那么我们自己能用costmap layer 来干什么呢?首先来看一个问题,假设你想让你的机器人不能去厨房或者其他一些地方,可能你会想在全局地图中的这些地方人为的放置一些假障碍,那机器人就去不了了。可假障碍如何放到机器人已经生成的costmap里?有人用假激光或者假的点云数据来制造假障碍,但是,很麻烦。如果你能创建一个专门存放这些假障碍的costmap ,然后把这个costmap作为插件(plugin)放到ROS自带的地图里去,这个问题就解决了。
ROS的官网wiki里有教你怎么新建costmap layer以及怎么插入到global_costmap 或者local_costmap里去,官方的tutorials请点击这里,教程里的例子是在你机器人前方1m处防止一个障碍点。可惜教程是建立在rosbulid编译环境下的,对于一路都是使用catkin的新手来说,怎么使得rosbuild 和catkin两个work space合起来工作,都成问题。所以,这里就教你如何在catkin环境下创建layer。
本文分为两部分:
1、如何在catkin 工作空间中创建New layer 插件
2、如何在程序中调用新创建的New layer
一、创建 layer 插件
在这部分,将创建一个simpler layer,这个layer的作用是在机器人前方1m处放置一个障碍物。
1. 首先要保证安装了costmap-2d这个包
即使当初安装ros的时候采用-full版本安装,也是没有costmap_2d这个包的,使用命令:
~$ sudo apt-get install ros-kinetic-costmap-2d ,(不是"_2d")
安装成功后,会在/opt/ros/kenetic/share/目录下看到costmap_2d这个包

2.首先像创建beginner_tutorials package一样,在catkin工作空间下创建simple_layers package。在终端中输入:
- cd ~/catkin_ws/src
- catkin_create_pkg simple_layers roscpp costmap_2d dynamic_reconfigure std_msgs rospy
2.创建layer 所需的头文件。
在创建好的simple_layers/include/simple_layers/ 文件夹下创建空白文档,命名为simple_layer.h,将下列程序复制进去并保存。
- #ifndef SIMPLE_LAYER_H_
- #define SIMPLE_LAYER_H_
- #include <ros/ros.h>
- #include <costmap_2d/layer.h>
- #include <costmap_2d/layered_costmap.h>
- #include <costmap_2d/GenericPluginConfig.h>
- #include <dynamic_reconfigure/server.h>
- namespace simple_layer_namespace
- {
- class SimpleLayer : public costmap_2d::Layer
- {
- public:
- SimpleLayer();
- virtual void onInitialize();
- virtual void updateBounds(double origin_x, double origin_y, double origin_yaw, double* min_x, double* min_y, double* max_x,
- double* max_y);
- virtual void updateCosts(costmap_2d::Costmap2D& master_grid, int min_i, int min_j, int max_i, int max_j);
- private:
- void reconfigureCB(costmap_2d::GenericPluginConfig &config, uint32_t level);
- double mark_x_, mark_y_;
- dynamic_reconfigure::Server<costmap_2d::GenericPluginConfig> *dsrv_;
- };
- }
- #endif
3.创建c++文件,在simpler_layers/src文件夹下创建空白文档,命名为simple_layer.cpp,输入下面程序,并保存。
- #include<simple_layers/simple_layer.h>
- #include <pluginlib/class_list_macros.h>
- PLUGINLIB_EXPORT_CLASS(simple_layer_namespace::SimpleLayer, costmap_2d::Layer) //注册插件
- using costmap_2d::LETHAL_OBSTACLE;
- namespace simple_layer_namespace
- {
- SimpleLayer::SimpleLayer() {}
- void SimpleLayer::onInitialize()
- {
- ros::NodeHandle nh("~/" + name_);
- current_ = true;
- dsrv_ = new dynamic_reconfigure::Server<costmap_2d::GenericPluginConfig>(nh);
- dynamic_reconfigure::Server<costmap_2d::GenericPluginConfig>::CallbackType cb = boost::bind(
- &SimpleLayer::reconfigureCB, this, _1, _2);
- dsrv_->setCallback(cb);
- }
- void SimpleLayer::reconfigureCB(costmap_2d::GenericPluginConfig &config, uint32_t level)
- {
- enabled_ = config.enabled;
- }
- void SimpleLayer::updateBounds(double origin_x, double origin_y, double origin_yaw, double* min_x,
