欢迎关注更多精彩
关注我,学习常用算法与数据结构,一题多解,降维打击。
问题描述
给定1个二数组,利用gpu转置并返回结果。
cpu 算法
void cpu_matrix_trnspose(int in[N][M], int out[M][N]) {
for (int y = 0; y < N; ++y) {
for (int x = 0; x < M; ++x) {
cpu_result[x][y] = matrix[y][x];
}
}
}
cpu耗时
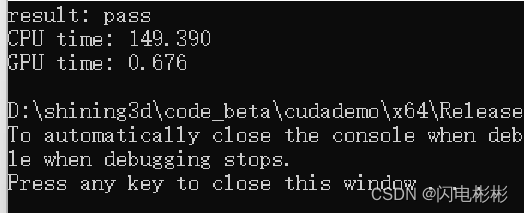
耗时149毫秒
gpu 算法-直接法
代码
__global__ void gpu_matrix_transpose(int in[N][M], int out[M][N]) {
int x = threadIdx.x + blockDim.x*blockIdx.x;
int y = threadIdx.y + blockDim.y*blockIdx.y;
if (x < M && y < N) {
out[x][y] = in[y][x];
}
}
耗时分析
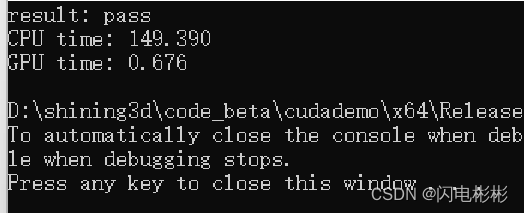
耗时0.676毫秒,提升了100多倍。
算法缺点
在gpu中数组是放在全局内存里,全局内存访问比较慢(相较于共享内存)。如果是连续访问则可以进行合并访存,效率上可以作一些弥补,如果一直随机访问效率会打折扣。
分析上述代码。
二维数组可以按行展开成一维数组。
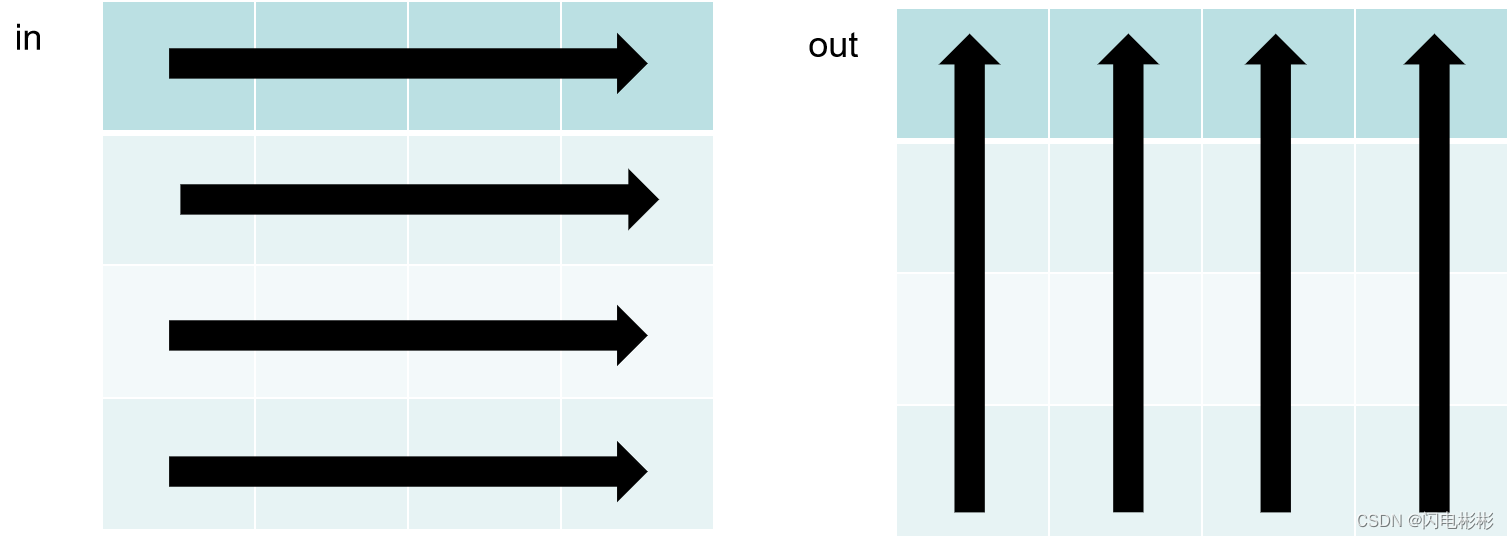
in[y][x]可以认为是按行访问(顺序访问)
out[x][y]则是按列访问,对于内存来说不是顺序访问,会降低效率。
gpu 算法分块法(块内顺序访问)
算法思路
共享内存访问效率比全局内存快速1个数量级。
但是共享内存大小有限制。
gpu中1个block内存所有线程可以共同访问一块共享内存。
block最多有1024个线程。
我们可以把矩阵分成多个(n*m)块,每个块32*32大小。
每个block可以对一个块进行转置。
转置1个块具体过程如下:
步骤1: 把in第(1,2)块按行访问存入到共享内存
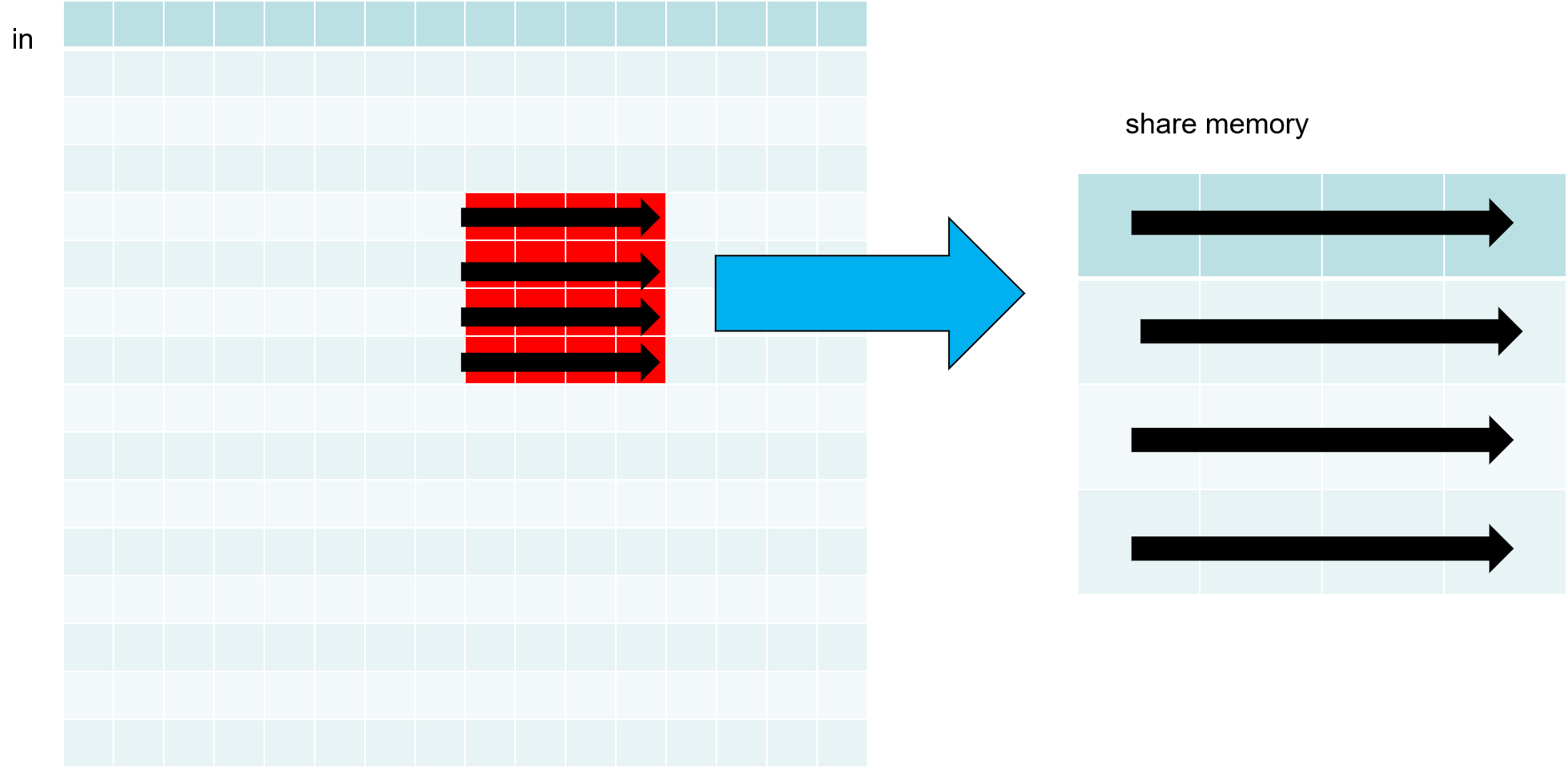
步骤2: 把share memory按列访问共享内存按行存入到out第(2,1)块

这样在访问in, out时都做到了按行访问和写入。对于share memory 访问都很快,无关访问顺序。
代码
#include "cuda_runtime.h"
#include <math.h>
#include<vector>
#include "device_launch_parameters.h"
