本文我们来介绍如何使用AI,将自己的知识库自动转换为知识图谱。
代码参考:https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1OpoLyKAWTVpkhy0VgVduprYypIFTSIrL#scrollTo=TtlKi-4r8grL
0. 实现效果
先来看下最终的实现效果:输入知识,大模型自动将知识中的实体、关系、属性等提取出来,并自动生成知识图谱。为了方便查看,代码中还对创建的知识谱图进行了可视化展示。
(1)对于某个知识提取出的知识图谱结构:

(2)可视化知识谱图的展示:
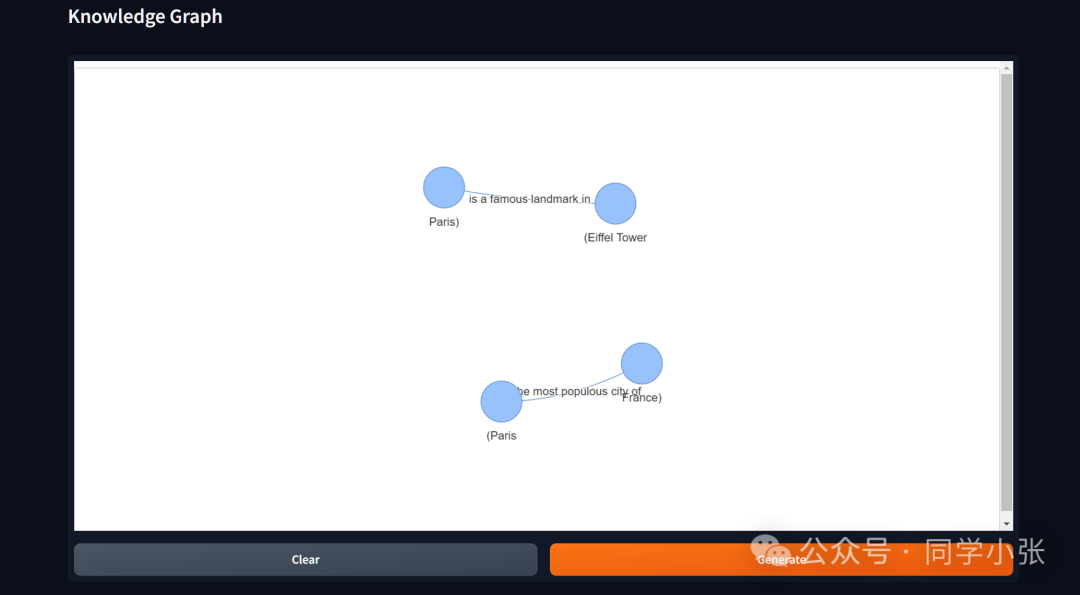
1. 代码实现过程
1.1 知识图谱结构的识别
将知识转化为知识图谱,最重要的步骤是将知识中的实体、关系、属性等提取出来。这也是代码的主要部分。这部分是通过Prompt来实现的。
(1)Prompt部分
# Prompt template for knowledge triple extraction
_DEFAULT_KNOWLEDGE_TRIPLE_EXTRACTION_TEMPLATE = (
"You are a networked intelligence helping a human track knowledge triples"
" about all relevant people, things, concepts, etc. and integrating"
" them with your knowledge stored within your weights"
" as well as that stored in a knowledge graph."
" Extract all of the knowledge triples from the text."
" A knowledge triple is a clause that contains a subject, a predicate,"
" and an object. The subject is the entity being described,"
" the predicate is the property of the subject that is being"
" described, and the object is the value of the property.\n\n"
"EXAMPLE\n"
"It's a state in the US. It's also the number 1 producer of gold in the US.\n\n"
f"Output: (Nevada, is a, state){KG_TRIPLE_DELIMITER}(Nevada, is in, US)"
f"{KG_TRIPLE_DELIMITER}(Nevada, is the number 1 producer of, gold)\n"
"END OF EXAMPLE\n\n"
"EXAMPLE\n"
"I'm going to the store.\n\n"
"Output: NONE\n"
"END OF EXAMPLE\n\n"
"EXAMPLE\n"
"Oh huh. I know Descartes likes to drive antique scooters and play the mandolin.\n"
f"Output: (Descartes, likes to drive, antique scooters){KG_TRIPLE_DELIMITER}(Descartes, plays, mandolin)\n"
"END OF EXAMPLE\n\n"
"EXAMPLE\n"
"{text}"
"Output:"
)
这个Prompt主要的任务是让大模型从语句中提取出知识三元组,即实体、关系、属性。看着有点像识别句子中的主谓宾。Prompt中给了几个示例,Few-shot的方式可以让大模型更好地理解用户的需求。
(2)调用大模型的基本流程
KNOWLEDGE_TRIPLE_EXTRACTION_PROMPT = PromptTemplate(
input_variables=["text"],
template=_DEFAULT_KNOWLEDGE_TRIPLE_EXTRACTION_TEMPLATE,
)
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0.9)
# Create an LLMChain using the knowledge triple extraction prompt
chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=KNOWLEDGE_TRIPLE_EXTRACTION_PROMPT)
# Run the chain with the specified text
text = "The city of Paris is the capital and most populous city of France. The Eiffel Tower is a famous landmark in Paris."
triples = chain.invoke(
{'text' : text}
).get('text')
(3)结果的解析
def parse_triples(response, delimiter=KG_TRIPLE_DELIMITER):
if not response:
return []
return response.split(delimiter)
triples_list = parse_triples(triples)
pprint(triples_list)
(4)执行结果示例:

1.2 知识图谱的可视化
示例代码中使用gradio框架进行了可视化界面的搭建。可视化不是本文重点,这里就不详细介绍了。可以看完整代码里的实现。大体是使用了 pyvis 和 networkx 来使用前面提取的三元组进行图结构的构建。
运行之后,打开提示中的链接,就可以看到可视化界面了。

这里有小小的疑问:为什么要同时使用pyvis和networkx?看代码中是先用三元组构建了networkx的图结构,然后将networkx结构转化成了pyvis结构,然后再使用pyvis进行可视化。这个过程有必要?不能直接利用三元组构建pyvis结构吗?期待各位大佬的解答!
2. 完整代码
下面将可直接运行的完整代码奉上(当然,缺依赖库的话还是要自己装一装的了):
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.chains import LLMChain
from langchain.graphs.networkx_graph import KG_TRIPLE_DELIMITER
from pprint import pprint
# Prompt template for knowledge triple extraction
_DEFAULT_KNOWLEDGE_TRIPLE_EXTRACTION_TEMPLATE = (
"You are a networked intelligence helping a human track knowledge triples"
" about all relevant people, things, concepts, etc. and integrating"
" them with your knowledge stored within your weights"
" as well as that stored in a knowledge graph."
" Extract all of the knowledge triples from the text."
" A knowledge triple is a clause that contains a subject, a predicate,"
" and an object. The subject is the entity being described,"
" the predicate is the property of the subject that is being"
" described, and the object is the value of the property.\n\n"
"EXAMPLE\n"
"It's a state in the US. It's also the number 1 producer of gold in the US.\n\n"
f"Output: (Nevada, is a, state){KG_TRIPLE_DELIMITER}(Nevada, is in, US)"
f"{KG_TRIPLE_DELIMITER}(Nevada, is the number 1 producer of, gold)\n"
"END OF EXAMPLE\n\n"
"EXAMPLE\n"
"I'm going to the store.\n\n"
"Output: NONE\n"
"END OF EXAMPLE\n\n"
"EXAMPLE\n"
"Oh huh. I know Descartes likes to drive antique scooters and play the mandolin.\n"
f"Output: (Descartes, likes to drive, antique scooters){KG_TRIPLE_DELIMITER}(Descartes, plays, mandolin)\n"
"END OF EXAMPLE\n\n"
"EXAMPLE\n"
"{text}"
"Output:"
)
KNOWLEDGE_TRIPLE_EXTRACTION_PROMPT = PromptTemplate(
input_variables=["text"],
template=_DEFAULT_KNOWLEDGE_TRIPLE_EXTRACTION_TEMPLATE,
)
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0.9)
# Create an LLMChain using the knowledge triple extraction prompt
chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=KNOWLEDGE_TRIPLE_EXTRACTION_PROMPT)
# Run the chain with the specified text
text = "The city of Paris is the capital and most populous city of France. The Eiffel Tower is a famous landmark in Paris."
triples = chain.invoke(
{'text' : text}
).get('text')
pprint(triples)
def parse_triples(response, delimiter=KG_TRIPLE_DELIMITER):
if not response:
return []
return response.split(delimiter)
