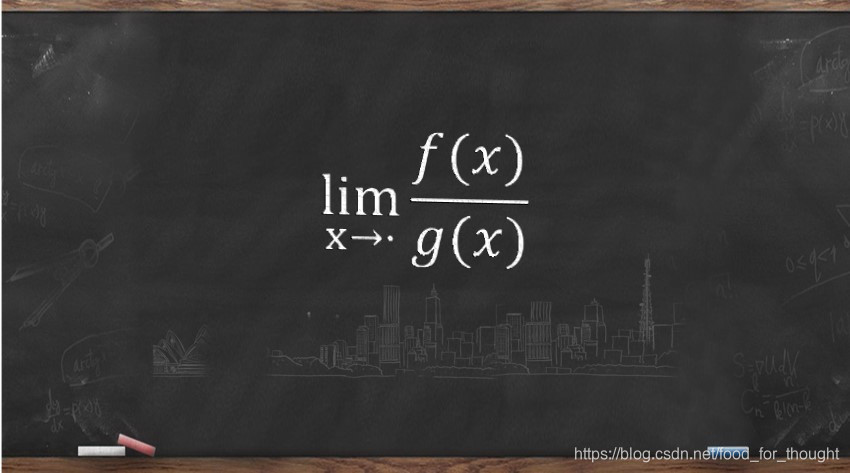
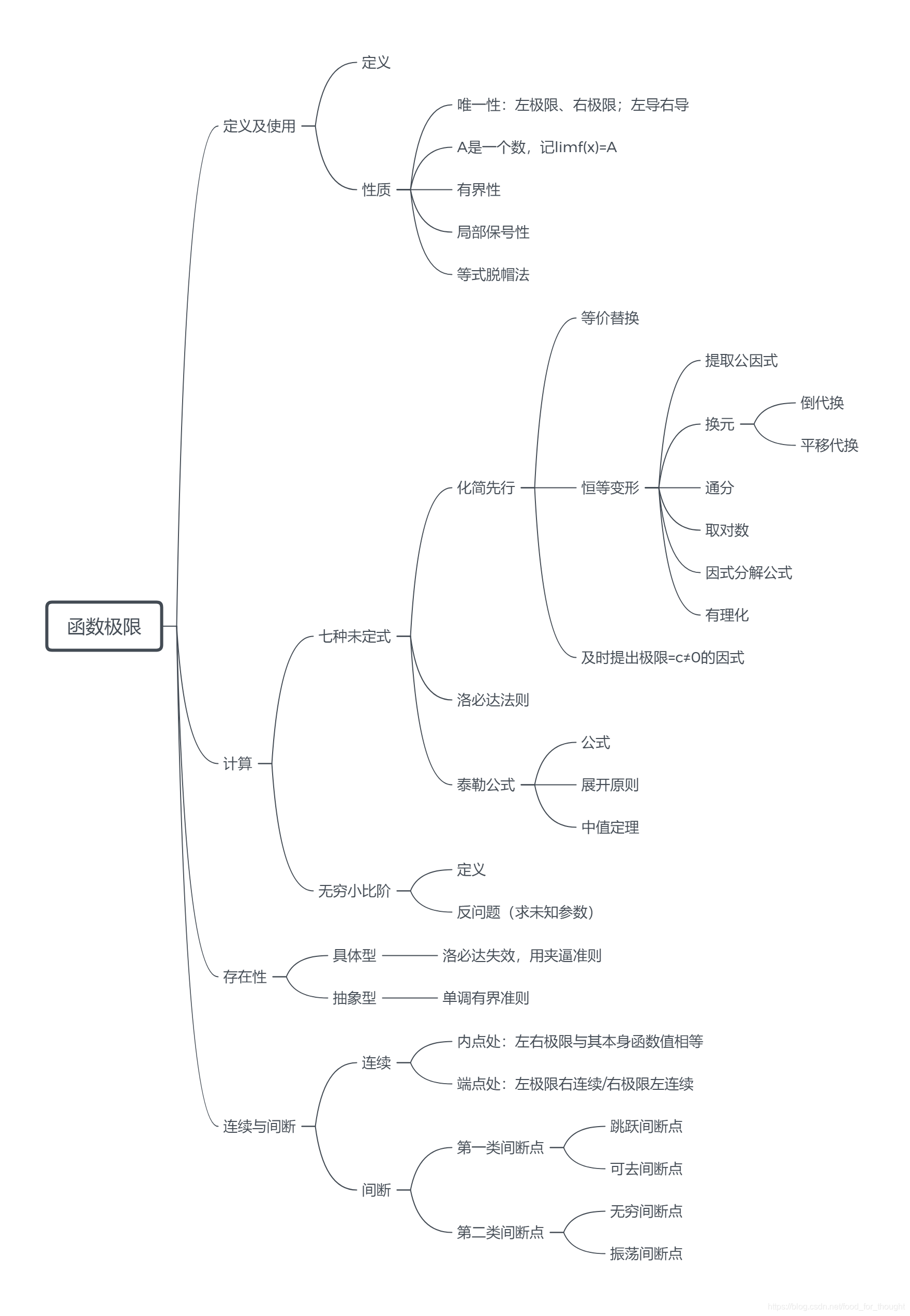
定义及使用
定义
lim x → ⋅ f ( x ) = A    ⟺    ∀ ε > 0 , x → ⋅ 时 , ∣ f ( x ) − A ∣ < ε { x → x 0 : ∃ δ > 0 , 0 < ∣ x − x 0 ∣ < δ x → ∞ : ∃ x > 0 , ∣ x ∣ > x \begin{aligned} &\lim_{x\to\cdot}f(x)=A\iff\\ &\forall\varepsilon>0,x\to\cdot时,|f(x)-A|<\varepsilon\\ &\begin{cases}x\to x_0:\exists\delta>0,0<|x-x_0|<\delta\\x\to\infty:\exists x>0,|x|>x\end{cases}\\ \end{aligned} x→⋅limf(x)=A⟺∀ε>0,x→⋅时,∣f(x)−A∣<ε{x→x0:∃δ>0,0<∣x−x0∣<δx→∞:∃x>0,∣x∣>x
性质
唯一性
A 唯 一 : 左 极 限 、 右 极 限 ; 左 导 、 右 导 [ 例 ] 求 lim x → 0 tan π x ∣ x ∣ ( x 2 − 1 ) I + = lim x → 0 + tan π x x ( x 2 − 1 ) = lim x → 0 + π x x ( − 1 ) = − π I − = lim x → 0 − π x ( − x ) ( − 1 ) = π    ⟹    I 不 ∃ [ 注 ] 如 ∣ x ∣ , e x , arctan x 需 要 考 虑 这 种 情 况 \begin{aligned} &A唯一:左极限、右极限;左导、右导\\ \color{maroon}[例]&求\lim_{x\to0}\frac{\tan\pi x}{|x|(x^2-1)}\\ &\color{black}I_+=\lim_{x\to0^+}\frac{\tan\pi x}{x(x^2-1)}=\lim_{x\to0^+}\frac{\pi x}{x(-1)}=-\pi\\ &I_-=\lim_{x\to0^-}\frac{\pi x}{(-x)(-1)}=\pi\\ &\implies I不\exists\\ \color{grey}[注]&如|x|,e^x,\arctan x需要考虑这种情况 \end{aligned} [例][注]A唯一:左极限、右极限;左导、右导求x→0lim∣x∣(x2−1)tanπxI+=x→0+limx(x2−1)tanπx=x→0+limx(−1)πx=−πI−=x→0−lim(−x)(−1)πx=π⟹I不∃如∣x∣,ex,arctanx需要考虑这种情况
A是一个数
A 是 一 个 数 , 记 lim x → ⋅ f ( x ) = A [ 例 ] 已 知 lim x → 1 f ( x ) 存 在 , f ( x ) = x − arctan ( x − 1 ) − 1 ( x − 1 ) 3 + 2 x 2 e x − 1 ⋅ lim x → 1 f ( x ) lim x → 1 f ( x ) = lim x → 1 ( x − 1 ) − arctan ( x − 1 ) ( x − 1 ) 3 + A lim x → 1 2 x 2 e x − 1    ⟹    A = lim t → 0 t − arctan t t 3 + 2 A    ⟹    A = − 1 3 ∴ f ( x ) = x − arctan ( x − 1 ) − 1 ( x − 1 ) 3 − 2 3 x 2 e x − 1 [ 注 ] 以 后 会 知 道 , " 只 要 存 在 " , 则 有 lim x → ⋅ f ( x ) = A , lim x → ∞ x n = A f ′ ′ ( x 0 ) = A ; ∫ a b f ( x ) d x = A ; ∬ D f ( x , y ) d σ = A \begin{aligned} &A是一个数,记\lim_{x\to\cdot}f(x)=A\\ \color{maroon}[例]&已知\lim_{x\to1}f(x)存在,f(x)=\frac{x-\arctan(x-1)-1}{(x-1)^3}+2x^2e^{x-1}\cdot\lim_{x\to1}f(x)\\ &\color{black}\lim_{x\to1}f(x)=\lim_{x\to1}\frac{(x-1)-\arctan(x-1)}{(x-1)^3}+A\lim_{x\to1}2x^2e^{x-1}\\ &\implies A=\lim_{t\to0}\frac{t-\arctan t}{t^3}+2A\\ &\implies A=-\frac13\\ &\therefore f(x)=\frac{x-\arctan(x-1)-1}{(x-1)^3}-\frac23x^2e^{x-1}\\ \color{grey}[注]&以后会知道,"只要存在",则有\lim_{x\to\cdot}f(x)=A,\lim_{x\to\infty}x_n=A\\ &f''(x_0)=A;\int_a^bf(x)dx=A;\iint_Df(x,y)d\sigma=A \end{aligned} [例][注]A是一个数,记x→⋅limf(x)=A已知x→1limf(x)存在,f(x)=(x−1)3x−arctan(x−1)−1+2x2ex−1⋅x→1limf(x)x→1limf(x)=x→1lim(x−1)3(x−1)−arctan(x−1)+Ax→1lim2x2ex−1⟹A=t→0limt3t−arctant+2A⟹A=−31∴f(x)=(x−1)3x−arctan(x−1)−1−32x2ex−1以后会知道,"只要存在",则有x→⋅limf(x)=A,x→∞limxn=Af′′(x0)=A;∫abf(x)dx=A;∬Df(x,y)dσ=A
有界性
x → ⋅ , ∣ f ( x ) ∣ ≤ M [ 例 ] 若 lim x → x 0 f ( x ) x − x 0 = A ( 存 在 ) , 求 lim x → x 0 f ( x ) lim x → x 0 f ( x ) = lim x → x 0 f ( x ) x − x 0 ⋅ ( x − x 0 ) = 0 ( 前 者 有 界 函 数 , 后 者 无 穷 小 ) [ 注 ] 若 增 加 “ f ( x ) 在 x 0 处 连 续 ”    ⟹    f ( x ) = lim x → x 0 f ( x ) = 0 \begin{aligned} &x\to\cdot,|f(x)|\leq M\\ \color{maroon}[例]&若\lim_{x\to x_0}\frac{f(x)}{x-x_0}=A(存在),求\lim_{x\to x_0}f(x)\\ &\color{black}\lim_{x\to x_0}f(x)=\lim_{x\to x_0}\frac{f(x)}{x-x_0}\cdot(x-x_0)=0(前者有界函数,后者无穷小)\\ \color{grey}[注]&若增加“f(x)在x_0处连续”\implies f(x)=\lim_{x\to x_0}f(x)=0 \end{aligned} [例][注]x→⋅,∣f(x)∣≤M若x→x0limx−x0f(x)=A(存在),求x→x0limf(x)x→x0limf(x)=x→x0limx−x0f(x)⋅(x−x0)=0(前者有界函数,后者无穷小)若增加“f(x)在x0处连续”⟹f(x)=x→x0limf(x)=0
局部保号性
x → ⋅ , 若 A > 0 ,    ⟹    f ( x ) > 0 ( 局 部 保 号 ) ( 不 等 式 脱 帽 法 ) [ 例 ] 证 明 : 当 x → 0 + 时 , 0 < tan 2 x − x 2 < x 4 成 立 lim x → 0 + tan 2 x − x 2 x 4 = lim x → 0 + ( tan x + x ) ( tan x − x ) x 4 = lim x → 0 + 2 x ⋅ 1 3 x 3 x 4 = 2 3 < 1 故 lim x → 0 + [ tan 2 x − x 2 x 4 − 1 ] < 0    ⟹    tan 2 x − x 2 x 4 − 1 < 0 即 tan 2 x − x 2 < x 4 ∵ x → 0 + 时 , tan x > x , 故 tan 2 x > x 2    ⟹    0 < tan 2 x − x 2 < x 4 \begin{aligned} &x\to\cdot,若A>0,\implies f(x)>0(局部保号)(不等式脱帽法)\\ \color{maroon}[例]&证明:当x\to0^+时,0<\tan^2x-x^2<x^4成立\\ &\color{black}\lim_{x\to0^+}\frac{\tan^2x-x^2}{x^4}=\lim_{x\to0^+}\frac{(\tan x+x)(\tan x-x)}{x^4}=\lim_{x\to0^+}\frac{2x\cdot\frac13x^3}{x^4}=\frac23<1\\ &故\lim_{x\to0^+}[\frac{\tan^2x-x^2}{x^4}-1]<0\implies\frac{\tan^2x-x^2}{x^4}-1<0\\ &即\tan^2x-x^2<x^4\\ &\because x\to0^+时,\tan x>x,故\tan^2x>x^2\implies0<\tan^2x-x^2<x^4 \end{aligned} [例]x→⋅,若A>0,⟹f(x)>0(局部保号)(不等式脱帽法)证明:当x→0+时,0<tan2x−x2<x4成立x→0+limx4tan2x−x2=x→0+limx4(tanx+x)(tanx−x)=x→0+limx42x⋅31x3=32<1故x→0+lim[x4tan2x−x2−1]<0⟹x4tan2x−x2−1<0即tan2x−x2<x4∵x→0+时,tanx>x,故tan2x>x2⟹0<tan2x−x2<x4
等式脱帽法