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long lld;
#define BLOCK_SIZE 32
#define M 3000
#define N 1000
__managed__ int matrix[N][M];
__managed__ int gpu_result[M][N];
__managed__ int cpu_result[M][N];
__global__ void gpu_matrix_transpose(int in[N][M], int out[M][N]) {
int x = threadIdx.x + blockDim.x*blockIdx.x;
int y = threadIdx.y + blockDim.y*blockIdx.y;
if (x < M && y < N) {
out[x][y] = in[y][x];
}
}
__global__ void gpu_shared_matrix_transpose(int in[N][M], int out[M][N]) {
int x = threadIdx.x + blockDim.x*blockIdx.x;
int y = threadIdx.y + blockDim.y*blockIdx.y;
__shared__ int ken[BLOCK_SIZE+1][BLOCK_SIZE+1];
if (x < M && y < N) {
ken[threadIdx.y][threadIdx.x] = in[y][x];
}
__syncthreads();
int x1 = threadIdx.x + blockDim.y*blockIdx.y;
int y1 = threadIdx.y + blockDim.x*blockIdx.x;
if (x1 < N && y1 < M) {
out[y1][x1] = ken[threadIdx.x][threadIdx.y];
}
}
void cpu_matrix_trnspose(int in[N][M], int out[M][N]) {
for (int y = 0; y < N; ++y) {
for (int x = 0; x < M; ++x) {
cpu_result[x][y] = matrix[y][x];
}
}
}
int main()
{
for (int y = 0; y < N; ++y) {
for (int x = 0; x < M; ++x) {
matrix[y][x] = x + y * M;
}
}
cudaEvent_t start, stop_gpu, stop_cpu;
cudaEventCreate(&start);
