近期OpenAI发布的GPT-4的效果好得让人惊艳!碾压了之前火到出圈的ChatGPT,通过同步发布的GPT-4 Technical Report一同看看到底发生了什么!
No.0
摘要
We report the development of GPT-4, a large-scale, multimodal model which can accept image and text inputs and produce text outputs. While less capable than humans in many real-world scenarios, GPT-4 exhibits human-level performance on various professional and academic benchmarks, including passing a simulated bar exam with a score around the top 10% of test takers. GPT-4 is a Transformerbased model pre-trained to predict the next token in a document. The post training alignment process results in improved performance on measures of factuality and adherence to desired behavior. A core component of this project was developing infrastructure and optimization methods that behave predictably across a wide range of scales. This allowed us to accurately predict some aspects of GPT-4’s performance based on models trained with no more than 1/1,000th the compute of GPT-4.
我们公布了GPT-4的发展,这是一个大规模的多模态模型,可以接受图像和文本输入并产生文本输出。虽然在许多现实场景中,GPT-4的能力不如人类,但它在各种专业和学术基准上表现出了人类的水平,包括以大约TOP-10%的成绩通过模拟律师资格考试。GPT-4是一个基于transformer的预训练模型,用于预测文档中的下一个标记。训练后的调整过程会提高对事实的衡量和对期望行为的坚持。这个项目的一个核心组成部分是开发基础设施和优化方法,这些方法可以在大范围内预测行为。这使得我们能够准确地预测GPT-4性能的某些方面,基于不超过GPT-4计算量的千分之一的训练模型。
No.1
引言
This technical report presents GPT-4, a large multimodal model capable of processing image and text inputs and producing text outputs. Such models are an important area of study as they have the potential to be used in a wide range of applications, such as dialogue systems, text summarization, and machine translation. As such, they have been the subject of substantial interest and progress in recent years [1–28].
本技术报告介绍了GPT-4,一种能够处理图像和文本输入并产生文本输出的大型多模态模型。这些模型是一个重要的研究领域,因为它们具有广泛应用的潜力,如对话系统、文本摘要和机器翻译。因此,近年来,它们一直是人们感兴趣和取得进展的主题[1-28]。
One of the main goals of developing such models is to improve their ability to understand and generate natural language text, particularly in more complex and nuanced scenarios. To test its capabilities in such scenarios, GPT-4 was evaluated on a variety of exams originally designed for humans. In these evaluations it performs quite well and often outscores the vast majority of human test takers.For example, on a simulated bar exam, GPT-4 achieves a score that falls in the top 10% of test takers. This contrasts with GPT-3.5, which scores in the bottom 10%.
开发此类模型的主要目标之一是提高它们理解和生成自然语言文本的能力,特别是在更复杂和微妙的场景中。为了测试它在这种情况下的能力,GPT-4在最初为人类设计的各种考试中进行了评估。在这些评估中,它表现得相当好,经常超过绝大多数人类考生。例如,在模拟律师资格考试中,GPT-4的成绩在考生中排名前10%。这与GPT-3.5形成了鲜明对比,后者的得分位于后10%。
On a suite of traditional NLP benchmarks, GPT-4 outperforms both previous large language models and most state-of-the-art systems (which often have benchmark-specific training or hand-engineering).On the MMLU benchmark [29, 30], an English-language suite of multiple-choice questions covering 57 subjects, GPT-4 not only outperforms existing models by a considerable margin in English, but also demonstrates strong performance in other languages. On translated variants of MMLU, GPT-4 surpasses the English-language state-of-the-art in 24 of 26 languages considered. We discuss these model capability results, as well as model safety improvements and results, in more detail in later sections.
在一套传统的NLP基准测试上,GPT-4优于以前的大型语言模型和大多数最先进的系统(通常具有特定于基准测试的训练或手工工程)。在MMLU基准测试[29,30]中,GPT-4不仅在英语测试中大大超过现有模型,而且在其他语言测试中也表现出色。在MMLU的翻译版本中,GPT-4在考虑的26种语言中有24种超过了最先进的英语。我们将在后面的章节中更详细地讨论这些模型性能的结果,以及模型安全性的改进和结果。
This report also discusses a key challenge of the project, developing deep learning infrastructure and optimization methods that behave predictably across a wide range of scales. This allowed us to make predictions about the expected performance of GPT-4 (based on small runs trained in similar ways) that were tested against the final run to increase confidence in our training.
本报告还讨论了该项目的一个关键挑战,即开发在大范围内可预测行为的深度学习基础设施和优化方法。这使得我们能够预测GPT-4的预期性能(基于以类似方式训练的小型运行),并与最终运行进行测试,以增加我们训练的信心。
Despite its capabilities, GPT-4 has similar limitations to earlier GPT models [1, 31, 32]: it is not fully reliable (e.g. can suffer from “hallucinations”), has a limited context window, and does not learn from experience. Care should be taken when using the outputs of GPT-4, particularly in contexts where reliability is important.
尽管GPT-4功能强大,但它与早期的GPT模型有相似的局限性[1,31,32]:它不完全可靠(例如,可能会出现“幻觉”),上下文窗口有限,并且不能从经验中学习。在使用GPT-4输出时应小心,特别是在可靠性很重要的情况下。
GPT-4’s capabilities and limitations create significant and novel safety challenges, and we believecareful study of these challenges is an important area of research given the potential societal impact.This report includes an extensive system card (after the Appendix) describing some of the risks weforesee around bias, disinformation, over-reliance, privacy, cybersecurity, proliferation, and more.It also describes interventions we made to mitigate potential harms from the deployment of GPT-4,including adversarial testing with domain experts, and a model-assisted safety pipeline.
GPT-4的能力和局限性带来了重大而全新的安全挑战,我们认为,考虑到潜在的社会影响,仔细研究这些挑战是一个重要的研究领域。本报告包括一个广泛的系统卡(在附录之后),描述了我们预计的关于偏见、虚假信息、过度依赖、隐私、网络安全、扩散等方面的一些风险。它还描述了我们为减轻GPT-4部署带来的潜在危害而采取的干预措施,包括与领域专家进行对抗性测试,以及一个模型辅助的安全管道。
No.2
本技术的范围与限制
This report focuses on the capabilities, limitations, and safety properties of GPT-4. GPT-4 is aTransformer-style model [33] pre-trained to predict the next token in a document, using both publiclyavailable data (such as internet data) and data licensed from third-party providers. The model wasthen fine-tuned using Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) [34]. Given boththe competitive landscape and the safety implications of large-scale models like GPT-4, this reportcontains no further details about the architecture (including model size), hardware, training compute,dataset construction, training method, or similar.
本报告主要介绍GPT-4的功能、限制和安全特性。GPT-4是一个transformer风格的模型[33]预训练,用于预测文档中的下一个令牌,使用公开可用数据(如互联网数据)和第三方提供商授权的数据。然后使用来自人类反馈的强化学习(RLHF)[34]对模型进行微调。考虑到竞争格局和大型模型(如GPT-4)的安全影响,本报告没有包含有关架构(包括模型大小)、硬件、训练计算、数据集构造、训练方法或类似内容的进一步细节。
We are committed to independent auditing of our technologies, and shared some initial steps andideas in this area in the system card accompanying this release.2 We plan to make further technicaldetails available to additional third parties who can advise us on how to weigh the competitive andsafety considerations above against the scientific value of further transparency.
我们致力于对我们的技术进行独立的核查,并在这个版本附带的系统卡中分享了这一领域的一些初始步骤和想法我们计划向更多的第三方提供进一步的技术细节,他们可以就如何权衡上述竞争和安全考虑与进一步透明的科学价值提供建议。
No.3
本可预测的伸缩性
A large focus of the GPT-4 project was building a deep learning stack that scales predictably. Theprimary reason is that for very large training runs like GPT-4, it is not feasible to do extensive model-specific tuning. To address this, we developed infrastructure and optimization methods that have very predictable behavior across multiple scales. These improvements allowed us to reliably predict some aspects of the performance of GPT-4 from smaller models trained using 1, 000× –10, 000× less compute.
GPT-4项目的一大重点是构建一个可预测扩展的深度学习堆栈。主要原因是,对于GPT-4这样的大型训练运行,进行广泛的特定于模型的调优是不可行的。为了解决这个问题,我们开发了跨多个尺度具有非常可预测行为的基础设施和优化方法。这些改进使我们能够从较小的模型中可靠地预测GPT-4性能的某些方面,这些模型使用的计算量减少了1000倍到10000倍。
3.1 损失预测
The final loss of properly-trained large language models is thought to be well approximated by powerlaws in the amount of compute used to train the model [35, 36, 2, 14, 15].
经过适当训练的大型语言模型的最终损失被认为很好地近似于用于训练模型的计算量的幂法则[35,36,2,14,15]。
To verify the scalability of our optimization infrastructure, we predicted GPT-4’s final loss on ourinternal codebase (not part of the training set) by fitting a scaling law with an irreducible loss term(as in Henighan et al. [15]): L(C) = aCb + c, from models trained using the same methodologybut using at most 10,000x less compute than GPT-4. This prediction was made shortly after the runstarted, without use of any partial results. The fitted scaling law predicted GPT-4’s final loss withhigh accuracy (Figure 1).
为了验证我们优化基础设施的可伸缩性,我们通过拟合一个具有不可约损失项(如Henighan等人[15])的缩放定律来预测GPT-4在内部代码库(不属于训练集)上的最终损失:L(C) = aC^b + C,来自使用相同方法训练的模型,但使用的计算量最多比GPT-4少10,000倍。这个预测是在运行开始后不久做出的,没有使用任何部分结果。拟合的标度律对GPT-4的最终损耗进行了高精度预测(图1)。

