目录
注:本文主要简述profinet从站开发涉及到的知识点。【不足之处后续慢慢补充】。
0、常见缩写及关键字注释
MRP: Media Redundancy Manager,媒体冗余管理。
MRP 定义了环中节点的类型:一个节点是 Media Redundancy Manager(MRM),
其它节点是 Media Redundancy Clients (MRC). MRM 监视着PROFINET ring。
Test Packets 成功,表明环是好的, MRM forwards no data between its ring ports。
只要网络连接由MRP恢复的时间小于: 3x cyclic I/O update rate ( othersupplier might 1~10x) ; 则无扰。
PROFINET IO 协议是允许网络间歇中断的。
DAP: Device Access Point
LLDP: Link Layer Discovery Protocol (see IEEE 802.1AB-2009)
NAP: Network Access Point (PNIO interface with its port submodules, see PNO-7.122 PROFINET
IO System Redundancy)
SAP: Service Access Point
UUID: Universally Unique Identifier (see ISO/IEC 11578:1996)
Signal: A process data object with acertain type, for example a UINT32 counter.
Terminology and abbreviations
=============================
Abstract syntax
Describes the parts (and their subparts) of different messages. See also "Transfer syntax".
Configuration
IO-device and IO-controller definition in an engineering tool.
Commissioning
Device initialization (Configuration is downloaded to IO-controller).
Engineering tool
A desktop program for configuring PLC. For example Siemens TIA portal.
Interface
Abstract group of ports. In Profinet context, interface typically doesn't mean a
specific network interface. This is a common cause of confusion.
Parameterization
Write parameter values to all submodules. Parameterization is done via
the Write and Control commands.
Port
Network interface. The physical connectors are referred to as "physical ports".
A "management port" is the network interface to which a controller / PLC connects.
Record data
Data that can be accessed with acyclic Profinet Read and Write. Addressed by
slot, subslot and index.
Transfer syntax
Coding of the different fields in a message. See also "Abstract syntax".
Abbreviations
-------------
ACK
Positively acknowledge
AKA
Also Known As
ALPMI
Alarm Protocol Machine Initiator. Trigger alarms.
ALPMR
Alarm Protocol Machine Responder. Responds to incoming alarms.
ALPMX
General term for ALPMI and ALPMR
AMR
Asset Management Record
AP
Application Process
APDU
Application (layer) Protocol Data Unit
API
Application Process Identifier (uint32). Used to differentiate between for example user profiles. Sometimes named "Profile ID".
API
Application Programming Interface. Application implementers use the API of the P-Net Profinet stack.
APMR
Acyclic Protocol Machine Receiver. Receives incoming alarm frames.
APMS
Acyclic Protocol Machine Sender. Sends alarm frames.
APMX
General term for APMR and APMS
APO
Application Process Object
AR
Application Relation. Consists of several communication relations (CR). Typically an IO AR, which is a connection to a PLC, but can also be an Supervisor AR.
ARP
Address Resolution Protocol, used to translate from an IP address to a MAC address.
AREP
Application Relationship End Point (uint32), pretty much an index into an array of AR.
ASDU
Application Service Data Unit
ASE
Application Service Element. For example logbook, time and diagnosis.
CBA
Component Based Automation, for the legacy Profinet CBA system. It used communication profile CP 3/3.
CC
Conformance Class (Performance level A to D)
CDML
Controller Description Markup Language. An XML file describing a controller, for certification.
CE
A marking for European Union declaration of conformity
CIDR
Classless Inter-Domain Routing. The CIDR notation ``/24`` tells how many bits of the netmask that should be enabled.
CIM
Communication Interface Management
CiR
Configuration in Run
CM
Context Management
CMDEV
Context Management Protocol Machine Device
CMI
CM Initiator
CMINA
Context Management Ip and Name Assignment protocol machine
CMIO
Context Management Input Output protocol machine
CMPBE
Context Management Parameter Begin End protocol machine
CMRDR
Context Management Read Record Responder protocol machine, responds to parameter read from the IO-controller.
CMRPC
Context Management RPC protocol machine
CMWRR
Context Management Write Record Responder protocol machine, responds to parameter write from the IO-controller.
CMSM
Context Management Surveillance protocol Machine, monitors the establishment of a connection. Also written as CM Server Protocol machine.
CP
Communication Profile. For example Profinet conformance class B is also known as CP 3/5.
CPF
Communication Profile Family. Profinet and Profibus is CPF = 3, Ethercat is CPF = 12.
CPM
Consumer Protocol Machine, for receiving cyclic data.
CPU
Central Processing Unit
CR
Communication Relation (Part of AR).
CREP
Communication Relationship EndPoint (uint32), pretty much an index into an array of input and output CR.
DA
Destination Address. It is the MAC address of the receiver.
DAP
Device Access Point
DCE
Distributed Computing Environment. Used with RPC.
DCP
Discovery and basic Configuration Protocol. Runs over Ethernet layer 2 (not IP or UDP).
DFP
Dynamic Frame Packing. Used with IRT protocol.
DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, for allocating IP addresses to devices.
DHT
Data Hold Timer
DLL
Data Link Layer
DLPDU
?
DNS
Domain Name System, for converting from host name to IP address.
DT
Device Tool
DUT
Device Under Test
EMC
ElectroMagnetic Compatibility
EPM
EndPoint Mapper
ES
Engineering System
FACK
Fragment acknowledge
FAL
Fieldbus Application Layer
FD
Full Duplex
FDB
Forwarding Database, used in MRP
FO
Fiber Optics
FSPM
FAL Service Protocol Machines
FSU
Fast Start Up (Store communication parameters in IO devices)
GAP
?
GSD
General Station Description. An XML file describing an IO-Device.
GSDML
GSD Markup Language
GUI
Graphical User Interface
HTTP
Hypertext Transfer Protocol
I&M
Identification & Maintenance. Has different blocks; IM0 to IM??.
ICMP
Internet Control Message Protocol. (Sent in an IP packet)
IDNA
Internationalized Domain Names for Applications
IE
Industrial Ethernet
IGMP
Internet Group Management Protocol. For multicast groups. Used in IPv4.
IO
Input Output
IOC
