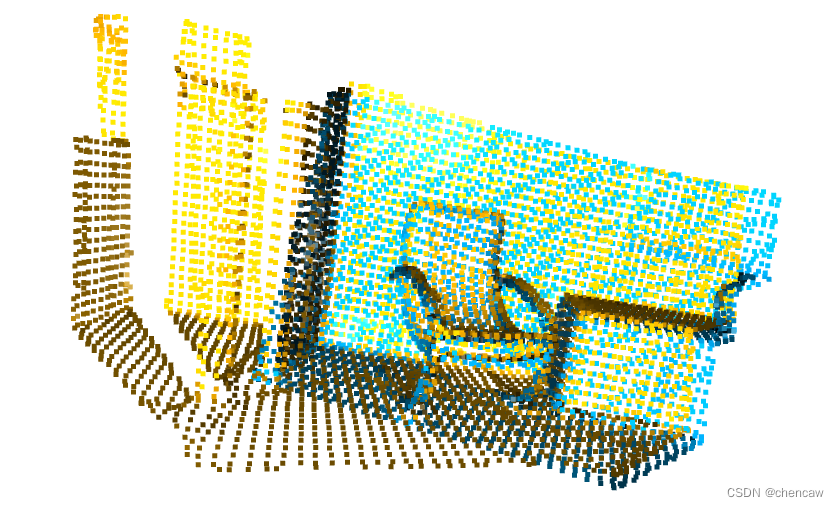
(3)发现结果还真不错,看看上一个教程icp中提到的两个指标fitness=6.745798e-01, inlier_rmse=3.051079e-02

注意:Open3D为全局注册提供了更快的实现。请参考快速全球注册。
4、局部细化(Local refinement)
(1)原理
出于性能的考虑,全局配准只在低采样的点云上执行。结果也不紧绷。我们使用点对面ICP来进一步细化对准。
(2)注意:下面的方法中使用了上一个教程中的点对面的配准方法
import open3d as o3d
import numpy as np
from copy import deepcopy
def draw_registration_result(source, target, transformation):
# source_temp = copy.deepcopy(source)
# target_temp = copy.deepcopy(target)
source_temp = deepcopy(source)
target_temp = deepcopy(target)
source_temp.paint_uniform_color([1, 0.706, 0])
target_temp.paint_uniform_color([0, 0.651, 0.929])
source_temp.transform(transformation)
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([source_temp, target_temp],
zoom=0.4559,
front=[0.6452, -0.3036, -0.7011],
lookat=[1.9892, 2.0208, 1.8945],
up=[-0.2779, -0.9482, 0.1556])
def preprocess_point_cloud(pcd, voxel_size):
print(":: Downsample with a voxel size %.3f." % voxel_size)
pcd_down = pcd.voxel_down_sample(voxel_size)
radius_normal = voxel_size * 2
print(":: Estimate normal with search radius %.3f." % radius_normal)
pcd_down.estimate_normals(
o3d.geometry.KDTreeSearchParamHybrid(radius=radius_normal, max_nn=30))
radius_feature = voxel_size * 5
print(":: Compute FPFH feature with search radius %.3f." % radius_feature)
pcd_fpfh = o3d.pipelines.registration.compute_fpfh_feature(
pcd_down,
o3d.geometry.KDTreeSearchParamHybrid(radius=radius_feature, max_nn=100))
return pcd_down, pcd_fpfh
def prepare_dataset(voxel_size):
print(":: Load two point clouds and disturb initial pose.")
demo_icp_pcds = o3d.data.DemoICPPointClouds()
source = o3d.io.read_point_cloud(demo_icp_pcds.paths[0])
target = o3d.io.read_point_cloud(demo_icp_pcds.paths[1])
trans_init = np.asarray([[0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0], [1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0],
[0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0], [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0]])
source.transform(trans_init)
draw_registration_result(source, target, np.identity(4))
source_down, source_fpfh = preprocess_point_cloud(source, voxel_size)
target_down, target_fpfh = preprocess_point_cloud(target, voxel_size)
return source, target, source_down, target_down, source_fpfh, target_fpfh
def execute_global_registration(source_down, target_down, source_fpfh,
target_fpfh, voxel_size):
distance_threshold = voxel_size * 1.5
print(":: RANSAC registration on downsampled point clouds.")
