0. 前言
今天给大家讲一下什么是PID控制,会尽量使用比较通俗易懂的语言给家讲解,带大家明白什么是PID控制,最后会在文章末尾附上华子上海海思开源的PID控制器源码。(下面讲的都是位置式PID,不讲解增量式PID)

1. PID控制的概念
按照惯例先上一波概念,百度百科里是这么解释的:
比例积分微分控制(proportional-integral-derivative control),简称PID控制,是最早发展起来的控制策略之一,由于其算法简单、鲁棒性好和可靠性高,被广泛应用于工业过程控制,仍有90%左右的控制回路具有PID结构。
简单的说,根据给定值和实际输出值构成控制偏差,将偏差按比例、积分和微分通过线性组合构成控制量,对被控对象进行控制。常规PID控制器作为一种线性控制器。
总之PID控制就是较早就有的一种很简单但在工业上应用很广的控制算法。PID控制器是线性控制器,不太适合拿来控制非线性的系统。
PID控制的公式如下:

2. 进一步了解PID控制
要了解PID控制首先我们要构造一个水槽系统,水槽的上端是可以进水的水管,进水的速度可控,下端是一个以固定速度出水的出水口。
假设进水速度是 u,出水速度是 o,水位实际的高度是 h ,水位需要控制到的目标高度是 h_ref,我们把目标高度与实际高度之间的差值叫做 error 记作 e:
![]()
PID控制器会根据e 的大小和变化调整进水速度 u 把水位实际高度 h 调整到目标高度 h_ref 。

2.1 什么是P(比例)控制
比例控制就是我控制的出水速度和偏差e的大小是成比例的,比例系数Kp,偏差e越大出水的速度就越快,偏差e越小出水的速度就越慢。
如果我们只要公式的第一项,不要后面的积分项和微分项就叫做纯P控制,公式为:
![]()
纯P控制有个缺点,就是会有静差,什么是静差呢?
我们想一下当e越小时我们的控制力度也越小,那么随着e越来越小我的出水速度u也越来越小,最终水位高度h会在某一时刻停下来不再上升,这时