IO Controller. Typically a PLC.
IOD
IO Device. An input-output device controlled by a PLC via Profinet communication.
IOCS
IO Consumer Status. Reported by IO-device (for output data) and IO-controller (for input data), per subslot. (uint8)
IOCR
IO Communication Relation
IOPS
IO Provider Status. Describes validity of IO data per subslot. Sent by IO-device (for input data) or IO-controller (for output data) together with data. (uint8)
IOxS
General term for IOCS and IOPS.
IOS
IO Supervisor. Typically an engineering tool running on a personal computer.
IP
Internet Protocol
IP
Ingress Protection. For example IP65 is a housing class suitable for outdoor installation.
iPar
Individual Parameters. Backups of these parameters are typically stored in a separate parameter server.
IRT
Isochronous Real-Time
LAN
Local Area Network
LED
Light Emitting Diode
LLC
?
LLDP
Link Layer Discovery Protocol, for neighbourhood detection.
LMPM
data Link layer Mapping Protocol Machine. Receives Ethernet frames.
LT
Length and Type field in Ethernet frame. Also known as EtherType.
MAC
Media Access Control
MAU
Medium Attachment Unit. Ethernet transceiver type. 0x0 = radio, 0x10 = Media type copper 100BaseTXFD
MC
Multicast (as opposed to unicast)
MC
Multicore (Codesys runtime variant for Raspberry Pi)
MCR
Multicast Communication Relationship
MDNS
Multicast DNS. A UDS based protocol for resolving hostname to IP address. Implemented by Bonjour and Avahi.
MIB
Management Information Base. A text file format describing Object Identifiers (OID) for Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) frames.
MIC
MRP interconnection Client. Routes traffic between two Ethernet rings (which are using MRP).
MIM
MRP Interconnection Manager. Controls the traffic between two Ethernet rings (which are using MRP).
MRA
Media redundancy manager with auto negotiation
MRC
Media redundancy client
MRM
Media redundancy manager
MRP
Media Redundancy Protocol. Use a normally off path in the Ethernet network, to form a ring topology.
MRPIC
Media Redundancy Protocol Interconnect (connects two MRP rings). Nodes have MIM or MIC roles.
MRPD
Media Redundancy for Planned Duplication. Send similar frames in both directions on an Ethernet ring.
MTU
Maximum Transfer Unit. The largest packet a network interface can handle. Typically 1500 bytes. This includes the IP header, but not the Ethernet header.
NACK
Negatively acknowledge
NDR
Network Data Representation. A header as first part of the DCE/RPC payload (sent via UDP). Contains info on how large the payload is, and how large responses that can be accepted.
NME
Network Management Engine
NRT
Non-Real Time Ethernet frames
NVM
Non-Volatile Memory. Typically flash memory chips.
OID
Object Identifier. Describes a field in a Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) frame.
OS
Operating System
OUI
Organizationally Unique Identifier. This is the three first bytes of the MAC address. The value for Profinet Multicast is 01:0E:CF.
PA
Process Automation (as opposed to production automation)
PCA
Provider, Consumer or Alarm.
PCF
Polymer Clad Fiber
PCP
Priority Code Point, for VLAN
PD
Physical Device. This is information related to an Ethernet port.
PDEV
Physical Device management. Physical interface and switch ports of a Profinet field device.
PDF
Portable Document Format
PDU
Protocol Data Unit
PI
PROFIBUS & PROFINET International. The Profinet interest group. See also PNO.
PICO
PI Certification Office
PITL
PI Test Laboratories. Performs certification testing.
PLC
Programmable Logic Controller. Often used as a Profinet IO-controller.
PN
See PROFINET
PNI
Primary Network Initialization. Siemens SinecPni is a tool for configuration of Profinet equipment.
PNIO
Profinet IO protocol
PNO
PROFIBUS Nutzerorganisation e.V, located in Germany. See also PI.
POF
Plastic Optical Fiber
PPM
Cyclic Provider Protocol Machine
PROFINET
Process Field Net
PS
?
PTCP
Precision Transparent Clock Protocol
RED
Redundancy
RPC
Remote Procedure Call. The protocol DCE/RPC runs on UDP and is used for configuration of the IO-Device during startup.
RS
Reporting system
RSI
Remote Service Interface
RTA
RealTime Acyclic protocol, for alarms.
RTC
Real Time Class
RTC
RealTime Cyclic protocol
RTE
Real Time Ethernet
RTOS
Real Time Operating System
SA
Source Address. It is the MAC address of the sender.
SAM
Source Address of ? Uses to restrict incoming DCP communication to a single remote MAC address (for 3 seconds).
SCL
Structured Control Language. Siemens name for the structured text (ST) programming language for PLCs.
SDU
Service Data Unit. This is the payload of a PDU.
SMA
Sample Moving Average. A smoothing function in the Wireshark Ethernet frame capture software.
SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol. For network topology detection.
SOE
Sequence Of Events
ST
Structured Text. A programming language for PLCs.
STP
Spanning Tree Protocol. An alternative to MRP (but slower)
STX
Structured Text. See ST.
TACK
Transport Acknowledge. Used for alarm transmission.
TED
Topology and Engineering Discovery
TIA
Totally Integrated Automation. An automation portal (engineering tool) by Siemens.
TIAP
See TIA.
TCI
Tool Calling Interface (The engineering tool can call specialized device-related tools)
TCP
Transmission Control Protocol, used on top of IP.
TLV
Type-Length-Value. A data structure in an LLDP Ethernet frame.
TPID
Tag protocol identifier, for VLAN.
TSDU
?
TSN
Time-Sensitive Networking
TTL
Time to live. A field in an LLDP Ethernet frame.
UC
Unicast (as opposed to multicast)
UDP
User Datagram Protocol, used on top of IP.
USI
User Structure Identifier (unit16) Describes alarm payloads.
UUID
Universally Unique Identifier. A 128-bit number for uniquely identifying information.
VLAN
Virtual LAN
VID
VLAN identifier
WLAN
Wireless LAN
XML
eXtended Markup Language
一般概念
FAL被定义为一组面向对象的ASE,每个ASE规范由三个部分组成:类定义、服务和协议规范。1、profinet简介
profinet符合 IEEE 802.xx 标准的工业以太网, 具有自动协商和自动交叉功能
■ 全双工传输
■ 交换式以太网
■ 百兆级以太网

