FPGA学习: Verilog刷题记录(4)
刷题网站 : HDLBits
第二章 : Verilog Language
第4节 :Procedures
-
Always blocks(combinational)
- 题目描述:Build an AND gate using both an assign statement and a combinational always block

-
题目分析:题目要求分别用assign语句和always语句来创建一个与门,明确语法如何使用的即可
-
解答:
/*我的解答*/ module top_module( input a, input b, output wire out_assign, output reg out_alwaysblock ); assign out_assign = a & b; always@(*) out_alwaysblock <= a & b; endmodule /*官网答案*/ 无 -
Always blocks(clocked)
-
题目描述:Build an XOR gate three ways, using an assign statement, a combinational always block, and a clocked always block. Note that the clocked always block produces a different circuit from the other two: There is a flip-flop so the output is delayed.
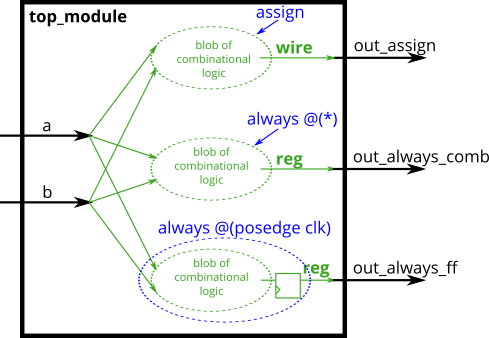
-
题目分析:题目要求我们用三种方式创建一个异或门,同样是知道语法如何就能完成
-
解答:
/*我的解答*/ module top_module( input clk, input a, input b, output wire out_assign, output reg out_always_comb, output reg out_always_ff ); // using assign statement assign out_assign = a ^ b; // using always(combinational) statement always@(*) out_always_comb = a ^ b; // usign always(clock) statement always@(posedge clk) out_always_ff <= a ^ b; endmodule /*官网解答*/ 无
-
-
if statement
-
题目描述:
Build a 2-to-1 mux that chooses between
aandb. Choosebif bothsel_b1andsel_b2are true. Otherwise, choosea. Do the same twice, once usingassignstatements and once using a procedural if statement.sel_b1 sel_b2 out_assign out_always 0 0 a 0 1 a 0 0 a 1 1 b -
题目分析: 题目要求我们分别用assign和always写一个复用电路,使用assign时可以用三目运算符来进行判断,使用always语句时,利用if-else来进行判断
-
解答:
/*我的解答*/ module top_module( input a, input b, input sel_b1, input sel_b2, output wire out_assign, output reg out_always ); //using assign statement,使用三目运算符表达 assign out_assign = (sel_b1 & sel_b2) ? b : a; //using always statement always@(*) begin if((sel_b1==1'b1) && (sel_b2 == 1'b1)) out_always <= b; else out_always <= a; end endmodule /*官网解答*/ 无
-
-
if statement latches
-
题目描述:The following code contains incorrect behaviour that creates a latch. Fix the bugs so that you will shut off the computer only if it’s really overheated, and stop driving if you’ve arrived at your destination or you need to refuel.
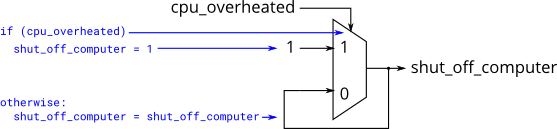
always @(*) begin if (cpu_overheated) shut_off_computer = 1; end always @(*) begin if (~arrived) keep_driving = ~gas_tank_empty; end -
题目分析:题目给了两个场景让我们来修改bug,这两种场景对应着使用if-else时产生锁存器latch的情况,我们只需要理清这两个场景中各变量的关系编写判断语句即可,题目中也有给出判断的条件。
-
解答:
/*我的解答*/ module top_module ( input cpu_overheated, output reg shut_off_computer, input arrived, input gas_tank_empty, output reg keep_driving ); // //只有当cpu过热时,你需要关闭电脑,其他情况可以不关 always @(*) begin if (cpu_overheated == 1'b1) shut_off_computer = 1'b1; else shut_off_computer = 1'b0; end //如果到达目的地或者需要加油,则停止驾驶,其他情况继续行驶 always @(*) begin if ((arrived == 1'b0) && (gas_tank_empty == 1'b0)) keep_driving = 1'b1; else keep_driving = 1'b0; end endmodule /*官网解答*/ 无
-
-
Case statement
-
题目描述:Case statements are more convenient than if statements if there are a large number of cases. So, in this exercise, create a 6-to-1 multiplexer. When
selis between 0 and 5, choose the corresponding data input. Otherwise, output 0. The data inputs and outputs are all 4 bits wide. -
题目分析:题目要求我们用case语句写一个多路选择器,当sel在0和5之间时输出对应data0-5,其余情况输出为0,需要注意两点,第一是endcase不要忘记写上,第二是注意输出位宽的问题。
-
解答:
/*我的解答*/ module top_module ( input [2:0] sel, input [3:0] data0, input [3:0] data1, input [3:0] data2, input [3:0] data3, input [3:0] data4, input [3:0] data5, output reg [3:0] out );// always@(*) begin // This is a combinational circuit case(sel) 3'b000: out = data0; 3'b001: out = data1; 3'b010: out = data2; 3'b011: out = data3; 3'b100: out = data4; 3'b101: out = data5; default: out = 4'b0000; endcase end endmodule /*官网解答*/ 无
-
-
Priority encoder
-
题目描述:Build a 4-bit priority encoder. For this problem, if none of the input bits are high (i.e., input is zero), output zero. Note that a 4-bit number has 16 possible combinations.
