目录
1.基于gensim的中文文本词向量训练与相似度匹配
- 导入必要的包
#! pip install gensim #安装gensim
from gensim.test.utils import common_texts,get_tmpfile
from gensim.models import Word2Vec
import pandas as pd
import jieba.posseg
import jieba.analyse- 准备语料
这里只做演示,所以采用一个很小的语料库,训练速度快。
data = pd.read_csv('data/sample_data.csv')
print(len(data))
print(data.head(3))- 数据预处理
def dataPrepos(text):
l = []
pos = ['n','nz','v','vd','vn','l','a','d'] #定义选取的词性(可选)
seg = jieba.posseg.cut(text) #对文本进行分词和词性标注
for i in seg: #形式 [pair(word,flag),...]
if i.word and i.flag in pos: #词性筛选
l.append(i.word)
return l
def dataPre(data):
idList, titleList, abstractList = data['id'], data['title'], data['abstract']
corpus = [] # 将所有文本存在一个列表中,每一个元素代表一段文本
for index in range(len(idList)):
text = '%s。%s' % (titleList[index],abstractList[index]) #把标题字段和摘要字段拼接 得到一个更长的文本
text = dataPrepos(text) #对拼接后的文本进行预处理 返回处理后的单词列表
text = ' '.join(text) #用" "把列表中的单词连接起来 构成一个字符串
corpus.append(text)
return corpus
corpus = dataPre(data)
corpus = [i.split(" ") for i in corpus] #对corpus中的每个文本字符串用空格分隔 返回一个2维列表
print(corpus)
- 训练词向量
#基于上述构建的语料训练词向量
#词向量维度100
#CBOW和SG都有一个窗口,窗口大小为5,表示中心词左边右边各5个词
#sg=1代表使用skip-gram算法否则是CBOW
#negative=5 负例采样数
#ns_exponent=0.75 3/4 指数
#min_count 设置词频 词频>=min_count的词 才训练词向量
#workers=4 与并行有关的参数
model = Word2Vec(corpus,size=100,window=5,min_count=1,workers=4,sg=1,negative=5,ns_exponent=0.75)print(model.vector_size) #词向量维度/大小
#训练的语料太小 所以结果不是很准确
model.most_similar('最靠近') #与词 '最靠近'(要求必须在词典中) 最为接近的前10(默认)个词以及相似度
#把训练好的词向量 保存在.txt中 用的时候直接读取 存储到字典中即可
model.wv.save_word2vec_format(fname='data/w2v.txt')查看一下data/w2v.txt文件:

第一行是语料中不同的单词数(基于语料构建的词典的大小)和词向量的维度;其余的每行第一个元素是单词,其后的100个数字,是该词的词向量表示。
2. Tensorflow训练中文词向量

- 导入必要的包
%matplotlib inline
from __future__ import print_function
import collections
import math
import numpy as np
import os
import random
import tensorflow as tf
import zipfile
from matplotlib import pylab
from matplotlib import font_manager
from six.moves import range
from six.moves.urllib.request import urlretrieve
from six.moves import cPickle as pickle
from sklearn.manifold import TSNE
- 加载语料