2、profinet协议栈

3、profinet数据帧

4、profinet网络解决方案示例

5、Application areas

6、FAL体系结构组成部分
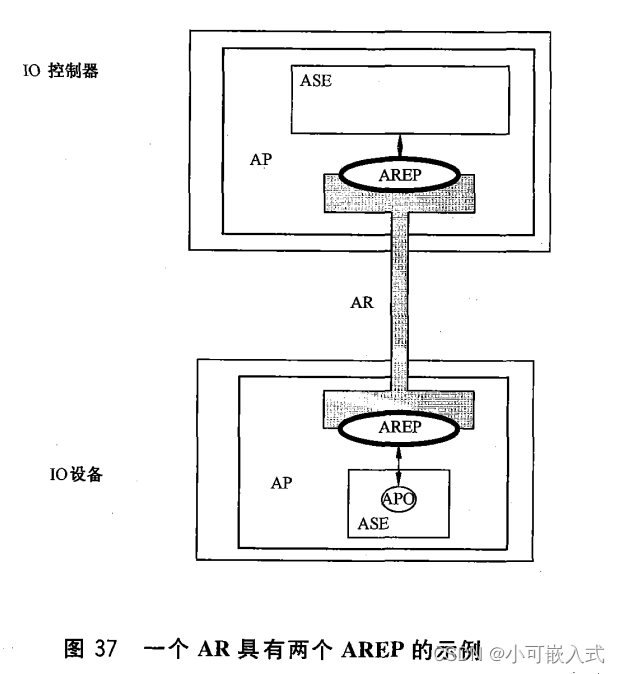
AR:应用关系
ASE:应用服务元素。提供用于对象管理的服务。它的服务可用来访问对象属性,删除和创建对象实例。
AREP: Application Relationship End Point (uint32)。相当于数组索引。



