BRISK特征点描述算法详解
简介
BRISK算法是2011年ICCV上《BRISK:Binary Robust Invariant Scalable Keypoints》文章中,提出来的一种特征提取算法,也是一种二进制的特征描述算子。
它具有较好的旋转不变性、尺度不变性,较好的鲁棒性等。在图像配准应用中,速度比较:SIFT<SURF<BRISK<FREAK<ORB,在对有较大模糊的图像配准时,BRISK算法在其中表现最为出色。
BRISK算法
特征点检测
BRISK算法主要利用FAST9-16进行特征点检测(为什么是主要?因为用到一次FAST5-8),可参见博客:FAST特征点检测算法。要解决尺度不变性,就必须在尺度空间进行特征点检测,于是BRISK算法中构造了图像金字塔进行多尺度表达。
建立尺度空间
构造n个octave层(用ci表示)和n个intra-octave层(用di表示),文章中n=4,i={0,1,…,n-1}。假设有图像img,octave层的产生:c0层就是img原图像,c1层是c0层的2倍下采样,c2层是c1层的2倍下采样,以此类推。intra-octave层的产生:d0层是img的1.5倍下采样,d1层是d0层的2倍下采样(即img的2*1.5倍下采样),d2层是d1层的2倍下采样,以此类推。
则ci、di层与原图像的尺度关系用t表示为:
t
(
c
i
)
=
2
i
,
t
(
d
i
)
=
2
i
⋅
1.5
t\left(c_{i}\right)=2^{i}, t\left(d_{i}\right)=2^{i} \cdot 1.5
t(ci)=2i,t(di)=2i⋅1.5,
ci、di层与原图像大小关系为:
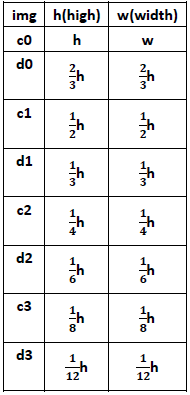
由于n=4,所以一共可以得到8张图,octave层之间尺度(缩放因子)是2倍关系,intra-octave层之间尺度(缩放因子)也是2倍关系。
特征点检测
对这8张图进行FAST9-16角点检测,得到具有角点信息的8张图,对原图像img进行一次FAST5-8角点检测(当做d(-1)层,虚拟层),总共会得到9幅有角点信息的图像。
非极大值抑制
对这9幅图像,进行空间上的非极大值抑制(同SIFT算法的非极大值抑制):特征点在位置空间(8邻域点)和尺度空间(上下层2x9个点),共26个邻域点的FAST的得分值要最大,否则不能当做特征点;此时得到的极值点还比较粗糙,需要进一步精确定位。
亚像素插值
进过上面步骤,得到了图像特征点的位置和尺度,在极值点所在层及其上下层所对应的位置,对FAST得分值(共3个)进行二维二次函数插值(x、y方向),得到真正意义上的得分极值点及其精确的坐标位置(作为特征点位置);再对尺度方向进行一维插值,得到极值点所对应的尺度(作为特征点尺度)。
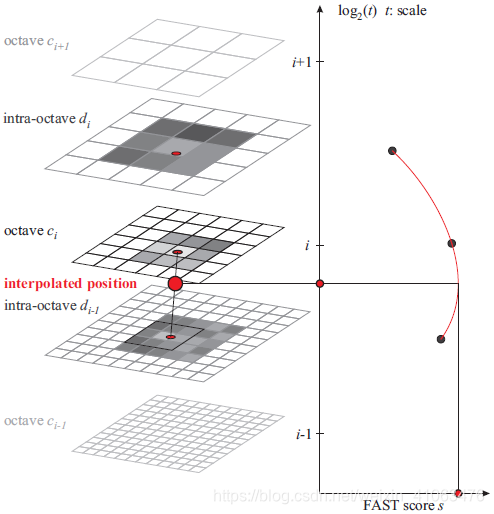
特征点描述
高斯滤波
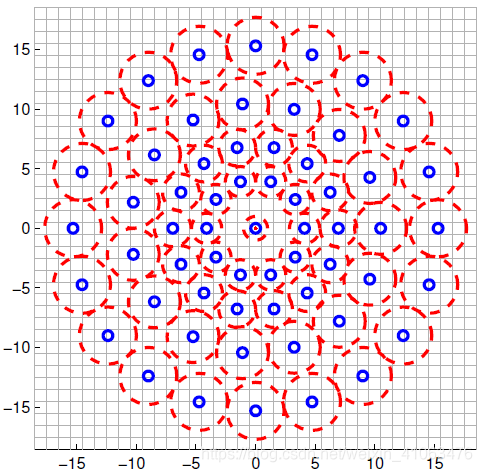
现在,我们得到了特征点的位置和尺度(t)后,要对特征点赋予其描述符。均匀采样模式:以特征点为中心,构建不同半径的同心圆,在每个圆上获取一定数目的等间隔采样点(所有采样点包括特征点,一共N个),由于这种邻域采样模式会引起混叠效应,所以需要对同心圆上的采样点进行高斯滤波。
采样模式如下图,蓝圈表示;以采样点为中心,为方差进行高斯滤波,滤波半径大小与高斯方差的大小成正比,红圈表示。最终用到的N个采样点是经过高斯平滑后的采样点。下图是t=1时的。(文章中:N=60)
局部梯度计算
由于有N个采样点,则采样点两两组合成一对,共有N(N-1)/2钟组合方式,所有组合方式的集合称作采样点对,用集合
A
=
{
(
p
i
,
p
j
)
∈
R
2
×
R
2
∣
i
<
N
∧
j
<
i
∧
i
,
j
∈
N
}
\mathcal{A}=\left\{\left(\mathbf{p}_{i}, \mathbf{p}_{j}\right) \in \mathbb{R}^{2} \times \mathbb{R}^{2} | i<N \wedge j<i \wedge i, j \in \mathbb{N}\right\}
A={(pi,pj)∈R2×R2∣i<N∧j<i∧i,j∈N}表示,其中像素分别是
I
(
p
i
,
σ
i
)
,
I
(
p
j
,
σ
j
)
I\left(\mathbf{p}_{i}, \sigma_{i}\right) ,I\left(\mathbf{p}_{j}, \sigma_{j}\right)
I(pi,σi),I(pj,σj),
σ
\sigma
σ表示尺度。用
g
(
p
i
,
p
j
)
\mathbf{g}\left(\mathbf{p}_{i}, \mathbf{p}_{j}\right)
g(pi,pj)表示特征点局部梯度集合,则有:
g
(
p
i
,
p
j
)
=
(
p
j
−
p
i
)
⋅
I
(
p
j
,
σ
j
)
−
I
(
p
i
,
σ
i
)
∥
p
j
−
p
i
∥
2
\mathbf{g}\left(\mathbf{p}_{i}, \mathbf{p}_{j}\right)=\left(\mathbf{p}_{j}-\mathbf{p}_{i}\right) \cdot \frac{I\left(\mathbf{p}_{j}, \sigma_{j}\right)-I\left(\mathbf{p}_{i}, \sigma_{i}\right)}{\left\|\mathbf{p}_{j}-\mathbf{p}_{i}\right\|^{2}}
