这篇文章14年发表在ECCV,可以说是CNN领域可视化理解的开山之作,这篇文献告诉我们CNN的每一层到底学习到了什么特征,然后作者通过可视化进行调整网络,提高了精度。在CNN的研究中,很多学者不明白,为什么通过某种调参、改动网络结构等精度会提高。而这篇文献的目的就是通过特征可视化,来告诉我们如何通过可视化的角度,查看我们的精度确实提高了,
2.1 Visualization with a deconvnet
想要理解一个convnet的operation首先需要解释中间层的feature activity。论文提出了一种方式来将这些activities 映射回输入像素空间,从而展示什么样的input pattern能够引起feature map中某个activation。文章通过Deconvolutional Network(deconvent)来实现这种映射过程。Here,they are not used in any learning capacity,just as a probe of an already trained convnet。
为了检验一个convnet,一个deconvnet在这个convnet的每一层都进行了连接,如图一所示,这提供了一个映射回image pixel的连续路径:
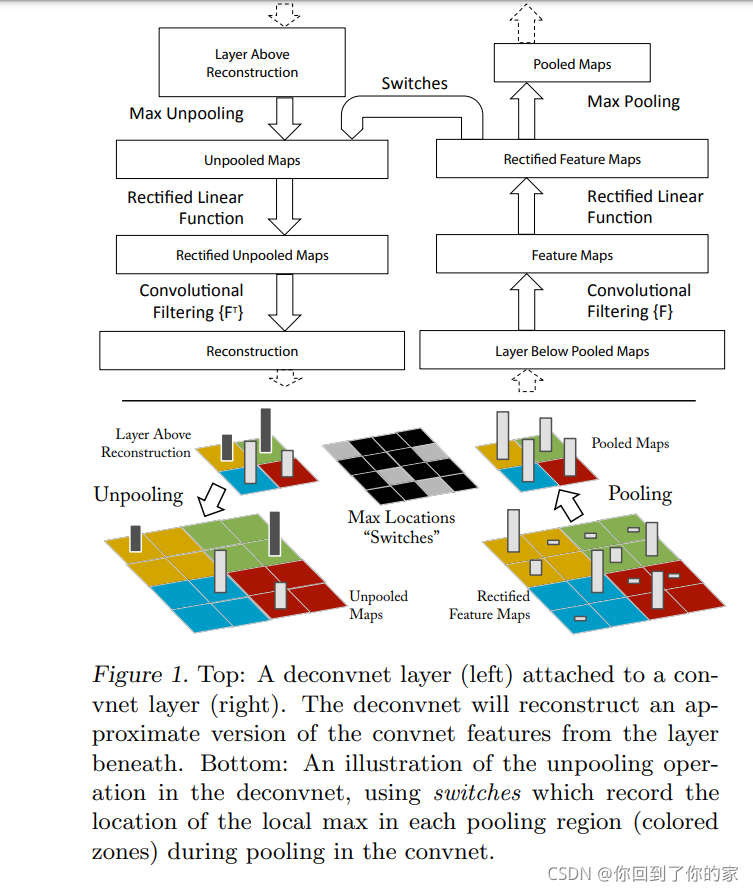
开始时,一个输入图片被提供给convnet并且通过各个层计算feature。为了检验某个给定的convnet activation,我们将这一层的其他所有activation设定为0并且将这个feature map作为输入给到连接的deconvnet layer中。接下来我们进行三个连续的操作:
- unpool
- rectify
- filter
通过这三步来reconstruct the activity in the layer beneath that gave rise to the chosen activation。这个过程将会重复,直到input pixel space is reached。
Unpooling
在convnet中,max pooling操作是不可逆的,但是我们可以获得一个合适的逆转过程,通过记录每个pooling区域的最大值位置,我们将这些位置存在一个集合中,称为switch variable。在deconvnet中,unpooling操作使用这些switch值来place the reconstruction from the layer above into appropriate locations,保留激活因素的结构性。这个过程在图1的底部进行了阐述。
Rectification
convnet使用relu非线性激活函数来修正feature map,使得feature map的值一直为正。为了获取每一层的有效的feature reconstruction(which also should be positive),we pass the reconstructed signal through a relu non-linearity。
Filtering
convnet使用学习到的filter来convolve the feature map from the previous layer。为了反转这个过程,deconvnet使用transposed versions of the same filters,但是应用于修正后的maps(而不是和convnet一样取在它之下的层的输出)。In practice this means flipping each filter vertically and horizontally。
从高层向下映射的过程使用了convnet中正向传播生成的switch信息。As these switch setting are peculiar to a given input image, the reconstruction obtained from a single input image, with structures weighted according to their contribution toward to the feature activation. Since the model is trained discriminatively, they implicitly show which parts of the input image are discriminative。Note that these projection are not samples from the model,since there is no generative process involved。
三、训练细节
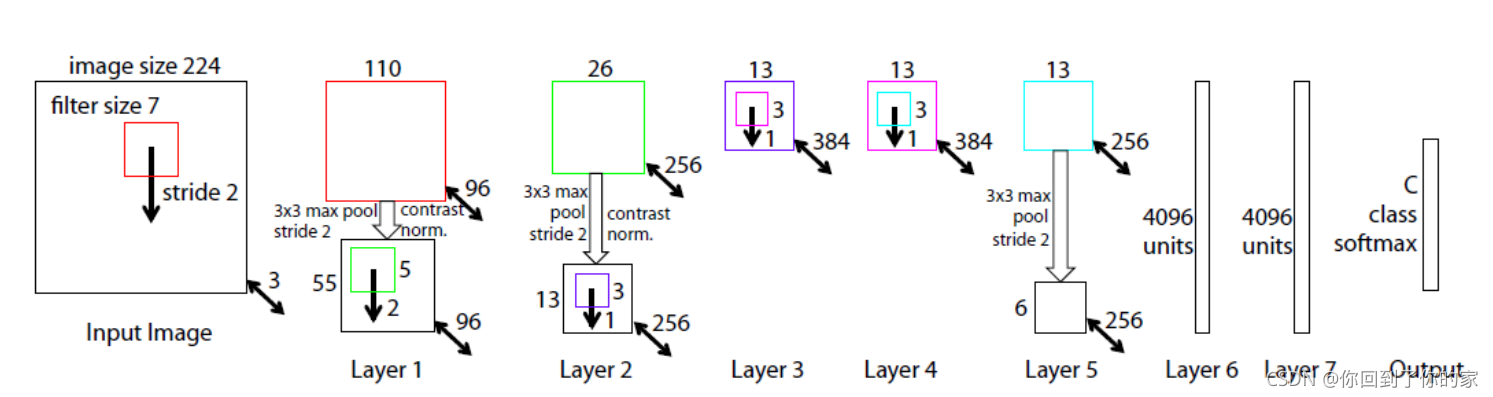
这一节描述了要在第四部分进行可视化的convnet模型,整体模型如图三所示:
四、Convnet可视化
利用第三节描述的模型,我们接下来使用deconvnet来可视化ImageNet validation set上的feature activation。
Feature Visualization:
图二展示了训练完成后我们模型的feature visualizations。但是,我们不是仅展示给定feature map后最强的activation,而是展示了top 9 activations。将这9个中的每一个映射回pixel space揭示出了能excite一个给定feature map的不同的structure,因此展示了它在输入变化下的不变性。伴随着这些可视化,我们展示了对应的image patches。这些图片本身相对visualization来说有着更大的变化性因为visualization仅仅关注每个patch中的discriminant structure。