print(" Since the downsampling voxel size is %.3f," % voxel_size)
print(" we use a liberal distance threshold %.3f." % distance_threshold)
result = o3d.pipelines.registration.registration_ransac_based_on_feature_matching(
source_down, target_down, source_fpfh, target_fpfh, True,
distance_threshold,
o3d.pipelines.registration.TransformationEstimationPointToPoint(False),
3, [
o3d.pipelines.registration.CorrespondenceCheckerBasedOnEdgeLength(
0.9),
o3d.pipelines.registration.CorrespondenceCheckerBasedOnDistance(
distance_threshold)
], o3d.pipelines.registration.RANSACConvergenceCriteria(100000, 0.999))
return result
def refine_registration(source, target, source_fpfh, target_fpfh, voxel_size):
distance_threshold = voxel_size * 0.4
print(":: Point-to-plane ICP registration is applied on original point")
print(" clouds to refine the alignment. This time we use a strict")
print(" distance threshold %.3f." % distance_threshold)
result = o3d.pipelines.registration.registration_icp(
source, target, distance_threshold, result_ransac.transformation,
o3d.pipelines.registration.TransformationEstimationPointToPlane())
return result
if __name__ == "__main__":
#(1)原始,下采样,查看
voxel_size = 0.05 # means 5cm for this dataset
source, target, source_down, target_down, source_fpfh, target_fpfh = prepare_dataset(
voxel_size)
#(2)ransac全局注册
result_ransac = execute_global_registration(source_down, target_down,
source_fpfh, target_fpfh,
voxel_size)
print(result_ransac)
draw_registration_result(source_down, target_down, result_ransac.transformation)
#(3)点对面细调整
result_icp = refine_registration(source, target, source_fpfh, target_fpfh,
voxel_size)
print(result_icp)
draw_registration_result(source, target, result_icp.transformation)
(3)测试结果
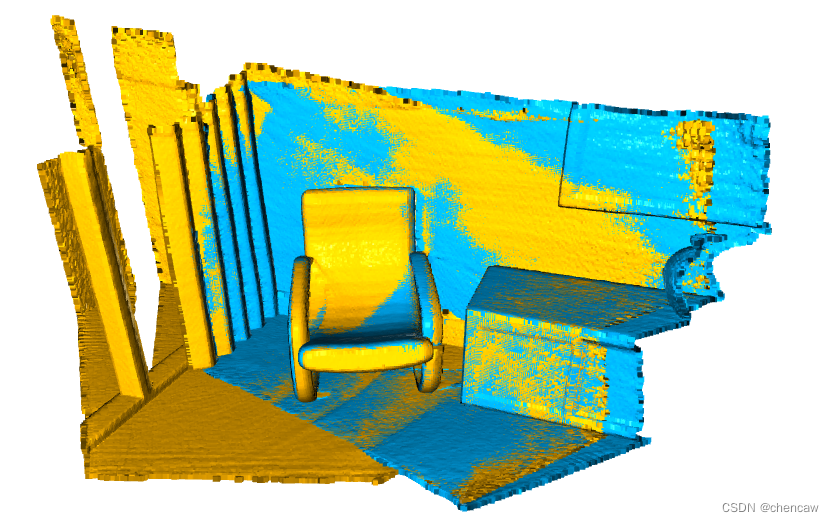
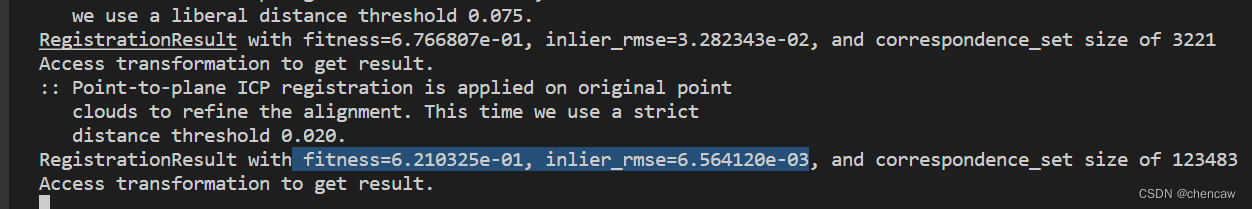
(4)匹配的参数真漂亮,参数为 fitness=6.210325e-01, inlier_rmse=6.564120e-03
5、快速全局注册(Fast global registration)
5.1原理
(1)描述
基于RANSAC的全局注册解决方案可能需要很长时间,因为有无数的模型建议和评估。[Zhou2016]提出了一种更快的方法,可以快速优化对应次数较少的线处理过程。由于每次迭代都不涉及模型提出和评估,[Zhou2016]提出的方法可以节省大量的计算时间。
(2)用到的函数
o3d.pipelines.registration.registration_fgr_based_on_correspondence(
source_down, target_down, correspondence_set,
o3d.pipelines.registration.FastGlobalRegistrationOption())
本教程将基于RANSAC的全局注册的运行时间与[Zhou2016]的实现进行比较。
5.2 测试代码
import open3d as o3d
import numpy as np
from copy import deepcopy
import time
def draw_registration_result(source, target, transformation):
# source_temp = copy.deepcopy(source)
# target_temp = copy.deepcopy(target)
source_temp = deepcopy(source)
target_temp = deepcopy(target)
source_temp.paint_uniform_color([1, 0.706, 0])
target_temp.paint_uniform_color([0, 0.651, 0.929])
source_temp.transform(transformation)
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([source_temp, target_temp],
zoom=0.4559,
front=[0.6452, -0.3036, -0.7011],
lookat=[1.9892, 2.0208, 1.8945],
up=[-0.2779, -0.9482, 0.1556])
def preprocess_point_cloud(pcd, voxel_size):
print(":: Downsample with a voxel size %.3f." % voxel_size)
pcd_down = pcd.voxel_down_sample(voxel_size)
radius_normal = voxel_size * 2
print(":: Estimate normal with search radius %.3f." % radius_normal)
pcd_down.estimate_normals(
o3d.geometry.KDTreeSearchParamHybrid(radius=radius_normal, max_nn=30))
radius_feature = voxel_size * 5
print(":: Compute FPFH feature with search radius %.3f." % radius_feature)
pcd_fpfh = o3d.pipelines.registration.compute_fpfh_feature(
pcd_down,
o3d.geometry.KDTreeSearchParamHybrid(radius=radius_feature, max_nn=100))
return pcd_down, pcd_fpfh
def prepare_dataset(voxel_size):
print(":: Load two point clouds and disturb initial pose.")
