英文是纯手打的!论文原文的summarizing and paraphrasing。可能会出现难以避免的拼写错误和语法错误,若有发现欢迎评论指正!文章偏向于笔记,谨慎食用!
目录
1. 省流版
1.1. 心得
(1)用自闭症数据集来预测智商??好吧(我真的想说这后面也没有圆回来!!!我还以为有什么惊为天人的发现呢!)
(2)从前面看是好简单的一个网络啊!后面看也没有很难
(3)这个随机选样本,hhhhh
(4)你有什么拓扑结构???我怎么没get到。提取的特征就是高级拓扑特征?
(5)宝宝你是一个...
1.2. 论文总结图

2. 论文逐段精读
2.1. Abstract
①Due to the complexity of brain connections and the change of topological structure in brain, IQ predictions always get inaccurate results
②They put forward a model including attention branch and global branch
2.2. Introduction
①There is no relevant topic of IQ prediction in ASD datasets
②Machine learning separate feature selection and regression. However, it is hard to obrain accurate advanced topological features from brain networks
③They proposed a Graph Convolutional Regression Network (GCR-Net) for IQ prediction
engrain v.使根深蒂固,深透,确立 adj.根深蒂固的
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Pipeline
①The schematic of GCR-Net
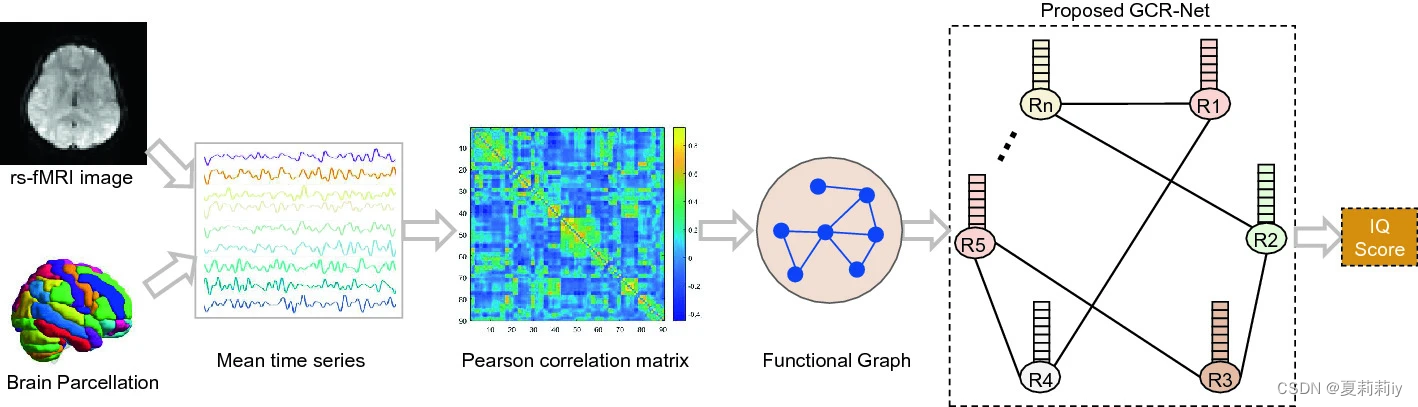
②Atlas: Automated Anatomical Labeling (AAL) with 116 ROIs
③Functional connectivity matrix : calculated by Pearson correlation
④The brain graph , where
are ROIs
2.3.2. Proposed Network
①Their overall framework:
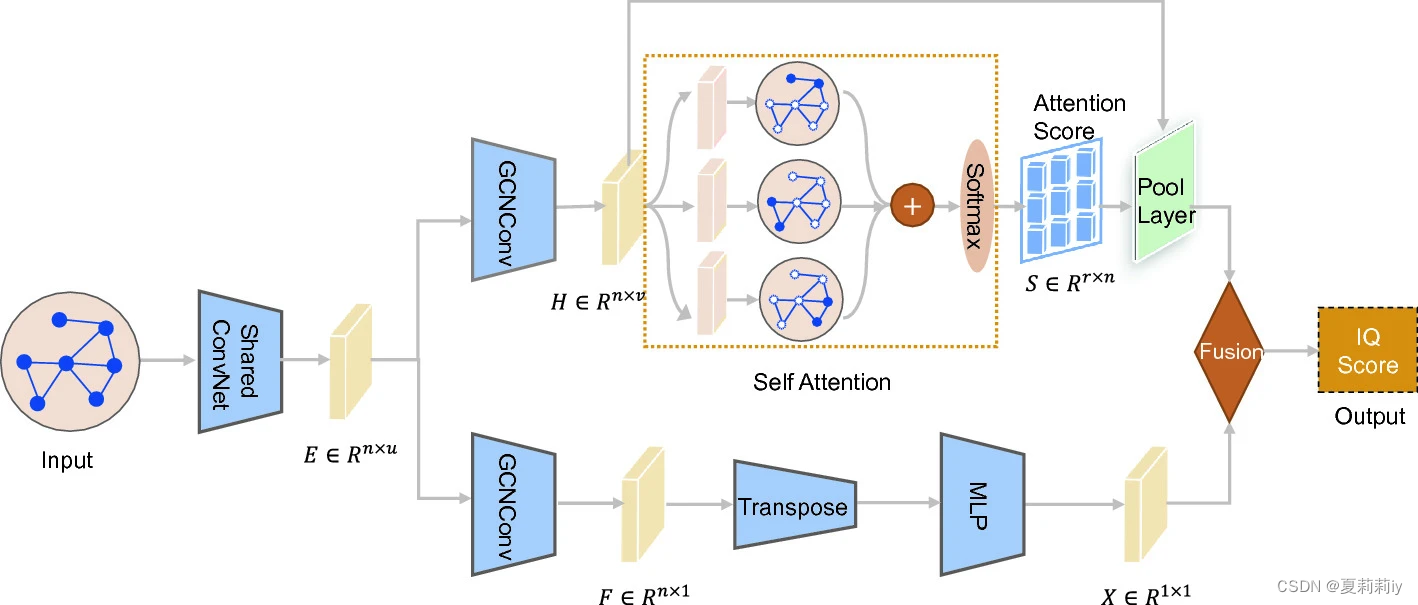
where denotes the node features
②The ConvNet includes a graph convolution (GC) layer and a dropout layer
(1)Attention branch
①The operation of GC:
where represents the degree matrix of
and they set
(等等,为什么我这里怎么也理解不了,这A是个啥玩意儿啊?);
denotes node features
②In the self attention module, the attention score can be calculated by:
③The pooling module contains matrix multiplication and maximum pooling. After pooling, it generates prediction
(2)Global branch
①The GC operation:
②Transposing and regrding it as a global (personal) feature
③MLP
(3)Finally, fusing and
with element-wise mean operation then giving the prediction
2.4. Experimental Results
2.4.1. Experimental Settings
(1)Settings
①Optimizer: Adam
②Learning rate: 0.001
③Weight decay: 0.0005
④⭐Poly learning rate: 0.9 power
⑤Maximum epoch: 100
⑥Loss function: mean square error (MSE)
⑦Hyper-parameters:
(2)Dataset
①Autism Brain Imaging Data Exchange (ABIDE) adopted
②Preprocessing pipelines: Connectome Computation System (CCS), Configurable Pipeline for the Analysis of Connectomes (CPAC), Data Processing Assistant for Resting-State fMRI (DPARSF), Neuroimaging Analysis Kit (NIAK)
③⭐Samples: randomly choosing 226 NT and 202 ASD
(3)Evaluation Metrics
①Cross validation: 3 fold, 2 for training and 1 for test
②Runs: mean of 3
③mean absolute error (MAE):
④root mean squared error (RMSE):
where is the predicted answer and
is the true label,
denotes the number of patients
2.4.2. Performance Evaluation
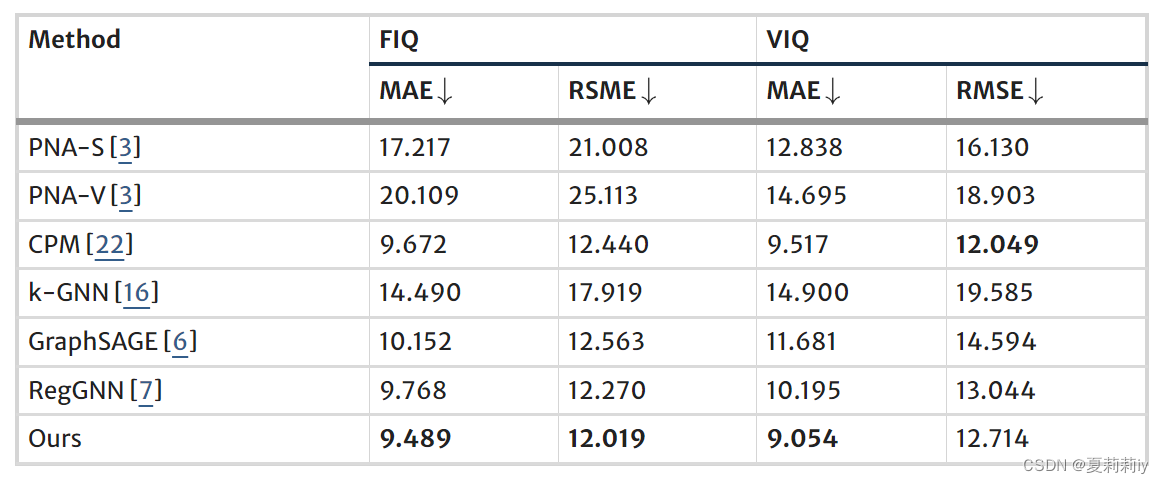
①Regression comparison in ASD:

②Regression comparison in NT:
2.4.3. Biomarker Detection
①5 most influential ROIs for IQ on ASD:
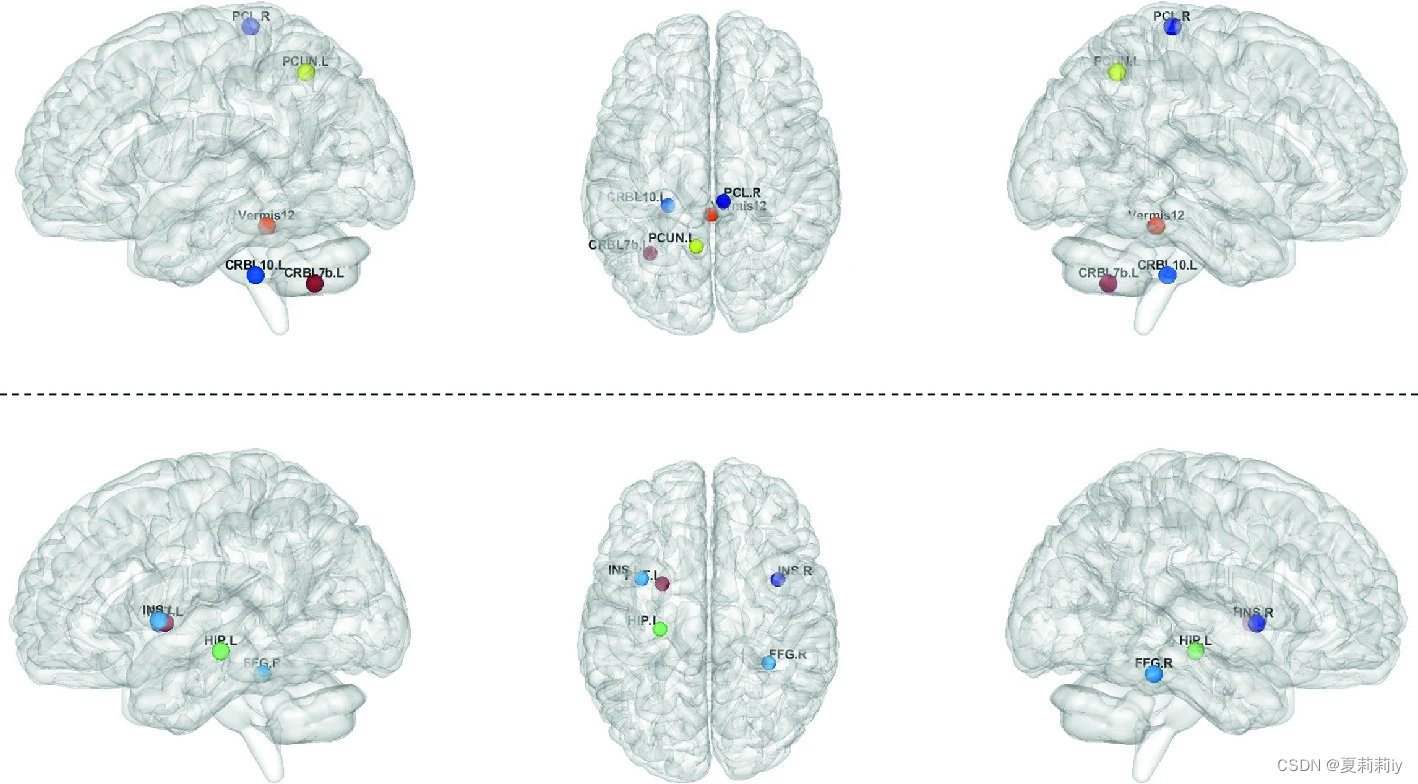
②5 most influential ROIs for IQ on NT:

③Analysing the similarity between predicted associated brain regions and medical research
episodic adj.不定期的;情节性的;偶尔发生的;有许多片段的;由松散片段组成的
2.5. Conclusion
No need for that.
3. 知识补充
3.1. Poly learning rate
参考学习1:Pytorch几种常用的学习率调整方式_pytorch poly-CSDN博客
参考学习2:pytorch动态调整学习率之Poly策略_poly学习率-CSDN博客
4. Reference List
Zhang H. et al. (2022) 'Intelligence Quotient Scores Prediction in rs-fMRI via Graph Convolutional Regression Network', CAAI International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 477-488. doi: Intelligence Quotient Scores Prediction in rs-fMRI via Graph Convolutional Regression Network | SpringerLink






















 782
782











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