![]()
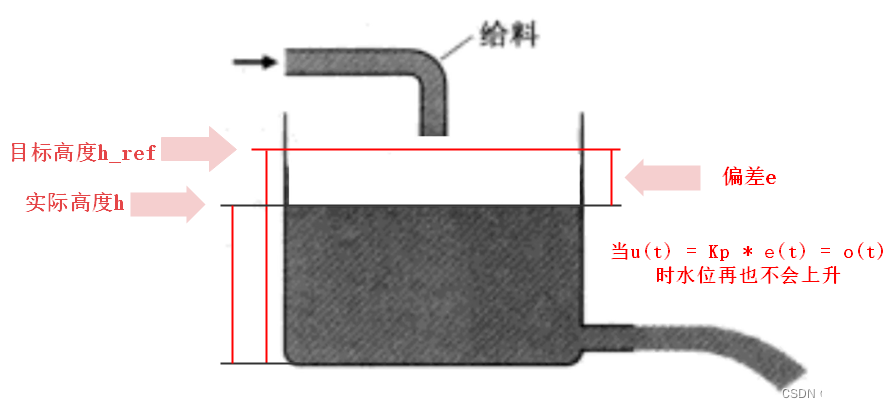
进水速度和出水速度相等了,导致水位不再上升了,这种现象就叫做静差。要想消除静差就需要引入积分控制。
2.2 什么是I(积分)控制
那积分控制是怎么消除静差的呢?不难想象有误差存在时,随着时间的推移积分项会不断地将误差e累积起来,最终作用在u上面加大出水速度使得实际水位h达到目标水位h_ref,这样就使得静差消失了。
如果我们在纯P控制里面再引入积分环节,就叫做PI控制,公式为:
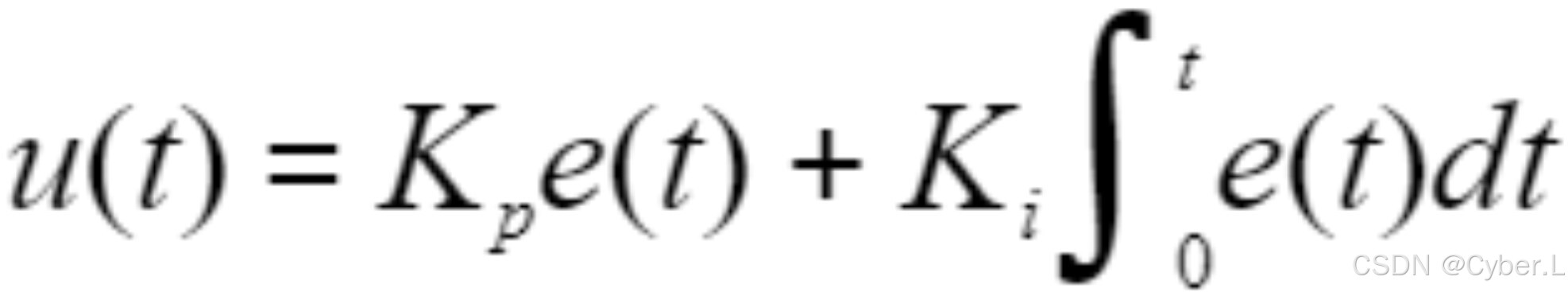
积分项会对最近一段时间的误差e进行积分;
积分项的值越大对出水速度u的影响越大;
积分项的值越小对出水速度u的影响越小。
由于积分控制是将历史的误差进行累积,所以积分项是有历史值的,它的控制是滞后的,那么如果现在这个水槽系统的出水口突然被堵住了,这时候没有一种超前的控制来抑制出水速度的话水位很容易超过目标水位一大截,这时候就要引入D(微分)控制 了。
2.3 什么是D(微分)控制
微分控制其实就是在PI控制中引入微分环节,通过对误差变化率的测量和控制来实现更加精确的控制 。
如果我们在PI控制器的公式里面再引入微分环节,就叫做PID控制,公式为:
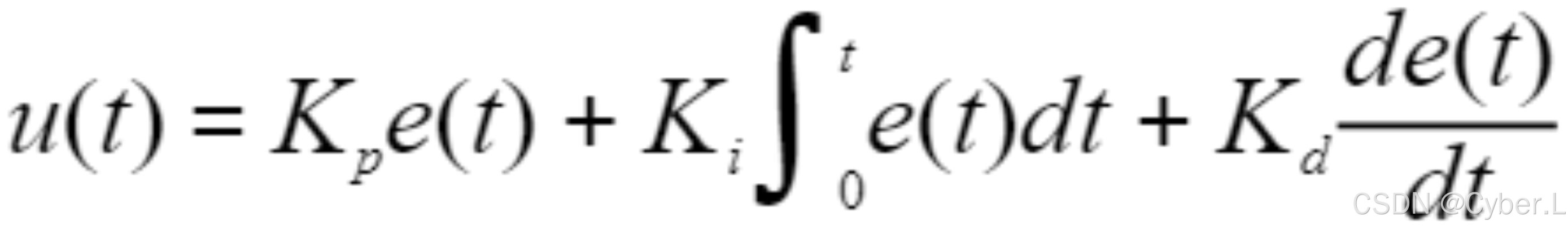
我们可以把最后面的微分环节看成偏差e的斜率。
斜率是正值说明偏差在变大,微分项的值是正值,加大出水速度u来减小偏差;
斜率是负值说明偏差在减小,微分项的值是负值,减小出水速度u以免超调。
为什么说微分控制是超前的呢?因为我是通过偏差e的变化率来调整输出的,如果我感知到偏差的变化趋势是在增大,我就会加大输出力度来减小误差,如果我感知到偏差的变化趋势是减小,我就会减小输出力度来防止超调,所以它的控制是超前的。
3. PID控制器的离散化
为什么要把控制器公式离散化呢?

