由于在看DRL论文中,很多公式都很难理解。因此最近在学习DRL的基本内容。
再此说明,非常推荐B站 “王树森 老师的DRL 强化学习” 本文的图表及内容,都是基于王老师课程的后自行理解整理出的内容。
目录
A.前文提示
在上篇文档中我们提到,训练AI agent 主要有两种方式。
一种是:基于Policy Π 的 Policy_Based_Learning method

一种是:基于 Optimal AC Func Value_Based_learning method
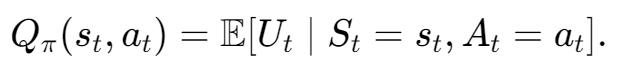

B. DQN Value_Based method
一、DQN算法介绍
游戏的目标是打赢游戏 = 强化学习中最大化奖励
DQN算法是Value based method,因此其依赖acion_value function
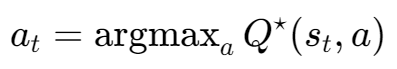
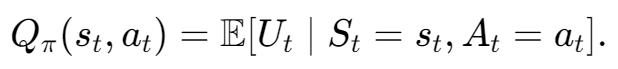
Value_Based method表示,在状态S下执行动作A的平均回报有多好(因为是考虑的期望)。(即Q*是一个先知,他能告诉每一个执行动作的平均回报)。DQN算法会选择Q值最高的动作
value-based method 即学习一个函数来近似Q*
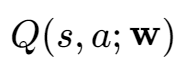
来近似估计
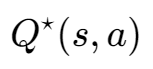
DQN算法的输入是S,输出是对于所有可能动作的打分(如果是左右上三个动作,即会产生一个3×1的向量)
二、TD算法的介绍
Temporal Difference Learning
目标使TD error变为0,即预计时间与实际值相等
TD error = Q(w)- TDTarget
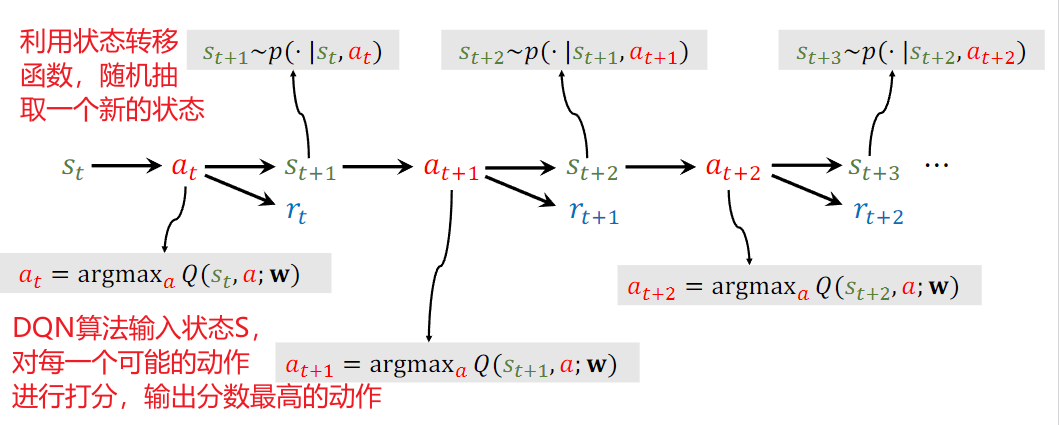
一个例子,从NYC到达ATL预计1000min 实际用了860min

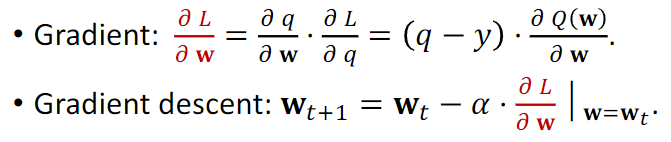

模型预测,
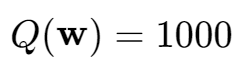
TD target = 300+600 = 900 300是实际值,600是估计值。
因此,TD target值相较于估测值Q(w)更加可靠。
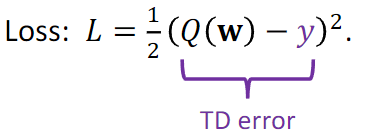