f ( x ) = A + α , lim x → ⋅ α = 0 ( 等 式 脱 帽 法 ) [ 例 ] 设 lim x → 0 ln [ 1 + f ( x ) sin x ] a x − 1 = A , a > 0 , a ≠ 1 , 求 lim x → 0 f ( x ) x 2 ln [ 1 + f ( x ) sin x ] a x − 1 = A + α    ⟹    ln [ 1 + f ( x ) sin x ] = ( a x − 1 ) ( A + α ) 1 + f ( x ) sin x = e ( a x − 1 ) ( A + α ) f ( x ) = [ e ( a x − 1 ) ( A + α ) − 1 ] sin x 则 lim x → 0 f ( x ) x 2 = lim x → 0 [ e ( a x − 1 ) ( A + α ) − 1 ] sin x x 2 = lim x → 0 ( a x − 1 ) ( A + α ) x = A ⋅ ln a \begin{aligned} &f(x)=A+\alpha,\lim_{x\to\cdot}\alpha=0(等式脱帽法)\\ \color{maroon}[例]&设\lim_{x\to0}\frac{\ln[1+\frac{f(x)}{\sin x}]}{a^x-1}=A,a>0,a\neq1,求\lim_{x\to0}\frac{f(x)}{x^2}\\ &\color{black}\frac{\ln[1+\frac{f(x)}{\sin x}]}{a^x-1}=A+\alpha\implies \ln[1+\frac{f(x)}{\sin x}]=(a^x-1)(A+\alpha)\\ &1+\frac{f(x)}{\sin x}=e^{(a^x-1)(A+\alpha)}\\ &f(x)=[e^{(a^x-1)(A+\alpha)}-1]\sin x\\ &则\lim_{x\to0}\frac{f(x)}{x^2}=\lim_{x\to0}\frac{[e^{(a^x-1)(A+\alpha)}-1]\sin x}{x^2}=\lim_{x\to0}\frac{(a^x-1)(A+\alpha)}x=A\cdot\ln a \end{aligned} [例]f(x)=A+α,x→⋅limα=0(等式脱帽法)设x→0limax−1ln[1+sinxf(x)]=A,a>0,a̸=1,求x→0limx2f(x)ax−1ln[1+sinxf(x)]=A+α⟹ln[1+sinxf(x)]=(ax−1)(A+α)1+sinxf(x)=e(ax−1)(A+α)f(x)=[e(ax−1)(A+α)−1]sinx则x→0limx2f(x)=x→0limx2[e(ax−1)(A+α)−1]sinx=x→0limx(ax−1)(A+α)=A⋅lna
计算
七种未定式
分 别 为 : 0 0 , ∞ ∞ , ∞ ⋅ 0 , ∞ − ∞ , ∞ 0 , 0 0 , 1 ∞ 技 巧 : 其 中 前 两 种 用 常 规 方 法 如 泰 勒 公 式 、 洛 必 达 法 则 直 接 求 解 第 三 、 四 种 情 况 遇 到 分 数 考 虑 通 分 、 倒 代 换 等 , 想 办 法 等 价 替 换 、 化 简 后 三 种 情 况 一 律 考 虑 取 对 数 其 中 遇 到 根 号 的 情 况 考 虑 有 理 化 、 通 分 , 遇 到 无 穷 大 的 情 况 考 虑 化 为 无 穷 小 , 如 除 以 某 个 数 , 倒 代 换 , 通 分 , 有 理 化 遇 到 三 角 函 数 考 虑 无 穷 小 乘 以 有 界 量 复 杂 函 数 可 以 考 虑 导 数 定 义 法 加 减 中 把 极 限 存 在 ( 不 管 是 否 为 0 ) 的 部 分 拆 项 先 算 出 来 , 乘 除 中 把 极 限 存 在 部 分 先 分 离 出 来 \begin{aligned} &分别为:\frac00,\frac\infty\infty,\infty\cdot0,\infty-\infty,\infty^0,0^0,1^\infty\\ 技巧:&其中前两种用常规方法如泰勒公式、洛必达法则直接求解\\ &第三、四种情况遇到分数考虑通分、倒代换等,想办法等价替换、化简\\ &后三种情况一律考虑取对数\\ &其中遇到根号的情况考虑有理化、通分,\\ &遇到无穷大的情况考虑化为无穷小,如除以某个数,倒代换,通分,有理化\\ &遇到三角函数考虑无穷小乘以有界量\\ &复杂函数可以考虑导数定义法\\ &加减中把极限存在(不管是否为0)的部分拆项先算出来,乘除中把极限存在部分先分离出来 \end{aligned} 技巧:分别为:00,∞∞,∞⋅0,∞−∞,∞0,00,1∞其中前两种用常规方法如泰勒公式、洛必达法则直接求解第三、四种情况遇到分数考虑通分、倒代换等,想办法等价替换、化简后三种情况一律考虑取对数其中遇到根号的情况考虑有理化、通分,遇到无穷大的情况考虑化为无穷小,如除以某个数,倒代换,通分,有理化遇到三角函数考虑无穷小乘以有界量复杂函数可以考虑导数定义法加减中把极限存在(不管是否为0)的部分拆项先算出来,乘除中把极限存在部分先分离出来
化简先行
等价替换
sin ∘ ∼ ∘ ∼ tan ∘ ∼ arcsin ∘ ∼ arctan ∘ ∼ ln ( 1 + ∘ ) ∼ e ∘ − 1 a ∘ − 1 = e ∘ ln a − 1 ∼ ∘ ln a ( 1 + ∘ ) k − 1 = e k ln ( 1 + ∘ ) − 1 ∼ k ln ( 1 + ∘ ) ∼ k ∘ 1 − c o s ∘ = 2 s i n 2 ( ∘ 2 ) ∼ 2 ( ∘ 2 ) 2 = ∘ 2 2 — — — — — — — — — — 以 下 是 进 阶 版 — — — — — — — — — — x − sin x ∼ 1 6 x 3 x − arcsin x ∼ − 1 6 x 3 x − tan x ∼ − 1 3 x 3 x − arctan x ∼ 1 3 x 3 x − ln ( 1 + x ) ∼ 1 2 x 2 tan x − sin x ∼ 1 2 x 3 1 − cos α x ∼ α 2 x 2 e x − 1 − x ∼ 1 2 x 2 1 + x − 1 − 1 2 x ∼ − 1 8 x 2 f ( x ) → 1 时 , ln f ( x ) ∼ f ( x ) − 1 [ 补 ] 若 α = ∘ ( β ) ( 即 lim x → ⋅ α β = 0 ) , 则 α + β ∼ β \begin{aligned} &\sin\circ\sim\circ\sim \tan\circ\sim \arcsin\circ\sim \arctan\circ\sim \ln(1+\circ)\sim e^\circ-1\\ &a^\circ-1=e^{\circ \ln a}-1\sim\circ\ln a\\ &(1+\circ)^k-1=e^{k\ln(1+\circ)}-1\sim k\ln(1+\circ)\sim k\circ\\ &1-cos\circ=2sin^2(\frac\circ2)\sim2(\frac\circ2)^2=\frac{\circ^2}{2}\\ &——————————以下是进阶版——————————\\ &x-\sin x \sim\frac16x^3\qquad x-\arcsin x\sim-\frac16x^3\qquad x-\tan x\sim-\frac13x^3\\ &x-\arctan x\sim\frac13x^3\qquad x-\ln(1+x)\sim\frac12x^2\qquad \tan x-\sin x\sim\frac12x^3\\ &1-\cos^\alpha x\sim\frac\alpha2x^2\qquad e^x-1-x\sim\frac12x^2\qquad\sqrt{1+x}-1-\frac12x\sim-\frac18x^2\\ &f(x)\to1时,\ln f(x)\sim f(x)-1\\ [补]&若\alpha=\circ(\beta)(即\lim_{x\to\cdot}\frac{\alpha}{\beta}=0),则\alpha+\beta\sim\beta\\ \end{aligned} [补]sin∘∼∘∼tan∘∼arcsin∘∼arctan∘∼ln(1+∘)∼e∘−1a∘−1=e∘lna−1∼∘lna(1+∘)k−1=ekln(1+∘)−1∼kln(1+∘)∼k∘1−cos∘=2sin2(2∘)∼2(2∘)2=2∘2——————————以下是进阶版——————————x−sinx∼61x3x−arcsinx∼−61x3x−tanx∼−31x3x−arctanx∼31x3x−ln(1+x)∼21x2tanx−sinx∼21x31−cosαx∼2αx2ex−1−x∼21x21+x−1−21x∼−81x2f(x)→1时,lnf(x)∼f(x)−1若α=∘(β)(即x→⋅limβα=0),则α+β∼β
1. lim x → 0 ( 3 + 2 tan x ) x − 3 x 3 sin 2 x + x 3 cos 1 x 由 x 3 cos 1 x 3 sin 2 x = 1 3 lim x → 0 x cos 1 x = 0 则 I = lim x → 0 3 x [ ( 1 + 2 3 tan x ) x − 1 ] 3 x 2 = lim x → 0 e x ln ( 1 + 2 3 tan x ) − 1 3 x 2 = lim x → 0 x ln ( 1 + 2 3 tan x ) 3 x 2 = 2 9 2. lim x → 1 − ln x ln ( 1 − x ) = lim x → 1 − ln ( 1 + x − 1 ) ln ( 1 − x ) = lim x → 1 − ( x − 1 ) ln ( 1 − x ) t = 1 − x → − lim t → 0 + t ln t = 0 3. lim x → ∞ e − x ( 1 + 1 x ) x 2 = lim x → ∞ e − x e x 2 ln ( 1 + 1 x ) = lim x → ∞ e x 2 ln ( 1 + 1 x ) − x 且 lim x → ∞ ( x 2 ln ( 1 + 1 x ) − x ) = lim x → ∞ x 2 ( ln ( 1 + 1 x ) − 1 x ) = lim x → ∞ x 2 ( − 1 2 ) ( 1 x ) 2 = − 1 2 4. lim x → 0 sin x + x 2 sin 1 x ( 1 + cos x ) ln ( 1 + x ) = lim x → 0 x 2 x = 1 2 ( 无 穷 小 乘 以 有 界 量 ) 5. lim x → 0 1 x 3 [ ( 2 + cos x 3 ) x − 1 ] = lim x → 0 1 x 3 [ ( 1 + cos x − 1 3 ) x − 1 ] = lim x → 0 1 x 3 ⋅ x ⋅ cos x − 1 3 = − 1 6 6. lim x → 0 cos x − cos x 3 sin 2 x = lim x → 0 cos x − 1 + 1 − cos x 3 x 2 = lim x → 0 cos x − 1 x 2 + lim x → 0 1 − cos x 3 x 2 = lim x → 0 − 1 4 x 2 x 2 + lim x → 0 1 6 x 2 x 2 = − 1 12 \begin{aligned} 1.&\color{maroon}\lim_{x\to0}\frac{(3+2\tan x)^x-3^x}{3\sin^2x+x^3\cos\frac1x}\\ &由\frac{x^3\cos\frac1x}{3\sin^2x}=\frac13\lim_{x\to0}x\cos\frac1x=0\\ &则I=\lim_{x\to0}\frac{3^x[(1+\frac23\tan x)^x-1]}{3x^2}\\ &=\lim_{x\to0}\frac{e^{x\ln(1+\frac23\tan x)}-1}{3x^2}\\ &=\lim_{x\to0}\frac{x\ln(1+\frac23\tan x)}{3x^2}=\frac29\\ 2.&\color{maroon}\lim_{x\to1^-}\ln x\ln(1-x)\\ =&\lim_{x\to1^-}\ln(1+x-1)\ln(1-x)\\ =&\lim_{x\to1^-}(x-1)\ln(1-x)\underrightarrow{t=1-x}-\lim_{t\to0^+}t\ln t=0\\ 3.