cudaEventCreate(&stop_gpu);
cudaEventCreate(&stop_cpu);
cudaEventRecord(start);
cudaEventSynchronize(start);
dim3 dimGrid((M+BLOCK_SIZE-1)/BLOCK_SIZE,(N+BLOCK_SIZE-1)/BLOCK_SIZE);
dim3 dimBlock(BLOCK_SIZE, BLOCK_SIZE);
for (int i = 0; i < 20; ++i) {
gpu_shared_matrix_transpose <<<dimGrid,dimBlock>>>(matrix, gpu_result);
cudaDeviceSynchronize();
}
cudaEventRecord(stop_gpu);
cudaEventSynchronize(stop_gpu);
cpu_matrix_trnspose(matrix, cpu_result);
cudaEventRecord(stop_cpu);
cudaEventSynchronize(stop_cpu);
float time_cpu, time_gpu;
cudaEventElapsedTime(&time_gpu, start, stop_gpu);
cudaEventElapsedTime(&time_cpu, stop_gpu, stop_cpu);
bool errors = false;
for (int y = 0; y < N; ++y) {
for (int x = 0; x < M; ++x) {
if (cpu_result[y][x] != gpu_result[y][x]) errors = true;
}
}
printf("result: %s\n", errors? "fault":"pass");
printf("CPU time: %.3f\nGPU time: %.3f\n", time_cpu, time_gpu/20);
cudaEventDestroy(start);
cudaEventDestroy(stop_gpu);
cudaEventDestroy(stop_cpu);
return 0;
}
耗时分析
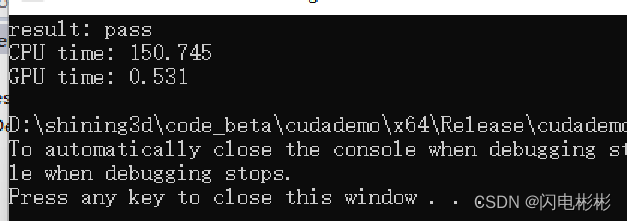
耗时0.531毫秒,比直接法提升了20%多。
本人码农,希望通过自己的分享,让大家更容易学懂计算机知识。创作不易,帮忙点击公众号的链接。

























 1462
1462











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








