✅作者简介:热爱科研的Matlab仿真开发者,擅长数据处理、建模仿真、程序设计、完整代码获取、论文复现及科研仿真。
🍎个人主页:Matlab科研工作室
🍊个人信条:格物致知,完整Matlab代码及仿真咨询内容私信。
🌿 往期回顾可以关注主页,点击搜索
🔥 内容介绍
脉搏波(PPG)信号是一种重要的生理信号,它反映了心脏的活动和血管系统的状态。PPG信号分析在医学诊断和健康监测中有着广泛的应用。本文将介绍PPG信号分析的基本原理、方法和应用。
PPG信号的产生
PPG信号是由心脏搏动引起的血管体积变化产生的。当心脏收缩时,血液被泵入动脉,导致动脉扩张,从而产生一个PPG信号峰值。当心脏舒张时,动脉收缩,PPG信号下降。
PPG信号特征
PPG信号具有以下特征:
-
**峰值:**对应于心脏收缩。
-
**波谷:**对应于心脏舒张。
-
**上升时间:**从波谷到峰值的持续时间。
-
**下降时间:**从峰值到波谷的持续时间。
-
**心率:**峰值之间的间隔。
PPG信号分析方法
PPG信号分析通常涉及以下步骤:
-
**预处理:**去除噪声和其他干扰。
-
**特征提取:**提取PPG信号的特征,如峰值、波谷、心率等。
-
**分类:**根据PPG信号特征将信号分类为正常或异常。
-
**解释:**解释PPG信号特征的生理意义。
PPG信号分析的应用
PPG信号分析在医学诊断和健康监测中有着广泛的应用,包括:
-
**心血管疾病诊断:**检测心律失常、心力衰竭和冠状动脉疾病等心血管疾病。
-
**呼吸系统疾病诊断:**检测睡眠呼吸暂停和慢性阻塞性肺病等呼吸系统疾病。
-
**健康监测:**监测心率、血压和血氧饱和度等健康指标。
-
**运动生理学:**评估运动时的生理反应。
-
**远程医疗:**通过可穿戴设备远程监测患者的健康状况。
结论
PPG信号分析是一种强大的工具,可用于诊断疾病、监测健康和评估生理反应。随着传感器技术和数据分析方法的不断发展,PPG信号分析在医学和健康保健领域将发挥越来越重要的作用。
📣 部分代码
%EMD computes Empirical Mode Decomposition%%% Syntax%%% IMF = EMD(X)% IMF = EMD(X,...,'Option_name',Option_value,...)% IMF = EMD(X,OPTS)% [IMF,ORT,NB_ITERATIONS] = EMD(...)%%% Description%%% IMF = EMD(X) where X is a real vector computes the Empirical Mode% Decomposition [1] of X, resulting in a matrix IMF containing 1 IMF per row, the% last one being the residue. The default stopping criterion is the one proposed% in [2]:%% at each point, mean_amplitude < THRESHOLD2*envelope_amplitude% &% mean of boolean array {(mean_amplitude)/(envelope_amplitude) > THRESHOLD} < TOLERANCE% &% |#zeros-#extrema|<=1%% where mean_amplitude = abs(envelope_max+envelope_min)/2% and envelope_amplitude = abs(envelope_max-envelope_min)/2%% IMF = EMD(X) where X is a complex vector computes Bivariate Empirical Mode% Decomposition [3] of X, resulting in a matrix IMF containing 1 IMF per row, the% last one being the residue. The default stopping criterion is similar to the% one proposed in [2]:%% at each point, mean_amplitude < THRESHOLD2*envelope_amplitude% &% mean of boolean array {(mean_amplitude)/(envelope_amplitude) > THRESHOLD} < TOLERANCE%% where mean_amplitude and envelope_amplitude have definitions similar to the% real case%% IMF = EMD(X,...,'Option_name',Option_value,...) sets options Option_name to% the specified Option_value (see Options)%% IMF = EMD(X,OPTS) is equivalent to the above syntax provided OPTS is a struct% object with field names corresponding to option names and field values being the% associated values%% [IMF,ORT,NB_ITERATIONS] = EMD(...) returns an index of orthogonality% ________% _ |IMF(i,:).*IMF(j,:)|% ORT = \ _____________________% /% ? || X ||?% i~=j%% and the number of iterations to extract each mode in NB_ITERATIONS%%% Options%%% stopping criterion options:%% STOP: vector of stopping parameters [THRESHOLD,THRESHOLD2,TOLERANCE]% if the input vector's length is less than 3, only the first parameters are% set, the remaining ones taking default values.