demo_icp_pcds = o3d.data.DemoICPPointClouds()
source = o3d.io.read_point_cloud(demo_icp_pcds.paths[0])
target = o3d.io.read_point_cloud(demo_icp_pcds.paths[1])
trans_init = np.asarray([[0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0], [1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0],
[0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0], [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0]])
source.transform(trans_init)
draw_registration_result(source, target, np.identity(4))
source_down, source_fpfh = preprocess_point_cloud(source, voxel_size)
target_down, target_fpfh = preprocess_point_cloud(target, voxel_size)
return source, target, source_down, target_down, source_fpfh, target_fpfh
def execute_global_registration(source_down, target_down, source_fpfh,
target_fpfh, voxel_size):
distance_threshold = voxel_size * 1.5
print(":: RANSAC registration on downsampled point clouds.")
print(" Since the downsampling voxel size is %.3f," % voxel_size)
print(" we use a liberal distance threshold %.3f." % distance_threshold)
result = o3d.pipelines.registration.registration_ransac_based_on_feature_matching(
source_down, target_down, source_fpfh, target_fpfh, True,
distance_threshold,
o3d.pipelines.registration.TransformationEstimationPointToPoint(False),
3, [
o3d.pipelines.registration.CorrespondenceCheckerBasedOnEdgeLength(
0.9),
o3d.pipelines.registration.CorrespondenceCheckerBasedOnDistance(
distance_threshold)
], o3d.pipelines.registration.RANSACConvergenceCriteria(100000, 0.999))
return result
def refine_registration(source, target, source_fpfh, target_fpfh, voxel_size):
distance_threshold = voxel_size * 0.4
print(":: Point-to-plane ICP registration is applied on original point")
print(" clouds to refine the alignment. This time we use a strict")
print(" distance threshold %.3f." % distance_threshold)
result = o3d.pipelines.registration.registration_icp(
source, target, distance_threshold, result_ransac.transformation,
o3d.pipelines.registration.TransformationEstimationPointToPlane())
return result
def execute_fast_global_registration(source_down, target_down, source_fpfh,
target_fpfh, voxel_size):
distance_threshold = voxel_size * 0.5
print(":: Apply fast global registration with distance threshold %.3f" \
% distance_threshold)
result = o3d.pipelines.registration.registration_fgr_based_on_feature_matching(
source_down, target_down, source_fpfh, target_fpfh,
o3d.pipelines.registration.FastGlobalRegistrationOption(
maximum_correspondence_distance=distance_threshold))
return result
if __name__ == "__main__":
#(1)原始,下采样,查看
voxel_size = 0.05 # means 5cm for this dataset
source, target, source_down, target_down, source_fpfh, target_fpfh = prepare_dataset(
voxel_size)
#(2)ransac全局注册,计算时间
start = time.time()
result_ransac = execute_global_registration(source_down, target_down,
source_fpfh, target_fpfh,
voxel_size)
print("Global registration took %.3f sec.\n" % (time.time() - start))
print(result_ransac)
draw_registration_result(source_down, target_down, result_ransac.transformation)
# #(3)点对面细调整
# result_icp = refine_registration(source, target, source_fpfh, target_fpfh,
# voxel_size)
# print(result_icp)
# draw_registration_result(source, target, result_icp.transformation)
# (4)快速全局注册,计算时间
start = time.time()
result_fast = execute_fast_global_registration(source_down, target_down,
source_fpfh, target_fpfh,
voxel_size)
print("Fast global registration took %.3f sec.\n" % (time.time() - start))
print(result_fast)
draw_registration_result(source_down, target_down, result_fast.transformation)
5.3 结论
PS:没仔细看,感觉和官网给的数据结果一样,速度没有快起来啊。大家有空仔细研究一下。
通过适当的配置,快速全局注册的精度甚至可以与ICP媲美。更多实验结果见[Zhou2016]。
除了基于fpfh特征的FGR,全局注册还可以通过registration_fgr_based_on_correspondence使用基于通信的FGR执行。如果您的通信前端不同于FPFH,但您仍然希望在给定一组假定通信时使用FGR,则此方法是有用的。调用方法如下:
注意,该方法和上面的测试方法不同。
o3d.pipelines.registration.registration_fgr_based_on_correspondence(
source_down, target_down, correspondence_set,
o3d.pipelines.registration.FastGlobalRegistrationOption())























 1217
1217











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