-
题目分析:需要我们编写一个优先编码器 ,优先编码器是一个组合电路(利用always语句+case语句完成),它是根据编码位置进行筛选的。优先编码器允许同时在几个输入端有输入信号,编码器按输入信号排定的优先顺序,只对同时输入的几个信号中优先权最高的一个进行编码。题目要求是当输入出现第一个高电平是,输出它的位置,比如8’b1001_0000 首先出现高电平的位置在第4位,所以输出应该是3‘d4。
-
解答:
/*我的解答*/ module top_module ( input [3:0] in, output reg [1:0] pos ); always@(*) begin case(in) 4'h2: pos = 2'd1; 4'h4: pos = 2'd2; 4'h6: pos = 2'd1; 4'h8: pos = 2'd3; 4'ha: pos = 2'd1; 4'hc: pos = 2'd2; 4'he: pos = 2'd1; default: pos = 2'd0; endcase end endmodule /*官网解答*/ module top_module ( input [3:0] in, output reg [1:0] pos ); always @(*) begin // Combinational always block case (in) 4'h0: pos = 2'h0; // I like hexadecimal because it saves typing. 4'h1: pos = 2'h0; 4'h2: pos = 2'h1; 4'h3: pos = 2'h0; 4'h4: pos = 2'h2; 4'h5: pos = 2'h0; 4'h6: pos = 2'h1; 4'h7: pos = 2'h0; 4'h8: pos = 2'h3; 4'h9: pos = 2'h0; 4'ha: pos = 2'h1; 4'hb: pos = 2'h0; 4'hc: pos = 2'h2; 4'hd: pos = 2'h0; 4'he: pos = 2'h1; 4'hf: pos = 2'h0; default: pos = 2'b0; // Default case is not strictly necessary because all 16 combinations are covered. endcase end // There is an easier way to code this. See the next problem (always_casez). endmodule
-
-
Priority encoder with casez
-
题目描述:Build a priority encoder for 8-bit inputs. Given an 8-bit vector, the output should report the first bit in the vector that is
1. Report zero if the input vector has no bits that are high. For example, the input8'b10010000should output3'd4, because bit[4] is first bit that is high.From the previous exercise, there would be 256 cases in the case statement. We can reduce this (down to 9 cases) if the case items in the case statement supported don’t-care bits. This is whatcase**z**is for: It treats bits that have the valuezas don’t-care in the comparison.For example, this would implement the 4-input priority encoder from the previous exercise:
always @(*) begin casez (in[3:0]) 4'bzzz1: out = 0; // in[3:1] can be anything 4'bzz1z: out = 1; 4'bz1zz: out = 2; 4'b1zzz: out = 3; default: out = 0; endcase end -
题目分析:和上题的题目差不多,但这次需要我们编写一个8位的优先编码器,它不同于4位的优先编码器,只有16种情况,8位的优先编码器共有2^8=256种情况,一一列举不显示,因此官网也给了一种不一样的方法,利用casez语句,它与case不同的区别就是使用casez时会将为二进制上为z的值视为无关项,也就是说我们只需要关注我们需要的位,其他位上的值可以用z来代替,这就可以大大简化我们需要列举的情况,除此之外还有casex,它们三者的区别如下:
- case :需要考虑0,1,x,z
- casez :只用考虑0,1,x,不需要关心z的值
- casex : 只用考虑 0,1 不用关心x与z的值
-
解答:
/*我的解答*/ module top_module ( input [7:0] in, output reg [2:0] pos ); always@(*) begin casez(in) 8'bzzzz_zzz1 : pos <= 3'd0; 8'bzzzz_zz1z : pos <= 3'd1; 8'bzzzz_z1zz : pos <= 3'd2; 8'bzzzz_1zzz : pos <= 3'd3; 8'bzzz1_zzzz : pos <= 3'd4; 8'bzz1z_zzzz : pos <= 3'd5; 8'bz1zz_zzzz : pos <= 3'd6; 8'b1zzz_zzzz : pos <= 3'd7; default : pos <= 3'd0; endcase end endmodule /*官网解答*/ 无
-
-
Avoiding latches
-
题目描述:Suppose you’re building a circuit to process scancodes from a PS/2 keyboard for a game. Given the last two bytes of scancodes received, you need to indicate whether one of the arrow keys on the keyboard have been pressed.Your circuit has one 16-bit input, and four outputs. Build this circuit that recognizes these four scancodes and asserts the correct output.