&\color{maroon}\lim_{x\to\infty}e^{-x}(1+\frac1x)^{x^2}\\ =&\lim_{x\to\infty}e^{-x}e^{x^2\ln(1+\frac1x)}\\ =&\lim_{x\to\infty}e^{x^2\ln(1+\frac1x)-x}\\ &且\lim_{x\to\infty}(x^2\ln(1+\frac1x)-x)\\ =&\lim_{x\to\infty}x^2(\ln(1+\frac1x)-\frac1x)\\ =&\lim_{x\to\infty}x^2(-\frac12)(\frac1x)^2=-\frac12\\ 4.&\color{maroon}\lim_{x\to0}\frac{\sin x+x^2\sin\frac1x}{(1+\cos x)\ln(1+x)}\\ =&\lim_{x\to0}\frac{x}{2x}=\frac12(无穷小乘以有界量)\\ 5.&\color{maroon}\lim_{x\to0}\frac1{x^3}[(\frac{2+\cos x}{3})^x-1]\\ =&\lim_{x\to0}\frac1{x^3}[(1+\frac{\cos x-1}{3})^x-1]\\ =&\lim_{x\to0}\frac1{x^3}\cdot x\cdot \frac{\cos x-1}3\\ =&-\frac16\\ 6.&\color{maroon}\lim_{x\to0}\frac{\sqrt{\cos x}-\sqrt[3]{\cos x}}{\sin^2x}\\ =&\lim_{x\to0}\frac{\sqrt{\cos x}-1+1-\sqrt[3]{\cos x}}{x^2}\\ =&\lim_{x\to0}\frac{\sqrt{\cos x}-1}{x^2}+\lim_{x\to0}\frac{1-\sqrt[3]{\cos x}}{x^2}\\ =&\lim_{x\to0}\frac{-\frac14x^2}{x^2}+\lim_{x\to0}\frac{\frac16x^2}{x^2}\\ =&-\frac1{12}\\ \end{aligned} 1.2.==3.====4.=5.===6.====x→0lim3sin2x+x3cosx1(3+2tanx)x−3x由3sin2xx3cosx1=31x→0limxcosx1=0则I=x→0lim3x23x[(1+32tanx)x−1]=x→0lim3x2exln(1+32tanx)−1=x→0lim3x2xln(1+32tanx)=92x→1−limlnxln(1−x)x→1−limln(1+x−1)ln(1−x)x→1−lim(x−1)ln(1−x)t=1−x−t→0+limtlnt=0x→∞lime−x(1+x1)x2x→∞lime−xex2ln(1+x1)x→∞limex2ln(1+x1)−x且x→∞lim(x2ln(1+x1)−x)x→∞limx2(ln(1+x1)−x1)x→∞limx2(−21)(x1)2=−21x→0lim(1+cosx)ln(1+x)sinx+x2sinx1x→0lim2xx=21(无穷小乘以有界量)x→0limx31[(32+cosx)x−1]x→0limx31[(1+3cosx−1)x−1]x→0limx31⋅x⋅3cosx−1−61x→0limsin2xcosx−3cosxx→0limx2cosx−1+1−3cosxx→0limx2cosx−1+x→0limx21−3cosxx→0limx2−41x2+x→0limx261x2−121
恒等变形
提取公因式
换元(倒代换、平移替换)
通分
因式分解公式
取对数
有理化
1. lim x → 0 ( 1 + x 1 − e − x − 1 x ) = lim x → 0 x + x 2 − 1 + e − x ( 1 − e − x ) ⋅ x ( 通 分 ) = lim x → 0 1 + 2 x − e − x 2 x = 1 + 1 2 = 3 2 2. lim x → ∞ e − x ( 1 + 1 x ) x 2 = lim x → ∞ e − x e x 2 ln ( 1 + 1 x ) ( 取 对 数 ) = e lim x → ∞ [ x 2 ln ( 1 + 1 x ) − x ] 令 x = 1 t → e lim t → 0 [ ln ( 1 + t ) t 2 − 1 t ] ( 倒 代 换 ) = e lim t → 0 ln ( 1 + t ) − t t 2 = e − 1 2 3. lim x → 0 + x ln ( ln x − 1 ln x + 1 ) = e lim x → 0 + ln ( ln x − 1 ln x + 1 ) ⋅ ln x = e lim x → 0 + ln ( 1 − 2 ln x + 1 ) ⋅ ln x = e lim x → 0 + − 2 ln x + 1 ⋅ ln x = e − 2 4. lim x → 0 + ( sin x x ) 1 1 − cos x = e lim x → 0 + 1 1 − cos x ( sin x x − 1 ) = e lim x → 0 + sin x − x 1 2 x 2 ⋅ x = e − 1 3 5. lim x → ∞ ( x 6 + x 5 6 − x 6 − x 5 6 ) 令 x = 1 t → lim t → 0 + 1 t 6 + 1 t 5 6 − 1 t 6 − 1 t 5 6 = lim t → 0 + ( 1 + t 6 t − 1 − t 6 t ) = lim t → 0 + ( 1 + t ) 1 6 − ( 1 − t ) 1 6 t = lim t → 0 + 1 + 1 6 t − ( 1 − 1 6 t ) + ∘ ( t ) t = lim t → 0 + 1 3 t + ∘ ( t ) t = 1 3 \begin{aligned} 1.&\color{maroon}\lim_{x\to0}(\frac{1+x}{1-e^{-x}}-\frac1x)\\ =&\lim_{x\to0}\frac{x+x^2-1+e^{-x}}{(1-e^{-x})\cdot x}(通分)\\ =&\lim_{x\to0}\frac{1+2x-e^{-x}}{2x}=1+\frac12=\frac32\\ 2.&\color{maroon}\lim_{x\to\infty}e^{-x}(1+\frac1x)^{x^2}\\ =&\lim_{x\to\infty}e^{-x}e^{x^2\ln(1+\frac1x)}(取对数)\\ =&e^{\lim_{x\to\infty}[x^2\ln(1+\frac1x)-x]}\\ \underrightarrow{令x=\frac1t}&e^{\lim_{t\to0}[\frac{\ln(1+t)}{t^2}-\frac1t]}(倒代换)\\ =&e^{\lim_{t\to0}\frac{\ln(1+t)-t}{t^2}}=e^{-\frac12}\\ 3.&\color{maroon}\lim_{x\to0^+}x^{\ln(\frac{\ln x-1}{\ln x+1})}\\ =&e^{\lim_{x\to0^+}\ln(\frac{\ln x-1}{\ln x+1})\cdot\ln x}\\ =&e^{\lim_{x\to0^+}\ln(1-\frac2{\ln x+1})\cdot \ln x}\\ =&e^{\lim_{x\to0^+}\frac{-2}{\ln x+1}\cdot\ln x}=e^{-2}\\ 4.&\color{maroon}\lim_{x\to0^+}(\frac{\sin x}{x})^\frac1{1-\cos x}\\ =&e^{\lim_{x\to0^+}\frac1{1-\cos x}(\frac{\sin x}x-1)}\\ =&e^{\lim_{x\to0^+}\frac{\sin x-x}{\frac12x^2\cdot x}}\\ =&e^{-\frac13}\\ 5.&\color{maroon}\lim_{x\to\infty}(\sqrt[6]{x^6+x^5}-\sqrt[6]{x^6-x^5})\\ \underrightarrow{令x=\frac1t}&\lim_{t\to0^+}\sqrt[6]{\frac1{t^6}+\frac1{t^5}}-\sqrt[6]{\frac1{t^6}-\frac1{t^5}}\\ =&\lim_{t\to0^+}(\frac{\sqrt[6]{1+t}}{t}-\frac{\sqrt[6]{1-t}}t)\\ =&\lim_{t\to0^+}\frac{(1+t)^\frac16-(1-t)^\frac16}{t}\\ =&\lim_{t\to0^+}\frac{1+\frac16t-(1-\frac16t)+\circ(t)}t\\ =&\lim_{t\to0^+}\frac{\frac13t+\circ(t)}{t}=\frac13\\ \end{aligned} 1.==2.==令x=t1=3.===4.===5.令x=t1====x→0lim(1−e−x1+x−x1)x→0lim(1−e−x)⋅xx+x2−1+e−x(通分)x→0lim2x1+2x−e−x=1+21=23x→∞lime−x(1+x1)x2x→∞lime−xex2ln(1+x1)(取对数)elimx→∞[x2ln(1+x1)−x]elimt→0[t2ln(1+t)−t1](倒代换)elimt→0t2ln(1+t)−t=e−21x→0+limxln(lnx+1lnx−1)elimx→0+ln(lnx+1lnx−1)⋅lnxelimx→0+ln(1−lnx+12)⋅lnxelimx→0+lnx+1−2⋅lnx=e−2x→0+lim(xsinx)1−cosx1elimx→0+1−cosx1(xsinx−1)elimx→0+21x2⋅xsinx−xe−31x→∞lim(6x6+x5−6x6−x5)t→0+lim6t61+t51−6t61−t51t→0+lim(t61+t−t61−t)t→0+limt(1+t)61−(1−t)61t→0+limt1+61t−(1−61t)+∘(t)t→0+limt31t+∘(t)=31