g(pi,pj)=(pj−pi)⋅∥pj−pi∥2I(pj,σj)−I(pi,σi)
定义短距离点对子集、长距离点对子集(L个):
S
=
{
(
p
i
,
p
j
)
∈
A
∣
∥
p
j
−
p
i
∥
<
δ
max
}
⊆
A
\mathcal{S}=\left\{\left(\mathbf{p}_{i}, \mathbf{p}_{j}\right) \in \mathcal{A} |\left\|\mathbf{p}_{j}-\mathbf{p}_{i}\right\|<\delta_{\max }\right\} \subseteq \mathcal{A}
S={(pi,pj)∈A∣∥pj−pi∥<δmax}⊆A
L
=
{
(
p
i
,
p
j
)
∈
A
∣
∥
p
j
−
p
i
∥
>
δ
min
}
⊆
A
\mathcal{L}=\left\{\left(\mathbf{p}_{i}, \mathbf{p}_{j}\right) \in \mathcal{A} |\left\|\mathbf{p}_{j}-\mathbf{p}_{i}\right\|>\delta_{\min }\right\} \subseteq \mathcal{A}
L={(pi,pj)∈A∣∥pj−pi∥>δmin}⊆A
其中 δ max = 9.75 t δ min = 13.67 t \delta_{\text {max}}=9.75 t \quad \delta_{\min }=13.67 t δmax=9.75tδmin=13.67t, t t t是特征点所在的尺度。
现在要利用上面得到的信息,来计算特征点的主方向(注意:此处只用到了长距离子集),如下:
g
=
(
g
x
g
y
)
=
1
L
⋅
∑
(
p
i
,
p
j
)
∈
L
g
(
p
i
,
p
j
)
\mathbf{g}=\left( \begin{array}{c}{g_{x}} \\ {g_{y}}\end{array}\right)=\frac{1}{L} \cdot \sum_{\left(\mathbf{p}_{i}, \mathbf{p}_{j}\right) \in \mathcal{L}} \mathbf{g}\left(\mathbf{p}_{i}, \mathbf{p}_{j}\right)
g=(gxgy)=L1⋅∑(pi,pj)∈Lg(pi,pj)
α
=
arctan
2
(
g
y
,
g
x
)
\alpha=\arctan 2\left(g_{y}, g_{x}\right)
α=arctan2(gy,gx)
特征描述符
要解决旋转不变性,则需要对特征点周围的采样区域进行旋转到主方向,旋转后得到新的采样区域,采样模式同上。BRISK描述子是二进制的特征,由采样点集合可得到N(N-1)/2对采样点对,就可以得到N(N-1)/2个距离的集合(包含长、短距离子集),考虑其中短距离子集中的512个短距离点对,进行二进制编码,判断方式如下:
b = { 1 , I ( p j α , σ j ) > I ( p i α , σ i ) 0 , otherwise b=\left\{\begin{array}{ll}{1,} & {I\left(\mathbf{p}_{j}^{\alpha}, \sigma_{j}\right)>I\left(\mathbf{p}_{i}^{\alpha}, \sigma_{i}\right)} \\ {0,} & {\text { otherwise }}\end{array}\right. b={1,0,I(pjα,σj)>I(piα,σi) otherwise
∀
(
p
i
α
,
p
j
α
)
∈
S
\forall\left(\mathbf{p}_{i}^{\alpha}, \mathbf{p}_{j}^{\alpha}\right) \in \mathcal{S}
∀(piα,pjα)∈S
其中,
I
(
p
j
α
,
σ
j
)
I\left(\mathbf{p}_{j}^{\alpha}, \sigma_{j}\right)
I(pjα,σj)带有上标,表示经过旋转a角度后的,新的采样点。由此可得到,512Bit的二进制编码,也就是64个字节(BRISK64)。
匹配方法
汉明距离进行比较,与其他二进制描述子的匹配方式一样。
实验
opencv代码
#include <cv.h>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/nonfree/features2d.hpp>
#include <opencv2/nonfree/nonfree.hpp>
#include <Windows.h>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//Load Image
Mat c_src1 = imread( "1.png");
Mat c_src2 = imread("2.png");
Mat src1 = imread( "1.png", CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE);
Mat src2 = imread( "2.png", CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE);
if( !src1.data || !src2.data )