以上我们提到的PID控制器的公式是连续的,但是在实际应用中,我们需要使用数字控制器进行控制,而数字控制器只能处理数字信号,因此需要将连续的PID公式离散化,转换为数字信号进行处理。
具体来说,离散化是将连续的PID公式在时间上进行采样,然后将采样点之间的差值用差分方程表示,从而得到离散化的PID控制器。离散化的PID控制器可以直接应用于数字控制器中,例如微处理器、DSP等,从而实现对被控对象的控制。
假设采样时间间隔为T,则在k时刻:
- 偏差为e(k);
- 积分为Σe(k) = e(k) + e(k-1) + e(k-2) + ... + e(0);
- 微分为(e(k) - e(k-1))/T。
离散化后的位置式PID控制器公式为:
u(k) = Kp * e(k) + Ki * Σe(k) + Kd * (e(k) - e(k-1))/T
其中,Kp、Ki、Kd分别为比例、积分、微分系数。
将公式离散化后,我们就可以通过该公式编写程序,定时采集偏差e,并调整输出。下面我会附上PID控制器源码。
4. PID控制器源码
头文件mcs_pid_ctrl.h如下:
/**
* @copyright Copyright (c) 2022, HiSilicon (Shanghai) Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
* Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without modification, are permitted provided that the
* following conditions are met:
* 1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following
* disclaimer.
* 2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the
* following disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
* 3. Neither the name of the copyright holder nor the names of its contributors may be used to endorse or promote
* products derived from this software without specific prior written permission.
* THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES,
* INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE
* DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT HOLDER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL,
* SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR
* SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY,
* WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE
* USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
* @file mcs_pid_ctrl.h
* @author MCU Algorithm Team
* @brief General PI controller.
* This file provides functions declaration of the PI controller module.
*/
/* Define to prevent recursive inclusion ------------------------------------------------------- */
#ifndef McuMagicTag_MCS_PID_CTRL_H
#define McuMagicTag_MCS_PID_CTRL_H
/**
* @defgroup PID PID
* @brief The PID module.
* @{
*/
/**
* @defgroup PID_STRUCT PID STRUCT
* @brief The PID control structure definition.
* @{
*/
/* Typedef definitions ------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
/**
* @brief General PID Controller struct members and parameters.
*/
typedef struct {
float error; /**< Error feedback. */
float errorLast; /**< Error feedback history values. */
float feedforward; /**< Feedforward item. */
float integral; /**< Integral item. */
float saturation; /**< Saturation value of the integral item. */
float differ; /**< Differential item. */
float kp; /**< Gained of the proportional item. */
float ki; /**< Gained of the integral item, multiplied by control period. */
float kd; /**< Gained of the differential item. */
float ns; /**< Filter parameter of the differential item. */
float ka; /**< Gained of the saturation item. */
float upperLimit; /**< The upper limit value of the pid comp output. */
float lowerLimit; /**< The lower limit value of the pid output. */
} PidHandle;
/**
* @}
*/
/**
* @defgroup PID_API PID API
* @brief The PID control API definitions.
* @{
*/
void PID_Reset(PidHandle *pidHandle);
void PID_Clear(PidHandle *pidHandle);
float PI_Exec(PidHandle *pidHandle);
float PID_Exec(PidHandle *pidHandle);
void PID_SetKp(PidHandle *pidHandle, float kp);
void PID_SetKi(PidHandle *pidHandle, float ki);
void PID_SetKd(PidHandle *pidHandle, float kd);
/**
* @}
*/
/**
* @}
*/
#endif
C文件mcs_pid_ctrl.c如下:
/**
* @copyright Copyright (c) 2022, HiSilicon (Shanghai) Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
* Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without modification, are permitted provided that the
* following conditions are met:
* 1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following
* disclaimer.
* 2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the
* following disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
* 3. Neither the name of the copyright holder nor the names of its contributors may be used to endorse or promote
* products derived from this software without specific prior written permission.
* THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES,
* INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE
* DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT HOLDER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL,
* SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR
* SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY,
* WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE
* USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
* @file mcs_pid_ctrl.c
* @author MCU Algorithm Team
* @brief This file provides functions of general PID controller
*/
#include "mcs_pid_ctrl.h"
#include "mcs_math.h"
#include "mcs_assert.h"
/**
* @brief Reset all member variables of PID controller to zero.
* @param pidHandle PID controller struct handle.
* @retval None.
