文献速递:人工智能医学影像分割------基于REMU-Net的肺结节分割
01
文献速递介绍
肺癌的死亡率很高。通过CT对肺结节进行早期筛查可以降低20%的肺癌死亡率。然而,在CT图像上,肺结节显得很小,其形态、亮度和其他特征与血管以及肺实质中的其他组织相似,使得视觉检查不足以区分它们。目前,肺结节的分割可以通过计算机视觉技术解决,但分割效果不佳将直接影响医生的下一步诊断。因此,探索如何提高肺结节分割的准确性将是有价值的。为了解决上述问题,Wang等提出了一种以中心为焦点的卷积神经网络。刘等提出了一种级联双路径残差网络。乌斯曼等提出了一种基于自适应ROI的体积肺结节分割方法,采用多视角残差学习。近年来,一些基于U-Net的改进方法在处理医学图像分割问题上表现良好,例如U-Net++、Attention U-Net、U-Net 3+等。其中,有许多方法专门应用于CT图像中肺结节的分割。童等提出了一种基于改进U-Net的肺结节分割方法。罗查等使用一种名为SegU-Net的新网络来分割肺结节。史等提出了一种基于多尺度残差U-Net的肺结节自动分割算法。表1显示了以前肺结节分割的方法。本文的主要贡献是创建了一种更适合肺结节分割的REMU-Net。REMU-Net中的R、E和M分别代表ResNeSt-SAM、增强模块和多尺度跳跃连接。增强模块和ResNeSt-SAM用于提高U-Net网络提取特征信息的有效性。开发了一种新的多尺度跳跃连接,以减少同一尺度上的信息丢失,同时也获得了其他尺度上的平衡信息。
Title
题目
Pulmonary nodule segmentation based on REMU‑Net
基于REMU-Net的肺结节分割
Abstract
摘要
In recent years, U-Net has shown excellent performance in medical image segmentation, but it cannot accurately segment nodules of smaller size when segmenting pulmonary nodules. To make it more accurate to segment pulmonary nodules in CT images, U-Net is improved to REMU-Net. First, ResNeSt, which is the state-of-the-art ResNet variant, is used as the backbone of the U-Net, and a spatial attention module is introduced into the Split-Attention block of ResNeSt to enable the network to extract more diverse and efcient features. Secondly, a feature enhancement module based on the atrous spatial pyramid pooling (ASPP) is introduced in the U-Net, which is utilized to obtain more abundant context information. Finally, replacing the skip connection of the U-Net with a multi-scale skip connection overcomes the limitation that the decoder subnet can only accept same-scale feature information. Experiments show that REMU-Net has a Dice score of 84.76% on the LIDC-IDRI dataset. The network has better segmentation performance than most other existing U-Net improvement networks.
近年来,U-Net在医学图像分割方面表现出色,但在分割肺结节时,无法准确分割较小尺寸的结节。为了更准确地在CT图像中分割肺结节,U-Net被改进为REMU-Net。首先,使用最先进的ResNet变体ResNeSt作为U-Net的主干,并将空间注意力模块引入到ResNeSt的Split-Attention块中,使网络能够提取更多样化和高效的特征。其次,在U-Net中引入了基于空洞空间金字塔池化(ASPP)的特征增强模块,用于获取更丰富的上下文信息。最后,通过使用多尺度跳跃连接替换U-Net的跳跃连接,克服了解码子网只能接受同尺度特征信息的限制。实验表明,在LIDC-IDRI数据集上,REMU-Net的Dice分数为84.76%。该网络的分割性能优于大多数现有的U-Net改进网络。
Results
结果
Figure 6 shows the trend of loss during the training of REMU-Net. To prevent too many training iterations, the model relies too much on the distribution of the training data and is prone to overftting. In this paper, the appropriate number of training iterations is determined by using the early stopping strategy. As can be seen from the graph, the large learning rate in the early stage leads to a large oscillation in the test set. Still, the loss curve generally shows a decreasing trend, indicating that the model is in the process of optimization and the prediction loss bias of the model gradually becomes smaller. After training 38 epochs, the loss of the validation set gradually stabilizes, and the loss function reaches a state of convergence around 50 epochs. Therefore, the number of training iterations in the experiments in this paper is set at 50.