vocabulary_size = 3000
def build_dataset(words):
count = [['UNK', -1]]
count.extend(collections.Counter(words).most_common(vocabulary_size - 1))
dictionary = dict()
for word, _ in count:
dictionary[word] = len(dictionary)
data = list()
unk_count = 0
for word in words:
if word in dictionary:
index = dictionary[word]
else:
index = 0 # dictionary['UNK']
unk_count = unk_count + 1
data.append(index)
count[0][1] = unk_count
reverse_dictionary = dict(zip(dictionary.values(), dictionary.keys()))
return data, count, dictionary, reverse_dictionary依旧采取之前处理好的corpus,是一个二维列表,我们需要把它转换为一个一维列表,列表中的每个元素为语料分词结果。
def maybe_pickle(target_data, set_filename, force=False):
if os.path.exists(set_filename) and not force:
if os.path.getsize(set_filename) > 0:
# You may override by setting force=True.
print('%s already present - Skipping pickling.' % set_filename)
return set_filename
print('Pickling %s.' % set_filename)
try:
with open(set_filename, 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(target_data, f, pickle.HIGHEST_PROTOCOL)
except Exception as e:
print('Unable to save data to', set_filename, ':', e)
#with open("wiki_cn_chunk.txt", 'r') as f:
def loadData(data_file="./datat/data.pickle", count_file="./data/count.pickle", dict_file="./data/dictionary.pickle", rev_dict_file="./data/reverse_dictionary.pickle", force=False):
if os.path.exists(data_file) and os.path.exists(count_file) and os.path.exists(dict_file) and os.path.exists(rev_dict_file) and not force:
try:
print("Pickle files found, try to load data from pickle files...")
with open(data_file, 'rb') as f:
data = pickle.load(f)
with open(count_file, 'rb') as f:
count = pickle.load(f)
with open(dict_file, 'rb') as f:
dictionary = pickle.load(f)
with open(rev_dict_file, 'rb') as f:
reverse_dictionary = pickle.load(f)
print("Data loaded from pickle files successfully")
print('Most common words (+UNK)', count[:5])
print('Least common words', count[-10:])
print('Sample data', data[:10])
return data, count, dictionary, reverse_dictionary
except Exception as e:
print('Unable to load data', ':', e)
else:
#lines = tf.compat.as_str(f.read().decode("utf-8")).strip().split()
#lines = f.read().strip().decode("utf-8", "ignore").split()
#print(lines[:10])
#global corpus
words = []
for line in corpus:
words.extend(list(line))
print('Data size %d' % len(words))
print(words[:10])
print("Cooking data from words loaded...")
data, count, dictionary, reverse_dictionary = build_dataset(words)
print('Most common words (+UNK)', count[:5])
print('Least common words', count[-10:])
print('Sample data', data[:10])
del words # Hint to reduce memory.
print("Saving cooked data into pickle files...")
maybe_pickle(dictionary, "dictionary.pickle")
maybe_pickle(reverse_dictionary, "reverse_dictionary.pickle")
maybe_pickle(count, "count.pickle")
maybe_pickle(data, "data.pickle")
return data, count, dictionary, reverse_dictionary
data, count, dictionary, reverse_dictionary = loadData()- 获取批数据

data_index = 0
def generate_batch(batch_size, num_skips, skip_window):
global data_index
assert batch_size % num_skips == 0
assert num_skips <= 2 * skip_window
batch = np.ndarray(shape=(batch_size), dtype=np.int32)
labels = np.ndarray(shape=(batch_size, 1), dtype=np.int32)
span = 2 * skip_window + 1 # [ skip_window target skip_window ]
buffer = collections.deque(maxlen=span)
for _ in range(span):
buffer.append(data[data_index])
data_index = (data_index + 1) % len(data)
for i in range(batch_size // num_skips):
target = skip_window # target label at the center of the buffer
targets_to_avoid = [ skip_window ]
for j in range(num_skips):
while target in targets_to_avoid:
target = random.randint(0, span - 1)
targets_to_avoid.append(target)
batch[i * num_skips + j] = buffer[skip_window]
labels[i * num_skips + j, 0] = buffer[target]
buffer.append(data[data_index])
data_index = (data_index + 1) % len(data)
return batch, labels
print('data:', [reverse_dictionary[di] for di in data[:8]])
for num_skips, skip_window in [(2, 1), (4, 2)]:
data_index = 0
batch, labels = generate_batch(batch_size=16, num_skips=num_skips, skip_window=skip_window)
print('\nwith num_skips = %d and skip_window = %d:' % (num_skips, skip_window))
print(' batch:', [reverse_dictionary[bi] for bi in batch])
print(' labels:', [reverse_dictionary[li] for li in labels.reshape(16)])
- 构建计算图