Figure 1. Performance of GPT-4 and smaller models. The metric is final loss on a dataset derivedfrom our internal codebase. This is a convenient, large dataset of code tokens which is not contained inthe training set. We chose to look at loss because it tends to be less noisy than other measures acrossdifferent amounts of training compute. A power law fit to the smaller models (excluding GPT-4) isshown as the dotted line; this fit accurately predicts GPT-4’s final loss. The x-axis is training computenormalized so that GPT-4 is 1.
图一:GPT-4和更小型号的性能。该指标是来自我们内部代码库的数据集的最终损失。这是一个方便的大型代码标记数据集,不包含在训练集中。我们之所以选择损失,是因为在不同的训练量计算中,它往往比其他测量方法噪音更小。拟合较小模型(GPT-4除外)的幂律如虚线所示;这个拟合准确地预测了GPT-4的最终损失。x轴是训练计算归一化使得GPT-4等于1。
3.2 在HumanEval上的扩展能力
Having a sense of the capabilities of a model before training can improve decisions around alignment,safety, and deployment. In addition to predicting final loss, we developed methodology to predictmore interpretable metrics of capability. One such metric is pass rate on the HumanEval dataset [37],which measures the ability to synthesize Python functions of varying complexity. We successfullypredicted the pass rate on a subset of the HumanEval dataset by extrapolating from models trainedwith at most 1, 000× less compute (Figure 2).
在训练之前了解模型的功能可以改善关于对齐、安全性和部署的决策。除了预测最终损失,我们还开发了一种方法来预测更多可解释的能力指标。其中一个指标是HumanEval数据集[37]的通过率,它衡量的是合成不同复杂度的Python函数的能力。我们成功地预测了HumanEval数据集子集的通过率,通过从最多1000倍的计算量训练的模型中推断(图2)。

