1.环境和目的
目的:实现对刻度尺的图形尺寸识别
环境:python+vscode,导入包如下:
import cv2
import numpy as np
from scipy.signal import convolve2d
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.linear_model import RANSACRegressor2.实现过程
2.1读取图像和灰度转换
# Usage remains the same
image_path = r"D:\study\pyhon\opencv\Hessian\12.png"
# Read image and convert to grayscale
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
# 将图像转换为灰度图像
gray_image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
edge_image = detect_edges_hessian(gray_image)2.2 hessian边缘处理,代码如下,通过调节condition值可以对边缘图像进行调整,可自行尝试;
def detect_edges_hessian(image, threshold=1e-3, blur_ksize=3):
"""Detect edges using the Hessian matrix method with improvements."""
if image is None:
print(f"Error: Could not read the image at {image_path}. Please check the path.")
return
# Image preprocessing: Gaussian blur
blurred_image = cv2.GaussianBlur(image, (blur_ksize, blur_ksize), 0)
# Compute derivatives
Ixx, Ixy, Iyy = compute_derivative_images(blurred_image)
# Compute eigenvalues
trace = Ixx + Iyy
det = Ixx * Iyy - Ixy**2
lambda1 = 0.5 * (trace + np.sqrt(trace**2 - 4*det))
lambda2 = 0.5 * (trace - np.sqrt(trace**2 - 4*det))
# Edge detection
edge_map = np.zeros_like(blurred_image, dtype=np.float64)
condition = (lambda2 < threshold)&(lambda1 > lambda2 * 10) # Adjust threshold strategy
edge_map[condition] = lambda2[condition] # Use λ2 for edge strength
# Normalize and scale
edge_map = normalize_and_scale(edge_map)
return edge_map上述代码中引用了几个子函数,函数代码如下:
def gaussian_derivative_kernel(size, sigma):
"""Generate Gaussian derivative kernels."""
ax = np.linspace(-(size//2), size//2, size)
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(ax, ax)
kernel = np.exp(-(xx**2 + yy**2) / (2*sigma**2))
kernel_x = -xx * kernel / (sigma**2)
kernel_y = -yy * kernel / (sigma**2)
return kernel_x, kernel_y
def compute_derivative_images(image, sigma=1):
"""Compute image derivatives using Gaussian derivative kernels."""
kernel_x, kernel_y = gaussian_derivative_kernel(3, sigma)
Ix = convolve2d(image, kernel_x, mode='same', boundary='symm')
Iy = convolve2d(image, kernel_y, mode='same', boundary='symm')
Ixx = convolve2d(Ix, kernel_x, mode='same', boundary='symm')
Ixy = convolve2d(Ix, kernel_y, mode='same', boundary='symm')
Iyy = convolve2d(Iy, kernel_y, mode='same', boundary='symm')
return Ixx, Ixy, Iyy
def normalize_and_scale(image):
"""Normalize and scale the image to 0-255."""
return np.uint8(255 * (image - np.min(image)) / (np.max(image) - np.min(image)))
效果图如下
原图:
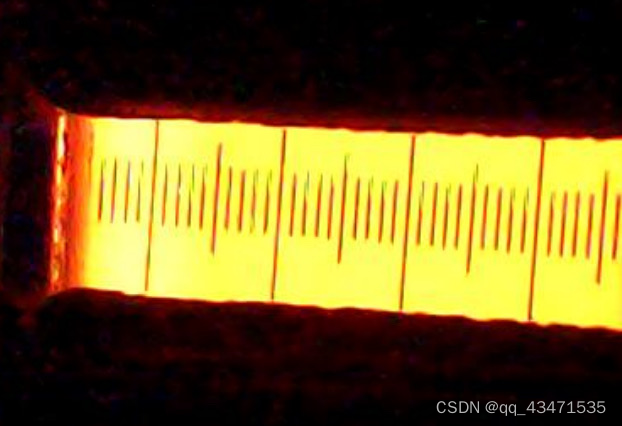
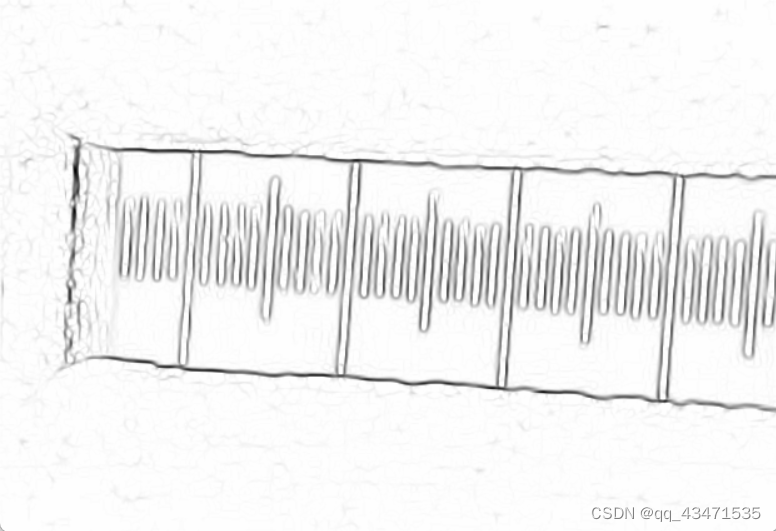
提取后图像:
2.4 边框提取,筛选,根据筛选数据进行直线拟合,得到线条,将得到的线条数据进行筛选合并和过滤,得到符合要求的线条,将筛选后的线条进行绘画显示
# 修改提取边缘点的函数以收集所有拟合的直线,并在最后进行合并
def extract_edge_points_and_merge_lines(edge_map,image):