7、PTCP服务
PTCP:精确透明时钟协议(Precision Transparent Clock Protocol)。



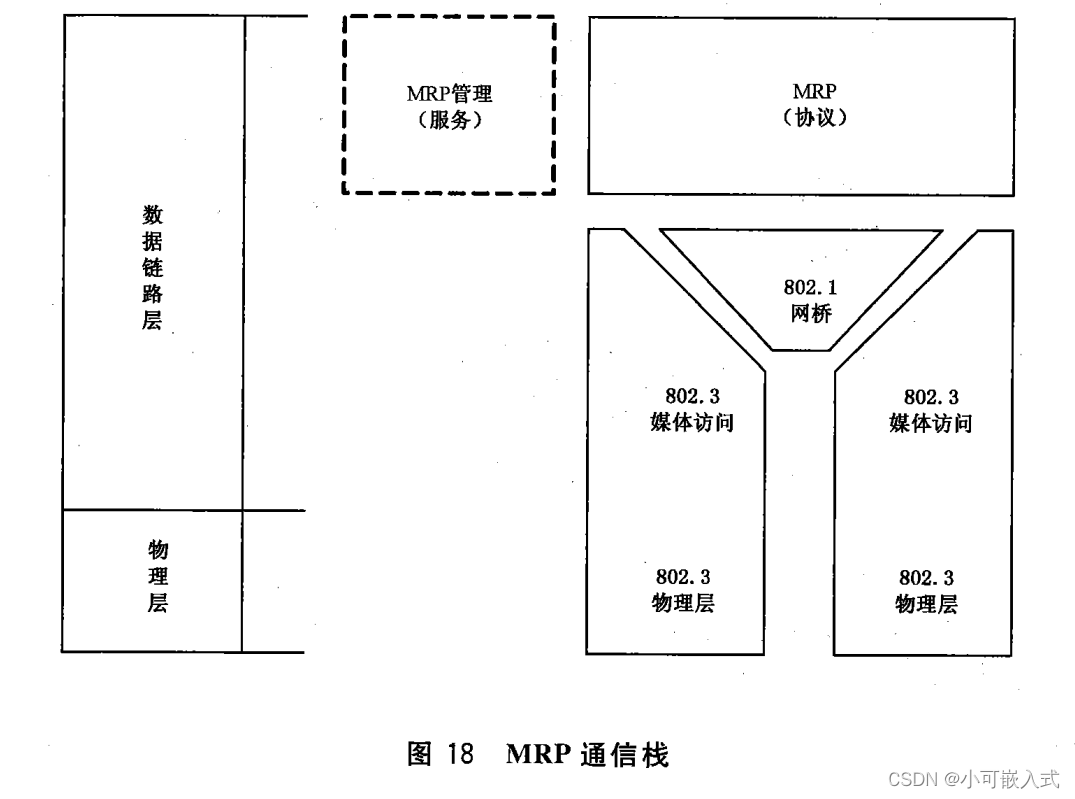
8、MRP媒体冗余服务

9、RPC服务
RPC: Remote Procedure Call. The protocol DCE/RPC runs on UDP and is used for configuration of the IO-Device during startup.