6. lim x → 0 1 + tan x − 1 + sin x x ln ( 1 + x ) − x 2 = lim x → 0 1 − 1 2 x 3 ⋅ tan x − sin x 1 + tan x + 1 + sin x = − 1 2 7. lim x → 0 cos x − cos x 3 sin 2 x [ 分 析 ] 令 cos x 6 = t , 原 式 = lim t → 1 − t 3 − t 2 1 − t 12 = − lim t → 1 − t − 1 t 12 − 1 = − lim t → 1 − t − 1 ( t − 1 ) ( t 11 + t 10 + … + 1 ) = − 1 12 [ 注 ] a n − b n = ( a − b ) ( a n − 1 + a n − 2 b + … + a b n − 2 + b n − 1 ) 8. lim x → + ∞ ( x + 1 + x 2 ) 1 x = e lim x → + ∞ 1 x ln ( x + 1 + x 2 ) = e lim x → + ∞ 1 x + 1 + x 2 ( 1 + 1 2 ( 1 + x 2 ) − 1 2 ⋅ 2 x ) = e lim x → + ∞ 1 1 + x 2 = e 0 = 1 9. lim x → 0 ( 1 + x 2 ) ( 1 − cos 2 x ) − 2 x 2 x 4 ( 拆 ) = lim x → 0 1 − cos 2 x − 2 x 2 x 4 + lim x → 0 x 2 ( 1 − cos 2 x ) x 4 = lim x → 0 1 − ( 1 − 1 2 ( 2 x ) 2 + 1 24 ( 2 x ) 4 + ∘ ( x 4 ) ) − 2 x 2 x 4 + 2 = lim x → 0 − 16 24 x 4 x 4 + 2 = 4 3 10. lim x → 0 1 − x 2 sin 2 x − tan 2 x x 2 [ ln ( 1 + x ) ] 2 = lim x → 0 1 − x 2 sin 2 x − sin 2 x + sin 2 x − tan 2 x x 4 = lim x → 0 sin x ( 1 − x 2 − 1 ) x 4 + lim x → 0 sin 2 x − tan 2 x x 4 = − 1 2 + lim x → 0 ( sin x + tan x ) ( sin x + tan ) x 4 = − 1 2 + lim x → 0 ( sin x + tan x ) ( − 1 2 x 3 ) x 4 = − 1 2 + ( − 1 2 ) ( 1 + 1 ) = − 3 2 \begin{aligned} 6.&\color{maroon}\lim_{x\to0}\frac{\sqrt{1+\tan x}-\sqrt{1+\sin x}}{x\ln(1+x)-x^2}\\ =&\lim_{x\to0}\frac{1}{-\frac12x^3}\cdot\frac{\tan x-\sin x}{\sqrt{1+\tan x}+\sqrt{1+\sin x}}=-\frac12\\ 7.&\color{maroon}\lim_{x\to0}\frac{\sqrt{\cos x}-\sqrt[3]{\cos x}}{\sin^2x}\\ [分析]&令\sqrt[6]{\cos x}=t,原式=\lim_{t\to1^-}\frac{t^3-t^2}{1-t^{12}}=-\lim_{t\to1^-}\frac{t-1}{t^{12}-1}\\ =&-\lim_{t\to1^-}\frac{t-1}{(t-1)(t^{11}+t^{10}+\ldots+1)}=-\frac1{12}\\ [注]&\color{red}a^n-b^n=(a-b)(a^{n-1}+a^{n-2}b+\ldots+ab^{n-2}+b^{n-1})\\ 8.&\color{maroon}\lim_{x\to+\infty}(x+\sqrt{1+x^2})^\frac1x\\ =&e^{\lim_{x\to+\infty}\frac1x\ln(x+\sqrt{1+x^2})}=e^{\lim_{x\to+\infty}\frac{1}{x+\sqrt{1+x^2}}(1+\frac12(1+x^2)^{-\frac12}\cdot2x)}\\ =&e^{\lim_{x\to+\infty}\frac{1}{\sqrt{1+x^2}}}=e^0=1\\ 9.&\color{maroon}\lim_{x\to0}\frac{(1+x^2)(1-\cos2x)-2x^2}{x^4}(拆)\\ =&\lim_{x\to0}\frac{1-\cos2x-2x^2}{x^4}+\lim_{x\to0}\frac{x^2(1-\cos2x)}{x^4}\\ =&\lim_{x\to0}\frac{1-(1-\frac12(2x)^2+\frac1{24}(2x)^4+\circ(x^4))-2x^2}{x^4}+2\\ =&\lim_{x\to0}\frac{-\frac{16}{24}x^4}{x^4}+2=\frac43\\ 10.&\color{maroon}\lim_{x\to0}\frac{\sqrt{1-x^2}\sin^2x-\tan^2x}{x^2[\ln(1+x)]^2}\\ =&\lim_{x\to0}\frac{\sqrt{1-x^2}\sin^2x-\sin^2x+\sin^2x-\tan^2x}{x^4}\\ =&\lim_{x\to0}\frac{\sin^x(\sqrt{1-x^2}-1)}{x^4}+\lim_{x\to0}\frac{\sin^2x-\tan^2x}{x^4}\\ =&-\frac12+\lim_{x\to0}\frac{(\sin x+\tan x)(\sin x+\tan )}{x^4}\\ =&-\frac12+\lim_{x\to0}\frac{(\sin x+\tan x)(-\frac12x^3)}{x^4}\\ =&-\frac12+(-\frac12)(1+1)=-\frac32\\ \end{aligned} 6.=7.[分析]=[注]8.==9.===10.=====x→0limxln(1+x)−x21+tanx−1+sinxx→0lim−21x31⋅1+tanx+1+sinxtanx−sinx=−21x→0limsin2xcosx−3cosx令6cosx=t,原式=t→1−lim1−t12t3−t2=−t→1−limt12−1t−1−t→1−lim(t−1)(t11+t10+…+1)t−1=−121an−bn=(a−b)(an−1+an−2b+…+abn−2+bn−1)x→+∞lim(x+1+x2)x1elimx→+∞x1ln(x+1+x2)=elimx→+∞x+1+x21(1+21(1+x2)−21⋅2x)elimx→+∞1+x21=e0=1x→0limx4(1+x2)(1−cos2x)−2x2(拆)x→0limx41−cos2x−2x2+x→0limx4x2(1−cos2x)x→0limx41−(1−21(2x)2+241(2x)4+∘(x4))−2x2+2x→0limx4−2416x4+2=34x→0limx2[ln(1+x)]21−x2sin2x−tan2xx→0limx41−x2sin2x−sin2x+sin2x−tan2xx→0limx4sinx(1−x2−1)+x→0limx4sin2x−tan2x−21+x→0limx4(sinx+tanx)(sinx+tan)−21+x→0limx4(sinx+tanx)(−21x3)−21+(−21)(1+1)=−23
11. lim x → ∞ x 2 ( a 1 x + a − 1 x − 2 ) , 其 中 常 数 a > 0 令 1 x = t I = lim t → 0 1 t 2 ( a t + a − t − 2 ) = lim t → 0 a t ln a + a − t ⋅ ln a − 1 2 t = ln 2 a 12. lim x → 0 ( cos x cos 2 x ) 1 x 2 I = e A , 其 中 A = lim x → 0 1 x 2 ( cos x cos 2 x − 1 ) = lim x → 0 cos x − cos 2 x x 2 cos 2 x = lim x → 0 cos x − cos 2 x x 2 = lim x → 0 cos x − 1 + 1 − cos 2 x x 2 = lim x → 0 cos x − 1 x 2 + lim x → 0 1 − cos 2 x x 2 = − 1 2 + lim x → 0 1 2 ( 2 x ) 2 x 2 = 3 2 故 I = e 3 2 13. lim x → + ∞ [ ( x 3 + x 2 − tan 1 x ) e 1 x − 1 + x 6 ] = lim x → + ∞ [ ( x 3 + x 2 ) e 1 x − 1 + x 6 ] − lim x → + ∞ tan 1 x ⋅ e 1 x t = 1 x → lim t → 0 + [ ( 1 t 3 + 1 2 t ) e t − 1 + 1 t 6 ] − 0 = lim t → 0 + ( 2 + t 2 ) e t − 2 1 + t 6 + 2 − 2 2 t 3 = lim t → 0 + ( 2 + t 2 ) e t − 2 2 t 3 − 2 lim t → 0 + 1 + t 6 − 1 2 t 3 = lim t → 0 + ( 2 + t 2 ) ( 1 + t + 1 2 t 2 + 1 6 t 3 + ∘ ( t 3 ) ) − 2 2 t 3 − 0 = lim t → 0 + 2 t + 2 t 2 + 4 3 t 3 2 t 3 = ∞ 14. lim x → 0 [ a x − ( 1 x 2 − a 2 ) ln ( 1 + a x ) ] . 其 中 a ≠ 0 = lim x → 0 [ a x − 1 x 2 ln ( 1 + a x ) ] + a 2 lim x → 0 ln ( 1 + a x ) = lim x → 0 a x − ln ( 1 + a x ) x 2 + 0 = lim x → 0 1 2 ( a x ) 2 x 2 = 1 2 a 2 15. lim x → 0 ( 1 + x ) 1 x − ( 1 + 2 x ) 1 2 x sin x = lim x → 0 e ln ( 1 + x ) / x − e ln ( 1 + 2 x ) / 2 x x = lim x → 0 e ln ( 1 + 2 x ) / 2 x ( e ln ( 1 + x ) / x − ln ( 1 + 2 x ) / 2 x − 1 ) x = e lim x → 0 ln ( 1 + x ) / x − ln ( 1 + 2 x ) / 2 x x = e lim x → 0 2 ln ( 1 + x ) − ln ( 1 + 2 x ) 2 x 2 = e ⋅ 2 ( x − 1 2 x 2 ) + ∘ ( x 2 ) − ( 2 x − 1 2 ( 2 x ) 2 ) − ∘ ( x 2 ) 2 x 2 = e ⋅ 1 2 = e 2 \begin{aligned} 11.&\color{maroon}\lim_{x\to\infty}x^2(a^{\frac1x}+a^{-\frac1x}-2),其中常数a>0\\ &令\frac1x=t\\ I&=\lim_{t\to0}\frac1{t^2}(a^t+a^{-t}-2)\\ &=\lim_{t\to0}\frac{a^t\ln a+a^{-t}\cdot\ln a^{-1}}{2t}\\ &=\ln^2a\\ 12.&\color{maroon}\lim_{x\to0}(\frac{\cos x}{\cos2x})^{\frac1{x^2}}\\ I&=e^A,其中A=\lim_{x\to0}\frac1{x^2}(\frac{\cos x}{\cos2x}-1)\\ &=\lim_{x\to0}\frac{\cos x-\cos2x}{x^2\cos2x}\\ &=\lim_{x\to0}\frac{\cos x-\cos2x}{x^2}\\ &=\lim_{x\to0}\frac{\cos x-1+1-\cos2x}{x^2}\\ &=\lim_{x\to0}\frac{\cos x-1}{x^2}+\lim_{x\to0}\frac{1-\cos2x}{x^2}\\ &=-\frac12+\lim_{x\to0}\frac{\frac12(2x)^2}{x^2}\\ &=\frac32\quad 故I=e^{\frac32}\\ 13.