- double* min_y, double* max_x, double* max_y)
- {
- if (!enabled_)
- return;
- mark_x_ = origin_x + cos(origin_yaw);
- mark_y_ = origin_y + sin(origin_yaw);
- *min_x = std::min(*min_x, mark_x_);
- *min_y = std::min(*min_y, mark_y_);
- *max_x = std::max(*max_x, mark_x_);
- *max_y = std::max(*max_y, mark_y_);
- }
- void SimpleLayer::updateCosts(costmap_2d::Costmap2D& master_grid, int min_i, int min_j, int max_i,
- int max_j)
- {
- if (!enabled_)
- return;
- unsigned int mx;
- unsigned int my;
- if(master_grid.worldToMap(mark_x_, mark_y_, mx, my)){
- master_grid.setCost(mx, my, LETHAL_OBSTACLE);
- }
- }
- } // end namespace
以上部分都和官方教程中没什么差别,下面开始是如何在ros中注册这个插件的关键步奏了,这部分可以参看 wiki pluginlib的说明 ,也可以看看 navigation里如何写自己的全局路径规划插件教程。如果,没有过写插件的基础,先照着Lz下面的教程执行一遍,再回过头去看上面的两个教程。
4.修改simpler_layers package下的Cmakerlists.txt文件。
添加:
- add_library(simple_layer src/simple_layer.cpp)
然后修改在include_directories(...)中添加include,修改后如下:
- include_directories(include ${catkin_INCLUDE_DIRS})
5.创建一个空白的costmap_plugins.xml文件,输入一下内容,将其存放在/catkin_ws/src/simpler_layers 文件夹下,也就是和Cmakelists.txt以及package.xml存放在同一路径下:
- <library path="lib/libsimple_layer">
- <class type="simple_layer_namespace::SimpleLayer" base_class_type="costmap_2d::Layer">
- <description>Demo Layer that adds a point 1 meter in front of the robot</description>
- </class>
- </library>
6.修改package.xml,将下面语句
- <costmap_2d plugin="${prefix}/costmap_plugins.xml" />
- <export>
- <costmap_2d plugin="${prefix}/costmap_plugins.xml" />
- </export>
上面步奏完成以后,就是编译了。
- cd ~/catkin_ws
- catkin_make
rospack plugins --attrib=plugin costmap_2d
应该会得到LZ这样的结果:
说明simple_layer 已经是一个可供ROS用的插件了。
二、如何在move_base中使用这个costmap layer插件
上面已经创建好了layer插件,并不意味着ROS就会使用它,我们得显式的global_costmap 或者 local_costmap中声明它。 当然首先可以看看wiki 配置layer costmap的教程。看不懂没关系,至少心里先有个大概印象。
在调用自己写的这个layer之前,先看看系统默认的global_costmap 和local_costmap使用了哪些layer。假设你已经安装了《ROS by example 1》中的rbx1 package。如果没有安装,可以按照下面的过程进行安装。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
安装rbx1包,参考https://www.cnblogs.com/TooyLee/p/7736732.html
1.首先安装一些依赖包
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
sudo apt-
get
install ros-kinetic-turtlebot-bringup \
ros-kinetic-turtlebot-create ros-kinetic-openni-* \
ros-kinetic-openni2-* ros-kinetic-freenect-* ros-kinetic-usb-cam \
ros-kinetic-laser-* ros-kinetic-hokuyo-node \
ros-kinetic-audio-common gstreamer0.10-pocketsphinx \
ros-kinetic-pocketsphinx ros-kinetic-slam-gmapping \
ros-kinetic-joystick-drivers python-rosinstall \
ros-kinetic-orocos-kdl ros-kinetic-python-orocos-kdl \
python-setuptools ros-kinetic-dynamixel-motor \
libopencv-dev python-opencv ros-kinetic-vision-opencv \
ros-kinetic-depthimage-to-laserscan ros-kinetic-arbotix-* \
ros-kinetic-turtlebot-teleop ros-kinetic-move-
base
\