图 6 展示了REMU-Net训练过程中损失的趋势。为了防止过多的训练迭代,模型过度依赖训练数据的分布,并容易出现过拟合。在本文中,通过使用早停策略来确定适当的训练迭代次数。从图中可以看出,早期较大的学习率导致测试集中出现较大的波动。然而,损失曲线总体呈现下降趋势,表明模型处于优化过程中,模型的预测损失偏差逐渐变小。经过38个周期的训练后,验证集的损失逐渐稳定,并且损失函数在大约50个周期左右达到收敛状态。因此,本文实验中的训练迭代次数设定为50次。
Methods
方法
The CT images used in this paper are from the LIDCIDRI public dataset . To avoid redundant information interfering with the efectiveness of network segmentation, the lung parenchyma is extracted from CT images using morphological methods before the data is input to the network. Pulmonary nodules represent only a small percentage of the CT images, which also means a large gap between the background class and the pulmonary nodule class. If the images are directly fed into the network, it will interfere with the training process of the network. To avoid these problems as much as possible, the lung parenchyma images are cropped into small 6464 blocks centered on pulmonary nodules. Figure 1 shows the input image and label. In this paper, 1487 CT images with pulmonary nodules labelled by more than two doctors are preprocessed and made into a dataset. They are divided into training sets, validation sets, and test sets according to 7:2:1, with 1041 pulmonary nodules as training sets, 297 pulmonary nodules as validation sets, and 149 pulmonary nodules as test sets. To refect the efect of feature enhancement, the input data is resized to a resolution of 256256 and normalization to increase the speed of network convergence. In addition, online data augmentation (fip vertically, horizontal mirror) is used to increase the diversity of the data
本文中使用的CT图像来自公共数据集LIDC-IDRI 。为了避免冗余信息干扰网络分割的有效性,在将数据输入网络之前,使用形态学方法从CT图像中提取肺实质。肺结节在CT图像中只占很小的比例,这也意味着背景类别与肺结节类别之间存在很大差距。如果图像直接输入到网络,将干扰网络的训练过程。为了尽可能避免这些问题,肺实质图像被裁剪成以肺结节为中心的小型6464块。图1展示了输入图像和标签。在本文中,由两位以上医生标记的1487张带有肺结节的CT图像被预处理并制成数据集。它们按照7:2:1的比例划分为训练集、验证集和测试集,训练集有1041个肺结节,验证集有297个肺结节,测试集有149个肺结节。为了反映特征增强的效果,输入数据被调整为256256的分辨率,并进行归一化处理以增加网络收敛速度。此外,还使用在线数据增强(垂直翻转、水平镜像)来增加数据的多样性。
Conclusions
结论
In this paper, U-Net based REMU-Net is proposed for more accurate segmentation of pulmonary nodules. Firstly, the network introduces ResNeSt and implements the crosstalk of spatial attention and channel attention in Split-Attention block. Secondly an enhancement model built based on ASPP is introduced at the bridge of encoder and decoder. Finally, novel multi-scale skip connection is designed. Tests on the LIDC-IDRI dataset showed that REMU-Net outperformed most improved U-Net structures in segmenting lung nodules. In addition, the network has better fexibility to choose a suitable architecture according to the computational resources and task requirements. In summary, the REMUNet based pulmonary nodule segmentation method proposed in this paper achieves efcient and accurate pulmonary nodule segmentation, especially for small-sized nodules with excellent segmentation performance. It provides strong support for the physician’s next diagnosis.