三、如何使用TD算法 训练DQN
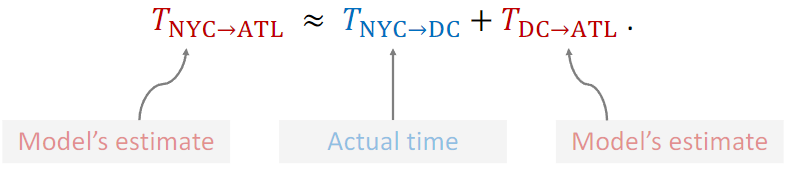

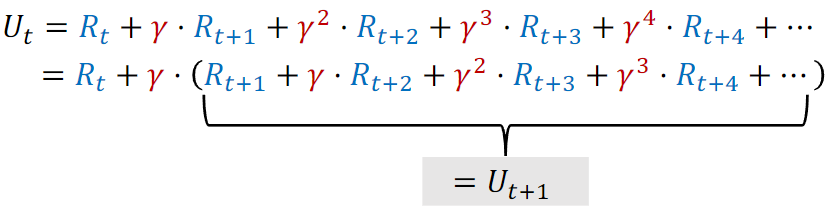
因此

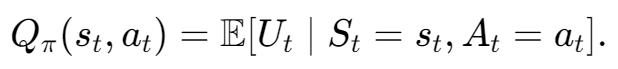


对两边同求期望,得到下面式子
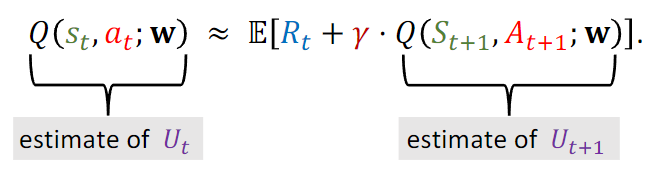

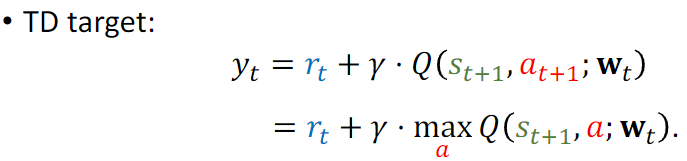
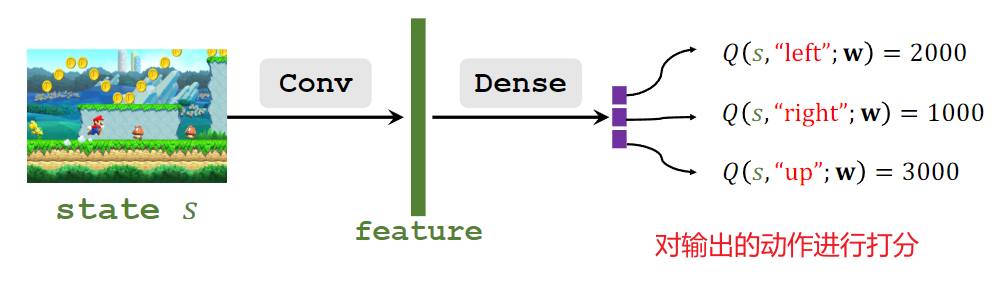
DQN算法根据当前状态St+1 对每一个动作进行打分。并选择分数最高的动作。

C. DQN算法总结
思想
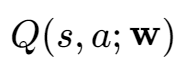
来近似估计
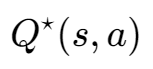
观测到状态S
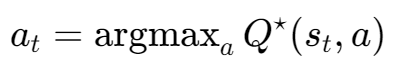
基于状态S,求得使Q值分数最大的A(实际的Q值)
有了 S 和 A 后
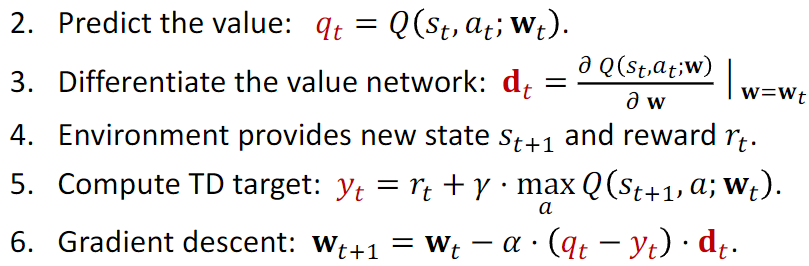

























 3362
3362

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