triples_list = parse_triples(triples)
pprint(triples_list)
from pyvis.network import Network
import networkx as nx
def create_graph_from_triplets(triplets):
G = nx.DiGraph()
for triplet in triplets:
subject, predicate, obj = triplet.strip().split(',')
G.add_edge(subject.strip(), obj.strip(), label=predicate.strip())
return G
def nx_to_pyvis(networkx_graph):
pyvis_graph = Network(notebook=True, cdn_resources='remote')
for node in networkx_graph.nodes():
pyvis_graph.add_node(node)
for edge in networkx_graph.edges(data=True):
pyvis_graph.add_edge(edge[0], edge[1], label=edge[2]["label"])
return pyvis_graph
def generateGraph():
triplets = [t.strip() for t in triples_list if t.strip()]
graph = create_graph_from_triplets(triplets)
pyvis_network = nx_to_pyvis(graph)
pyvis_network.toggle_hide_edges_on_drag(True)
pyvis_network.toggle_physics(False)
pyvis_network.set_edge_smooth('discrete')
html = pyvis_network.generate_html()
html = html.replace("'", "\"")
return f"""<iframe style="width: 100%; height: 600px;margin:0 auto" name="result" allow="midi; geolocation; microphone; camera;
display-capture; encrypted-media;" sandbox="allow-modals allow-forms
allow-scripts allow-same-origin allow-popups
allow-top-navigation-by-user-activation allow-downloads" allowfullscreen=""
allowpaymentrequest="" frameborder="0" srcdoc='{html}'></iframe>"""
import gradio as gr
demo = gr.Interface(
generateGraph,
inputs=None,
outputs='html',
title="Knowledge Graph",
allow_flagging='never',
live=True,
)
demo.launch(
height=800,
width="100%"
)
3. 可能遇到的坑
如果你使用的是参考链接中的原代码,则很可能会遇到下面的问题。
(1)报错:module gradio has no attribute outputs. gradio版本4.16
解决:outputs=gr.outputs.HTML 改为 outputs='html'
4. 总结
本文我们主要是学习了如何利用AI将知识转化为知识图谱的结构。其中最主要的,就是从知识中提取出三元组,这就强依赖Prompt和大模型的能力了。然后,锦上添花的,代码实现了知识图谱结构的可视化。尽管简单,但思路绝对值得借鉴。
如何学习大模型
现在社会上大模型越来越普及了,已经有很多人都想往这里面扎,但是却找不到适合的方法去学习。
作为一名资深码农,初入大模型时也吃了很多亏,踩了无数坑。现在我想把我的经验和知识分享给你们,帮助你们学习AI大模型,能够解决你们学习中的困难。
我已将重要的AI大模型资料包括市面上AI大模型各大白皮书、AGI大模型系统学习路线、AI大模型视频教程、实战学习,等录播视频免费分享出来,需要的小伙伴可以扫取。

一、AGI大模型系统学习路线
很多人学习大模型的时候没有方向,东学一点西学一点,像只无头苍蝇乱撞,我下面分享的这个学习路线希望能够帮助到你们学习AI大模型。

二、AI大模型视频教程

三、AI大模型各大学习书籍

四、AI大模型各大场景实战案例

五、结束语
学习AI大模型是当前科技发展的趋势,它不仅能够为我们提供更多的机会和挑战,还能够让我们更好地理解和应用人工智能技术。通过学习AI大模型,我们可以深入了解深度学习、神经网络等核心概念,并将其应用于自然语言处理、计算机视觉、语音识别等领域。同时,掌握AI大模型还能够为我们的职业发展增添竞争力,成为未来技术领域的领导者。
再者,学习AI大模型也能为我们自己创造更多的价值,提供更多的岗位以及副业创收,让自己的生活更上一层楼。
因此,学习AI大模型是一项有前景且值得投入的时间和精力的重要选择。




















 1273
1273

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








