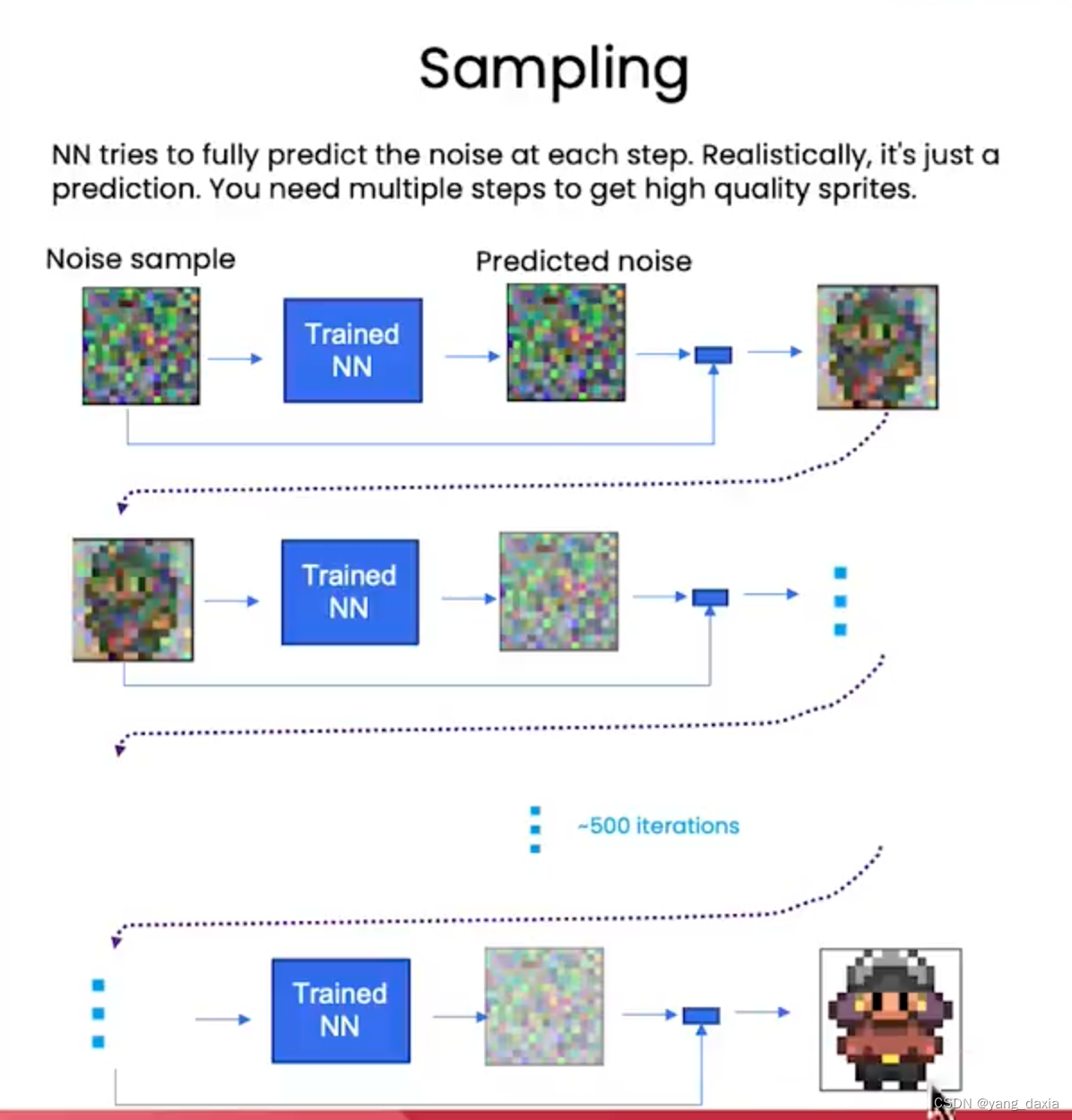
sampling
推理过程
- 输入噪声sample,
- 模型预测噪声
- 获取新sample。模型减去预测的噪声+新噪声(DDPM sampling)包含3个系数
- 如此循环很多次,即可获取高质量的sampling
ddpm sample代码
# sample using standard algorithm
@torch.no_grad()
def sample_ddpm(n_sample, save_rate=20):
# x_T ~ N(0, 1), sample initial noise
samples = torch.randn(n_sample, 3, height, height).to(device)
# array to keep track of generated steps for plotting
intermediate = []
for i in range(timesteps, 0, -1):
print(f'sampling timestep {i:3d}', end='\r')
# reshape time tensor
t = torch.tensor([i / timesteps])[:, None, None, None].to(device)
# sample some random noise to inject back in. For i = 1, don't add back in noise
z = torch.randn_like(samples) if i > 1 else 0
eps = nn_model(samples, t) # predict noise e_(x_t,t)
