关于光流法请看我之前的博客Lukas-Kanade光流法。这里介绍Horn-Schunck光流法。
Horn-Schunck光流法求得的是稠密光流,需要对每一个像素计算光流值,计算量比较大。而Lucas-Kanade光流法只需计算若干点的光流,是一种稀疏光流。
数学原理这里就不介绍了,直接说算法步骤。
用uij与vij分别表示图像像素点(i,j)处的水平方向光流值与垂直方向光流值,每次迭代后的更新方程为
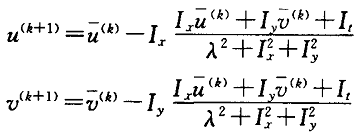
n为迭代次数,lamda反映了对图像数据及平滑约束的可信度,当图像数据本身含有较大噪声时,此时需要加大lamda的值,相反,当输入图像含有较少的噪声时,此时可减小lamda的值。
代表u邻域与v邻域的平均值,一般采用相应4邻域内的均值
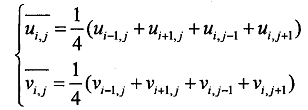
也可以采用33、55的窗口用模板平滑,窗口不宜过大,过大会破坏光流假设。
Ix、Iy分别是图像对x、y的偏导数。It是两帧图像间对时间的导数。
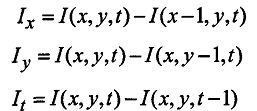
当然你也可以考虑相邻像素及相邻两帧图像的影响,Horn-Schunck 提出通过 4 次有限差分来得到

这里只考虑了前后两帧图像。考虑连续三帧图像的话有如下方法:
一种性能更优的 3D-Sobel 算子 如下图所示。该算子在x 、y 、t方向上分别使用不同的模板对连续3帧图像进行卷积计算 得出中间帧的位于模板中心的像素在三个方向上的梯度 。

迭代一定次数后u、v收敛,光流计算停止。在实际的计算中迭代初值可取U(0) =0、V(0)=0。
算法改进
对于一般场景基本等式只有在图像中灰度梯度值较大的点处才成立。因此为了增强算法的稳定性和准确性 我们仅在梯度较大的点处才使用亮度恒常性约束,而在梯度较小的点处只使用流场一致性约束。定义如下权函数

下面是我的实现,使用了图像金字塔,关于图像金字塔,请看Lukas-Kanade光流法。(写代码时传错一个参数,调了几个小时哭)
[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
#ifndef __HORNSCHUNCK__
#define __HORNSCHUNCK__
class HornSchunckTracker
{
private:
unsigned int max_pyramid_layer;
unsigned int original_imgH;
unsigned int original_imgW;
BYTE**pre_pyr;//the pyramid of previous frame image,img1_pyr[0] is of max size
BYTE**next_pyr;//the frame after img1_pyr
int*height;
int*width;
double*optical_field_U;
double*optical_field_V;
bool isusepyramid;
double lamda;//取20
const double precision = 1;
const int maxiteration=300;
double threshold;//最小的光流阈值
double scale_factor;//缩放因子
private:
void get_max_pyramid_layer();
void pyramid_down(BYTE*&src_gray_data, const int src_h,
const int src_w, BYTE*& dst, int&dst_h, int&dst_w);
void pyramid_up(double*src,int srcW,int srcH,double*dst,int dstW,int dstH);
void lowpass_filter(double*&src, const int H, const int W, double*&smoothed);
void get_fx_fy_ft(BYTE*img1, BYTE*img2, int w, int h, double*fx, double*fy, double*ft);
void build_pyramid(BYTE**&original_gray);
double get_average4(double*src, const int height, const int width, const int i, const int j);
void bilinear(double* lpSrc, double* lpDst, int nW, int nH, int H1, int W1);
void bilinear(BYTE* lpSrc, BYTE* lpDst, int nW, int nH, int H1, int W1);
public:
HornSchunckTracker();
~HornSchunckTracker();
void get_pre_frame(BYTE*&gray);//use only at the beginning
void discard_pre_frame();
//set the next frame as pre_frame,must dicard pre_pyr in advance
void get_pre_frame();
//use every time,must after using get_pre_frame(BYTE**pyr)
void get_next_frame(BYTE*&gray);
void get_info(const int nh, const int nw);
void set_paras(double lamda,double threshold,double scalefactor);
void run_single_frame();
void HornSchunck();
void get_optical_flow(double*&u, double*&v);
};
#endif
[cpp] view plaincopyprint?
