快速傅立叶变换(FFT)的海面模拟
在这篇文章中,我们将根据Tessendorf的论文[1]中的方程来实现统计波浪模型,以模拟海洋水。 使用快速傅立叶变换,我们将能够实现实时交互的帧速率。以下提供两个截图,首先是简单的光照渲染,之后的是网格模型的渲染。

文章使用了一个高度函数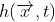 ,其中
,其中 为坐标(x,z)(我们这里令y为高度),时间为t(说明我们的高度会随时间变化)。
为坐标(x,z)(我们这里令y为高度),时间为t(说明我们的高度会随时间变化)。

其中,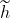 是我们的频域函数,我们的海面模拟实际则是将频域空间转换为空域空间(即IDFT)。其中:
是我们的频域函数,我们的海面模拟实际则是将频域空间转换为空域空间(即IDFT)。其中:

L为海面网格尺寸,且有:

由于我们要在计算机中利用索引计算,因此我们需要设 为0,1,2,...,N-1,
为0,1,2,...,N-1, 为0,1,2,...,M-1,因此有:
为0,1,2,...,M-1,因此有:

那么我们的n,m便可以写成 ,
, 的表达式:
的表达式:

把 ,
, 代入
代入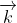 得:
得:

我们现在把最初的高度函数改写成 ,
, 的函数:
的函数:

我们现在看一下它的频域函数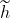 ,以及关于
,以及关于 ,
, 的函数
的函数 :
:

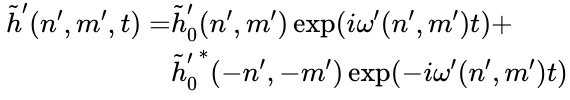
其中k为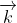 的模,t为时间(与h函数中是同一个t)。
的模,t为时间(与h函数中是同一个t)。是
的共轭复数。
![]()
g为重力加速度,代入 ,
, 的
的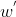 为:
为:

最后就剩下我们的函数和其共轭复数
了,我们可以把
也改写为
 ,
, 的形式:
的形式:

其中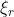 ,
, 是独立的高斯随机变量,
是独立的高斯随机变量, 是菲利普频谱有如下形式:
是菲利普频谱有如下形式:

其A是菲利普频谱参数(影响波高),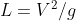 为可能出现的最大波浪,V为风速。同理我们可以吧
为可能出现的最大波浪,V为风速。同理我们可以吧 改写为
改写为 :
:
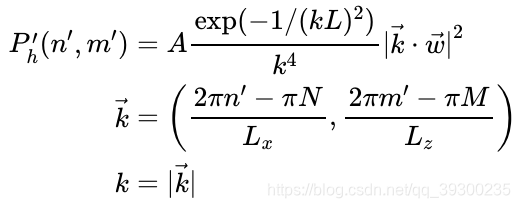
现在,我们应该拥有渲染波高场所需的一切,但是我们将评估用于生成断续波的位移矢量和用于在每个顶点进行照明计算的法线矢量。 位移矢量由下式给出:
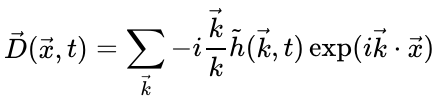
法线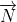 则由下列函数得出:
则由下列函数得出:

所有的数学运算已经完成了。那我们的FFT如何应用在这里呢,由于我们的IDFT公式为:

DFT公式为:

我们发现它们几乎一样,IDFT就在e指数上少了负号,而且在前面多了系数1/N。根据为另一篇https://blog.csdn.net/qq_39300235/article/details/103453909讲解的FFT方法则可以直接使用,我们的代码:
#ifndef FFT_H
#define FFT_H
#include <math.h>
#include "complex.h"
class cFFT {
private:
unsigned int N;
unsigned int log_2_N;
float pi2;
bool invers_FFT;
unsigned int *reversed;
complex **T;
complex *c;
protected:
public:
cFFT(unsigned int N,bool I);//N为傅立叶N值,I为是否为IFFT
~cFFT();
unsigned int reverse(unsigned int i);
complex t(unsigned int x, unsigned int N);
void fft(complex* input, int stride, int offset);
};
#endif
类实现在:
#include "fft.h"
cFFT::cFFT(unsigned int N,bool I) : N(N), invers_FFT(I),reversed(0), T(0), pi2(2 * M_PI) {
c = 0;
log_2_N = log(N)/log(2);
reversed = new unsigned int[N]; // 预反转
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) reversed[i] = reverse(i);
int pow2 = 1;
T = new complex*[log_2_N]; // 预处理T(所有W值)
for (int i = 0; i < log_2_N; i++) {
T[i] = new complex[pow2];
for (int j = 0; j < pow2; j++)
if (invers_FFT)
T[i][j] = t(j, pow2 * 2).conj();//复数的模为1时倒数等于共轭
else
T[i][j] = t(j, pow2 * 2);
pow2 *= 2;
}
c = new complex[N];
}
cFFT::~cFFT() {
if (c) delete [] c;
if (T) {
for (int i = 0; i < log_2_N; i++) if (T[i]) delete [] T[i];
delete [] T;
}
if (reversed) delete [] reversed;
}
unsigned int cFFT::reverse(unsigned int i) {
unsigned int res = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < log_2_N; j++) {
//反序
if((i>>j)&1) res|=(1<<(log_2_N-j-1));
}
return res;
}
complex cFFT::t(unsigned int x, unsigned int N) {
return complex(cos(-1*pi2 * x / N), sin(-1*pi2 * x / N));
}
void cFFT::fft(complex* input, int stride, int offset) {
//获取反转后的数据放入c数组
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) c[i] = input[reversed[i] * stride + offset];
int w_= 0;//执行第一次循环次数
for(int l=2;l<=N;l*=2){
int m=l/2;
for(complex* p=c;p!=c+N;p+=l){
for (int i=0; i<m; i++) {
//蝴蝶变换(W在构造函数中计算过保存在T中)
complex tW=T[w_][i]*p[i+m];
p[i+m]=p[i]-tW;
p[i]=p[i]+tW;
}
}
w_++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++){
input[i * stride + offset] = c[i];
}
}
FFT和IFFT的差别也就只需在cFFT::t()函数中进行区分即可,而我们的海面模型正好是不需要1/N系数的,因此该系数省略。
我们接下来看我们海面的的代码:
#ifndef FFT_OCEAN_hpp
#define FFT_OCEAN_hpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <GL/glew.h>
#include <GLFW/glfw3.h>
#include <glm/glm.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/matrix_transform.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/type_ptr.hpp>
#include "complex.h"
#include "fft.h"
#include "shader.h"
#include <vector>
using namespace glm;
struct vertex_ocean{
GLfloat x,y,z;//vertex
GLfloat nx,ny,nz;//normal
GLfloat tx,ty; //texcoords
GLfloat a,b,c;//htilde0
GLfloat _a,_b,_c;//htilde0mk conjugate
GLfloat ox,oy,oz; // original position
};
class cOcean {
private: // flag to render geometry or surface
float g; // gravity constant
int N, Nplus1; // dimension -- N should be a power of 2
float A; // phillips spectrum parameter -- affects heights of waves
vec2 w; // wind parameter
float length; // length parameter
complex *h_tilde, // for fast fourier transform
*h_tilde_slopex, *h_tilde_slopez,
*h_tilde_dx, *h_tilde_dz;
cFFT *fft; // fast fourier transform
float stride=0.1;
vertex_ocean *vertices; // vertices for vertex buffer object
unsigned int *indices; // indicies for vertex buffer object
unsigned int indices_count; // number of indices to render
GLuint VAO,vbo_vertices, ebo_indices; // vertex buffer objects
Shader ocean_Shader,nrm_Shader;
GLint vertex, normal, texCooed; // attributes and uniforms
protected:
public:
cOcean(const int N, const float A, const vec2 w, const float length,const std::string& vs,const std::string& fs,const std::string& nvs,const std::string& nfs,const std::string& ngeo);
~cOcean();
void release();
float dispersion(int n_prime, int m_prime); // deep water
float phillips(int n_prime, int m_prime); // phillips spectrum
complex hTilde_0(int n_prime, int m_prime);
complex hTilde(float t, int n_prime, int m_prime);
void evaluateWavesFFT(float t);
void render(float t, glm::vec3 view_pos, glm::mat4 Projection, glm::mat4 View, glm::mat4 Model, bool use_fft);
};
#endif /* FFT_OCEAN_hpp */
#include "FFT_OCEAN.hpp"
float uniformRandomVariable() {
return (float)rand()/RAND_MAX;
}
complex gaussianRandomVariable() {
float x1, x2, w;
do {
x1 = 2.f * uniformRandomVariable() - 1.f;
x2 = 2.f * uniformRandomVariable() - 1.f;
w = x1 * x1 + x2 * x2;
} while ( w >= 1.f );
w = sqrt((-2.f * log(w)) / w);
return complex(x1 * w, x2 * w);
}
cOcean::cOcean(const int N, const float A, const vec2 w, const float length,const std::string& vs,const std::string& fs,const std::string& nvs,const std::string& nfs,const std::string& ngeo) :
g(9.81), N(N), Nplus1(N+1), A(A), w(w), length(length),
vertices(0), indices(0), h_tilde(0), h_tilde_slopex(0), h_tilde_slopez(0), h_tilde_dx(0), h_tilde_dz(0), fft(0), ocean_Shader(vs.c_str(),fs.c_str()),nrm_Shader(nvs.c_str(),nfs.c_str(),ngeo.c_str())
{
h_tilde = new complex[N*N];
h_tilde_slopex = new complex[N*N];
h_tilde_slopez = new complex[N*N];
h_tilde_dx = new complex[N*N];
h_tilde_dz = new complex[N*N];
fft = new cFFT(N,1);
vertices = new vertex_ocean[Nplus1*Nplus1];
indices = new unsigned int[Nplus1*Nplus1*10];
int index;
complex htilde0, htilde0mk_conj;
for (int m_prime = 0; m_prime < Nplus1; m_prime++) {
for (int n_prime = 0; n_prime < Nplus1; n_prime++) {
index = m_prime * Nplus1 + n_prime;
htilde0 = hTilde_0( n_prime, m_prime);
htilde0mk_conj = hTilde_0(-n_prime, -m_prime).conj();
vertices[index].tx = float(n_prime)/Nplus1;
vertices[index].ty = float(m_prime)/Nplus1;
vertices[index].a = htilde0.a;
vertices[index].b = htilde0.b;
vertices[index]._a = htilde0mk_conj.a;
vertices[index]._b = htilde0mk_conj.b;
vertices[index].ox = vertices[index].x = (n_prime - N / 2.0f) * length / N;
vertices[index].oy = vertices[index].y = 0.0f;
vertices[index].oz = vertices[index].z = (m_prime - N / 2.0f) * length / N;
vertices[index].nx = 0.0f;
vertices[index].ny = 1.0f;
vertices[index].nz = 0.0f;
}
}
indices_count = 0;
for (int m_prime = 0; m_prime < N; m_prime++) {
for (int n_prime = 0; n_prime < N; n_prime++) {
index = m_prime * Nplus1 + n_prime;
indices[indices_count++] = index; // two triangles
indices[indices_count++] = index + Nplus1;
indices[indices_count++] = index + Nplus1 + 1;
indices[indices_count++] = index;
indices[indices_count++] = index + Nplus1 + 1;
indices[indices_count++] = index + 1;
}
}
glGenVertexArrays(1,&VAO);
glGenBuffers(1, &vbo_vertices);
glGenBuffers(1, &ebo_indices);
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vbo_vertices);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(vertex_ocean)*(Nplus1)*(Nplus1), nullptr, GL_DYNAMIC_DRAW);
glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, ebo_indices);
glBufferData(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, indices_count*sizeof(unsigned int), indices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glBindVertexArray(0);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER,0);
glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER,0);
ocean_Shader.use();
ocean_Shader.setFloat("hei_Lim", A);
ocean_Shader.close();