ros-kinetic-map-server ros-kinetic-fake-localization \
ros-kinetic-amcl git subversion mercurial
|
其中,ros-kinetic-hokuyo-node(北阳激光雷达)、gstreamer0.10-pocketsphinx和ros-kinetic-pocketsphinx(语音识别库)和ros-kinetic-arbotix-*(模拟器)在ros kinetic版本中没有,如果用到需要源码编译
2.下载rbx1和arbotix源码并编译
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
mkdir -p ~/dev/catkin_ws/src
cd ~/dev/catkin_ws/src
catkin_init_workspace
git clone https:
//github.com/pirobot/rbx1.git
git clone https:
//github.com/vanadiumlabs/arbotix_ros.git
|
其他包没用到就没有用到就没有编译
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- roslaunch rbx1_bringup fake_turtlebot.launch
- roslaunch rbx1_nav fake_move_base_blank_map.launch
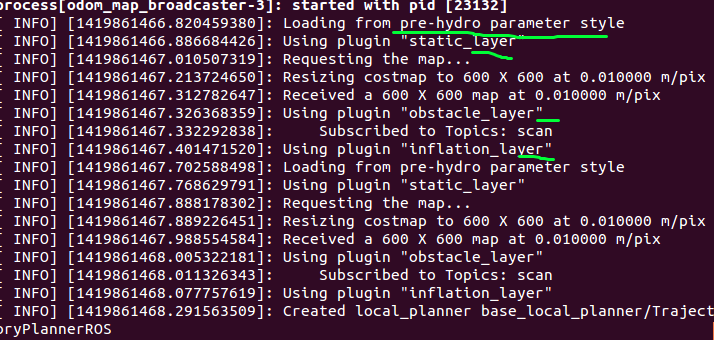
你会看到pre-hydro 字样。说明当前的costmap是默认的配置,也就是static_layer,obstacle_layer,inflation_layer这三层。
下面我们来把创建的simple_layer,放入全局global_costmap中。要想使得ROS接受你的插件,要在参数中用plugins指明,也就是主要修改move_base中涉及到costmap的yaml文件,下面给出我的修改:1.costmap_common_params.yaml
- obstacle_range: 2.5
- raytrace_range: 3.0
- robot_radius: 0.49
- inflation_radius: 0.1
- max_obstacle_height: 0.6
- min_obstacle_height: 0.0
- obstacles:
- observation_sources: scan
- scan: {data_type: LaserScan, topic: /scan, marking: true, clearing: true, expected_update_rate: 0}
一定要注意,这里添加了一个obstales,说明障碍物层的数据来源scan,"obstacles:"的作用是强调命名空间。
2.global_costmap_params.yaml
- global_costmap:
- global_frame: /map
- robot_base_frame: /base_footprint
- update_frequency: 1.0
- publish_frequency: 0
- static_map: true
- rolling_window: false
- resolution: 0.01
- transform_tolerance: 1.0
- map_type: costmap
- plugins:
- - {name: static_map, type: "costmap_2d::StaticLayer"}
- - {name: obstacles, type: "costmap_2d::VoxelLayer"}
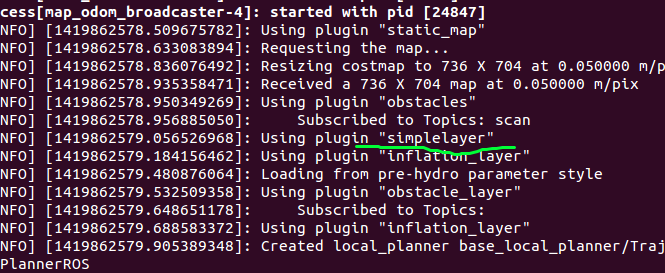
- - {name: simplelayer, type: "simple_layer_namespace::SimpleLayer"}
- - {name: inflation_layer, type: "costmap_2d::InflationLayer"}
3.local_costmap_params.yaml
- local_costmap:
- global_frame: /map
- robot_base_frame: /base_footprint
- update_frequency: 3.0
- publish_frequency: 1.0
- static_map: false
- rolling_window: true
- width: 6.0
- height: 6.0
- resolution: 0.01
- transform_tolerance: 1.0
- map_type: costmap
另外一个与路径规划相关的base_local_planner_params,yaml不用修改。
这里由于只在全局层添加simple_layer,所以local_costmap还是使用的默认layer插件。然后我们运行这个新配置的move_base launch文件,你会发现simplerlayer已经添加进global_costmap了,而local_costmap还是默认的pre-hydro格式。
最后在rviz中看看global_costmap中有没有加入这个障碍物点。下面是我在实验室环境的地图,红色标记的地方是人为加入的障碍物。按照上面的程序,障碍物应该出现在机器人正前方1m出,下面这个效果是lz自己的程序。
障碍物的膨胀系数,可以用下面的命令进行动态调试:
- rosrun rqt_reconfigure rqt_reconfigure
由于网上关于这部分的教程很少,lz也是自己慢慢摸索出来的,查看了很多ros answer,一一列出在下面。同时,这个地址有一个别人创建的行人layer,为你定制自己的移动障碍物层有很好的借鉴意义。
原文参考:http://blog.csdn.net/heyijia0327/article/details/42241831#insertcode


























 1063
1063

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