"""从边缘图中提取边缘点坐标"""
edge_map=255-edge_map
all_lines = []
edge_points = extract_edge_points(edge_map,image)
for contour in edge_points:
coef, intercept= fit_line_with_ransac(contour,image)
if coef:
all_lines.append((coef, intercept))
# 合并相似的直线
merged_lines = merge_and_filter_lines(all_lines)
# 在图像上绘制合并后的直线
for slope, intercept in merged_lines:
draw_line_on_image(image, slope, intercept)
cv2.imshow("Edges with Merged Lines Fitted", image)
def draw_line_on_image(image, coef, intercept):
"""在图像上绘制拟合的直线"""
print(coef,intercept)
height, width = image.shape[:2]
print(height, width)
# 选择合适的范围来显示直线,这里简单地使用图像的宽度范围
x = np.linspace(0, width, num=width)
y = coef * x + intercept
# 确保y值在图像范围内
y = np.clip(y, 0, height-1).astype(int)
x = x.astype(int)
# 在图像上绘制直线
for i in range(len(x)-1):
cv2.line(image, (x[i], y[i]), (x[i+1], y[i+1]), (0, 0, 255), 2)上述代码中引用了几个子函数,函数代码如下:
def extract_edge_points(edge_map, image):
# 将边缘图二值化处理
_, thresh = cv2.threshold(edge_map, 8, 250, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
# 寻找轮廓
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
height,width=image.shape[:2]
min_area=width*height*0.00035
max_area=width*height*0.003
#print(min_area,max_area)
contours1=[]
#print("**************")
for contour in contours:
# 计算轮廓面积
area = cv2.contourArea(contour)
# 检查面积是否在设定范围内
if min_area < area < max_area:
contours1.append(contour)
print(len(contours1))
return contours1
def fit_line_with_ransac(points,image, max_iterations=2000, stop_probability=0.99, residual_threshold=5):
points = remove_short_edges(points, 8,image)
if len(points) > 4:
# 确保points是NumPy数组
points = np.array(points)
# 初始化RANSAC回归器,调整参数以提高拟合质量
ransac = RANSACRegressor(
LinearRegression(),
min_samples=2,
max_trials=max_iterations,
stop_probability=stop_probability,
residual_threshold=residual_threshold
)
# 拟合数据
ransac.fit(points[:, 0].reshape(-1, 1), points[:, 1])
# 获取最优模型的系数和截距
coef = ransac.estimator_.coef_[0]
intercept = ransac.estimator_.intercept_
else:
coef = None
intercept = None
return coef, intercept
def remove_short_edges(contour, min_length,image):
# Ensure contour is a numpy array and squeeze it to handle both single and multi-dimensional inputs
contour = np.squeeze(contour)
if contour.ndim != 2 or contour.shape[1] != 2:
raise ValueError("Contour should be a 2D array with each row representing a point (x, y).")
new_contour = [contour[0]]
for i in range(1, len(contour)):
p1 = contour[i-1]
p2 = contour[i]
if edge_length(p1, p2) >= min_length:
new_contour.append(p2)
new_contour = np.array(new_contour, dtype=np.int32)
# Check if the contour has points to draw
if new_contour.size > 0:
cv2.drawContours(image, [new_contour], -1, (0, 100, 0), 2)
else:
print("No points left to draw after removing short edges.")