{
cout<< "Error reading images " << std::endl;
return -1;
}
//feature detect
BRISK detector;
vector<KeyPoint> kp1, kp2;
double start = GetTickCount();
detector.detect( src1, kp1 );
detector.detect( src2, kp2 );
//cv::BRISK extractor;
Mat des1,des2;//descriptor
detector.compute(src1, kp1, des1);
detector.compute(src2, kp2, des2);
Mat res1,res2;
int drawmode = DrawMatchesFlags::DRAW_RICH_KEYPOINTS;
drawKeypoints(c_src1, kp1, res1, Scalar::all(-1), drawmode);//画出特征点
drawKeypoints(c_src2, kp2, res2, Scalar::all(-1), drawmode);
cout<<"size of description of Img1: "<<kp1.size()<<endl;
cout<<"size of description of Img2: "<<kp2.size()<<endl;
BFMatcher matcher(NORM_HAMMING);
vector<DMatch> matches;
matcher.match(des1, des2, matches);
double end = GetTickCount();
cout<<"耗时:"<<(end - start) <<"ms"<<endl;
Mat img_match;
drawMatches(src1, kp1, src2, kp2, matches, img_match);
cout<<"number of matched points: "<<matches.size()<<endl;
imshow("matches",img_match);
cvWaitKey(0);
cvDestroyAllWindows();
return 0;
}
实验结果

视频地址
http://v.youku.com/v_show/id_XMTI5MzI3Mzk0OA==.html
代码分析
由于代码都很长,只列出了brisk类的两个方法,其余详见:…\opencv\sources\modules\features2d\src\brisk.c
// construct the image pyramids(构造图像金字塔)
void
BriskScaleSpace::constructPyramid(const cv::Mat& image)
{
// set correct size:
pyramid_.clear();
// fill the pyramid:
pyramid_.push_back(BriskLayer(image.clone()));
if (layers_ > 1)
{
pyramid_.push_back(BriskLayer(pyramid_.back(), BriskLayer::CommonParams::TWOTHIRDSAMPLE));//d0层是2/3
}
const int octaves2 = layers_;
for (uchar i = 2; i < octaves2; i += 2)
{
pyramid_.push_back(BriskLayer(pyramid_[i - 2], BriskLayer::CommonParams::HALFSAMPLE));//c?层是前两层的1/2
pyramid_.push_back(BriskLayer(pyramid_[i - 1], BriskLayer::CommonParams::HALFSAMPLE));//d?层是前两层的1/2(除d0层外)
}
}
//提取特征点
void
BriskScaleSpace::getKeypoints(const int threshold_, std::vector<cv::KeyPoint>& keypoints)
{
// make sure keypoints is empty
keypoints.resize(0);
keypoints.reserve(2000);
// assign thresholds
int safeThreshold_ = (int)(threshold_ * safetyFactor_);
std::vector<std::vector<cv::KeyPoint> > agastPoints;
agastPoints.resize(layers_);
// go through the octaves and intra layers and calculate fast corner scores:
for (int i = 0; i < layers_; i++)
{
// call OAST16_9 without nms
BriskLayer& l = pyramid_[i];
l.getAgastPoints(safeThreshold_, agastPoints[i]);
}
if (layers_ == 1)
{
// just do a simple 2d subpixel refinement...