vertex=ocean_Shader.getAttibLoaction("aPos");
normal=ocean_Shader.getAttibLoaction("normal");
texCooed=ocean_Shader.getAttibLoaction("texCoords");
}
cOcean::~cOcean() {
if (h_tilde) delete [] h_tilde;
if (h_tilde_slopex) delete [] h_tilde_slopex;
if (h_tilde_slopez) delete [] h_tilde_slopez;
if (h_tilde_dx) delete [] h_tilde_dx;
if (h_tilde_dz) delete [] h_tilde_dz;
if (fft) delete fft;
if (vertices) delete [] vertices;
if (indices) delete [] indices;
}
void cOcean::release() {
glDeleteBuffers(1, &ebo_indices);
glDeleteBuffers(1, &vbo_vertices);
}
float cOcean::dispersion(int n_prime, int m_prime) {
float w_0 = 2.0f * M_PI / 200.0f;
float kx = M_PI * (2 * n_prime - N) / length;
float kz = M_PI * (2 * m_prime - N) / length;
return floor(sqrt(g * sqrt(kx * kx + kz * kz)) / w_0) * w_0;
}
float cOcean::phillips(int n_prime, int m_prime) {
vec2 k(M_PI * (2 * n_prime - N) / length,M_PI * (2 * m_prime - N) / length);
float k_length = glm::length(k);
if (k_length < 0.000001) return 0.0;
float k_length2 = k_length * k_length;
float k_length4 = k_length2 * k_length2;
float k_dot_w = glm::dot(glm::normalize(k),glm::normalize(w));
float k_dot_w2 = k_dot_w * k_dot_w;
float w_length = glm::length(w);
float L = w_length * w_length / g;
float L2 = L * L;
float damping = 0.001;
float l2 = L2 * damping * damping;
return A * exp(-1.0f / (k_length2 * L2)) / k_length4 * k_dot_w2 * exp(-k_length2 * l2);
}
complex cOcean::hTilde_0(int n_prime, int m_prime) {
complex r = gaussianRandomVariable();
return r * sqrt(phillips(n_prime, m_prime) / 2.0f);
}
complex cOcean::hTilde(float t, int n_prime, int m_prime) {
int index = m_prime * Nplus1 + n_prime;
complex htilde0(vertices[index].a, vertices[index].b);
complex htilde0mkconj(vertices[index]._a, vertices[index]._b);
float omegat = dispersion(n_prime, m_prime) * t;
float cos_ = cos(omegat);
float sin_ = sin(omegat);
complex c0(cos_, sin_);
complex c1(cos_, -sin_);
complex res = htilde0 * c0 + htilde0mkconj * c1;
return res;
}
void cOcean::render(float t, glm::vec3 view_pos, glm::mat4 Projection, glm::mat4 View, glm::mat4 Model, bool use_fft) {
evaluateWavesFFT(t);
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vbo_vertices);
glBufferSubData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0, sizeof(vertex_ocean) * Nplus1 * Nplus1, vertices);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(vertex);
glVertexAttribPointer(vertex, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, sizeof(vertex_ocean), 0);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(normal);
glVertexAttribPointer(normal, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, sizeof(vertex_ocean), (void *)(3*sizeof(GLfloat)));
glEnableVertexAttribArray(texCooed);
glVertexAttribPointer(texCooed, 2, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, sizeof(vertex_ocean), (void *)(6*sizeof(GLfloat)));
ocean_Shader.use();
ocean_Shader.setMat4("projection", Projection);
ocean_Shader.setMat4("view", View);
ocean_Shader.setVec3("viewPos", view_pos);
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
for (int j=0;j<3;j++) {
Model=glm::translate(glm::mat4(1.0), glm::vec3(i*length*stride,0,j*length*stride));
ocean_Shader.setMat4("model", Model);
glDrawElements(GL_TRIANGLES, indices_count, GL_UNSIGNED_INT, 0);
}
}
glBindVertexArray(0);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0);
ocean_Shader.close();
}
//FFT只能用于N为2的k次
void cOcean::evaluateWavesFFT(float t) {
float kx, kz, len, lambda = -1.0f;
int index, index1;
for (int m_prime = 0; m_prime < N; m_prime++) {