batch_size = 128
embedding_size = 128 # Dimension of the embedding vector.
skip_window = 2 # How many words to consider left and right.
num_skips = 4 # How many times to reuse an input to generate a label.
# We pick a random validation set to sample nearest neighbors. here we limit the
# validation samples to the words that have a low numeric ID, which by
# construction are also the most frequent.
valid_size = 16 # Random set of words to evaluate similarity on.
valid_window = 100 # Only pick dev samples in the head of the distribution.
valid_examples = np.array(random.sample(range(valid_window), valid_size))
num_sampled = 64 # Number of negative examples to sample.
graph = tf.Graph()
with graph.as_default(), tf.device('/cpu:0'):
# Input data.
train_dataset = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=[batch_size])
train_labels = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[batch_size, 1])
valid_dataset = tf.constant(valid_examples, dtype=tf.int32)
# Variables.
embeddings = tf.Variable(
tf.random_uniform([vocabulary_size, embedding_size], -1.0, 1.0))
softmax_weights = tf.Variable(
tf.truncated_normal([vocabulary_size, embedding_size],
stddev=1.0 / math.sqrt(embedding_size)))
softmax_biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([vocabulary_size]))
# Model.
# Look up embeddings for inputs.
embed = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embeddings, train_dataset)
# Compute the softmax loss, using a sample of the negative labels each time.
loss = tf.reduce_mean(
tf.nn.sampled_softmax_loss(softmax_weights, softmax_biases, train_labels, embed,
num_sampled, vocabulary_size))
# Optimizer.
# Note: The optimizer will optimize the softmax_weights AND the embeddings.
# This is because the embeddings are defined as a variable quantity and the
# optimizer's `minimize` method will by default modify all variable quantities
# that contribute to the tensor it is passed.
# See docs on `tf.train.Optimizer.minimize()` for more details.
optimizer = tf.train.AdagradOptimizer(1.0).minimize(loss)
norm = tf.sqrt(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(embeddings), 1, keep_dims=True))
normalized_embeddings = embeddings / norm
valid_embeddings = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(normalized_embeddings, valid_dataset)
similarity = tf.matmul(valid_embeddings, normalized_embeddings, transpose_b=True)
- 创建会话

num_steps = 6001
#num_steps = 100001
#num_steps = 5000001
#max_steps = len(data) * num_skips - 100
with tf.Session(graph=graph) as session:
tf.initialize_all_variables().run()
print('Initialized')
average_loss = 0
for step in range(num_steps):
batch_data, batch_labels = generate_batch(
batch_size, num_skips, skip_window)
feed_dict = {train_dataset : batch_data, train_labels : batch_labels}
_, l = session.run([optimizer, loss], feed_dict=feed_dict)
average_loss += l
if step % 2000 == 0:
if step > 0:
average_loss = average_loss / 2000
# The average loss is an estimate of the loss over the last 2000 batches.
print('Average loss at step %d: %f' % (step, average_loss))
average_loss = 0
final_embeddings = normalized_embeddings.eval()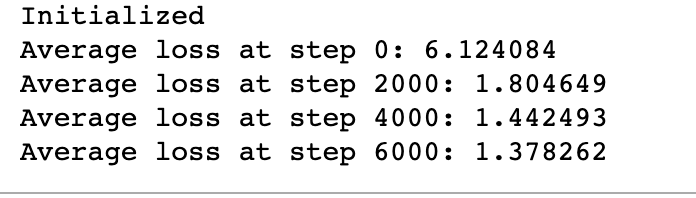
3.中文词向量可视化

num_points = 200
#使用TSNE进行降维可视化 把词向量从128维->2维
tsne = TSNE(perplexity=30, n_components=2, init='pca', n_iter=5000)
two_d_embeddings = tsne.fit_transform(final_embeddings[1:num_points+1, :])#设置中文字体 fname为本地中文字体路径
myfont = font_manager.FontProperties(fname='/System/Library/Fonts/Hiragino Sans GB.ttc')
def plot(embeddings, labels):
assert embeddings.shape[0] >= len(labels), 'More labels than embeddings'
pylab.figure(figsize=(15,15)) # in inches
for i, label in enumerate(labels):
x, y = embeddings[i,:]
pylab.scatter(x, y)
pylab.annotate(label, xy=(x, y), xytext=(5, 2), textcoords='offset points',
ha='right', va='bottom',fontproperties=myfont)
pylab.show()
words = [reverse_dictionary[i] for i in range(1, num_points+1)]
plot(two_d_embeddings, words)























 9251
9251











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