Figure 2. Performance of GPT-4 and smaller models. The metric is mean log pass rate on a subset ofthe HumanEval dataset. A power law fit to the smaller models (excluding GPT-4) is shown as the dottedline; this fit accurately predicts GPT-4’s performance. The x-axis is training compute normalized so thatGPT-4 is 1.
图2。GPT-4和更小型号的性能。度量是HumanEval数据集子集上的平均日志通过率。拟合较小模型(GPT-4除外)的幂律如虚线所示;这个拟合准确地预测了GPT-4的性能。x轴是训练计算归一化使得GPT-4等于1。
For an individual problem in HumanEval, performance may occasionally worsen with scale. Despite these challenges, we find an approximate power law relationship −EP [log(pass_rate(C))] = α∗C−k where k and α are positive constants, and P is a subset of problems in the dataset. We hypothesize that this relationship holds for all problems in this dataset. In practice, very low pass rates are difficult or impossible to estimate, so we restrict to problems P and models M such that given some large sample budget, every problem is solved at least once by every model.
对于HumanEval中的单个问题,性能有时会随着规模的扩大而恶化。尽管存在这些挑战,我们发现了一个近似的幂律关系−EP [log(pass_rate(C))] = α∗C−k,其中k和α是正常数,P是数据集中问题的子集。我们假设这种关系适用于这个数据集中的所有问题。在实践中,非常低的通过率是很难或不可能估计的,因此我们限制问题P和模型M,这样给定一些大的样本预算,每个问题至少被每个模型解决一次。
We registered predictions for GPT-4’s performance on HumanEval before training completed, using only information available prior to training. All but the 15 hardest HumanEval problems were split into 6 difficulty buckets based on the performance of smaller models. The results on the 3rd easiest bucket are shown in Figure 2, showing that the resulting predictions were very accurate for this subset of HumanEval problems where we can accurately estimate log(pass_rate) for several smaller models. Predictions on the other five buckets performed almost as well, the main exception being GPT-4 underperforming our predictions on the easiest bucket.
在训练完成之前,我们在HumanEval上对GPT-4的性能进行了预测,仅使用训练前可用的信息。除了15个最难的HumanEval问题外,其余问题都根据较小模型的表现分为6个难度级别。图2中显示了第三个最简单桶的结果,显示出对HumanEval问题的这个子集的结果预测非常准确,其中我们可以准确地估计几个较小模型的日志(pass_rate)。对其他五个类别的预测表现几乎一样好,主要的例外是GPT-4在最容易的类别上的预测表现不佳。
Certain capabilities remain hard to predict. For example, the Inverse Scaling Prize [38] proposedseveral tasks for which model performance decreases as a function of scale. Similarly to a recentresult by Wei et al. [39], we find that GPT-4 reverses this trend, as shown on one of the tasks calledHindsight Neglect [40] in Figure 3.
某些能力仍然难以预测。例如,逆缩放奖[38]提出了几个模型性能随缩放函数而下降的任务。与Wei等人最近的结果类似,我们发现GPT-4扭转了这一趋势,如图3中一个名为后见之明忽视的任务[40]所示。

Figure 3. Performance of GPT-4 and smaller models on the Hindsight Neglect task. Accuracy is shownon the y-axis, higher is better. ada, babbage, and curie refer to models available via the OpenAI API[41].
图3。GPT-4和较小模型在事后忽视任务中的表现。精度表示在y轴上,越高越好。ada, babbage和curie是通过OpenAI API[41]提供的模型。
We believe that accurately predicting future capabilities is important for safety. Going forward weplan to refine these methods and register performance predictions across various capabilities beforelarge model training begins, and we hope this becomes a common goal in the field.
我们相信,准确预测未来的能力对安全非常重要。展望未来,我们计划在大型模型训练开始之前改进这些方法,并在各种能力之间登记性能预测,我们希望这成为该领域的共同目标。
No.4
能力
We tested GPT-4 on a diverse set of benchmarks, including simulating exams that were originallydesigned for humans.3 We did no specific training for these exams. A minority of the problems in theexams were seen by the model during training; for each exam we run a variant with these questions removed and report the lower score of the two. We believe the results to be representative. For further details on contamination (methodology and per-exam statistics), see Appendix C.
我们在一系列不同的基准上测试了GPT-4,包括最初为人类设计的模拟考试,我们没有为这些考试做专门的训练。考试中的少数问题是模型在训练中发现的;对于每次考试,我们都运行一个去掉这些问题的变体,并报告两个问题中较低的分数。我们认为这个结果是有代表性的。有关混合的更多细节(方法和每次检查的统计数据),请参见附录C。
Exams were sourced from publicly-available materials. Exam questions included both multiple-choice and free-response questions; we designed separate prompts for each format, and images wereincluded in the input for questions which required it. The evaluation setup was designed basedon performance on a validation set of exams, and we report final results on held-out test exams.Overall scores were determined by combining multiple-choice and free-response question scoresusing publicly available methodologies for each exam. See Appendix A for further details on theexam evaluation methodology.
考试材料都是公开的。考试题目包括多项选择题和自由回答题;我们为每种格式设计了单独的提示,并且在需要的问题的输入中包含了图像。评估设置是基于一组验证考试的表现而设计的,并且我们报告了测试考试的最终结果。综合分数由多项选择题和自由回答题的分数结合决定,并采用了公开的方法。有关考试评估方法的详细信息请参见附录A。
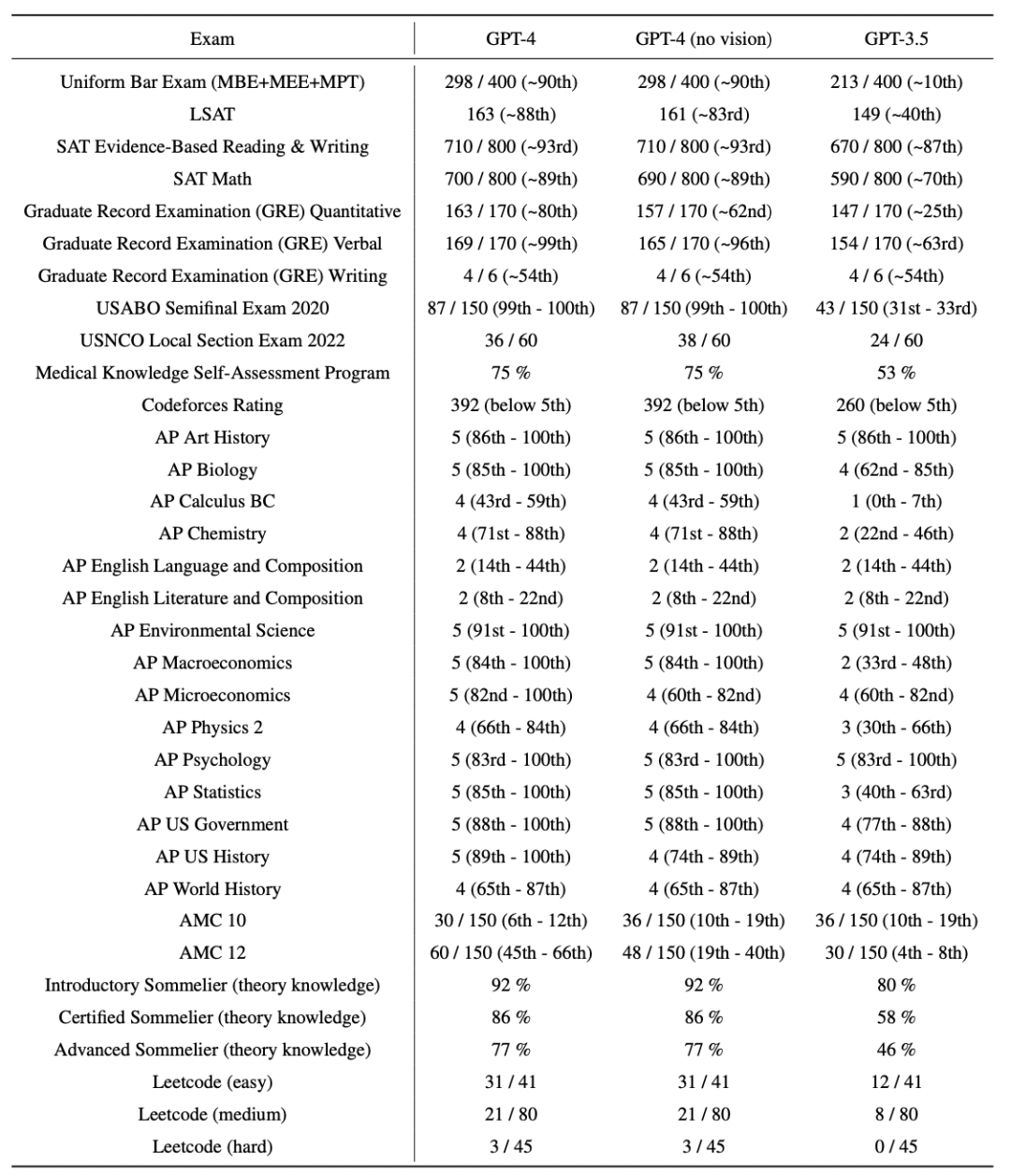
Table1. GPT performance on academic and professional exams. In each case, we simulate theconditions and scoring of the real exam. We report GPT-4’s final score graded according to exam-specific rubrics, as well as the percentile of test-takers achieving GPT-4’s score.
表1 GPT在学术和专业考试中的表现。在每种情况下,我们都模拟了真实考试的条件和分数。我们报告GPT-4的最终分数评分根据考试特定的规则,以及考生达到GPT-4的分数的百分比。