Scancode [15:0] Arrow key 16'he06bleft arrow 16'he072down arrow 16'he074right arrow 16'he075up arrow Anything else none -
题目分析:需要我们编写一个选择电路,选择的条件如表格所示,不过需要注意是否出现锁存器的情况,这里用if-else或case都可以
-
解答:
/*我的解答1:用if-else*/ module top_module ( input [15:0] scancode, output reg left, output reg down, output reg right, output reg up ); always@(*) begin up = 1'b0; down = 1'b0; left = 1'b0; right = 1'b0; //必须写上,否则会产生锁存 if(scancode == 16'he06b) left <= 1'b1; else if (scancode == 16'he072 ) down <= 1'b1; else if (scancode == 16'he074) right <= 1'b1; else if (scancode == 16'he075) up <= 1'b1; else begin left <= 1'b0; down<= 1'b0; right<= 1'b0; up <= 1'b0; end end endmodule/*我的解答2:用case*/ module top_module ( input [15:0] scancode, output reg left, output reg down, output reg right, output reg up ); always@(*) begin //up = 1'b0; down = 1'b0; left = 1'b0; right = 1'b0; //建议写上 case(scancode) 16'he06b : left <= 1'b1; default : left <= 1'b0; endcase case(scancode) 16'he072 : down <= 1'b1; default : down <= 1'b0; endcase case(scancode) 16'he074 : right <= 1'b1; default : right <= 1'b0; endcase case(scancode) 16'he075 : up <= 1'b1; default : up <= 1'b0; endcase end endmodule
-
总结
-
Always
对于可综合的硬件,有两种类型的always语句块是有意义的 组合电路: always@(*) 时钟电路: always@(posedge clk) 对于组合电路来说,用assign表达或是always都是可以的,关键是要看用那个更加的方便 不同的是用assign是左右两边的操作类型都必须是net型,而使用always是变量必须是reg型 对于时序电路来说,使用always仍是创建了一个组合电路但同时也在输出端创建了一组触发器或是寄存器 -
阻塞与非阻塞
阻塞赋值(=)与非阻塞赋值(<=)只能在程序块内使用 在用always生成的组合电路赋值时,使用阻塞赋值 在用always生成的时钟电路赋值时,使用非阻塞赋值 这是一般规则,遵循即可 -
锁存器
当设计电路是,必须首先思考的 1.我要生成什么样的逻辑门 2.组合电路有那些输入,那些输出 3.组合电路是否需要跟着一组触发器 锁存器是一个常见的错误,(除非需要用到) 因为语法正确,并不意味着生成了正确的电路(锁存器) 如果生成了锁存器一般会给出警告 "Watch out for Warning (10240): ... inferring latch(es)" 生成锁存器的情况: 1.组合电路中,输出变量赋值给自己,导致了锁存 2.组合电路中,使用if-else或case时没有将所有情况的输出都赋值,这表示说用if时尽可能带上else,用case时尽可能写上default,可以避免锁存器的产生






















 596
596











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