% default: [0.05,0.5,0.05]%% FIX (int): disable the default stopping criterion and do exactly <FIX>% number of sifting iterations for each mode%% FIX_H (int): disable the default stopping criterion and do <FIX_H> sifting% iterations with |#zeros-#extrema|<=1 to stop [4]%% bivariate/complex EMD options:%% COMPLEX_VERSION: selects the algorithm used for complex EMD ([3])% COMPLEX_VERSION = 1: "algorithm 1"% COMPLEX_VERSION = 2: "algorithm 2" (default)%% NDIRS: number of directions in which envelopes are computed (default 4)% rem: the actual number of directions (according to [3]) is 2*NDIRS%% other options:%% T: sampling times (line vector) (default: 1:length(x))%% MAXITERATIONS: maximum number of sifting iterations for the computation of each% mode (default: 2000)%% MAXMODES: maximum number of imfs extracted (default: Inf)%% DISPLAY: if equals to 1 shows sifting steps with pause% if equals to 2 shows sifting steps without pause (movie style)% rem: display is disabled when the input is complex%% INTERP: interpolation scheme: 'linear', 'cubic', 'pchip' or 'spline' (default)% see interp1 documentation for details%% MASK: masking signal used to improve the decomposition according to [5]%%% Examples%%%X = rand(1,512);%%IMF = emd(X);%%IMF = emd(X,'STOP',[0.1,0.5,0.05],'MAXITERATIONS',100);%%T=linspace(0,20,1e3);%X = 2*exp(i*T)+exp(3*i*T)+.5*T;%IMF = emd(X,'T',T);%%OPTIONS.DISLPAY = 1;%OPTIONS.FIX = 10;%OPTIONS.MAXMODES = 3;%[IMF,ORT,NBITS] = emd(X,OPTIONS);%%% References%%% [1] N. E. Huang et al., "The empirical mode decomposition and the% Hilbert spectrum for non-linear and non stationary time series analysis",% Proc. Royal Soc. London A, Vol. 454, pp. 903-995, 1998%% [2] G. Rilling, P. Flandrin and P. Gon鏰lves% "On Empirical Mode Decomposition and its algorithms",% IEEE-EURASIP Workshop on Nonlinear Signal and Image Processing% NSIP-03, Grado (I), June 2003%% [3] G. Rilling, P. Flandrin, P. Gon鏰lves and J. M. Lilly.,% "Bivariate Empirical Mode Decomposition",% Signal Processing Letters (submitted)%% [4] N. E. Huang et al., "A confidence limit for the Empirical Mode% Decomposition and Hilbert spectral analysis",% Proc. Royal Soc. London A, Vol. 459, pp. 2317-2345, 2003%% [5] R. Deering and J. F. Kaiser, "The use of a masking signal to improve% empirical mode decomposition", ICASSP 2005%%% See also% emd_visu (visualization),% emdc, emdc_fix (fast implementations of EMD),% cemdc, cemdc_fix, cemdc2, cemdc2_fix (fast implementations of bivariate EMD),% hhspectrum (Hilbert-Huang spectrum)%%% G. Rilling, last modification: 3.2007% gabriel.rilling@ens-lyon.frfunction [imf,ort,nbits] = emd(varargin)[x,t,sd,sd2,tol,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs,display_sifting,sdt,sd2t,r,imf,k,nbit,NbIt,MAXITERATIONS,FIXE,FIXE_H,MAXMODES,INTERP,mask] = init(varargin{:});if display_siftingfig_h = figure;end%main loop : requires at least 3 extrema to proceedwhile (~stop_EMD(r,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs) && (k < MAXMODES+1 || MAXMODES == 0) && ~any(mask))% current modem = r;% mode at previous iterationmp = m;%computation of mean