samples = denoise_add_noise(samples, i, eps, z)
if i % save_rate ==0 or i==timesteps or i<8:
intermediate.append(samples.detach().cpu().numpy())
intermediate = np.stack(intermediate)
return samples, intermediate
# helper function; removes the predicted noise (but adds some noise back in to avoid collapse)
def denoise_add_noise(x, t, pred_noise, z=None):
if z is None:
z = torch.randn_like(x)
noise = b_t.sqrt()[t] * z
mean = (x - pred_noise * ((1 - a_t[t]) / (1 - ab_t[t]).sqrt())) / a_t[t].sqrt()
return mean + noise
问题1、不加入新噪声结果如何?结果会很差
unet
先下采样,再上采样。模型预测噪声。
关键需要引入两个embed。上下文embed和时间embed
- 上下文embed用于控制模型生产的内容
- 时间embed和步长以及噪声级别相关
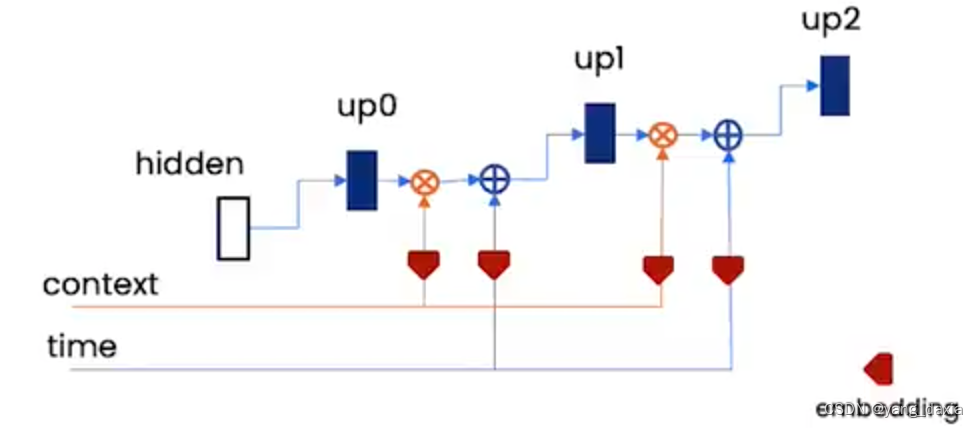
# embed context and timestep
cemb1 = self.contextembed1(c).view(-1, self.n_feat * 2, 1, 1) # (batch, 2*n_feat, 1,1)
