A Systematic Evaluation of GPT-4V’s Multimodal Capability for Medical Image Analysis
1.Keyword
GPT-4V - 多模态模型
Medical Image - 医学影像图片
Radiology Report Generation - 放射性报告生成
Medical Visual Question Answering - 医学视觉问答
Medical Visual Grounding - 找到文本所指的内容在图像中的位置
Large Language Model Evaluation - 大模型评估
2. Research Problem
- 本文对GPT-4V在医学图像分析上的能力进行评测,主要是聚焦在3个任务: 1. Radiology Report Generation 2. Medical Visual Question Answering 3. Medical Visual Grounding
- For the evaluation, a set of prompts is designed for each task to induce the corresponding capability of GPT4V to produce sufficiently good outputs
- Three evaluation ways including quantitative analysis, human evaluation, and case study are employed to achieve an in-depth and extensive evaluation
3. Key Contributions
- 比较了传统的评测NLP模型能力的指标( precision, recall, F1 score, BLEU, CIDEr, ROUGE, METEOR)与人为(该领域专家)评测的差异。通过实验证明传统的评价指标对于open-end类型的问题(问题无法通过 yes or no简要的进行回答,需要一段或者一句更加详细的文本来回答问答) 无法正确的评估。所以需要一种全新的Evaluation Metrics是迫在眉睫的。
- GPT-4V在Radiology Report Generation 和 Medical Visual Question Answering task表现很好,尽管GPT-4V并非是一个专门针对医学领域的模型,其表现也接近SOAT。但是在Medical Visual Grounding task表现很糟糕,在该任务下还有很大的提高空间。
4. Methodology
Dataset: The study utilized MIMIC-CXR for radiology reports, the VQA-RAD dataset for visual question answering and MS-CXR for Medical Visual Grounding.
Model architecture: GPT-4V, a multimodal model capable of processing both text and images.
Training procedure: Utilizing zero-short or few-short prompt to generate response from GPT-4V
Evaluation metrics: Included traditional NLP metrics (BLEU, ROUGE, METEOR, CIDEr) and human evaluation(真的就只是找了该领域专家对随机抽取的100个测试数据结果进行评估,我一开始还以为是用的Agent来做=。=)s for qualitative assessment.
5. Main Results
-
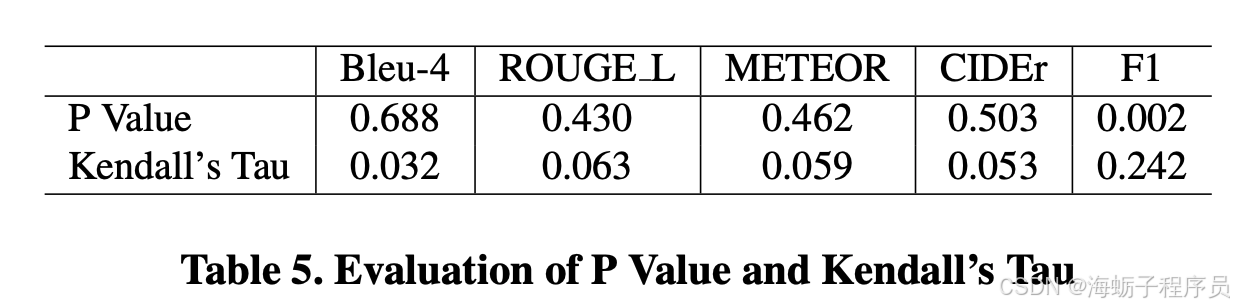
传统指标认为GPT-4V生成的结果都很差,但是专家对GPT-4V生成的结果却认为还不错。


-
因此,作者又对传统metric的结果和human evaluation的结果进行了对比,比如采用了肯达尔系数和p-value。传统指标和专家都对GPT-4V生成的结果进行评级,二者的肯达尔系数在0值左右徘徊(肯达尔系数的范围是1到-1, 1代表两个排名完全一致,-1代表完全不一致,0代表二者互相独立。)
Kendall’s τ Coefficient
Definition: Kendall’s τ (tau) coefficient is a statistic used to measure the ordinal association between two quantities. It assesses how well the relationship between two variables can be described using a monotonic function. The coefficient is calculated based on the number of concordant and discordant pairs of observations.
























 2006
2006

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