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "HornSchunckTracker.h"
HornSchunckTracker::HornSchunckTracker()
{
isusepyramid = true;
}
HornSchunckTracker::~HornSchunckTracker()
{
for (int i = 0; i < max_pyramid_layer; i++)
{
if (pre_pyr[i])
delete[]pre_pyr[i];
if (next_pyr[i])
delete[]next_pyr[i];
}
delete[]pre_pyr;
delete[]next_pyr;
if (height)
delete[]height;
if (width)
delete[]width;
}
void HornSchunckTracker::get_max_pyramid_layer()
{
double minsize = 80;
double temp = original_imgH > original_imgW ?
original_imgW : original_imgH;
double tt = log(temp / minsize) / log(scale_factor);
if (tt>4)
{
max_pyramid_layer = 5;
return;
}
max_pyramid_layer = tt;
}
void HornSchunckTracker::build_pyramid(BYTE**&pyramid)
{
for (int i = 1; i < max_pyramid_layer; i++)
{
pyramid_down(pyramid[i - 1], height[i - 1],
width[i - 1], pyramid[i], height[i], width[i]);
}
}
void HornSchunckTracker::pyramid_down(BYTE*&src_gray_data,
const int src_h, const int src_w, BYTE*& dst, int&dst_h, int&dst_w)
{
dst_h = src_h / scale_factor;
dst_w = src_w / scale_factor;
assert(dst_w > 3 && dst_h > 3);
//BYTE*smoothed = new BYTE[src_h*src_w];
dst = new BYTE[dst_h*dst_w];
//lowpass_filter(src_gray_data, src_h, src_w,smoothed);
bilinear(src_gray_data, dst, src_w, src_h, dst_h, dst_w);
/*for (int i = 0; i < dst_h - 1; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < dst_w - 1; j++)
{
int srcY = 2 * i + 1;
int srcX = 2 * j + 1;
double re = src_gray_data[srcY*src_w + srcX] * 0.25;
re += src_gray_data[(srcY - 1)*src_w + srcX] * 0.125;
re += src_gray_data[(srcY + 1)*src_w + srcX] * 0.125;
re += src_gray_data[srcY*src_w + srcX - 1] * 0.125;
re += src_gray_data[srcY*src_w + srcX + 1] * 0.125;
re += src_gray_data[(srcY - 1)*src_w + srcX + 1] * 0.0625;
re += src_gray_data[(srcY - 1)*src_w + srcX - 1] * 0.0625;
re += src_gray_data[(srcY + 1)*src_w + srcX - 1] * 0.0625;
re += src_gray_data[(srcY + 1)*src_w + srcX + 1] * 0.0625;
dst[i*dst_w + j] = re;
}
for (int i = 0; i < dst_h; i++)
dst[i*dst_w + dst_w - 1] = dst[i*dst_w + dst_w - 2];
for (int i = 0; i < dst_w; i++)
dst[(dst_h - 1)*dst_w + i] = dst[(dst_h - 2)*dst_w + i];*/
}
void HornSchunckTracker::get_pre_frame(BYTE*&gray)//use only at the beginning
{
pre_pyr[0] = gray;
build_pyramid(pre_pyr);
//save_gray("1.bmp", pre_pyr[1], height[1], width[1]);
}
void HornSchunckTracker::discard_pre_frame()
{
for (int i = 0; i < max_pyramid_layer; i++)
delete[]pre_pyr[i];
}
//set the next frame as pre_frame,must dicard pre_pyr in advance
void HornSchunckTracker::get_pre_frame()
{
for (int i = 0; i < max_pyramid_layer; i++)
pre_pyr[i] = next_pyr[i];
}
//use every time,must after using get_pre_frame(BYTE**pyr)
void HornSchunckTracker::get_next_frame(BYTE*&gray)
{
next_pyr[0] = gray;
build_pyramid(next_pyr);
//save_gray("1.bmp", next_pyr[1], height[1], width[1]);
}
void HornSchunckTracker::get_info(const int nh, const int nw)