&\color{maroon}\lim_{x\to+\infty}[(x^3+\frac x2-\tan\frac1x)e^{\frac1x}-\sqrt{1+x^6}]\\ =&\lim_{x\to+\infty}[(x^3+\frac x2)e^{\frac1x}-\sqrt{1+x^6}]-\lim_{x\to+\infty}\tan\frac1x\cdot e^{\frac1x}\\ \underrightarrow{t=\frac1x}&\lim_{t\to0^+}[(\frac1{t^3}+\frac1{2t})e^t-\sqrt{1+\frac1{t^6}}]-0\\ =&\lim_{t\to0^+}\frac{(2+t^2)e^t-2\sqrt{1+t^6}+2-2}{2t^3}\\ =&\lim_{t\to0^+}\frac{(2+t^2)e^t-2}{2t^3}-2\lim_{t\to0^+}\frac{\sqrt{1+t^6}-1}{2t^3}\\ =&\lim_{t\to0^+}\frac{(2+t^2)(1+t+\frac12t^2+\frac16t^3+\circ(t^3))-2}{2t^3}-0\\ =&\lim_{t\to0^+}\frac{2t+2t^2+\frac43t^3}{2t^3}=\infty\\ 14.&\color{maroon}\lim_{x\to0}[\frac ax-(\frac1{x^2}-a^2)\ln(1+ax)].其中a\neq0\\ =&\lim_{x\to0}[\frac ax-\frac1{x^2}\ln(1+ax)]+a^2\lim_{x\to0}\ln(1+ax)\\ =&\lim_{x\to0}\frac{ax-\ln(1+ax)}{x^2}+0\\ =&\lim_{x\to0}\frac{\frac12(ax)^2}{x^2}=\frac12a^2\\ 15.&\color{maroon}\lim_{x\to0}\frac{(1+x)^{\frac1x}-(1+2x)^{\frac1{2x}}}{\sin x}\\ =&\lim_{x\to0}\frac{e^{\ln(1+x)/x}-e^{\ln(1+2x)/2x}}{x}\\ =&\lim_{x\to0}\frac{e^{\ln(1+2x)/2x}(e^{\ln(1+x)/x-\ln(1+2x)/2x}-1)}x\\ =&e\lim_{x\to0}\frac{\ln(1+x)/x-\ln(1+2x)/2x}{x}\\ =&e\lim_{x\to0}\frac{2\ln(1+x)-\ln(1+2x)}{2x^2}\\ =&e\cdot\frac{2(x-\frac12x^2)+\circ(x^2)-(2x-\frac12(2x)^2)-\circ(x^2)}{2x^2}\\ =&e\cdot\frac12=\frac e2\\ \end{aligned} 11.I12.I13.=t=x1====14.===15.======x→∞limx2(ax1+a−x1−2),其中常数a>0令x1=t=t→0limt21(at+a−t−2)=t→0lim2tatlna+a−t⋅lna−1=ln2ax→0lim(cos2xcosx)x21=eA,其中A=x→0limx21(cos2xcosx−1)=x→0limx2cos2xcosx−cos2x=x→0limx2cosx−cos2x=x→0limx2cosx−1+1−cos2x=x→0limx2cosx−1+x→0limx21−cos2x=−21+x→0limx221(2x)2=23故I=e23x→+∞lim[(x3+2x−tanx1)ex1−1+x6]x→+∞lim[(x3+2x)ex1−1+x6]−x→+∞limtanx1⋅ex1t→0+lim[(t31+2t1)et−1+t61]−0t→0+lim2t3(2+t2)et−21+t6+2−2t→0+lim2t3(2+t2)et−2−2t→0+lim2t31+t6−1t→0+lim2t3(2+t2)(1+t+21t2+61t3+∘(t3))−2−0t→0+lim2t32t+2t2+34t3=∞x→0lim[xa−(x21−a2)ln(1+ax)].其中a̸=0x→0lim[xa−x21ln(1+ax)]+a2x→0limln(1+ax)x→0limx2ax−ln(1+ax)+0x→0limx221(ax)2=21a2x→0limsinx(1+x)x1−(1+2x)2x1x→0limxeln(1+x)/x−eln(1+2x)/2xx→0limxeln(1+2x)/2x(eln(1+x)/x−ln(1+2x)/2x−1)ex→0limxln(1+x)/x−ln(1+2x)/2xex→0lim2x22ln(1+x)−ln(1+2x)e⋅2x22(x−21x2)+∘(x2)−(2x−21(2x)2)−∘(x2)e⋅21=2e
及时提出极限=c≠0的因式
1. lim x → 3 + cos x ln ( x − 3 ) ln ( e x − e 3 ) = cos 3 lim x → 3 + ln ( x − 3 ) ln ( e x − e 3 ) = cos 3 lim x → 3 + 1 x − 3 ⋅ e x − e 3 e x = cos 3 e 3 lim x → 3 + e x − e 3 x − 3 = cos 3 e 3 lim x → 3 + e x 1 = cos 3 \begin{aligned} 1.&\color{maroon}\lim_{x\to3^+}\frac{\cos x\ln(x-3)}{\ln(e^x-e^3)}\\ =&\cos3\lim_{x\to3^+}\frac{\ln(x-3)}{\ln(e^x-e^3)}\\ =&\cos3\lim_{x\to3^+}\frac1{x-3}\cdot\frac{e^x-e^3}{e^x}\\ =&\frac{\cos3}{e^3}\lim_{x\to3^+}\frac{e^x-e^3}{x-3}\\ =&\frac{\cos3}{e^3}\lim_{x\to3^+}\frac{e^x}1=\cos3\\ \end{aligned} 1.====x→3+limln(ex−e3)cosxln(x−3)cos3x→3+limln(ex−e3)ln(x−3)cos3x→3+limx−31⋅exex−e3e3cos3x→3+limx−3ex−e3e3cos3x→3+lim1ex=cos3
洛必达法则
1. lim x → ⋅ f ( x ) g ( x ) = lim x → ⋅ f ′ ( x ) g ′ ( x ) 2. lim x → a ∫ a x f ( t ) d t ∫ a x g ( t ) d t = lim x → a f ( x ) g ( x ) 3. lim x → a ∫ a φ ( x ) f ( t ) d t ∫ a ϕ ( x ) g ( t ) d t = lim x → a f [ φ ( x ) ] ⋅ φ ′ ( x ) g [ ϕ ( x ) ] ⋅ ϕ ′ ( x ) [ 注 ] 1. 0 0 型 2. 可 导 3. 结 果 为 0 , c ≠ 0 , ∞ \begin{aligned} 1.&\lim_{x\to\cdot}\frac{f(x)}{g(x)}=\lim_{x\to\cdot}\frac{f'(x)}{g'(x)}\\ 2.&\lim_{x\to a}\frac{\int_a^xf(t)dt}{\int_a^xg(t)dt}=\lim_{x\to a}\frac{f(x)}{g(x)}\\ 3.&\lim_{x\to a}\frac{\int_a^\varphi(x)f(t)dt}{\int_a^\phi(x)g(t)dt}=\lim_{x\to a}\frac{f[\varphi(x)]\cdot\varphi'(x)}{g[\phi(x)]\cdot\phi'(x)}\\ [注]&1.\frac00型\quad2.可导\quad3.结果为0,c\neq0,\infty\\ \end{aligned} 1.2.3.[注]x→⋅limg(x)f(x)=x→⋅limg′(x)f′(x)x→alim∫axg(t)dt∫axf(t)dt=x→alimg(x)f(x)x→alim∫aϕ(x)g(t)dt∫aφ(x)f(t)dt=x→alimg[ϕ(x)]⋅ϕ′(x)f[φ(x)]⋅φ′(x)1.00型2.可导3.结果为0,c̸=0,∞
1. lim x → 0 ∫ 0 x sin 2 t 4 + t 2 ∫ 0 x ( t + 1 − 1 ) d t d t = lim x → 0 ∫ 0 x sin 2 t 4 + t 2 d t ∫ 0 x ( t + 1 − 1 ) d t = lim x → 0 sin 2 x 4 + x 2 x + 1 − 1 = lim x → 0 2 x 2 ( 1 2 x ) = 2 2. lim x → ∞ ∫ 1 x [ t 2 ( e 1 t − 1 ) − t ] d t x 2 ln ( 1 + 1 x ) = lim x → ∞ = x 2 ( e 1 x − 1 ) − x 1 x = 1 t → lim t → 0 + ( e t − 1 t 2 − 1 t ) = lim t → 0 + e t − 1 − t t 2 = 1 2 \begin{aligned} 1.&\color{maroon}\lim_{x\to0}\int_0^x\frac{\sin2t}{\sqrt{4+t^2}\int_0^x(\sqrt{t+1}-1)dt}dt\\ =&\lim_{x\to0}\frac{\int_0^x\frac{\sin2t}{\sqrt{4+t^2}}dt}{\int_0^x(\sqrt{t+1}-1)dt}\\ =&\lim_{x\to0}\frac{\frac{\sin2x}{\sqrt{4+x^2}}}{\sqrt{x+1}-1}\\ =&\lim_{x\to0}\frac{2x}{2(\frac12x)}=2\\ 2.&\color{maroon}\lim_{x\to\infty}\frac{\int_1^x[t^2(e^\frac1t-1)-t]dt}{x^2\ln(1+\frac1x)}\\ =&\lim_{x\to\infty}=\frac{x^2(e^\frac1x-1)-x}{1}\underrightarrow{x=\frac1t}\lim_{t\to0^+}(\frac{e^t-1}{t^2}-\frac1t)\\ =&\lim_{t\to0^+}\frac{e^t-1-t}{t^2}=\frac12\\ \end{aligned} 1.===2.==x→0lim∫0x4+t2∫0x(t+1−1)dtsin2tdtx→0lim∫0x(t+1−1)dt∫0x4+t2sin2tdtx→0limx+1−14+x2sin2xx→0lim2(21x)2x=2x→∞limx2ln(1+x1)∫1x[t2(et1−1)−t]dtx→∞lim=1x2(ex1−1)−xx=t1t→0+lim(t2et−1−t1)t→0+limt2et−1−t=21
泰勒公式
公式