本文提出了基于U-Net的REMU-Net,用于更准确地分割肺结节。首先,网络引入ResNeSt,并在Split-Attention块中实现空间注意力和通道注意力的交叉作用。其次,在编码器和解码器的桥接处引入了基于ASPP构建的增强模型。最后,设计了新型的多尺度跳跃连接。在LIDC-IDRI数据集上的测试表明,REMU-Net在分割肺结节方面优于大多数改进的U-Net结构。此外,该网络具有更好的灵活性,可以根据计算资源和任务需求选择合适的架构。总之,本文提出的基于REMU-Net的肺结节分割方法实现了高效准确的肺结节分割,尤其是对小尺寸结节具有出色的分割性能。它为医生的下一步诊断提供了有力支持。
Figure
图
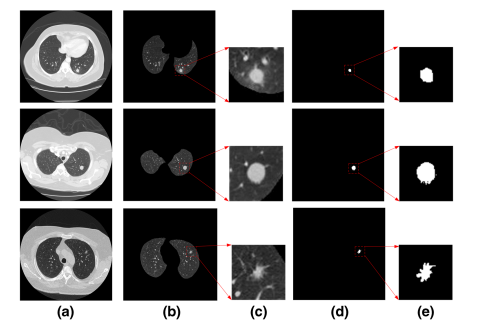
Fig. 1 The input image and label. a CT image, b lung parenchyma, c input image, d pulmonary nodule mask, e input label
图 1 输入图像和标签。a CT图像,b 肺实质,c 输入图像,d 肺结节掩模,e 输入标签
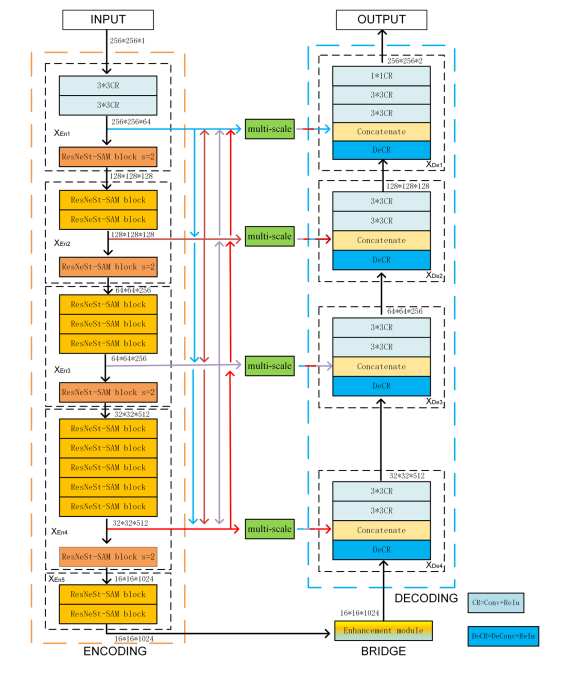
Fig. 2 REMU-Net structure
图 2 REMU-Net结构
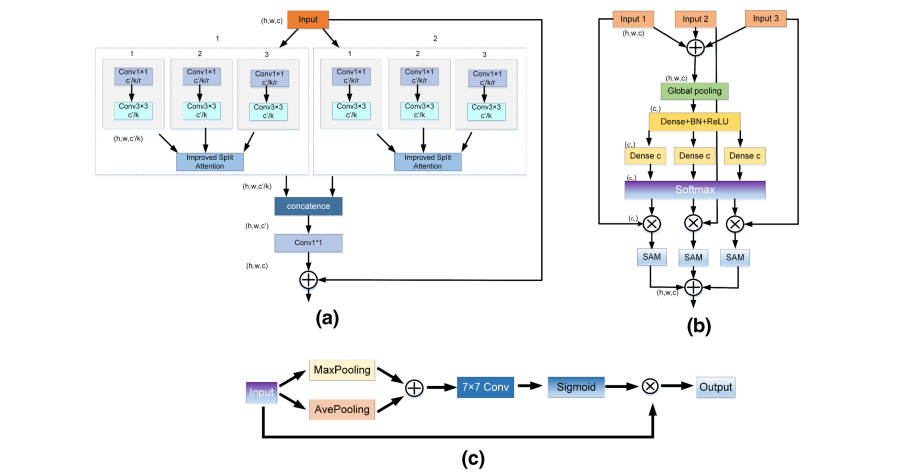