*/
void PID_Reset(PidHandle *pidHandle)
{
MCS_ASSERT_PARAM(pidHandle != NULL);
/* Reset the PID parameter. */
pidHandle->error = 0.0f;
pidHandle->errorLast = 0.0f;
pidHandle->feedforward = 0.0f;
pidHandle->integral = 0.0f;
pidHandle->saturation = 0.0f;
pidHandle->differ = 0.0f;
pidHandle->kp = 0.0f;
pidHandle->ki = 0.0f;
pidHandle->kd = 0.0f;
pidHandle->ns = 0.0f;
pidHandle->ka = 0.0f;
/* Reset the Limiting Value. */
pidHandle->upperLimit = 0.0f;
pidHandle->lowerLimit = 0.0f;
}
/**
* @brief Clear historical values of PID controller.
* @param pidHandle PID controller struct handle.
* @retval None.
*/
void PID_Clear(PidHandle *pidHandle)
{
MCS_ASSERT_PARAM(pidHandle != NULL);
/* Clear historical values of PID controller. */
pidHandle->differ = 0.0f;
pidHandle->integral = 0.0f;
pidHandle->saturation = 0.0f;
pidHandle->feedforward = 0.0f;
pidHandle->error = 0.0f;
pidHandle->errorLast = 0.0f;
}
/**
* @brief Execute simplified PI controller calculation, static clamping, no feedfoward.
* @param pidHandle PI controller struct handle.
* @retval PI control output.
*/
float PI_Exec(PidHandle *pidHandle)
{
MCS_ASSERT_PARAM(pidHandle != NULL);
/* Proportional Item */
float p = pidHandle->kp * pidHandle->error;
/* Integral Item */
float i = pidHandle->ki * pidHandle->error + pidHandle->integral;
i = Clamp(i, pidHandle->upperLimit, pidHandle->lowerLimit);
pidHandle->integral = i;
/* static clamping and output calculaiton */
float val = p + i;
float out = Clamp(val, pidHandle->upperLimit, pidHandle->lowerLimit);
return out;
}
/**
* @brief Execute PID controller calculation. dynamic clamping, feedfoward compenstaion
* @param pidHandle PID controller struct handle.
* @retval PID control output.
*/
float PID_Exec(PidHandle *pidHandle)
{
MCS_ASSERT_PARAM(pidHandle != NULL);
/* Proportional Item */
float p = pidHandle->kp * pidHandle->error;
/* Integral Item */
float i = pidHandle->ki * (pidHandle->error - pidHandle->ka * pidHandle->saturation) + pidHandle->integral;
i = Clamp(i, Max(0.0f, pidHandle->upperLimit), Min(0.0f, pidHandle->lowerLimit));
pidHandle->integral = i;
/* Differential Item */
float d = pidHandle->kd * pidHandle->ns * (pidHandle->error - pidHandle->errorLast) - \
pidHandle->differ * (pidHandle->ns - 1.0f);
pidHandle->errorLast = pidHandle->error;
pidHandle->differ = d;
/* Output value update and saturation value calculation */
float val = p + i + d + pidHandle->feedforward;
float out = Clamp(val, pidHandle->upperLimit, pidHandle->lowerLimit);
pidHandle->saturation = val - out;
return out;
}
/**
* @brief Set the proportional parameter kp of PID controller.
* @param pidHandle PID controller struct handle.
* @param kp The proportional parameter.
* @retval None.
*/
void PID_SetKp(PidHandle *pidHandle, float kp)
{
MCS_ASSERT_PARAM(pidHandle != NULL);
MCS_ASSERT_PARAM(kp >= 0.0f);
pidHandle->kp = kp;
}
/**
* @brief Set the integral parameter ki of PID controller.
* @param pidHandle PID controller struct handle.
* @param ki The integral parameter.
* @retval None.
*/
void PID_SetKi(PidHandle *pidHandle, float ki)
{
MCS_ASSERT_PARAM(pidHandle != NULL);
MCS_ASSERT_PARAM(ki >= 0.0f);
pidHandle->ki = ki;
}
/**
* @brief Set the derivative parameter kd of PID controller.
* @param pidHandle PID controller struct handle.
* @param kd The derivative parameter.
* @retval None.
*/
void PID_SetKd(PidHandle *pidHandle, float kd)
{
MCS_ASSERT_PARAM(pidHandle != NULL);
MCS_ASSERT_PARAM(kd >= 0.0f);
pidHandle->kd = kd;
}


























 3万+
3万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