泰 勒 发 现 , 任 何 可 导 函 数 都 可 以 写 成 ∑ a n x n , 这 样 , 任 何 可 导 函 数 都 具 有 了 统 一 美 , 也 可 以 统 一 计 算 当 x → 0 时 , 就 如 以 下 常 见 的 函 数 泰 勒 展 开 式 , 最 后 的 ∘ ( x 3 ) 被 称 作 佩 亚 诺 余 项 sin x = x − 1 6 x 3 + 1 5 ! x 5 − x 7 7 ! + ⋯ + ( − 1 ) n x 2 n + 1 ( 2 n + 1 ) ! + ⋯ = ∑ n = 0 ∞ ( − 1 ) n ⋅ x 2 n + 1 ( 2 n + 1 ) ! e x = 1 + x + x 2 2 + x 3 6 + ⋯ + x n n ! + ⋯ = ∑ n = 0 ∞ x n n ! cos x = 1 − 1 2 x 2 + 1 24 x 4 − x 6 6 ! + ⋯ + ( − 1 ) n x 2 n ( 2 n ) ! + ⋯ = ∑ n = 0 ∞ ( − 1 ) n ⋅ x 2 n ( 2 n ) ! ln ( 1 + x ) = x − 1 2 x 2 + 1 3 x 3 − ⋯ + ( − 1 ) n − 1 x n n + ⋯ = ∑ n = 1 ∞ ( − 1 ) n − 1 ⋅ x n n ( 1 + x ) α = 1 + α x + α ( α − 1 ) 2 x 2 + ∘ ( x 2 ) tan x = x + 1 3 x 3 + ∘ ( x 3 ) arcsin x = x + 1 6 x 3 + 1 120 x 5 + ∘ ( x 5 ) arctan x = x − 1 3 x 3 + ∘ ( x 3 ) \begin{aligned} &泰勒发现,任何可导函数都可以写成\sum a_nx^n,这样,任何可导函数都具有了统一美,也可以统一计算\\ &当x\to0时,就如以下常见的函数泰勒展开式,最后的\circ(x^3)被称作佩亚诺余项\\ &\sin x=x-\frac16x^3+\frac{1}{5!}x^5-\frac{x^7}{7!}+\cdots+(-1)^n\frac{x^{2n+1}}{(2n+1)!}+\cdots=\sum_{n=0}^\infty(-1)^n\cdot\frac{x^{2n+1}}{(2n+1)!}\\ &e^x=1+x+\frac{x^2}{2}+\frac{x^3}{6}+\cdots+\frac{x^n}{n!}+\cdots=\sum_{n=0}^{\infty}\frac{x^n}{n!}\\ &\cos x=1-\frac12x^2+\frac1{24}x^4-\frac{x^6}{6!}+\cdots+(-1)^n\frac{x^{2n}}{(2n)!}+\cdots=\sum_{n=0}^\infty(-1)^n\cdot\frac{x^{2n}}{(2n)!}\\ &\ln(1+x)=x-\frac12x^2+\frac13x^3-\cdots+(-1)^{n-1}\frac{x^n}n+\cdots=\sum_{n=1}^\infty(-1)^{n-1}\cdot\frac{x^n}n\\ &(1+x)^\alpha=1+\alpha x+\frac{\alpha(\alpha-1)}{2}x^2+\circ(x^2)\quad\tan x=x+\frac13x^3+\circ(x^3)\\ &\arcsin x=x+\frac16x^3+\frac1{120}x^5+\circ(x^5)\quad\arctan x=x-\frac13x^3+\circ(x^3)\\ \end{aligned} 泰勒发现,任何可导函数都可以写成∑anxn,这样,任何可导函数都具有了统一美,也可以统一计算当x→0时,就如以下常见的函数泰勒展开式,最后的∘(x3)被称作佩亚诺余项sinx=x−61x3+5!1x5−7!x7+⋯+(−1)n(2n+1)!x2n+1+⋯=n=0∑∞(−1)n⋅(2n+1)!x2n+1ex=1+x+2x2+6x3+⋯+n!xn+⋯=n=0∑∞n!xncosx=1−21x2+241x4−6!x6+⋯+(−1)n(2n)!x2n+⋯=n=0∑∞(−1)n⋅(2n)!x2nln(1+x)=x−21x2+31x3−⋯+(−1)n−1nxn+⋯=n=1∑∞(−1)n−1⋅nxn(1+x)α=1+αx+2α(α−1)x2+∘(x2)tanx=x+31x3+∘(x3)arcsinx=x+61x3+1201x5+∘(x5)arctanx=x−31x3+∘(x3)
展开原则
1. A B 型 , 上 下 同 阶 2. A − B 型 , 幂 次 最 低 , 即 将 A , B 分 别 展 开 至 系 数 不 相 等 的 x 的 最 低 次 幂 为 止 \begin{aligned} &1.\frac AB型,上下同阶\\ &2.A-B型,幂次最低,即将A,B分别展开至系数不相等的x的最低次幂为止\\ \end{aligned} 1.BA型,上下同阶2.A−B型,幂次最低,即将A,B分别展开至系数不相等的x的最低次幂为止
1. lim x → 0 arctan x − x x 3 = lim x → 0 x − 1 3 x 3 − x x 3 = − 1 3 2. x → 0 时 , cos x − e − x 2 2 与 a x b 为 等 价 无 穷 小 , 求 a , b cos x = 1 − 1 2 x 2 + 1 24 x 4 + ∘ ( x 4 ) e − x 2 2 = 1 − x 2 2 + x 4 8 + ∘ ( x 4 ) I = − 1 12 x 4 + ∘ ( x 4 ) ∴ a = − 1 12 , b = 4 3. lim x → 0 1 + 1 2 x 2 − 1 + x 2 ( cos x − e x 2 2 ) sin x 2 2 = lim x → 0 1 8 x 4 − x 4 2 = − 1 4 4. lim x → 0 ∑ n = 1 ∞ 2 n n ! x 2 n arctan x 2 = lim x → 0 2 x 2 + 2 2 2 ! x 4 + … x 2 = 2 5. lim x → 0 e x + ln ( 1 − x ) − 1 x − arctan x = lim x → 0 e x + ln ( 1 − x ) − 1 1 3 x 3 = lim x → 0 1 + 1 2 x 2 + x + 1 6 x 3 + ∘ ( x 3 ) − x − 1 2 x 2 − 1 3 x 3 + ∘ ( x 3 ) − 1 1 3 x 3 = lim x → 0 − 1 6 x 3 1 3 x 3 = − 1 2 \begin{aligned} 1.&\color{maroon}\lim_{x\to0}\frac{\arctan x-x}{x^3}\\ =&\lim_{x\to0}\frac{x-\frac13x^3-x}{x^3}=-\frac13\\ 2.&\color{maroon}x\to0时,\cos x-e^{-\frac{x^2}{2}}与ax^b为等价无穷小,求a,b\\ &\cos x=1-\frac12x^2+\frac1{24}x^4+\circ(x^4)\ \ \ \ e^{-\frac{x^2}{2}}=1-\frac{x^2}{2}+\frac{x^4}{8}+\circ(x^4)\\ &I=-\frac1{12}x^4+\circ(x^4)\ \ \ \therefore a=-\frac1{12},b=4\\ 3.&\color{maroon}\lim_{x\to0}\frac{1+\frac12x^2-\sqrt{1+x^2}}{(\cos x-e^{\frac{x^2}2})\sin\frac{x^2}2}\\ =&\lim_{x\to0}\frac{\frac18x^4}{-\frac{x^4}2}=-\frac14\\ 4.&\color{maroon}\lim_{x\to0}\frac{\sum_{n=1}^\infty\frac{2^n}{n!}x^{2n}}{\arctan x^2}\\ =&\lim_{x\to0}\frac{2x^2+\frac{2^2}{2!}x^4+\ldots}{x^2}=2\\ 5.&\color{maroon}\lim_{x\to0}\frac{e^x+\ln(1-x)-1}{x-\arctan x}\\ =&\lim_{x\to0}\frac{e^x+\ln(1-x)-1}{\frac13x^3}\\ =&\lim_{x\to0}\frac{1+\frac12x^2+x+\frac16x^3+\circ(x^3)-x-\frac12x^2-\frac13x^3+\circ(x^3)-1}{\frac13x^3}\\ =&\lim_{x\to0}\frac{-\frac16x^3}{\frac13x^3}=-\frac12\\ \end{aligned} 1.=2.3.=4.=5.===x→0limx3arctanx−xx→0limx3x−31x3−x=−31x→0时,cosx−e−2x2与axb为等价无穷小,求a,bcosx=1−21x2+241x4+∘(x4) e−2x2=1−2x2+8x4+∘(x4)I=−121x4+∘(x4) ∴a=−121,b=4x→0lim(cosx−e2x2)sin2x21+21x2−1+x2x→0lim−2x481x4=−41x→0limarctanx2∑n=1∞n!2nx2nx→0limx22x2+2!22x4+…=2x→0limx−arctanxex+ln(1−x)−1x→0lim31x3ex+ln(1−x)−1x→0lim31x31+21x2+x+61x3+∘(x3)−x−21x2−31x3+∘(x3)−1x→0lim31x3−61x3=−21
中值定理
拉 格 朗 日 中 值 定 理 : 设 f ( x ) { [ a , b ] 连 续 ( a , b ) 可 导    ⟹    f ( b ) − f ( a ) = f ′ ( ξ ) ( b − a ) , ∃ ξ ∈ ( a , b ) \begin{aligned} &拉格朗日中值定理:设f(x)\begin{cases}[a,b]连续\\(a,b)可导\end{cases}\implies f(b)-f(a)=f'(\xi)(b-a),\exists\xi\in(a,b)\\ \end{aligned} 拉格朗日中值定理:设f(x){[a,b]连续(a,b)可导⟹f(b)−f(a)=f′(ξ)(b−a),∃ξ∈(a,b)