Figure 4. GPT performance on academic and professional exams. In each case, we simulate the conditions and scoring of the real exam. Exams are ordered from low to high based on GPT-3.5 performance. GPT-4 outperforms GPT-3.5 on most exams tested. To be conservative we report the lower end of the range of percentiles, but this creates some artifacts on the AP exams which have very wide scoring bins. For example although GPT-4 attains the highest possible score on AP Biology (5/5), this is only shown in the plot as 85th percentile because 15 percent of test-takers achieve that score.
图4。GPT在学术和专业考试中的表现。在每种情况下,我们都模拟了真实考试的条件和分数。考试根据GPT-3.5的表现从低到高排序。GPT-4在大多数考试中表现优于GPT-3.5。保守起见,我们报告的是百分位数范围的低端,但这在AP考试中产生了一些伪影,因为AP考试的得分范围非常广。例如,虽然GPT-4在AP生物学上获得了最高的分数(5/5),但这只在图中显示为第85百分位,因为15%的考生达到了这个分数。
GPT-4 exhibits human-level performance on the majority of these professional and academic exams. Notably, it passes a simulated version of the Uniform Bar Examination with a score in the top 10% of test takers (Table 1, Figure 4).
GPT-4在大多数专业和学术考试中表现出人类水平。值得注意的是,它以前10%的分数通过了统一律师考试的模拟版本(表1,图4)。
The model’s capabilities on exams appear to stem primarily from the pre-training process and are not significantly affected by RLHF. On multiple choice questions, both the base GPT-4 model and the RLHF model perform equally well on average across the exams we tested (see Appendix B).
该模型在考试中的能力似乎主要来自于训练前的过程,并没有受到RLHF的显著影响。在多项选择题上,基础GPT-4模型和RLHF模型在我们测试的考试中平均表现一样好(见附录B)。
We also evaluated the pre-trained base GPT-4 model on traditional benchmarks designed for evaluating language models. For each benchmark we report, we ran contamination checks for test data appearing in the training set (see Appendix D for full details on per-benchmark contamination).4 We used few-shot prompting [1] for all benchmarks when evaluating GPT-4.
我们还在为评估语言模型而设计的传统基准上评估了预训练的基础GPT-4模型。对于我们报告的每个基准,我们对出现在训练集中的测试数据进行了污染检查(关于每个基准污染的完整细节,请参阅附录D)在评估GPT-4时,我们对所有基准测试都使用了few-shot提示[1].
GPT-4 considerably outperforms existing language models, as well as previously state-of-the-art (SOTA) systems which often have benchmark-specific crafting or additional training protocols (Table 2).
GPT-4大大优于现有的语言模型,以及以前最先进的(SOTA)系统,后者通常具有特定于基准的制作或额外的训练协议(表2)。