例如,在第五层的第一行第二列,图片patches看似几乎没有共同点,但是visualization揭示出这个feature map聚焦在背景的草地,并不是foreground的物体。每个layer的projections都展示出了网络中feature的hierarchical nature。 第二层responds to corners以及其他edge/color的结合。第三层有着更复杂的不变性,会捕获一个相似的纹理(例如第一行第一列的mesh patterns,文本 R2,C4)。第四层显示出了明显的variation,但是更class-specific:例如狗的脸(R1,C1);鸟的腿(R4,C2)。第五层显示出了整个物体且带有明显的pose variation,例如键盘(R1,C11)以及狗(R4)、
Feature Evolution during Training
图4可视化了the progression during training of the strongest activation(在所有的训练数据中)within a given feature map projected back to pixel space。Sudden jumps in appearance result from a change in the image from which the strongest activation originates。模型中较低层可以看出在几轮epoch后就已经收敛了。然而,较上层的layer仅在一个相对较大的epochs(40-50)后才会develop,这证实了我们需要让整个模型训练直到完全收敛为止。
Feature Invariance
图五展示了五张测试图片,这些图片被以多种degrees进行translated、rotated以及scaled,我们观察在整个过程中changes in the feature vectors from the top and the bottom layers of the model,relative to the untransformed feature。小的变换对于模型的第一层有显著的影响,但是对于最顶层的feature layer影响相对较小,being quasilinear for translation 以及 scaling。整个网络的输出对于translation以及scaling是稳定的。通常来讲,输出相对rotation并不是不变的,除了物体本身是rotational symmetry的情况(例如entertainment center)。
4.1 Architecture Selection
对于一个训练好的模型进行可视化不仅能给我们关于这个模型operation的insight,还可以帮助我们选取一种好的结构。通过可视化Krizhevsky等人模型的第一层以及第二层(图6 b和d),我们发现了非常明显的问题。第一层的filter是a mix of extremely high and low frequency information, with little coverage of the mid frequencies。此外,第二层可视化展示了第一层卷积时采用的较大的stride 4带来的alising artifacts。为了解决这些问题,我们采用了如下的方式:
- 将第一层的filter size从 11 × 11 11\times 11 11×11降低到了 7 × 7 7\times7 7×7
- 将stride修改为2而不是4
这个新的网络结构在第一层以及第二层保有了更多的信息,如图6 c和e所示。更重要的是,这种改进也提高了分类的准确率(在5.1节中介绍了这一点)
4.2 Occlusion Sensitivity
对图片分类任务来说,一个很自然的问题是,这个模型是在判定图片中我们需要的对象的信息,还是仅仅在判断这个对象周围的背景信息。图7尝试通过系统性地用grey square来occluding输入图片的不同部分,以及监控classifier的输出来解决这个问题。这个例子很清晰的说明了这个模型正在定位scene内的对象信息,因为当这个对象被occluded时probability of the correct class drops significantly。图7同样展示了visualizations from the strongest feature map of the top convolution layer,in addtion to activity in this map(summed over spatial locations)as a function of occluder position。当occluder包括了出现在visualization中的图像区域时,我们能够观察到a strong drop in activity in the feature map。这展示了visualization genuinely corresponds to the image structure that stimulate that feature map,hence validating the other visualizations shown in figure4 and figure 2.
4.3 Correspondence Analysis
深度神经网络和许多现有的方法不同的是并没有一个清晰的mechanism for establishing correspondence between specific object parts in different images(例如faces have a particular spatial configuration of the eyes and nose)。然而,一个intriguing possibility is that deep models might be implicitly computing them。为了探索这个性质,
























 692
692

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