temb1 = self.timeembed1(t).view(-1, self.n_feat * 2, 1, 1)
up2 = self.up1(cemb1*up1 + temb1, down2)
训练
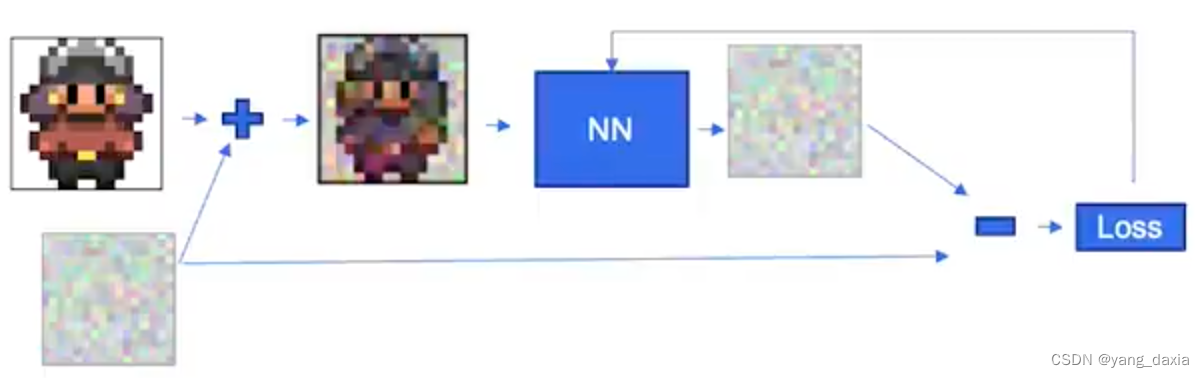
对原始sample加入噪声,然后模型预测噪声,再求loss。每次只随机加一个噪声即可(随机的过程与t时间步长相关)
# training without context code
# set into train mode
nn_model.train()
for ep in range(n_epoch):
print(f'epoch {ep}')
# linearly decay learning rate
optim.param_groups[0]['lr'] = lrate*(1-ep/n_epoch)
pbar = tqdm(dataloader, mininterval=2 )
for x, _ in pbar: # x: images
optim.zero_grad()
x = x.to(device)
# perturb data
noise = torch.randn_like(x)
t = torch.randint(1, timesteps + 1, (x.shape[0],)).to(device)
x_pert = perturb_input(x, t, noise)
# use network to recover noise
pred_noise = nn_model(x_pert, t / timesteps)