Fig. 3 Architectural of ResNeSt-SAM. a ResNeSt-SAM, b improved Split-Attention block, c spatial attention module
图 3 ResNeSt-SAM的架构。a ResNeSt-SAM,b 改进的Split-Attention块,c 空间注意力模块
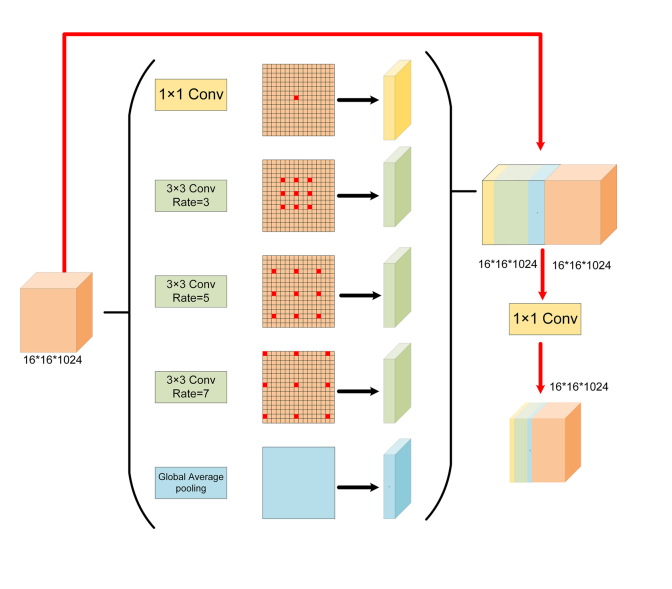
Fig. 4 Enhancement module architecture
图 4 增强模块架构
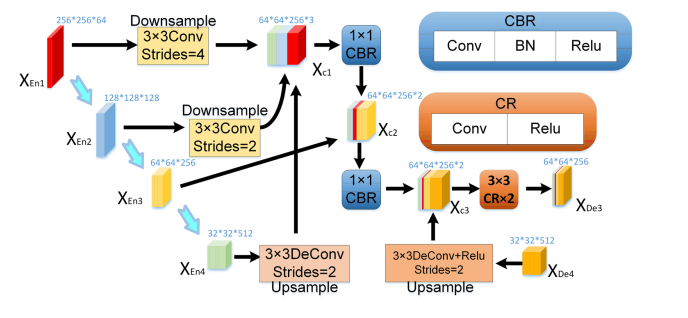
Fig. 5 Graphical diagram for constructing the feature map of decoder layers XDe3
图 5 构建解码层XDe3特征图的图形图表
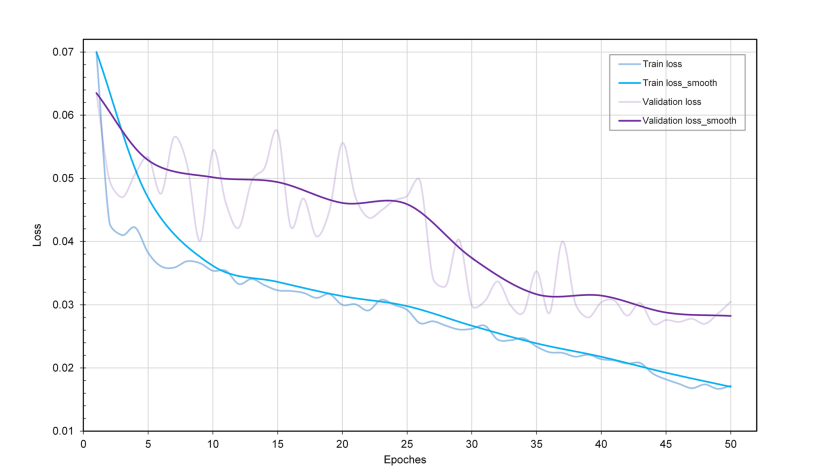
Fig. 6 Curve of loss. Loss smooth is the average loss every fve epochs
图 6 损失曲线。损失平滑是每五个周期的平均损失。
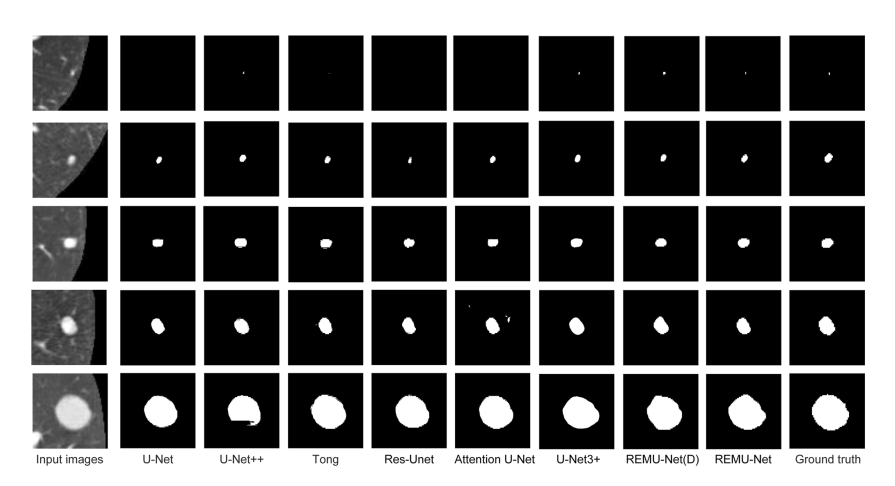

Fig. 7 Segmentation results
