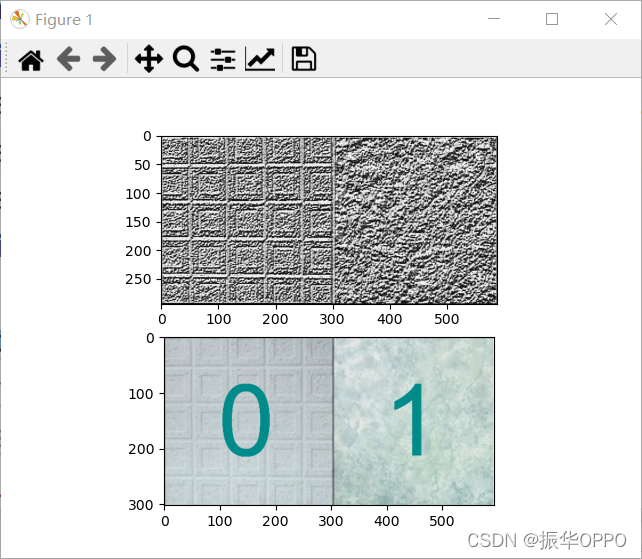
将下图左右两种不同类型的纹理区域分开,方法输出结果是一幅与该图像等大小的二值图像,左边为0,右边为1,或者相反,灰色边框线在设计的方法中不作考虑,自行去除。

import matplotlib.image as mpimg
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from cv2 import cv2
from sklearn.multiclass import OneVsRestClassifier
from sklearn.svm import SVR
from skimage import feature as skft
from PIL import Image,ImageDraw,ImageFont
class Texture():
def __init__(self):
self.radius = 1
self.n_point = self.radius * 8
def loadPicture(self):
train_index = 0
test_index = 0
train_data = np.zeros((10, 171, 171))
test_data = np.zeros((8, 171, 171))
train_label = np.zeros(10)
test_label = np.zeros(8)
for i in np.arange(2):
image = mpimg.imread('dataset1/'+str(i)+'.tiff')
data = np.zeros((513, 513))
data[0:image.shape[0], 0:image.shape[1]] = image
index = 0
for row in np.arange(3):
for col in np.arange(3):
if index < 5:
train_data[train_index, :, :] = data[171*row:171*(row+1),171*col:171*(col+1)]
train_label[train_index] = i
train_index += 1
else:
test_data[test_index, :, :] = data[171*row:171*(row+1),171*col:171*(col+1)]
test_label[test_index] = i
test_index += 1
index += 1
return train_data, test_data, train_label, test_label
def texture_detect(self):
train_data, test_data, train_label, test_label = self.loadPicture()
n_point = self.n_point
radius = self.radius
train_hist = np.zeros((10, 256))
test_hist = np.zeros((8, 256))
for i in np.arange(10):
lbp=skft.local_binary_pattern(train_data[i], n_point, radius, 'default')
max_bins = int(lbp.max() + 1)
train_hist[i], _ = np.histogram(lbp, normed=True, bins=max_bins, range=(0, max_bins))
for i in np.arange(8):
lbp = skft.local_binary_pattern(test_data[i], n_point, radius, 'default')
max_bins = int(lbp.max() + 1)
test_hist[i], _ = np.histogram(lbp, normed=True, bins=max_bins, range=(0, max_bins))
return train_hist, test_hist
def classifer(self):
train_data, test_data, train_label, test_label = self.loadPicture()
train_hist, test_hist = self.texture_detect()
svr_rbf = SVR(kernel='rbf', C=1e3, gamma=0.1)
model= OneVsRestClassifier(svr_rbf, -1)
model.fit(train_hist, train_label)
image=cv2.imread('dataset1/image.png',cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
image=cv2.resize(image,(588,294))
img_ku=skft.local_binary_pattern(image,8,1,'default')
thresh=cv2.adaptiveThreshold(image,255,cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C,cv2.THRESH_BINARY,11,2)
img_data=np.zeros((1,98,98))
data=np.zeros((294,588))
data[0:image.shape[0],0:image.shape[1]]=image
img = Image.open('texture.png')
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
myfont = ImageFont.truetype('C:/windows/fonts/Arial.ttf', size=180)
fillcolor = "#008B8B"
width, height = img.size
for row in np.arange(3):
for col in np.arange(6):
img_data[0,:,:]=data[98*row:98*(row+1),98*col:98*(col+1)]
lbp= skft.local_binary_pattern(img_data[0], 8, 1, 'default')
max_bins=int(lbp.max()+1)
img_hist, _ = np.histogram(lbp, normed=True, bins=max_bins, range=(0, max_bins))
predict=model.predict(img_hist.reshape(1,-1))
if(predict==0):
draw.text((width/6, height/6), '0', font=myfont, fill=fillcolor)
data[98*row:98*(row+1),98*col:98*(col+1)]=0
else:
draw.text((2*width /3, height/6), '1', font=myfont, fill=fillcolor)
data[98*row:98*(row+1),98*col:98*(col+1)]=255
plt.subplot(211)
plt.imshow(img_ku,'gray')
plt.subplot(212)
plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
test = Texture()
accuracy = test.classifer()
上面一张图是结果LBP算子特征提取后的图片,下面一张图使用SVM进行纹理分类后得到的结果,与预测的左上图纹理相同标为0,与右上图相同标为1。
在Linux的各大发行版中,Ubuntu及其衍生版本一直享有对用户友好的美誉。Ubuntu是一个开源操作系统,它的系统和软件可以在官方网站(http://cn.ubuntu.com)免费下载,并且提供了详细的安装方式说明。

























 560
560











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