and stopping criterionif FIXE[stop_sift,moyenne] = stop_sifting_fixe(t,m,INTERP,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs);elseif FIXE_Hstop_count = 0;[stop_sift,moyenne] = stop_sifting_fixe_h(t,m,INTERP,stop_count,FIXE_H,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs);else[stop_sift,moyenne] = stop_sifting(m,t,sd,sd2,tol,INTERP,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs);end% in case the current mode is so small that machine precision can cause% spurious extrema to appearif (max(abs(m))) < (1e-10)*(max(abs(x)))if ~stop_siftwarning('emd:warning','forced stop of EMD : too small amplitude')elsedisp('forced stop of EMD : too small amplitude')endbreakend% sifting loopwhile ~stop_sift && nbit<MAXITERATIONSif(~MODE_COMPLEX && nbit>MAXITERATIONS/5 && mod(nbit,floor(MAXITERATIONS/10))==0 && ~FIXE && nbit > 100)disp(['mode ',int2str(k),', iteration ',int2str(nbit)])if exist('s','var')disp(['stop parameter mean value : ',num2str(s)])end[im,iM] = extr(m);disp([int2str(sum(m(im) > 0)),' minima > 0; ',int2str(sum(m(iM) < 0)),' maxima < 0.'])end%siftingm = m - moyenne;%computation of mean and stopping criterionif FIXE[stop_sift,moyenne] = stop_sifting_fixe(t,m,INTERP,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs);elseif FIXE_H[stop_sift,moyenne,stop_count] = stop_sifting_fixe_h(t,m,INTERP,stop_count,FIXE_H,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs);else[stop_sift,moyenne,s] = stop_sifting(m,t,sd,sd2,tol,INTERP,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs);end% displayif display_sifting && ~MODE_COMPLEXNBSYM = 2;[indmin,indmax] = extr(mp);[tmin,tmax,mmin,mmax] = boundary_conditions(indmin,indmax,t,mp,mp,NBSYM);envminp = interp1(tmin,mmin,t,INTERP);envmaxp = interp1(tmax,mmax,t,INTERP);envmoyp = (envminp+envmaxp)/2;if FIXE || FIXE_Hdisplay_emd_fixe(t,m,mp,r,envminp,envmaxp,envmoyp,nbit,k,display_sifting)elsesxp=2*(abs(envmoyp))./(abs(envmaxp-envminp));sp = mean(sxp);display_emd(t,m,mp,r,envminp,envmaxp,envmoyp,s,sp,sxp,sdt,sd2t,nbit,k,display_sifting,stop_sift)defopts.display = 0;defopts.t = 1:max(size(x));defopts.maxiterations = 2000;defopts.fix = 0;defopts.maxmodes = 0;defopts.interp = 'spline';defopts.fix_h = 0;defopts.mask = 0;defopts.ndirs = 4;defopts.complex_version = 2;opts = defopts;if(nargin==1)inopts = defopts;elseif nargin == 0error('not enough arguments')endnames = fieldnames(inopts);for nom = names'if ~any(strcmpi(char(nom), opt_fields))error(['bad option field name: ',char(nom)])endif ~isempty(eval(['inopts.',char(nom)])) % empty values are discardedeval(['opts.',lower(char(nom)),' = inopts.',char(nom),';'])endendt = opts.t;stop = opts.stop;display_sifting = opts.display;MAXITERATIONS = opts.maxiterations;FIXE = opts.fix;MAXMODES = opts.maxmodes;INTERP = opts.interp;FIXE_H = opts.fix_h;mask = opts.mask;ndirs = opts.ndirs;complex_version = opts.complex_version;if ~isvector(x)error('X must have only one row or one column')endif size(x,1) > 1x = x.';endif ~isvector(t)error('option