此证实服务用于CL RPC(无连接RPC)建立连接、释放连接。通过CL RPC传送高层的读服务、写服务,传送高层的“End of Parameter”和“Application Ready”服务。
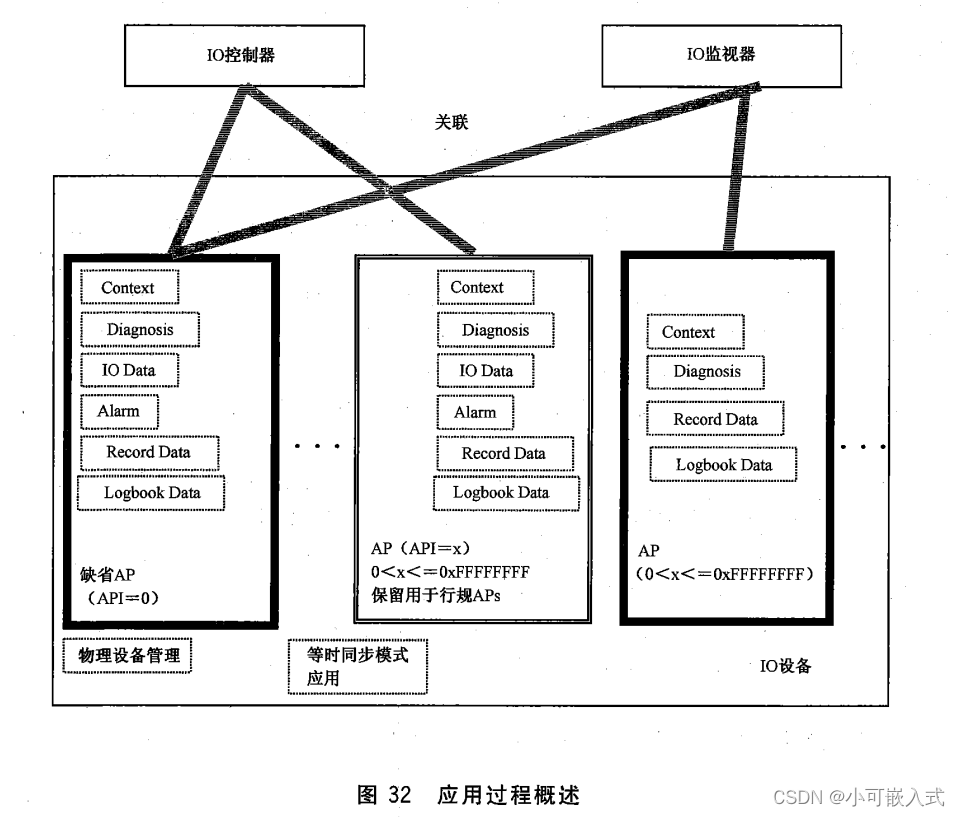
10、应用过程




11、应用关系
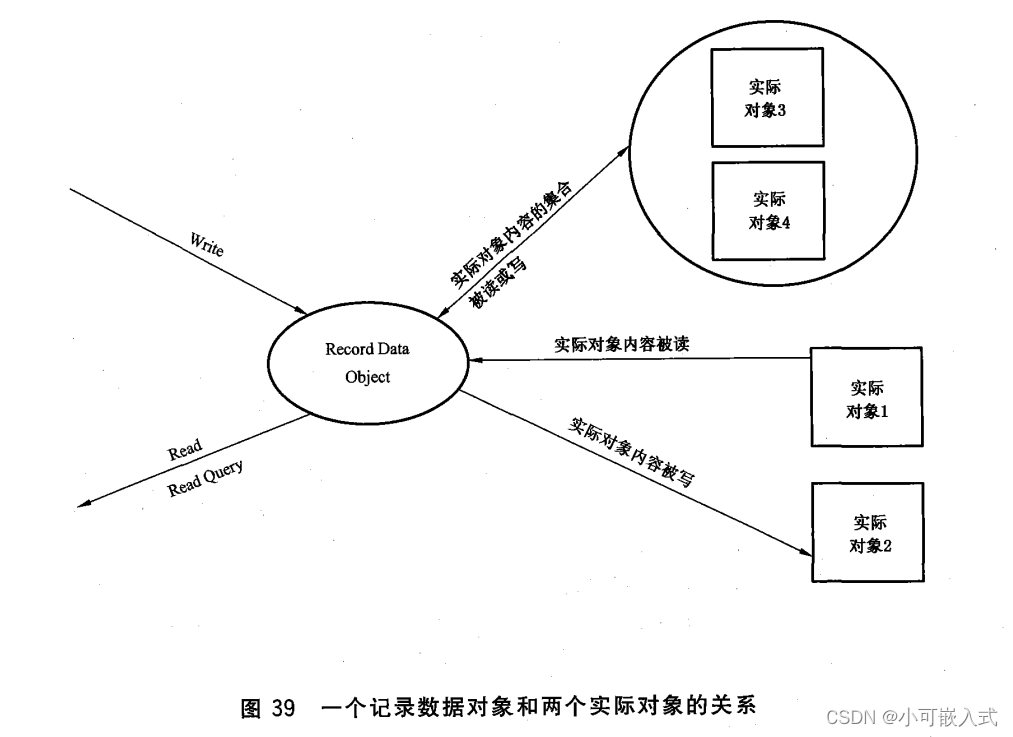
12、ASE
12.1 记录数据ASE



























 580
580

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