{
original_imgH = nh;
original_imgW = nw;
if (isusepyramid)
get_max_pyramid_layer();
else
max_pyramid_layer = 1;
pre_pyr = new BYTE*[max_pyramid_layer];
next_pyr = new BYTE*[max_pyramid_layer];
height = new int[max_pyramid_layer];
width = new int[max_pyramid_layer];
height[0] = nh;
width[0] = nw;
}
//低通滤波
void HornSchunckTracker::lowpass_filter(double*&src, const int H, const int W, double*&smoothed)
{
//tackle with border
for (int i = 0; i < H; i++)
{
smoothed[i*W] = src[i*W];
smoothed[i*W + W - 1] = src[i*W + W - 1];
}
for (int i = 0; i < W; i++)
{
smoothed[i] = src[i];
smoothed[(H - 1)*W + i] = src[(H - 1)*W + i];
}
for (int i = 1; i < H - 1; i++)
for (int j = 1; j < W - 1; j++)
{
double re = 0;
re += src[i*W + j] * 0.25;
re += src[(i - 1)*W + j] * 0.125;
re += src[i*W + j + 1] * 0.125;
re += src[i*W + j - 1] * 0.125;
re += src[(i + 1)*W + j] * 0.125;
re += src[(i - 1)*W + j - 1] * 0.0625;
re += src[(i + 1)*W + j - 1] * 0.0625;
re += src[(i - 1)*W + j + 1] * 0.0625;
re += src[(i + 1)*W + j + 1] * 0.0625;
smoothed[i*W + j] = re;
}
}
void HornSchunckTracker::get_fx_fy_ft(BYTE*img1, BYTE*img2, int w, int h, double*fx, double*fy, double*ft)
{
for (int i = 0; i < h - 1; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < w - 1; j++)
{
fx[i*w + j] = 0.25*(img1[i*w + j + 1] - img1[i*w + j] + img1[(i + 1)*w + j + 1] - img1[(i + 1)*w + j]
+ img2[i*w + j + 1] - img2[i*w + j] + img2[(i + 1)*w + j + 1] - img2[(i + 1)*w + j]);
fy[i*w + j] = 0.25 * (img1[(i + 1)*w + j] - img1[i*w + j] +img1[(i + 1)*w + j + 1] - img1[i*w + j + 1]
+ img2[(i + 1)*w + j] - img2[i*w + j] + img2[(i + 1)*w + j + 1] - img2[i*w + j + 1]);
ft[i*w + j] = 0.25 * (img2[i*w + j] - img1[i*w + j] +img2[(i + 1)*w + j] - img1[(i + 1)*w + j] +
img2[(i + 1)*w + j + 1] - img1[(i + 1)*w + j + 1] + img2[i*w + j + 1] - img1[i*w + j + 1]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < h; i++)
{
//fx[i*w] = fx[i*w + w - 2];
fx[i*w + w - 1] = fx[i*w + w - 2];
//fy[i*w] = fy[i*w + w - 2];
fy[i*w + w - 1] = fy[i*w + w - 2];
//ft[i*w] = ft[i*w + w - 2];
ft[i*w + w - 1] = ft[i*w + w - 2];
}
for (int j = 0; j < w; j++)
{
//fx[j] = fx[h + j];
fx[(h - 1)*w + j] = fx[(h - 2)*w + j];
//fy[j] = fy[h + j];
fy[(h - 1)*w + j] = fy[(h - 2)*w + j];
//ft[j] = ft[h + j];
ft[(h - 1)*w + j] = ft[(h - 2)*w + j];
}
}
//取得计算得到的光流值,u、v为out型参数
void HornSchunckTracker::get_optical_flow(double*&u, double*&v)
{
assert(optical_field_U&&optical_field_V);
u = optical_field_U;
v = optical_field_V;
}
//int save_gray(char * savebmp_file, LPBYTE gray, int height, int width);
//返回求得的光流场,大小为原始图像大小
void HornSchunckTracker::HornSchunck()
{
//save_gray("22.bmp", pre_pyr[0], height[0], width[0]);
//初始化光流场为0
if (optical_field_U)
delete[]optical_field_U;
if (optical_field_V)
delete[]optical_field_V;
optical_field_U = new double[width[max_pyramid_layer - 1]