Table 2. Performance of GPT-4 on academic benchmarks. We compare GPT-4 alongside the bestSOTA (with benchmark-specific training) and the best SOTA for an LM evaluated few-shot. GPT-4outperforms existing LMs on all benchmarks, and beats SOTA with benchmark-specific training on alldatasets except DROP. For each task we report GPT-4’s performance along with the few-shot methodused to evaluate. For GSM-8K, we included part of the training set in the GPT-4 pre-training mix(see Appendix E), and we use chain-of-thought prompting [11] when evaluating. For multiple-choicequestions, we present all answers (ABCD) to the model and ask it to choose the letter of the answer,similarly to how a human would solve such a problem.
表2。GPT-4在学术基准上的表现。我们将GPT-4与最佳SOTA(基准特定训练)和最佳SOTA用于LM评估。gpt -4在所有基准测试上都优于现有的lm,并在除DROP之外的所有数据集上通过基准特定训练击败SOTA。对于每一项任务,我们报告GPT-4的性能以及用于评估的few-shot方法。对于GSM-8K,我们在GPT-4预训练组合中包含了部分训练集(见附录E),并且在评估时使用了思维链提示[11]。对于多项选择题,我们将所有答案(ABCD)呈现给模型,并要求它选择答案的字母,类似于人类如何解决这样的问题。
Many existing ML benchmarks are written in English. To gain an initial understanding of GPT-4’s capabilities in other languages, we translated the MMLU benchmark [29, 30] – a suite of multiple- choice problems spanning 57 subjects – into a variety of languages using Azure Translate (see Appendix F for example translations and prompts). We find that GPT-4 outperforms the English- language performance of GPT 3.5 and existing language models (Chinchilla [2] and PaLM [3]) for the majority of languages we tested, including low-resource languages such as Latvian, Welsh, and Swahili (Figure 5).
许多现有的ML基准测试都是用英语编写的。为了初步了解GPT-4在其他语言中的功能,我们使用Azure Translate将MMLU基准测试[29,30]——一套涵盖57个主题的多项选择题——翻译成各种语言(参见附录F的示例翻译和提示)。我们发现,对于我们测试的大多数语言,包括低资源语言,如拉脱维亚语、威尔士语和斯瓦希里语,GPT-4的英语语言性能优于GPT 3.5和现有语言模型(Chinchilla[2]和PaLM[3])(图5)。
GPT-4 substantially improves over previous models in the ability to follow user intent [57]. On a dataset of 5,214 prompts submitted to ChatGPT [58] and the OpenAI API [41], the responses generated by GPT-4 were preferred over the responses generated by GPT-3.5 on 70.2% of prompts.
GPT-4在跟踪用户意图[57]的能力方面大大改进了以前的模型。在提交给ChatGPT[58]和OpenAI API[41]的5214个提示的数据集中,GPT-4生成的响应在70.2%的提示上优于GPT-3.5生成的响应。

Figure 5. Performance of GPT-4 in a variety of languages compared to prior models in English onMMLU. GPT-4 outperforms the English-language performance of existing language models [2, 3] forthe vast majority of languages tested, including low-resource languages such as Latvian, Welsh, andSwahili.
图5。与MMLU上的英语先前模型相比,GPT-4在多种语言中的性能。对于绝大多数测试语言,包括低资源语言,如拉脱维亚语、威尔士语和斯瓦希里语,GPT-4优于现有语言模型的英语表现[2,3]。
We are open-sourcing OpenAI Evals7, our framework for creating and running benchmarks for evaluating models like GPT-4 while inspecting performance sample by sample. Evals is compatible with existing benchmarks, and can be used to track performance of models in deployment. We plan to increase the diversity of these benchmarks over time to represent a wider set of failure modes and a harder set of tasks.
我们正在开源OpenAI Evals7,这是我们的框架,用于创建和运行评估GPT-4等模型的基准,同时逐个样本检查性能样本。评估与现有的基准测试兼容,并可用于跟踪部署中模型的性能。我们计划随着时间的推移增加这些基准的多样性,以代表更广泛的故障模式和更难的任务集。
4.1 可视化输入
GPT-4 accepts prompts consisting of both images and text, which—parallel to the text-only set-ting—lets the user specify any vision or language task. Specifically, the model generates text outputsgiven inputs consisting of arbitrarily interlaced text and images. Over a range of domains—includingdocuments with text and photographs, diagrams, or screenshots—GPT-4 exhibits similar capabilitiesas it does on text-only inputs. An example of GPT-4’s visual input can be found in Table 3. The stan-dard test-time techniques developed for language models (e.g. few-shot prompting, chain-of-thought,etc) are similarly effective when using both images and text - see Appendix G for examples.
GPT-4接受由图像和文本组成的提示,这与纯文本设置并行,允许用户指定任何视觉或语言任务。具体来说,该模型在给定由任意交错的文本和图像组成的输入时生成文本输出。gpt -4在一系列域中(包括带有文本和照片、图表或屏幕截图的文档)显示出与纯文本输入类似的功能。在表3中可以找到GPT-4可视化输入的示例。为语言模型开发的标准测试时间技术(例如,少镜头提示,思维链等)在使用图像和文本时同样有效——参见附录G的例子。

Table 3. Example prompt demonstrating GPT-4’s visual input capability. The prompt consists of aquestion about an image with multiple panels which GPT-4 is able to answer.
表3。演示GPT-4可视化输入能力的示例提示符。提示由一个关于GPT-4能够回答的具有多个面板的图像的问题组成。
Preliminary results on a narrow set of academic vision benchmarks can be found in the GPT-4 blogpost [59]. We plan to release more information about GPT-4’s visual capabilities in follow-up work.
关于狭隘的学术视觉基准的初步结果可以在GPT-4的博客文章[59]中找到。我们计划在后续工作中发布更多关于GPT-4视觉能力的信息。
No.5
限制
Despite its capabilities, GPT-4 has similar limitations as earlier GPT models. Most importantly, it still is not fully reliable (it “hallucinates” facts and makes reasoning errors). Great care should be taken when using language model outputs, particularly in high-stakes contexts, with the exact protocol (such as human review, grounding with additional context, or avoiding high-stakes uses altogether) matching the needs of specific applications. See our System Card for details.
尽管GPT-4功能强大,但它与早期GPT模型有相似的局限性。最重要的是,它仍然不完全可靠(它会“产生幻觉”事实并犯推理错误)。在使用语言模型输出时,特别是在高风险上下文中,应该非常小心,使用与特定应用程序的需求相匹配的确切协议(例如人工检查、附加上下文接地或完全避免高风险使用)。详情请参阅我们的系统卡。
GPT-4 significantly reduces hallucinations relative to previous GPT-3.5 models (which have them- selves been improving with continued iteration). GPT-4 scores 19 percentage points higher than our latest GPT-3.5 on our internal, adversarially-designed factuality evaluations (Figure 6).
与之前的GPT-3.5模型相比,GPT-4显著减少了幻觉(随着不断迭代,GPT-3.5模型自身也在不断改进)。在我们内部的、对抗性设计的事实性评估中,GPT-4的得分比我们最新的GPT-3.5高出19个百分点(图6)。