kz = M_PI * (2.0f * m_prime - N) / length;
for (int n_prime = 0; n_prime < N; n_prime++) {
kx = M_PI*(2 * n_prime - N) / length;
len = sqrt(kx * kx + kz * kz);
index = m_prime * N + n_prime;
h_tilde[index] = hTilde(t, n_prime, m_prime);
h_tilde_slopex[index] = h_tilde[index] * complex(0, kx);
h_tilde_slopez[index] = h_tilde[index] * complex(0, kz);
if (len < 0.000001f) {
h_tilde_dx[index] = complex(0.0f, 0.0f);
h_tilde_dz[index] = complex(0.0f, 0.0f);
} else {
h_tilde_dx[index] = h_tilde[index] * complex(0, -kx/len);
h_tilde_dz[index] = h_tilde[index] * complex(0, -kz/len);
}
}
}
for (int m_prime = 0; m_prime < N; m_prime++) {
fft->fft(h_tilde, 1, m_prime * N);
fft->fft(h_tilde_slopex, 1, m_prime * N);
fft->fft(h_tilde_slopez, 1, m_prime * N);
fft->fft(h_tilde_dx, 1, m_prime * N);
fft->fft(h_tilde_dz, 1, m_prime * N);
}
for (int n_prime = 0; n_prime < N; n_prime++) {
fft->fft(h_tilde, N, n_prime);
fft->fft(h_tilde_slopex, N, n_prime);
fft->fft(h_tilde_slopez, N, n_prime);
fft->fft(h_tilde_dx, N, n_prime);
fft->fft(h_tilde_dz, N, n_prime);
}
int sign;
float signs[] = { 1.0f, -1.0f };
vec3 n;
for (int m_prime = 0; m_prime < N; m_prime++) {
for (int n_prime = 0; n_prime < N; n_prime++) {
index = m_prime * N + n_prime; // index into h_tilde..
index1 = m_prime * Nplus1 + n_prime; // index into vertices
sign = signs[(n_prime + m_prime) & 1];
h_tilde[index] = h_tilde[index] * sign;
// height
vertices[index1].y = stride*h_tilde[index].a;
// displacement
h_tilde_dx[index] = h_tilde_dx[index] * sign;
h_tilde_dz[index] = h_tilde_dz[index] * sign;
vertices[index1].x = stride*(vertices[index1].ox + h_tilde_dx[index].a * lambda);
vertices[index1].z = stride*(vertices[index1].oz + h_tilde_dz[index].a * lambda);
// normal
h_tilde_slopex[index] = h_tilde_slopex[index] * sign;
h_tilde_slopez[index] = h_tilde_slopez[index] * sign;
n = glm::normalize(vec3(0.0f - h_tilde_slopex[index].a, 1.0f, 0.0f - h_tilde_slopez[index].a));
vertices[index1].nx = n.x;
vertices[index1].ny = n.y;
vertices[index1].nz = n.z;
// for tiling
if (n_prime == 0 && m_prime == 0) {
vertices[index1 + N + Nplus1 * N].y = stride*h_tilde[index].a;
vertices[index1 + N + Nplus1 * N].x = stride*(vertices[index1 + N + Nplus1 * N].ox + h_tilde_dx[index].a * lambda);
vertices[index1 + N + Nplus1 * N].z = stride*(vertices[index1 + N + Nplus1 * N].oz + h_tilde_dz[index].a * lambda);
vertices[index1 + N + Nplus1 * N].nx = n.x;
vertices[index1 + N + Nplus1 * N].ny = n.y;
vertices[index1 + N + Nplus1 * N].nz = n.z;
}
if (n_prime == 0) {
vertices[index1 + N].y = stride*h_tilde[index].a;
vertices[index1 + N].x = stride*(vertices[index1 + N].ox + h_tilde_dx[index].a * lambda);
vertices[index1 + N].z = stride*(vertices[index1 + N].oz + h_tilde_dz[index].a * lambda);
vertices[index1 + N].nx = n.x;
vertices[index1 + N].ny = n.y;
vertices[index1 + N].nz = n.z;
}
if (m_prime == 0) {
vertices[index1 + Nplus1 * N].y = stride*h_tilde[index].a;
vertices[index1 + Nplus1 * N].x = stride*(vertices[index1 + Nplus1 * N].ox + h_tilde_dx[index].a * lambda);
vertices[index1 + Nplus1 * N].z = stride*(vertices[index1 + Nplus1 * N].oz + h_tilde_dz[index].a * lambda);
vertices[index1 + Nplus1 * N].nx = n.x;
vertices[index1 + Nplus1 * N].ny = n.y;
vertices[index1 + Nplus1 * N].nz = n.z;
}
}
}
}
用OPENGL绘制出的效果则为:

References:
1. Tessendorf, Jerry. Simulating Ocean Water. In SIGGRAPH 2002 Course Notes #9 (Simulating Nature: Realistic and Interactive Techniques), ACM Press.























 1460
1460

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