* height[max_pyramid_layer - 1]];
optical_field_V = new double[width[max_pyramid_layer - 1]
* height[max_pyramid_layer - 1]];
memset(optical_field_U, 0, sizeof(double)*width[max_pyramid_layer - 1]
* height[max_pyramid_layer - 1]);
memset(optical_field_V, 0, sizeof(double)*width[max_pyramid_layer - 1]
* height[max_pyramid_layer - 1]);
//使用金字塔计算光流
for (int i = max_pyramid_layer - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
double*Ix = new double[width[i] * height[i]];
double*Iy = new double[width[i] * height[i]];
double*It = new double[width[i] * height[i]];
//求偏导
get_fx_fy_ft(pre_pyr[i], next_pyr[i], width[i], height[i], Ix, Iy, It);
//将光流场平滑
double*smoothed_U = new double[width[i] * height[i]];
double*smoothed_V = new double[width[i] * height[i]];
if (i == max_pyramid_layer - 1)
{
memset(smoothed_U, 0, sizeof(double)*width[i] * height[i]);
memset(smoothed_V, 0, sizeof(double)*width[i] * height[i]);
}
else
{
lowpass_filter(optical_field_U, height[i], width[i], smoothed_U);
lowpass_filter(optical_field_V, height[i], width[i], smoothed_V);
}
double error = 1000000;
int iteration = 0;
//迭代计算每个像素的光流,直到收敛或达到最大迭代次数
while (error > precision&&iteration < maxiteration)
{
iteration++;
error = 0;
//计算该层金字塔的光流
for (int j = 0; j < height[i]; j++)
for (int k = 0; k < width[i]; k++)
{
//采用改进方法,光流速度需大于阈值,这样不仅准确度增加,计算量也会减小
double w = Ix[j*width[i] + k] * Ix[j*width[i] + k]
+ Iy[j*width[i] + k] * Iy[j*width[i] + k] > threshold ? 1 : 0;
double u_pre = optical_field_U[j*width[i] + k];
double v_pre = optical_field_V[j*width[i] + k];
double utemp = smoothed_U[j*width[i] + k];//get_average4(optical_field_U, height[i], width[i], j, k);
double vtemp = smoothed_V[j*width[i] + k]; //get_average4(optical_field_V, height[i], width[i], j, k);
double denominator = lamda + w*(Ix[j*width[i] + k] * Ix[j*width[i] + k]
+ Iy[j*width[i] + k] * Iy[j*width[i] + k]);
double numerator = Ix[j*width[i] + k] * utemp + Iy[j*width[i] + k] *
vtemp + It[j*width[i] + k];
optical_field_U[j*width[i] + k] = utemp - Ix[j*width[i] + k] *w*numerator / denominator;
optical_field_V[j*width[i] + k] = vtemp - Iy[j*width[i] + k] *w*numerator / denominator;
error += pow(optical_field_U[j*width[i] + k] - u_pre,2) +
pow(optical_field_V[j*width[i] + k] - v_pre,2);
}
//下一次迭代前重新平滑光流场
if (error >exp(double(max_pyramid_layer-i))*precision&&iteration < maxiteration)
{
lowpass_filter(optical_field_U, height[i], width[i], smoothed_U);
lowpass_filter(optical_field_V, height[i], width[i], smoothed_V);
}
}
delete[]smoothed_U, smoothed_V,Ix,Iy,It;
if (i == 0)//得到最终光流场
{
return;
}
//下一层的光流场
double*new_of_u = new double[width[i - 1] * height[i - 1]];
double*new_of_v = new double[width[i - 1] * height[i - 1]];
//上采样
pyramid_up(optical_field_U, width[i], height[i], new_of_u, width[i - 1], height[i - 1]);
pyramid_up(optical_field_V, width[i], height[i], new_of_v, width[i - 1], height[i - 1]);