1. lim x → 0 ( 1 + x ) 2 x − e 2 [ 1 − ln ( 1 + x ) ] x = lim x → 0 ( 1 + x ) 2 x − e 2 x + e 2 lim x → 0 ln ( 1 + x ) x = lim x → 0 e 2 ln ( 1 + x ) / x − e 2 x + e 2 = lim x → 0 e ξ ( 2 ln ( 1 + x ) x − 2 ) x + e 2 = 2 e 2 lim x → 0 ln ( 1 + x ) x − 1 x + e 2 = 2 e 2 lim x → 0 ln ( 1 + x ) − x x 2 + e 2 = 2 e 2 lim x → 0 − 1 2 x 2 x 2 + e 2 = 0 2. lim x → ∞ ( x 6 + x 5 6 − x 6 − x 5 6 ) = lim x → ∞ f ′ ( ξ ) ( 2 x 5 ) = lim x → ∞ 1 6 ξ − 5 6 ( 2 x 5 ) = lim x → ∞ 1 6 ⋅ x 6 ( − 5 6 ) ( 2 x 5 ) = lim x → ∞ 1 6 x − 5 ( 2 x 5 ) = 1 3 \begin{aligned} 1.&\color{maroon}\lim_{x\to0}\frac{(1+x)^{\frac2x}-e^2[1-\ln(1+x)]}{x}\\ =&\lim_{x\to0}\frac{(1+x)^{\frac2x}-e^2}{x}+e^2\lim_{x\to0}\frac{\ln(1+x)}{x}\\ =&\lim_{x\to0}\frac{e^{2\ln(1+x)/x}-e^2}{x}+e^2\\ =&\lim_{x\to0}\frac{e^\xi(\frac{2\ln(1+x)}x-2)}{x}+e^2\\ =&2e^2\lim_{x\to0}\frac{\frac{\ln(1+x)}{x}-1}{x}+e^2\\ =&2e^2\lim_{x\to0}\frac{\ln(1+x)-x}{x^2}+e^2\\ =&2e^2\lim_{x\to0}\frac{-\frac12x^2}{x^2}+e^2=0\\ 2.&\color{maroon}\lim_{x\to\infty}(\sqrt[6]{x^6+x^5}-\sqrt[6]{x^6-x^5})\\ =&\lim_{x\to\infty}f'(\xi)(2x^5)\\ =&\lim_{x\to\infty}\frac16\xi^{-\frac56}(2x^5)\\ =&\lim_{x\to\infty}\frac16\cdot x^{6(-\frac56)}(2x^5)\\ =&\lim_{x\to\infty}\frac16x^{-5}(2x^5)=\frac13\\ \end{aligned} 1.======2.====x→0limx(1+x)x2−e2[1−ln(1+x)]x→0limx(1+x)x2−e2+e2x→0limxln(1+x)x→0limxe2ln(1+x)/x−e2+e2x→0limxeξ(x2ln(1+x)−2)+e22e2x→0limxxln(1+x)−1+e22e2x→0limx2ln(1+x)−x+e22e2x→0limx2−21x2+e2=0x→∞lim(6x6+x5−6x6−x5)x→∞limf′(ξ)(2x5)x→∞lim61ξ−65(2x5)x→∞lim61⋅x6(−65)(2x5)x→∞lim61x−5(2x5)=31
无穷小比阶
定义
lim x → ⋅ f ( x ) g ( x ) 0 0 → { c ≠ 0 , 同 阶 无 穷 小 ( c = 1 , 等 价 无 穷 小 ) 0 , 高 阶 无 穷 小 ∞ , 低 阶 无 穷 小 如 { lim x → 0 sin x x = 1 lim x → 0 x 2 x = 0 lim x → 0 x x 2 = ∞ \begin{aligned} &\lim_{x\to\cdot}\frac{f(x)}{g(x)}\underrightarrow{\quad\frac00\quad}\begin{cases}c\neq0,同阶无穷小(c=1,等价无穷小)\\0,高阶无穷小\\\infty,低阶无穷小\end{cases}\\ &\qquad\qquad\quad如\begin{cases}\lim_{x\to0}\frac{\sin x}x=1\\\lim_{x\to0}\frac{x^2}x=0\\\lim_{x\to0}\frac x{x^2}=\infty\end{cases} \end{aligned} x→⋅limg(x)f(x)00⎩⎪⎨⎪⎧c̸=0,同阶无穷小(c=1,等价无穷小)0,高阶无穷小∞,低阶无穷小如⎩⎪⎨⎪⎧limx→0xsinx=1limx→0xx2=0limx→0x2x=∞
反问题、求未知参数
1. 当 x → 0 + 时 , 下 列 ( ) 与 x 1 同 阶 A . 1 + x − 1 B . ln ( 1 + x ) − x C . cos ( sin x ) − 1 D . x x − 1 [ 分 析 ] A . ( 1 + x ) 1 2 − 1 ∼ 1 2 x 1 B . ln ( 1 + x ) − x ∼ − 1 2 x 2 C . cos ( sin x ) − 1 ∼ − 1 2 ( sin x ) 2 D . x x − 1 = e x ln x − 1 ∼ x ln x 是 比 x 低 阶 的 无 穷 小 2. 当 x → 0 + 时 , 比 较 α , β , γ 的 阶 α = ∫ 0 x cos t 2 d t β = ∫ 0 x 2 tan t d t γ = ∫ 0 x sin t 3 d t lim x → 0 + γ α = lim x → 0 + sin x 3 2 ⋅ 1 2 x cos x 2 = 1 2 lim x → 0 + x 3 2 x 1 2 = 0    ⟹    γ = ∘ ( α ) lim x → 0 + β γ = lim x → 0 + tan x − 2 x sin x 3 2 ⋅ 1 2 x = 0    ⟹    β = ∘ ( γ )    ⟹    由 高 阶 至 低 阶 : β → γ → α \begin{aligned} 1.&\color{maroon}当x\to0^+时,下列(\quad)与x^1同阶\\ &A.\sqrt{1+x}-1\quad B.\ln(1+x)-x\\ &C.\cos(\sin x)-1\quad D.x^x-1\\ [分析]&A.(1+x)^\frac12-1\sim\frac12x^1\\ &B.\ln(1+x)-x\sim-\frac12x^2\\ &C.\cos(\sin x)-1\sim-\frac12(\sin x)^2\\ &D.x^x-1=e^{x\ln x}-1\sim x\ln x是比x低阶的无穷小\\ 2.&\color{maroon}当x\to0^+时,比较\alpha,\beta,\gamma的阶\\ &\alpha=\int_0^x\cos t^2dt\quad\beta=\int_0^{x^2}\tan\sqrt{t}dt\quad\gamma=\int_0^{\sqrt x}\sin t^3dt\\ &\lim_{x\to0^+}\frac{\gamma}{\alpha}=\lim_{x\to0^+}\frac{\sin x^{\frac32}\cdot\frac1{2\sqrt x}}{\cos x^2}\\ &=\frac12\lim_{x\to0^+}\frac{x^{\frac32}}{x^{\frac12}}=0\\ &\implies\gamma=\circ(\alpha)\\ &\lim_{x\to0^+}\frac{\beta}{\gamma}=\lim_{x\to0^+}\frac{\tan x-2x}{\sin x^{\frac32}\cdot\frac1{2\sqrt x}}=0\\ &\implies \beta=\circ(\gamma)\\ &\implies 由高阶至低阶:\beta\to\gamma\to\alpha\\ \end{aligned} 1.[分析]2.当x→0+时,下列()与x1同阶A.1+x−1B.ln(1+x)−xC.cos(sinx)−1D.xx−1A.(1+x)21−1∼21x1B.ln(1+x)−x∼−21x2C.cos(sinx)−1∼−21(sinx)2D.xx−1=exlnx−1∼xlnx是比x低阶的无穷小当x→0+时,比较α,β,γ的阶α=∫0xcost2dtβ=∫0x2tantdtγ=∫0xsint3dtx→0+limαγ=x→0+limcosx2sinx23⋅2x1=21x→0+limx21x23=0⟹γ=∘(α)x→0+limγβ=x→0+limsinx23⋅2x1tanx−2x=0⟹β=∘(γ)⟹由高阶至低阶:β→γ→α
存在性
具体型,但洛必达失效
用 夹 逼 准 则 [ 例 ] 记 S ( x ) = ∫ 0 x ∣ sin t ∣ d t , ( 1 ) 证 明 当 n π ≤ x < ( n + 1 ) π 时 , 2 n ≤ S ( x ) < 2 ( n + 1 ) ( 2 ) 求 lim x → + ∞ ∫ 0 x ∣ sin t ∣ d t x ( 1 ) S ( n π ) = ∫ 0 n π ∣ sin t ∣ d t = 2 n S ( ( n + 1 ) π ) = ∫ 0 ( n + 1 ) π ∣ sin t ∣ d t = 2 ( n + 1 ) 又 S ′ ( x ) = ∣ sin x ∣ ≥ 0    ⟹    S ( x ) 单 调 递 增 故 当 n π ≤ x < ( n + 1 ) π 时 , 2 n = S ( n π ) ≤ S ( x ) < S ( ( n + 1 ) π ) = 2 ( n + 1 ) ( 2 ) 2 n ( n + 1 ) π ≤ ∫ 0 x ∣ sin t ∣ d t x < 2 ( n + 1 ) n π x → + ∞    ⟹    n → ∞    ⟹    由 夹 逼 准 则 得 : 2 π [ 注 ] 1. lim x → + ∞ ∫ 0 x ∣ sin t ∣ d t x 2. lim x → + ∞ ∫ 0 x ∣ cos t ∣ d t x 3. lim x → + ∞ ∫ 0 x ( t − [ t ] ) d t x \begin{aligned} &用夹逼准则\\ [例]&\color{maroon}记S(x)=\int_0^x\mid \sin t\mid dt,\\ &\color{maroon}(1)证明当n\pi\leq x<(n+1)\pi时,2n\leq S(x)<2(n+1)\\ &\color{maroon}(2)求\lim_{x\to+\infty}\frac{\int_0^x\mid\sin t\mid dt}{x}\\ &(1)S(n\pi)=\int_0^{n\pi}\mid \sin t\mid dt=2n\\ &S((n+1)\pi)=\int_0^{(n+1)\pi}\mid\sin t\mid dt=2(n+1)\\ &又S'(x)=\mid\sin x\mid\geq0\implies S(x)单调递增\\ &故当n\pi\leq x<(n+1)\pi时,2n=S(n\pi)\leq S(x)<S((n+1)\pi)=2(n+1)\\ &(2)\frac{2n}{(n+1)\pi}\leq\frac{\int_0^x\mid\sin t\mid dt}{x}<\frac{2(n+1)}{n\pi}\\ &x\to+\infty\implies n\to\infty\implies 由夹逼准则得:\frac2{\pi}\\ [注]&1.\lim_{x\to+\infty}\frac{\int_0^x\mid\sin t\mid dt}x\\ &2.\lim_{x\to+\infty}\frac{\int_0^x\mid\cos t\mid dt}x\\ &3.\lim_{x\to+\infty}\frac{\int_0^x(t-[t])dt}x \end{aligned} [例][注]用夹逼准则记S(x)=∫0x∣sint∣dt,(1)证明当nπ≤x<(n+1)π时,2n≤S(x)<2(n+1)(2)求x→+∞limx∫0x∣sint∣dt(1)S(nπ)=∫0nπ∣sint∣dt=2nS((n+1)π)=∫0(n+1)π∣sint∣dt=2(n+1)又S′(x)=∣sinx∣≥0⟹S(x)单调递增故当nπ≤x<(n+1)π时,2n=S(nπ)≤S(x)<S((n+1)π)=2(n+1)(2)(n+1)π2n≤x∫0x∣sint∣dt<nπ2(n+1)x→+∞⟹n→∞⟹由夹逼准则得:π21.x→+∞limx∫0x∣sint∣dt2.x→+∞limx∫0x∣cost∣dt3.x→+∞limx∫0x(t−[t])dt
抽象型——单调有界准则