cv2.imshow("Edges Detected by Improved Hessian11", image)
# Convert new_contour back to a proper 2D numpy array without extra dimensions
return np.array(new_contour, dtype=np.int32)
def merge_and_filter_lines(lines, slope_threshold_merge=1.5, intercept_threshold=10, slope_threshold_filter=8):
"""
合并斜率和截距相近的直线,然后进一步筛选出斜率非常接近的直线。
"""
# 合并斜率和截距相近的直线
merged_lines = []
for line in lines:
slope, intercept = line
found_similar = False
for i, (merged_slope, merged_intercept) in enumerate(merged_lines):
if abs(slope - merged_slope) < slope_threshold_merge and abs(intercept - merged_intercept) < intercept_threshold:
new_slope = (merged_slope + slope) / 2
new_intercept = (merged_intercept + intercept) / 2
merged_lines[i] = (new_slope, new_intercept)
found_similar = True
break
if not found_similar:
merged_lines.append(line)
# 筛选斜率非常接近的直线
filtered_lines = []
for line in merged_lines:
slope, _ = line
if not any(abs(slope - other_slope) > slope_threshold_filter for other_slope, _ in filtered_lines):
filtered_lines.append(line)
"""
k_set=0
b_set=0
for y in filtered_lines:
k,b=y
k_set +=k/len(filtered_lines)
b_set +=b/len(filtered_lines)
filtered_line22=[]
filtered_lines22=[]
for _,b1 in filtered_lines:
#if abs(b1-b_set)<600:
k2=k_set
b2=b1
filtered_line22=(k2,b2)
filtered_lines22.append(filtered_line22)
print(k2,b2)
"""
return filtered_lines
效果如下:
加入过滤后的couters图形:
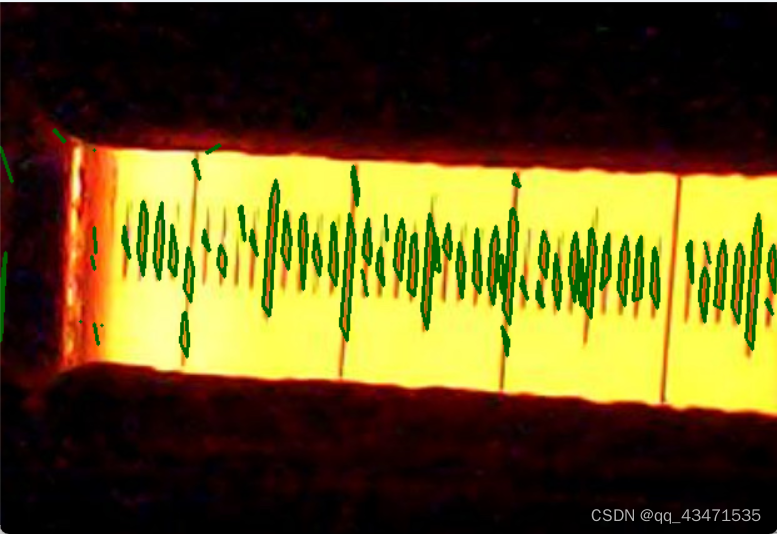
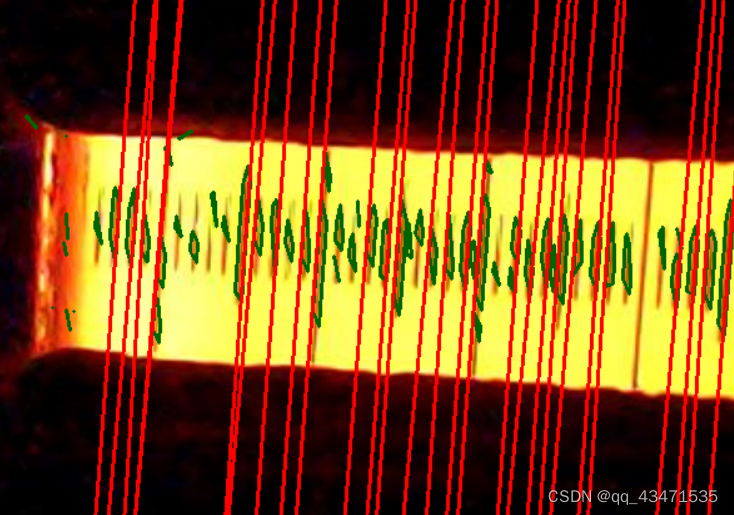
拟合合并过滤后的直线图形:
总结:
距离计算部分需结合指定长度进行各个直线部分的相似匹配,得到均值斜率,基于此进行截距的计算,得到直线间的间隔。
缺陷:目前的图像在得到直线方面不足,无法对所有需要的轮廓进行识别,thinking中。




















 1638
1638











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