//将每个像素的光流按缩放因子放大,得到下一层的光流场的初值
//double scale = double(height[i - 1]) / height[i];
for (int j = 0; j < height[i - 1]; j++)
for (int k = 0; k < width[i - 1]; k++)
{
new_of_u[j*width[i - 1] + k] *= scale_factor;
new_of_v[j*width[i - 1] + k] *= scale_factor;
}
delete[]optical_field_U, optical_field_V;
optical_field_U = new_of_u;
optical_field_V = new_of_v;
}
}
//上采样,采用双线性插值,用双立方插值应该更精确
void HornSchunckTracker::pyramid_up(double*src, int srcW, int srcH, double*dst, int dstW, int dstH)
{
bilinear(src, dst, srcW, srcH, dstH, dstW);
}
//双线性插值
void HornSchunckTracker::bilinear(double* lpSrc, double* lpDst, int nW, int nH, int H1, int W1)
{
float fw = float(nW) / W1;
float fh = float(nH) / H1;
int y1, y2, x1, x2, x0, y0;
float fx1, fx2, fy1, fy2;
for (int i = 0; i < H1; i++)
{
y0 = i*fh;
y1 = int(y0);
if (y1 == nH - 1) y2 = y1;
else y2 = y1 + 1;
fy1 = y1 - y0;
fy2 = 1.0f - fy1;
for (int j = 0; j < W1; j++)
{
x0 = j*fw;
x1 = int(x0);
if (x1 == nW - 1) x2 = x1;
else x2 = x1 + 1;
fx1 = y1 - y0;
fx2 = 1.0f - fx1;
float s1 = fx1*fy1;
float s2 = fx2*fy1;
float s3 = fx2*fy2;
float s4 = fx1*fy2;
double c1, c2, c3, c4;
c1 = lpSrc[y1*nW + x1];
c2 = lpSrc[y1*nW + x2];
c3 = lpSrc[y2*nW + x1];
c4 = lpSrc[y2*nW + x2];
double r;
r = (c1*s3) + (c2*s4) + (c3*s2) + (c4*s1);
lpDst[i*W1 + j] = r;
}
}
}
//双线性插值
void HornSchunckTracker::bilinear(BYTE* lpSrc, BYTE* lpDst, int nW, int nH, int H1, int W1)
{
float fw = float(nW) / W1;
float fh = float(nH) / H1;
int y1, y2, x1, x2, x0, y0;
float fx1, fx2, fy1, fy2;
for (int i = 0; i < H1; i++)
{
y0 = i*fh;
y1 = int(y0);
if (y1 == nH - 1) y2 = y1;
else y2 = y1 + 1;
fy1 = y1 - y0;
fy2 = 1.0f - fy1;
for (int j = 0; j < W1; j++)
{
x0 = j*fw;
x1 = int(x0);
if (x1 == nW - 1) x2 = x1;
else x2 = x1 + 1;
fx1 = y1 - y0;
fx2 = 1.0f - fx1;
float s1 = fx1*fy1;
float s2 = fx2*fy1;
float s3 = fx2*fy2;
float s4 = fx1*fy2;
double c1, c2, c3, c4;
c1 = lpSrc[y1*nW + x1];
c2 = lpSrc[y1*nW + x2];
c3 = lpSrc[y2*nW + x1];
c4 = lpSrc[y2*nW + x2];
double r;
r = (c1*s3) + (c2*s4) + (c3*s2) + (c4*s1);
lpDst[i*W1 + j] = BYTE(r);
}
}
}
void HornSchunckTracker::set_paras(double lamda, double threshold, double scalefactor)
{
this->lamda = lamda;
this->threshold = threshold;
scale_factor = scalefactor;
}
//double HornSchunckTracker::get_average4(double*src, const int height, const int width, const int i, const int j)
//{
// if (j < 0 || j >= width) return 0;
// if (i < 0 || i >= height) return 0;
//
// double val = 0.0;
// int tmp = 0;
// if ((i - 1) >= 0){
// ++tmp;
// val += src[(i - 1)*width + j];
// }
// if (i + 1<height){
// ++tmp;
// val += src[(i + 1)*width + j];
// }
// if (j - 1 >= 0){
// ++tmp;
// val += src[i*width + j - 1];
// }
// if (j + 1<width){
// ++tmp;
// val += src[i*width + j + 1];
// }
// return val / tmp;
//
//}






















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