const size_t num = agastPoints[0].size();
for (size_t n = 0; n < num; n++)
{
const cv::Point2f& point = agastPoints.at(0)[n].pt;
// first check if it is a maximum:
if (!isMax2D(0, (int)point.x, (int)point.y))
continue;
// let's do the subpixel and float scale refinement:
BriskLayer& l = pyramid_[0];
int s_0_0 = l.getAgastScore(point.x - 1, point.y - 1, 1);
int s_1_0 = l.getAgastScore(point.x, point.y - 1, 1);
int s_2_0 = l.getAgastScore(point.x + 1, point.y - 1, 1);
int s_2_1 = l.getAgastScore(point.x + 1, point.y, 1);
int s_1_1 = l.getAgastScore(point.x, point.y, 1);
int s_0_1 = l.getAgastScore(point.x - 1, point.y, 1);
int s_0_2 = l.getAgastScore(point.x - 1, point.y + 1, 1);
int s_1_2 = l.getAgastScore(point.x, point.y + 1, 1);
int s_2_2 = l.getAgastScore(point.x + 1, point.y + 1, 1);
float delta_x, delta_y;
float max = subpixel2D(s_0_0, s_0_1, s_0_2, s_1_0, s_1_1, s_1_2, s_2_0, s_2_1, s_2_2, delta_x, delta_y);
// store:
keypoints.push_back(cv::KeyPoint(float(point.x) + delta_x, float(point.y) + delta_y, basicSize_, -1, max, 0));
}
return;
}
float x, y, scale, score;
for (int i = 0; i < layers_; i++)
{
BriskLayer& l = pyramid_[i];
const size_t num = agastPoints[i].size();
if (i == layers_ - 1)
{
for (size_t n = 0; n < num; n++)
{
const cv::Point2f& point = agastPoints.at(i)[n].pt;
// consider only 2D maxima...
if (!isMax2D(i, (int)point.x, (int)point.y))
continue;
bool ismax;
float dx, dy;
getScoreMaxBelow(i, (int)point.x, (int)point.y, l.getAgastScore(point.x, point.y, safeThreshold_), ismax, dx, dy);
if (!ismax)
continue;
// get the patch on this layer:
int s_0_0 = l.getAgastScore(point.x - 1, point.y - 1, 1);
int s_1_0 = l.getAgastScore(point.x, point.y - 1, 1);
int s_2_0 = l.getAgastScore(point.x + 1, point.y - 1, 1);
int s_2_1 = l.getAgastScore(point.x + 1, point.y, 1);
int s_1_1 = l.getAgastScore(point.x, point.y, 1);
int s_0_1 = l.getAgastScore(point.x - 1, point.y, 1);
int s_0_2 = l.getAgastScore(point.x - 1, point.y + 1, 1);
int s_1_2 = l.getAgastScore(point.x, point.y + 1, 1);
int s_2_2 = l.getAgastScore(point.x + 1, point.y + 1, 1);
float delta_x, delta_y;
float max = subpixel2D(s_0_0, s_0_1, s_0_2, s_1_0, s_1_1, s_1_2, s_2_0, s_2_1, s_2_2, delta_x, delta_y);
// store:
keypoints.push_back(
cv::KeyPoint((float(point.x) + delta_x) * l.scale() + l.offset(),
(float(point.y) + delta_y) * l.scale() + l.offset(), basicSize_ * l.scale(), -1, max, i));
}
}
else
{
// not the last layer:
for (size_t n = 0; n < num; n++)
{
const cv::Point2f& point = agastPoints.at(i)[n].pt;
// first check if it is a maximum:
if (!isMax2D(i, (int)point.x, (int)point.y))
continue;
// let's do the subpixel and float scale refinement:
bool ismax=false;
score = refine3D(i, (int)point.x, (int)point.y, x, y, scale, ismax);
if (!ismax)
{
continue;
}
// finally store the detected keypoint:
if (score > float(threshold_))
{
keypoints.push_back(cv::KeyPoint(x, y, basicSize_ * scale, -1, score, i));
}
}
}
}
}
参考文献
1、BRISK:binary robust invariant scalable keypoints,2011,ICCV.





















 2542
2542











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