Figure 6. Performance of GPT-4 on nine internal adversarially-designed factuality evaluations. Accuracyis shown on the y-axis, higher is better. An accuracy of 1.0 means the model’s answers are judged tobe in agreement with human ideal responses for all questions in the eval. We compare GPT-4 to threeearlier versions of ChatGPT [58] based on GPT-3.5; GPT-4 improves on the latest GPT-3.5 model by 19percentage points, with significant gains across all topics.
图6。GPT-4在9个内部对抗性设计的事实性评估中的表现。精度表示在y轴上,越高越好。如果准确率为1.0,则在评价过程中,对所有问题的回答都被判定为符合人类的理想答案。我们将GPT-4与基于GPT-3.5的ChatGPT[58]的三个早期版本进行比较;GPT-4在最新的GPT-3.5模型的基础上提高了19个百分点,在所有主题上都有显著提高。
GPT-4 makes progress on public benchmarks like TruthfulQA [60], which tests the model’s ability to separate fact from an adversarially-selected set of incorrect statements (Figure 7). These questions are paired with factually incorrect answers that are statistically appealing. The GPT-4 base model is only slightly better at this task than GPT-3.5; however, after RLHF post-training we observe large improvements over GPT-3.5.8 Table 4 shows both a correct and an incorrect answer. GPT-4 resists selecting common sayings (you can’t teach an old dog new tricks), however it still can miss subtle details (Elvis Presley was not the son of an actor, so Perkins is the correct answer).
GPT-4在TruthfulQA[60]等公共基准测试上取得了进展,该基准测试模型从对抗选择的一组不正确的语句中分离事实的能力(图7)。这些问题与统计上具有吸引力的事实错误答案配对。GPT-4基本模型在这项任务上只比GPT-3.5稍微好一点;然而,经过RLHF训练后,我们观察到比GPT-3.5.8有很大的改进,表4显示了正确和错误的答案。GPT-4拒绝选择俗语(你不能教老狗新把戏),但它仍然会遗漏一些微妙的细节(猫王不是演员的儿子,所以帕金斯是正确答案)。

Figure 7. Performance of GPT-4 on TruthfulQA. Accuracy is shown on the y-axis, higher is better. Wecompare GPT-4 under zero-shot prompting, few-shot prompting, and after RLHF fine-tuning. GPT-4significantly outperforms both GPT-3.5 and Anthropic-LM from Bai et al. [61].
图7。GPT-4在TruthfulQA上的表现。精度表示在y轴上,越高越好。我们比较了零镜头提示、少镜头提示和RLHF微调后的GPT-4。GPT-4的性能显著优于Bai等的GPT-3.5和Anthropic-LM[61]。

Table 4: Example of GPT-4 giving correct and incorrect responses on TruthfulQA
表4:GPT-4在TruthfulQA上给出正确和不正确回答的例子
GPT-4 generally lacks knowledge of events that have occurred after the vast majority of its pre-training data cuts off in September 20219, and does not learn from its experience. It can sometimes make simple reasoning errors which do not seem to comport with competence across so many domains, or be overly gullible in accepting obviously false statements from a user. It can fail at hard problems the same way humans do, such as introducing security vulnerabilities into code it produces.
GPT-4通常缺乏对其绝大多数训练前数据在2021年9月中断后发生的事件的知识,并且不从经验中学习。它有时会犯一些简单的推理错误,这些错误似乎与许多领域的能力不相符,或者过于容易受骗,接受用户的明显错误陈述。它可以像人类一样在棘手的问题上失败,比如在它生成的代码中引入安全漏洞。
GPT-4 can also be confidently wrong in its predictions, not taking care to double-check work when it’s likely to make a mistake. Interestingly, the pre-trained model is highly calibrated (its predicted confidence in an answer generally matches the probability of being correct). However, after the post-training process, the calibration is reduced (Figure 8).
GPT-4的预测也有可能是错误的,当它可能出错时,它没有仔细检查工作。有趣的是,预训练的模型是高度校准的(它对答案的预测置信度通常与正确的概率相匹配)。然而,经过后训练过程后,校准降低了(图8)。

Figure 8. Left: Calibration plot of the pre-trained GPT-4 model on a subset of the MMLU dataset.The model’s confidence in its prediction closely matches the probability of being correct. The dotteddiagonal line represents perfect calibration. Right: Calibration plot of the post-trained GPT-4 model onthe same subset of MMLU. The post-training hurts calibration significantly.
图8。左图:MMLU数据集子集上预训练的GPT-4模型的校准图。模型对其预测的信心与正确的概率紧密匹配。虚线对角线代表完美的校准。右图:训练后的GPT-4模型在MMLU的同一子集上的校准图。训练后会严重影响校准。
GPT-4 has various biases in its outputs that we have taken efforts to correct but which will take some time to fully characterize and manage. We aim to make GPT-4 and other systems we build have reasonable default behaviors that reflect a wide swath of users’ values, allow those systems to be customized within some broad bounds, and get public input on what those bounds should be. See OpenAI [62] for more details.
GPT-4在输出中有各种偏差,我们已经努力纠正,但需要一些时间来完全描述和管理。我们的目标是使GPT-4和我们构建的其他系统具有合理的默认行为,这些行为反映了广泛的用户价值观,允许这些系统在一些广泛的范围内进行定制,并就这些范围应该是什么获得公众的输入。详见OpenAI[62]。
No.6
风险&消解措施
We invested significant effort towards improving the safety and alignment of GPT-4. Here we highlight our use of domain experts for adversarial testing and red-teaming, and our model-assisted safety pipeline [63] and the improvement in safety metrics over prior models.
我们投入了大量的精力来提高GPT-4的安全性和一致性。在这里,我们强调了我们使用领域专家进行对抗性测试和红队,以及我们的模型辅助安全管道[63]以及相对于先前模型的安全度量的改进。
Adversarial Testing via Domain Experts: GPT-4 poses similar risks as smaller language models, such as generating harmful advice, buggy code, or inaccurate information. However, the additional capabilities of GPT-4 lead to new risk surfaces. To understand the extent of these risks, we engaged over 50 experts from domains such as long-term AI alignment risks, cybersecurity, biorisk, and international security to adversarially test the model. Their findings specifically enabled us to test model behavior in high-risk areas which require niche expertise to evaluate, as well as assess risks that will become relevant for very advanced AIs such as power seeking [64]. Recommendations and training data gathered from these experts fed into our mitigations and improvements for the model;for example, we’ve collected additional data to improve GPT-4’s ability to refuse requests on how to synthesize dangerous chemicals (Table 5).
通过领域专家进行对抗性测试:GPT-4与较小的语言模型存在类似的风险,例如生成有害的建议、有bug的代码或不准确的信息。然而,GPT-4的额外功能导致了新的风险面。为了了解这些风险的程度,我们聘请了来自长期人工智能对齐风险、网络安全、生物风险和国际安全等领域的50多名专家对模型进行对抗性测试。他们的发现特别使我们能够在高风险领域测试模型行为,这需要利基专业知识来评估,以及评估与非常先进的人工智能(如权力寻求)相关的风险[64]。从这些专家那里收集的建议和培训数据为我们对模型的缓解和改进提供了支持;例如,我们已经收集了额外的数据来提高GPT-4拒绝如何合成危险化学品请求的能力(表5)。

