这一部分主要是关于用BP算法来计算梯度,在这一章中,主要解决下面三个问题:
1.梯度的意义(what the gradients mean?)
2.在网络中梯度如何通过反向传播(how they flow backwards in the circuit?)
3.如何调整?( how they communicate which part of the circuit should increase or decrease and with what force to make the final output higher.)
梯度的意义
梯度的意义与在向量代数中曾经给出,它表示一个函数在某一点变化最快的方向(即方向导数最大值),梯度是一个向量。例如:
再如,sigmoid函数的梯度:
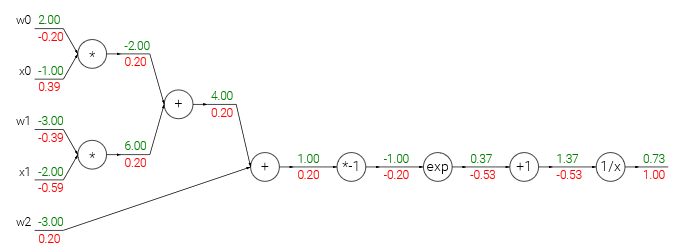
w = [2,-3,-3] # assume some random weights and data
x = [-1, -2]
# forward pass
dot = w[0]*x[0] + w[1]*x[1] + w[2]
f = 1.0 / (1 + math.exp(-dot)) # sigmoid function
# backward pass through the neuron (backpropagation)
ddot = (1 - f) * f # gradient on dot variable, using the sigmoid gradient derivation
dx = [w[0] * ddot, w[1] * ddot] # backprop into x
dw = [x[0] * ddot, x[1] * ddot, 1.0 * ddot] # backprop into w
# we're done! we have the gradientr circuit
- 在网络中梯度如何通过反向传播
在神经网络中常用的计算有三种即加法、乘法、取最大(add,mul,max),每一种计算称为一个gate,经过不同的gate梯度发生的变化如下:
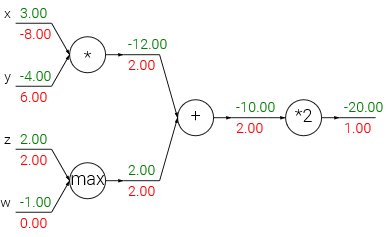
加法:梯度不变
乘法:按照链式法则相乘
取最大:对于最大值,乘以1.0,其余乘以0.0
- 矩阵与矩阵相乘后的梯度求算
import numpy as np
W = np.random.randn(5, 10)
X = np.random.randn(10, 3)
D = W.dot(X)
# now suppose we had the gradient on D from above in the circuit
dD = np.random.randn(*D.shape) # same shape as D
dW = dD.dot(X.T) #.T gives the transpose of the matrix
dX = W.T.dot(dD)
print W
print "#############################"
print X
print "#############################"
print D
print "#############################"
print dD
print "#############################"
print dW
print "#############################"
print dX








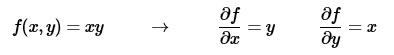
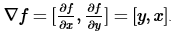
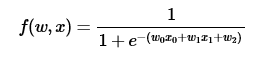

















 2262
2262

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