# loss is mean squared error between the predicted and true noise
loss = F.mse_loss(pred_noise, noise)
loss.backward()
optim.step()
控制生成
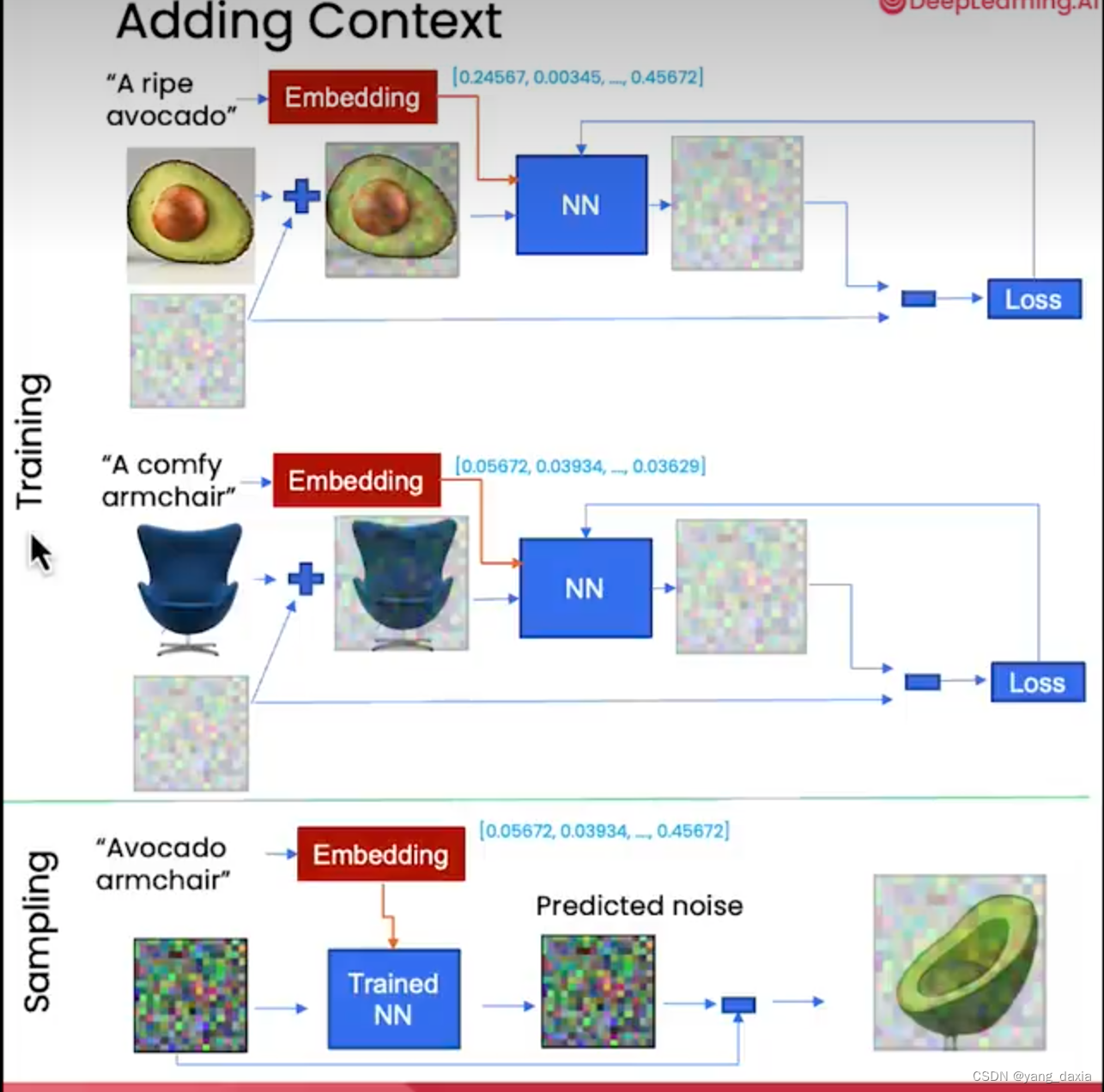
通过在模型中加入embedding即可控制生成。训练的时候给图片语言描述,通过embedding网络生成vector输入到网络。在推理的时候给不同的embedding即可输出不同的结果。
控制embed*, 时间embed是+。理解为控制相当于softmax()或者mask
- embedding可以是语言的embed。长度为1000等
- embedding可以是简单的类别,如长度为5的5个类别。
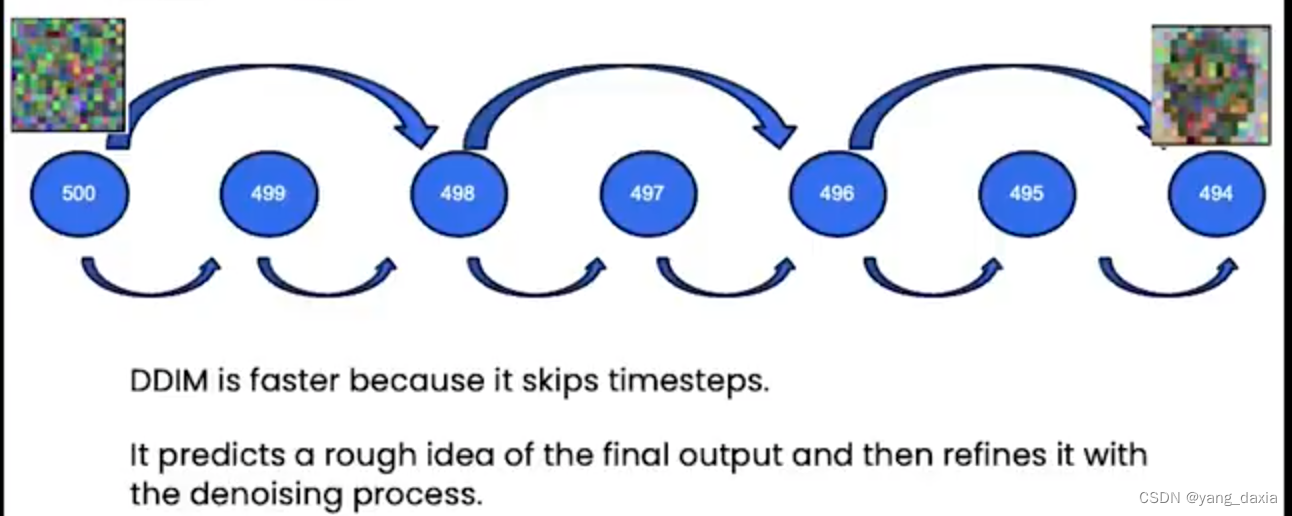
加速sampling——DDIM
原始的DDPM是一个隐马尔可夫过程,采样需要一步一步,500多步才能获取很好的结果,过程很慢。
DDIM跳过了一些时间步长,先预测一个粗糙的结果,然后在逐步的refine。
总结
扩散模型可以用于图像生成、图像编辑、音乐生成等领域。
后续学习更好的sampling、stable diffusion
参考:https://learn.deeplearning.ai/courses/diffusion-models/
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1R14y1D7kx?p=1























 340
340

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