Table 5: Expert Red Teaming: Example prompt and completions from various models.
表5:专家红色团队:来自不同模型的示例提示和完成。
Model-Assisted Safety Pipeline: As with prior GPT models, we fine-tune the model’s behavior using reinforcement learning with human feedback (RLHF) [34, 57] to produce responses better aligned with the user’s intent. However, after RLHF, our models can still be brittle on unsafe inputs as well as sometimes exhibit undesired behaviors on both safe and unsafe inputs. These undesired behaviors can arise when instructions to labelers were underspecified during reward model data collection portion of the RLHF pipeline. When given unsafe inputs, the model may generate undesirable content, such as giving advice on committing crimes. Furthermore, the model may also become overly cautious on safe inputs, refusing innocuous requests or excessively hedging. To steer our models towards appropriate behaviour at a more fine-grained level, we rely heavily on our models themselves as tools. Our approach to safety consists of two main components, an additional set of safety-relevant RLHF training prompts, and rule-based reward models (RBRMs).
模型辅助的安全管道:与之前的GPT模型一样,我们使用强化学习和人类反馈(RLHF)[34,57]对模型的行为进行微调,以产生更好地符合用户意图的响应。然而,在RLHF之后,我们的模型在不安全输入上仍然很脆弱,有时在安全输入和不安全输入上都表现出不希望看到的行为。在RLHF管道的奖励模型数据收集部分,当对标签器的指令未指定时,就会出现这些不希望出现的行为。当给出不安全的输入时,模型可能会生成不受欢迎的内容,例如给出犯罪建议。此外,模型也可能对安全输入过于谨慎,拒绝无害的请求或过度对冲。为了在更细粒度的级别上引导我们的模型走向适当的行为,我们在很大程度上依赖于我们的模型本身作为工具。我们的安全方法包括两个主要组成部分,一套额外的安全相关RLHF训练提示,以及基于规则的奖励模型(RBRMs)。
Our rule-based reward models (RBRMs) are a set of zero-shot GPT-4 classifiers. These classifiers provide an additional reward signal to the GPT-4 policy model during RLHF fine-tuning that targets correct behavior, such as refusing to generate harmful content or not refusing innocuous requests. The RBRM takes three inputs: the prompt (optional), the output from the policy model, and a human-written rubric (e.g., a set of rules in multiple-choice style) for how this output should be evaluated. Then, the RBRM classifies the output based on the rubric. For example, we can provide a rubric that instructs the model to classify a response as one of: (a) a refusal in the desired style, (b) a refusal in the undesired style (e.g., evasive or rambling), (c) containing disallowed content, or (d) a safe non-refusal response. Then on the set of safety-relevant training prompts, which request harmful content such as illicit advice, we can reward GPT-4 for refusing these requests. Conversely, we can reward GPT-4 for not refusing requests on a subset of prompts guaranteed to be safe and answerable. This technique is related to work by Glaese et al. [65] and Perez et al. [66]. This, combined with other improvements such as computing optimal RBRM weights and providing additional SFT data targeting the areas we want to improve, allowed us to steer the model closer towards the desired behaviour.
我们基于规则的奖励模型(RBRMs)是一组零概率GPT-4分类器。这些分类器在RLHF针对正确行为(例如拒绝生成有害内容或不拒绝无害请求)进行微调期间向GPT-4策略模型提供额外的奖励信号。RBRM有三个输入:提示(可选)、策略模型的输出和人类编写的用于如何评估输出的规则(例如,一组多项选择风格的规则)。然后,RBRM根据标题对输出进行分类。例如,我们可以提供一个规则,指示模型将响应分类为:(a)期望风格的拒绝,(b)不期望风格的拒绝(例如,逃避或漫无伦次),(c)包含不允许的内容,或(d)安全的非拒绝响应。然后,在安全相关的训练提示集上,我们可以奖励GPT-4拒绝这些请求的有害内容,例如非法建议。相反,我们可以奖励GPT-4,因为它没有拒绝对保证安全和可回答的提示子集的请求。该技术与Glaese等人[65]和Perez等人[66]的工作有关。这与其他改进相结合,例如计算最佳RBRM权重和提供针对我们想要改进的领域的额外SFT数据,使我们能够引导模型更接近所需的行为。
Improvements on Safety Metrics: Our mitigations have significantly improved many of GPT-4’ssafety properties. We’ve decreased the model’s tendency to respond to requests for disallowed content(Table 6) by 82% compared to GPT-3.5, and GPT-4 responds to sensitive requests (e.g., medicaladvice and self-harm, Table 7) in accordance with our policies 29% more often (Figure 9). On theRealToxicityPrompts dataset [67], GPT-4 produces toxic generations only 0.73% of the time, whileGPT-3.5 generates toxic content 6.48% of time.
安全度量的改进:我们的缓解措施显著改善了GPT-4的许多安全属性。与GPT-3.5相比,我们已经将模型对不允许内容请求的响应趋势(表6)降低了82%,并且GPT-4根据我们的策略对敏感请求(例如,医疗建议和自我伤害,表7)的响应频率提高了29%(图9)。在RealToxicityPrompts数据集[67]上,GPT-4仅产生0.73%的有毒生成时间,而GPT-3.5产生有毒内容的时间为6.48%。