若 f ( x ) 单 调 递 增 ( 递 减 ) , 且 有 上 ( 下 ) 界    ⟹    lim x → + ∞ f ( x ) = ∃ [ 例 ] 设 x ≥ 0 , f ( x ) 满 足 f ′ ( x ) = 1 x 2 + f 2 ( x ) , f ( 0 ) = 1 , 证 明 ( 1 ) f ′ ( x ) ≤ 1 1 + x 2 , x ≥ 0 ( 2 ) lim x → + ∞ f ( x ) 存 在 且 其 值 小 与 1 + π 2 ( 1 ) f ′ ( x ) > 0    ⟹    f ( x ) 单 调 递 增    ⟹    f ( x ) ≥ f ( 0 ) = 1 故 f ′ ( x ) = 1 x 2 + f 2 ( x ) ≤ 1 x 2 + 1 ( 2 ) f ( x ) = f ( a ) + ∫ a x f ′ ( x ) d t , 故 f ( x ) = f ( 0 ) + ∫ 1 x 1 t 2 + f 2 ( t ) d t ≤ 1 + ∫ 0 x 1 t 2 + 1 d t = 1 + arctan x < 1 + π 2 , 故 f ( x ) 有 上 界 由 单 调 有 界 准 则 , 得 lim x → + ∞ f ( x ) 存 在 且 lim x → + ∞ f ( x ) = 1 + ∫ 0 + ∞ 1 t 2 + f 2 ( t ) d t < 1 + ∫ 0 + ∞ 1 t 2 + 1 d t = 1 + π 2 \begin{aligned} &若f(x)单调递增(递减),且有上(下)界\implies \lim_{x\to+\infty}f(x)=\exists\\ [例]&\color{maroon}设x\geq0,f(x)满足f'(x)=\frac1{x^2+f^2(x)},f(0)=1,证明\\ &\color{maroon}(1)f'(x)\leq\frac1{1+x^2},x\geq0\\ &\color{maroon}(2)\lim_{x\to+\infty}f(x)存在且其值小与1+\frac{\pi}2\\ &(1)f'(x)>0\implies f(x)单调递增\implies f(x)\geq f(0)=1\\ &故f'(x)=\frac1{x^2+f^2(x)}\leq\frac1{x^2+1}\\ &(2)f(x)=f(a)+\int_a^xf'(x)dt,故f(x)=f(0)+\int_1^x\frac1{t^2+f^2(t)}dt\leq1+\int_0^x\frac1{t^2+1}dt\\ &=1+\arctan x<1+\frac{\pi}2,故f(x)有上界\\ &由单调有界准则,得\lim_{x\to+\infty}f(x)存在且\lim_{x\to+\infty}f(x)=1+\int_0^{+\infty}\frac1{t^2+f^2(t)}dt<1+\int_0^{+\infty}\frac1{t^2+1}dt=1+\frac{\pi}2\\ \end{aligned} [例]若f(x)单调递增(递减),且有上(下)界⟹x→+∞limf(x)=∃设x≥0,f(x)满足f′(x)=x2+f2(x)1,f(0)=1,证明(1)f′(x)≤1+x21,x≥0(2)x→+∞limf(x)存在且其值小与1+2π(1)f′(x)>0⟹f(x)单调递增⟹f(x)≥f(0)=1故f′(x)=x2+f2(x)1≤x2+11(2)f(x)=f(a)+∫axf′(x)dt,故f(x)=f(0)+∫1xt2+f2(t)1dt≤1+∫0xt2+11dt=1+arctanx<1+2π,故f(x)有上界由单调有界准则,得x→+∞limf(x)存在且x→+∞limf(x)=1+∫0+∞t2+f2(t)1dt<1+∫0+∞t2+11dt=1+2π
应用–连续与间断
1. 由 于 “ 一 切 初 等 函 数 在 其 定 义 区 域 内 必 连 续 ” , 故 只 研 究 两 类 特 殊 的 点 { 无 定 义 点 ( 间 断 ) 分 段 函 数 的 分 段 点 2. 连 续 ( 1 ) 内 点 处 : lim x → x 0 + f ( x ) = lim x → x 0 − f ( x ) = f ( x )    ⟹    f ( x ) 在 x 0 处 连 续 ( 2 ) 端 点 处 : { lim x → a + f ( x ) = f ( a ) ( 左 端 点 右 连 续 ) lim x → b − f ( x ) = f ( b ) ( 右 端 点 左 连 续 ) f ( x ) 在 ( a , b ) 内 连 续 称 f ( x ) 在 [ a , b ] 上 连 续 3. 间 断 : ( 前 提 : f ( x ) 在 x = x 0 左 右 两 侧 均 有 定 义 ) ( 1 ) 若 lim x → x 0 + f ( x ) , lim x → x 0 − f ( x ) 均 存 在 但 lim x → x 0 + f ( x ) ̸ = lim x → x 0 − f ( x )    ⟹    x 0 为 跳 跃 间 断 点 ( 2 ) lim x → x 0 + f ( x ) , lim x → x 0 − f ( x ) 均 存 在 且 lim x → x 0 + f ( x ) = lim x → x 0 − f ( x ) , 但 ̸ = f ( x )    ⟹    x 0 为 可 去 间 断 点 以 上 统 称 第 一 类 间 断 点 ( 3 ) lim x → x 0 + f ( x ) , lim x → x 0 − f ( x ) 至 少 一 个 不 存 在 , 且 不 存 在 = ∞    ⟹    x 0 为 无 穷 间 断 点 ( 4 ) lim x → x 0 + f ( x ) , lim x → x 0 − f ( x ) 至 少 一 个 不 存 在 且 不 存 在 为 振 荡 不 存 在    ⟹    x 0 为 振 荡 间 断 点 ( 3 ) ( 4 ) 属 于 第 二 类 间 断 点 \begin{aligned} 1.&由于“一切初等函数在其定义区域内必连续”,故只研究两类特殊的点\begin{cases}无定义点(间断)\\分段函数的分段点\end{cases}\\ 2.&连续\\ (1)&内点处:\lim_{x\to x_0^+}f(x)=\lim_{x\to x_0^-}f(x)=f(x)\implies f(x)在x_0处连续\\ (2)&端点处:\begin{cases}\lim_{x\to a^+}f(x)=f(a)(左端点右连续)\\\lim_{x\to b^-}f(x)=f(b)(右端点左连续)\\f(x)在(a,b)内连续\end{cases}称f(x)在[a,b]上连续\\ 3.&间断:(前提:f(x)在x=x_0左右两侧均有定义)\\ (1)&若\lim_{x\to x_0^+}f(x),\lim_{x\to x_0^-}f(x)均存在但\lim_{x\to x_0^+}f(x)\not=\lim_{x\to x_0^-}f(x)\implies x_0为跳跃间断点\\ (2)&\lim_{x\to x_0^+}f(x),\lim_{x\to x_0^-}f(x)均存在且\lim_{x\to x_0^+}f(x)=\lim_{x\to x_0^-}f(x),但\not=f(x)\implies x_0为可去间断点\\ &以上统称第一类间断点\\ (3)&\lim_{x\to x_0^+}f(x),\lim_{x\to x_0^-}f(x)至少一个不存在,且不存在=\infty\implies x_0为无穷间断点\\ (4)&\lim_{x\to x_0^+}f(x),\lim_{x\to x_0^-}f(x)至少一个不存在且不存在为振荡不存在\implies x_0为振荡间断点\\ &(3)(4)属于第二类间断点\\ \end{aligned} 1.2.(1)(2)3.(1)(2)(3)(4)由于“一切初等函数在其定义区域内必连续”,故只研究两类特殊的点{无定义点(间断)分段函数的分段点连续内点处:x→x0+limf(x)=x→x0−limf(x)=f(x)⟹f(x)在x0处连续端点处:⎩⎪⎨⎪⎧limx→a+f(x)=f(a)(左端点右连续)limx→b−f(x)=f(b)(右端点左连续)f(x)在(a,b)内连续称f(x)在[a,b]上连续间断:(前提:f(x)在x=x0左右两侧均有定义)若x→x0+limf(x),x→x0−limf(x)均存在但x→x0+limf(x)̸=x→x0−limf(x)⟹x0为跳跃间断点x→x0+limf(x),x→x0−limf(x)均存在且x→x0+limf(x)=x→x0−limf(x),但̸=f(x)⟹x0为可去间断点以上统称第一类间断点x→x0+limf(x),x→x0−limf(x)至少一个不存在,且不存在=∞⟹x0为无穷间断点x→x0+limf(x),x→x0−limf(x)至少一个不存在且不存在为振荡不存在⟹x0为振荡间断点(3)(4)属于第二类间断点
[ 例 ] 当 x ∈ ( − 1 2 , 1 ] 时 , 确 定 f ( x ) = tan π x ∣ x ∣ ( x 2 − 1 ) 的 间 断 点 并 判 断 其 类 型 1. { lim x → 0 + tan π x x ( x − 1 ) = − π lim x → 0 − tan π x − x ( x − 1 ) = π    ⟹    x = 0 为 跳 跃 间 断 点 2. lim x → 1 tan π x x ( x + 1 ) ( x − 1 ) = 1 2 lim x → 1 tan π x x − 1 = π 2    ⟹    x = 1 为 可 去 间 断 点 3. lim x → 1 2 tan π x x ( x 2 − 1 ) = ∞    ⟹    x = 1 2 为 无 穷 间 断 点 \begin{aligned} \ [例]&\color{maroon}当x\in(-\frac12,1]时,确定f(x)=\frac{\tan \pi x}{\mid x\mid(x^2-1)}的间断点并判断其类型\\ &1.\begin{cases}\lim_{x\to0^+}\frac{\tan\pi x}{x(x^-1)}=-\pi\\\lim_{x\to0^-}\frac{\tan\pi x}{-x(x^-1)}=\pi\end{cases}\implies x=0为跳跃间断点\\ &2.\lim_{x\to1}\frac{\tan\pi x}{x(x+1)(x-1)}=\frac12\lim_{x\to1}\frac{\tan\pi x}{x-1}=\frac{\pi}2\implies x=1为可去间断点\\ &3.\lim_{x\to\frac12}\frac{\tan\pi x}{x(x^2-1)}=\infty\implies x=\frac12为无穷间断点\\ \end{aligned} [例]当x∈(−21,1]时,确定f(x)=∣x∣(x2−1)tanπx的间断点并判断其类型1.{limx→0+x(x−1)tanπx=−πlimx→0−−x(x−1)tanπx=π⟹x=0为跳跃间断点2.x→1limx(x+1)(x−1)tanπx=21x→1limx−1tanπx=2π⟹x=1为可去间断点3.x→21limx(x2−1)tanπx=∞⟹x=21为无穷间断点
























 1242
1242

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