field T must have only one row or one column')endif ~isreal(t)error('time instants T must be a real vector')endif size(t,1) > 1t = t';endif (length(t)~=length(x))error('X and option field T must have the same length')endif ~isvector(stop) || length(stop) > 3error('option field STOP must have only one row or one column of max three elements')endif ~all(isfinite(x))error('data elements must be finite')endif size(stop,1) > 1stop = stop';endL = length(stop);if L < 3stop(3)=defstop(3);endif L < 2stop(2)=defstop(2);endif ~ischar(INTERP) || ~any(strcmpi(INTERP,{'linear','cubic','spline'}))error('INTERP field must be ''linear'', ''cubic'', ''pchip'' or ''spline''')end%special procedure when a masking signal is specifiedif any(mask)if ~isvector(mask) || length(mask) ~= length(x)error('masking signal must have the same dimension as the analyzed signal X')endif size(mask,1) > 1mask = mask.';endopts.mask = 0;imf1 = emd(x+mask,opts);imf2 = emd(x-mask,opts);if size(imf1,1) ~= size(imf2,1)warning('emd:warning',['the two sets of IMFs have different sizes: ',int2str(size(imf1,1)),' and ',int2str(size(imf2,1)),' IMFs.'])endS1 = size(imf1,1);S2 = size(imf2,1);if S1 ~= S2if S1 < S2tmp = imf1;imf1 = imf2;imf2 = tmp;endimf2(max(S1,S2),1) = 0;endimf = (imf1+imf2)/2;endsd = stop(1);sd2 = stop(2);tol = stop(3);lx = length(x);sdt = sd*ones(1,lx);sd2t = sd2*ones(1,lx);if FIXEMAXITERATIONS = FIXE;if FIXE_Herror('cannot use both ''FIX'' and ''FIX_H'' modes')endendMODE_COMPLEX = ~isreal(x)*complex_version;if MODE_COMPLEX && complex_version ~= 1 && complex_version ~= 2error('COMPLEX_VERSION parameter must equal 1 or 2')end% number of extrema and zero-crossings in residualner = lx;nzr = lx;r = x;if ~any(mask) % if a masking signal is specified "imf" already exists at this stageimf = [];endk = 1;% iterations counter for extraction of 1 modenbit=0;% total iterations counterNbIt=0;end%---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
⛳️ 运行结果

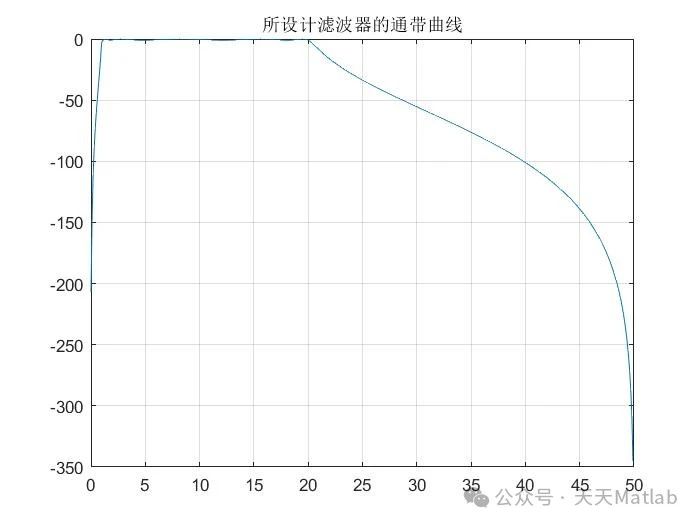
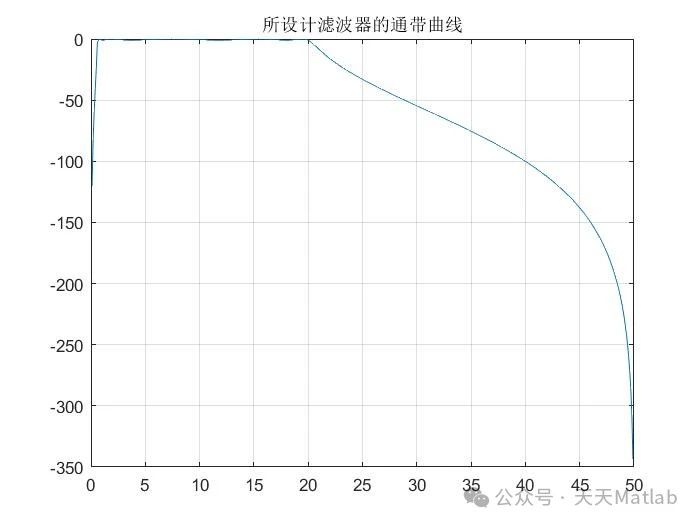


🔗 参考文献
[1] 蒋文俊.智能手机脉搏波信号实时检测与分析[D].清华大学,2015.
[2] 蒋文俊.智能手机脉搏波信号实时检测与分析[D].清华大学[2024-02-29].DOI:CNKI:CDMD:2.1015.039039.
🎈 部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除
🎁 关注我领取海量matlab电子书和数学建模资料
👇 私信完整代码和数据获取及论文数模仿真定制
1 各类智能优化算法改进及应用
生产调度、经济调度、装配线调度、充电优化、车间调度、发车优化、水库调度、三维装箱、物流选址、货位优化、公交排班优化、充电桩布局优化、车间布局优化、集装箱船配载优化、水泵组合优化、解医疗资源分配优化、设施布局优化、可视域基站和无人机选址优化、背包问题、 风电场布局、时隙分配优化、 最佳分布式发电单元分配、多阶段管道维修、 工厂-中心-需求点三级选址问题、 应急生活物质配送中心选址、 基站选址、 道路灯柱布置、 枢纽节点部署、 输电线路台风监测装置、 集装箱船配载优化、 机组优化、 投资优化组合、云服务器组合优化、 天线线性阵列分布优化
2 机器学习和深度学习方面
2.1 bp时序、回归预测和分类
2.2 ENS声神经网络时序、回归预测和分类
2.3 SVM/CNN-SVM/LSSVM/RVM支持向量机系列时序、回归预测和分类
2.4 CNN/TCN卷积神经网络系列时序、回归预测和分类
2.5 ELM/KELM/RELM/DELM极限学习机系列时序、回归预测和分类
2.6 GRU/Bi-GRU/CNN-GRU/CNN-BiGRU门控神经网络时序、回归预测和分类
2.7 ELMAN递归神经网络时序、回归\预测和分类
2.8 LSTM/BiLSTM/CNN-LSTM/CNN-BiLSTM/长短记忆神经网络系列时序、回归预测和分类
2.9 RBF径向基神经网络时序、回归预测和分类

























 561
561

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