Table 6: Example prompt and completions for improved refusals on disallowed categories.
表6:对不允许的类别进行改进拒绝的提示符和补全示例。

Table 7. Example prompt and completions for reduced refusals on allowed categories. Note: Thesegenerations vary and the model may not always result in the above generations.
表7所示。减少对允许类别的拒绝的提示符和补全示例。注意:这些代是不同的,模型可能并不总是得到上述的代。
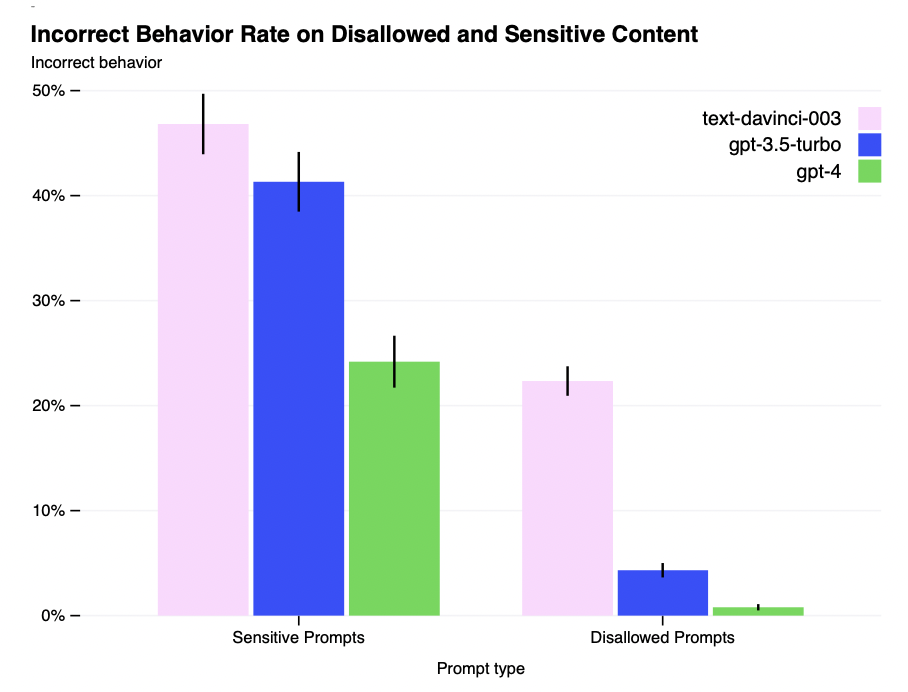
Figure 9. Rate of incorrect behavior on sensitive and disallowed prompts. Lower values are better.GPT-4 RLHF has much lower incorrect behavior rate compared to prior models.
图9。敏感提示和不允许提示的错误行为率。值越低越好。与现有模型相比,GPT-4 RLHF具有更低的错误行为率。
Overall, our model-level interventions increase the difficulty of eliciting bad behavior but doing so is still possible. For example, there still exist “jailbreaks” (e.g., adversarial system messages, see Figure 10 in the System Card for more details) to generate content which violate our usage guidelines. So long as these limitations exist, it’s important to complement them with deployment-time safety techniques like monitoring for abuse as well as a pipeline for fast iterative model improvement.
总的来说,我们的模型级干预增加了引发不良行为的难度,但这样做仍然是可能的。例如,仍然存在“越狱”(例如,对抗性系统消息,参见系统卡中的图10以了解更多细节)来生成违反我们使用指南的内容。只要这些限制存在,就有必要使用部署时安全技术(如监控滥用和用于快速迭代模型改进的管道)来补充它们。
GPT-4 and successor models have the potential to significantly influence society in both beneficial and harmful ways. We are collaborating with external researchers to improve how we understand and assess potential impacts, as well as to build evaluations for dangerous capabilities that may emerge in future systems. We will soon publish recommendations on steps society can take to prepare for AI’s effects and initial ideas for projecting AI’s possible economic impacts.
GPT-4及其后续型号有可能以有益和有害的方式对社会产生重大影响。我们正在与外部研究人员合作,以提高我们对潜在影响的理解和评估,以及对未来系统中可能出现的危险能力进行评估。我们将很快发布关于社会为应对人工智能影响可以采取的措施的建议,以及预测人工智能可能产生的经济影响的初步想法。
No.7
结论
We characterized GPT-4, a large multimodal model with human-level performance on certain difficultprofessional and academic benchmarks. GPT-4 outperforms existing large language models on acollection of NLP tasks, and exceeds the vast majority of reported state-of-the-art systems (whichoften include task-specific fine-tuning). We find that improved capabilities, whilst usually measuredin English, can be demonstrated in many different languages. We highlighted how predictable scalingallowed us to make accurate predictions on the loss and capabilities of GPT-4.
我们描述了GPT-4,这是一个在某些困难的专业和学术基准上具有人类水平表现的大型多模态模型。GPT-4在NLP任务集合上优于现有的大型语言模型,并且超过了绝大多数报道的最先进的系统(通常包括特定于任务的微调)。我们发现,虽然通常用英语来衡量能力的提高,但可以用许多不同的语言来证明。我们强调了可预测的扩展如何使我们能够对GPT-4的损耗和能力做出准确的预测。
GPT-4 presents new risks due to increased capability, and we discussed some of the methods andresults taken to understand and improve its safety and alignment. Though there remains much work tobe done, GPT-4 represents a significant step towards broadly useful and safely deployed AI systems.
GPT-4由于性能的提高而带来了新的风险,我们讨论了一些方法和结果,以了解和提高其安全性和一致性。虽然还有很多工作要做,但GPT-4代表着朝着广泛有用和安全部署的人工智能系统迈出了重要一步。
公众号内直接回复【NLP论文】即可获取高清PDF下载链接

数据分析与挖掘
数据结构与算法
深度学习与大数据框架
欢迎关注,感谢“在看”,随缘稀罕~
























 208
208

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








