标签: machine_learning
bias & variance
Estimator(估计量): a function of the data that is used to infer the value of an unknown parameter in a statistical model,can be writed like
θ^(X)
.”估计量”是样本空间映射到样本估计值的一个函数 (Then an “estimator” is a function that maps the sample space to a set of sample estimates.)估计量用来估计未知总体的参数,它有时也被称为估计子;一次估计是指把这个函数应用在一组已知的数据集上,求函数的结果。对于给定的参数,可以有许多不同的估计量。
Estimand:The parameter being estimated,like
θ
.
Estimate: a particular realization of this random variable
θ^(X)
is called the “estimate”,like
θ^(x)
.
Bias: The bias of
θˆ
is defined as
B(θˆ)
=
E(θˆ)−θ
. It is the distance between the average of the collection of estimates, and the single parameter being estimated. It also is the expected value of the error, since
E(θˆ)−θ=E(θˆ−θ)
.The estimator
θˆ
is an unbiased estimator of
θ
if and only if
B(θˆ)=0
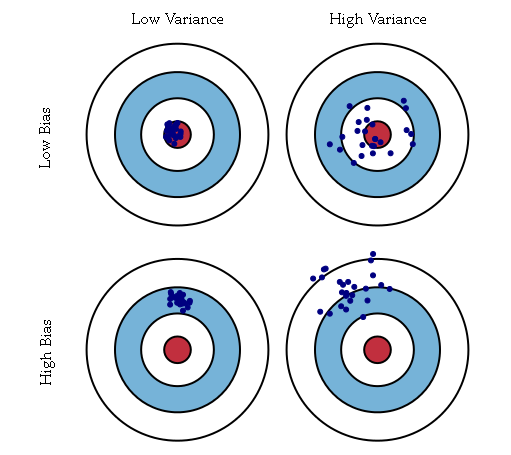
.example: If the parameter is the bull’s-eye of a target, and the arrows are estimates, then a relatively high absolute value for the bias means the average position of the arrows is off-target, and a relatively low absolute bias means the average position of the arrows is on target. They may be dispersed, or may be clustered.
Variance(方差):The variance of
θˆ
is simply the expected value of the squared sampling deviations; that is,
var(θˆ)=E[(θˆ−E(θˆ))2]
. It is used to indicate how far, on average, the collection of estimates are from the expected value(期望) of the estimates.example :If the parameter is the bull’s-eye of a target, and the arrows are estimates, then a relatively high variance means the arrows are dispersed, and a relatively low variance means the arrows are clustered. Some things to note: even if the variance is low, the cluster of arrows may still be far off-target, and even if the variance is high, the diffuse collection of arrows may still be unbiased. Finally, note that even if all arrows grossly miss the target, if they nevertheless all hit the same point, the variance is zero.
The relationship between bias and variance is analogous to the relationship between accuracy and precision.
从以上描述可以看出,bias表示预测值的均值与实际值的差值;而variance表示预测结果作为一个随机变量时的方差,其描述中类比靶心的例子较为明了。http://blog.csdn.net/ywl22/article/details/8606166。
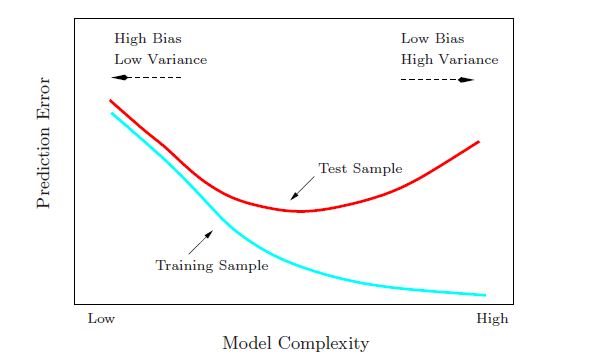
Bias、variance与复杂度的关系
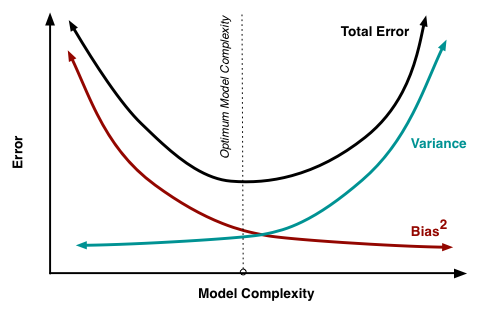
note:the sample mean
样本均值是总体均值的无偏估计,而样本方差却不是总体方差的无偏估计,其小于总体方差。
Mean squared error
In statistics, the mean squared error (MSE) of an estimator measures the average of the squares of the “errors”, that is, the difference between the estimator and what is estimated.MSE is a risk function, corresponding to the expected value of the squared error loss or quadratic loss.(损失函数or代价函数?)
MSE(θ^)=Var(θ^)+(Bias(θ^,θ))2
=E[(θˆ−E(θˆ))2]+(E(θˆ)−θ)2
proof
ps:
In statistics, the bias (or bias function) of an estimator is the difference between this estimator’s expected value and the true value of the parameter being estimated. An estimator or decision rule with zero bias is called unbiased. Otherwise the estimator is said to be biased.























 679
679

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