图 7 分割结果

Fig. 8 Segmentation results of juxta-pleural nodules, GGO and juxta-vascular nodules
图 8 胸膜旁结节、磨玻璃影(GGO)和血管旁结节的分割结果
Table
表
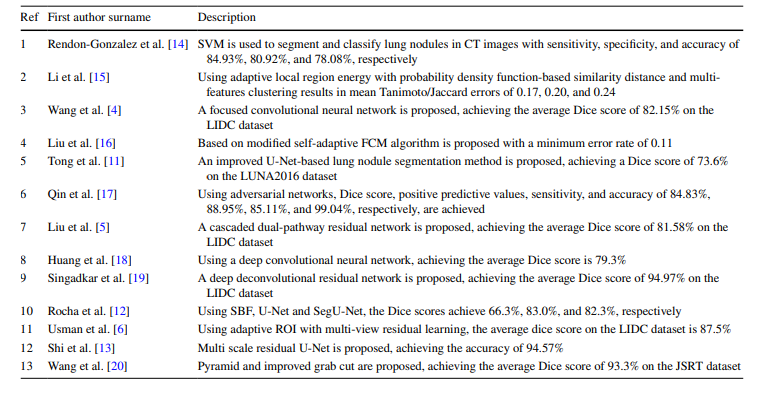
Table 1 Previous approaches to segmentation of pulmonary nodules
表 1 肺结节分割的先前方法

Table 2 Ablation experiments results
表 2 消融实验结果
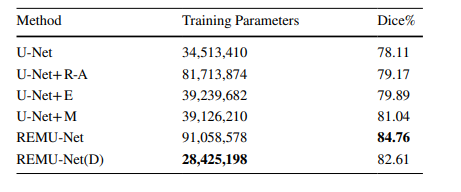
Table 3 Training parameters for diferent structures
表 3 不同结构的训练参数
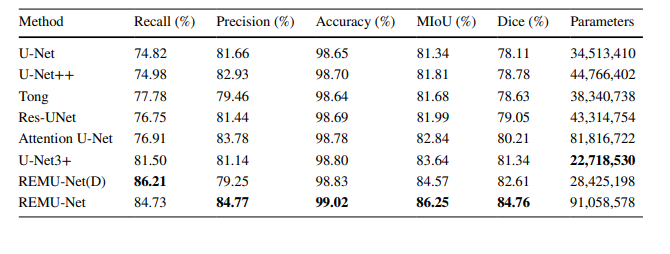
Table 4 The results of diferent U-Net improvement networks
表 4 不同U-Net改进网络的结果





















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








