一、项目介绍
项目背景:
骨折是常见的医疗问题,及时准确的诊断对患者的治疗和康复至关重要。传统的骨折诊断依赖于医生的经验和影像学检查,如X光片、CT扫描等。然而,人工诊断存在主观性和疲劳等问题。随着深度学习技术的发展,基于计算机视觉的自动骨折检测系统能够辅助医生快速、准确地识别骨折,提高诊断效率和准确性。
项目目标:
本项目旨在利用YOLOv10(You Only Look Once version 10)目标检测算法,开发一个高效的骨折检测系统。该系统能够自动从医学影像中检测出骨折区域,并区分骨折类型(如Fracture、No_Fracture、object),为医生提供辅助诊断工具。
技术栈:
-
深度学习框架:PyTorch
-
目标检测算法:YOLOv10
-
数据集:包含Fracture、No_Fracture、object三类标签的医学影像数据集
-
开发环境:Python、CUDA、OpenCV等
系统功能:
-
骨折检测:系统能够从输入的医学影像中自动检测出骨折区域,并标注出骨折类型。
-
分类与定位:系统不仅能识别骨折,还能区分骨折类型(Fracture、No_Fracture、object),并给出骨折区域的位置信息(边界框)。
-
可视化结果:系统将检测结果可视化,标注出骨折区域,并提供置信度评分。
-
批量处理:支持批量处理医学影像,适用于医院或诊所的大规模影像分析需求。
应用场景:
-
医院影像科:辅助医生快速筛查骨折影像,减少漏诊和误诊。
-
急诊室:在紧急情况下,快速提供骨折检测结果,帮助医生制定治疗方案。
-
远程医疗:通过自动化的骨折检测系统,为偏远地区的患者提供及时的诊断服务。
目录
七、项目源码(视频下方简介内)
基于深度学习YOLOv10的骨折检测系统(YOLOv10+YOLO数据集+UI界面+Python项目源码+模型)_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
基于深度学习YOLOv10的骨折检测系统(YOLOv10+YOLO数据集+UI界面+Python项目源码+模型)
二、项目功能展示
系统功能
✅ 图片检测:可对图片进行检测,返回检测框及类别信息。
✅ 视频检测:支持视频文件输入,检测视频中每一帧的情况。
✅ 摄像头实时检测:连接USB 摄像头,实现实时监测。
✅参数实时调节(置信度和IoU阈值)
-
图片检测
该功能允许用户通过单张图片进行目标检测。输入一张图片后,YOLO模型会实时分析图像,识别出其中的目标,并在图像中框出检测到的目标,输出带有目标框的图像。





-
视频检测
视频检测功能允许用户将视频文件作为输入。YOLO模型将逐帧分析视频,并在每一帧中标记出检测到的目标。最终结果可以是带有目标框的视频文件或实时展示,适用于视频监控和分析等场景。
-
摄像头实时检测
该功能支持通过连接摄像头进行实时目标检测。YOLO模型能够在摄像头拍摄的实时视频流中进行目标检测,实时识别并显示检测结果。此功能非常适用于安防监控、无人驾驶、智能交通等应用,提供即时反馈。
核心特点:
- 高精度:基于YOLO模型,提供精确的目标检测能力,适用于不同类型的图像和视频。
- 实时性:特别优化的算法使得实时目标检测成为可能,无论是在视频还是摄像头实时检测中,响应速度都非常快。
- 批量处理:支持高效的批量图像和视频处理,适合大规模数据分析。
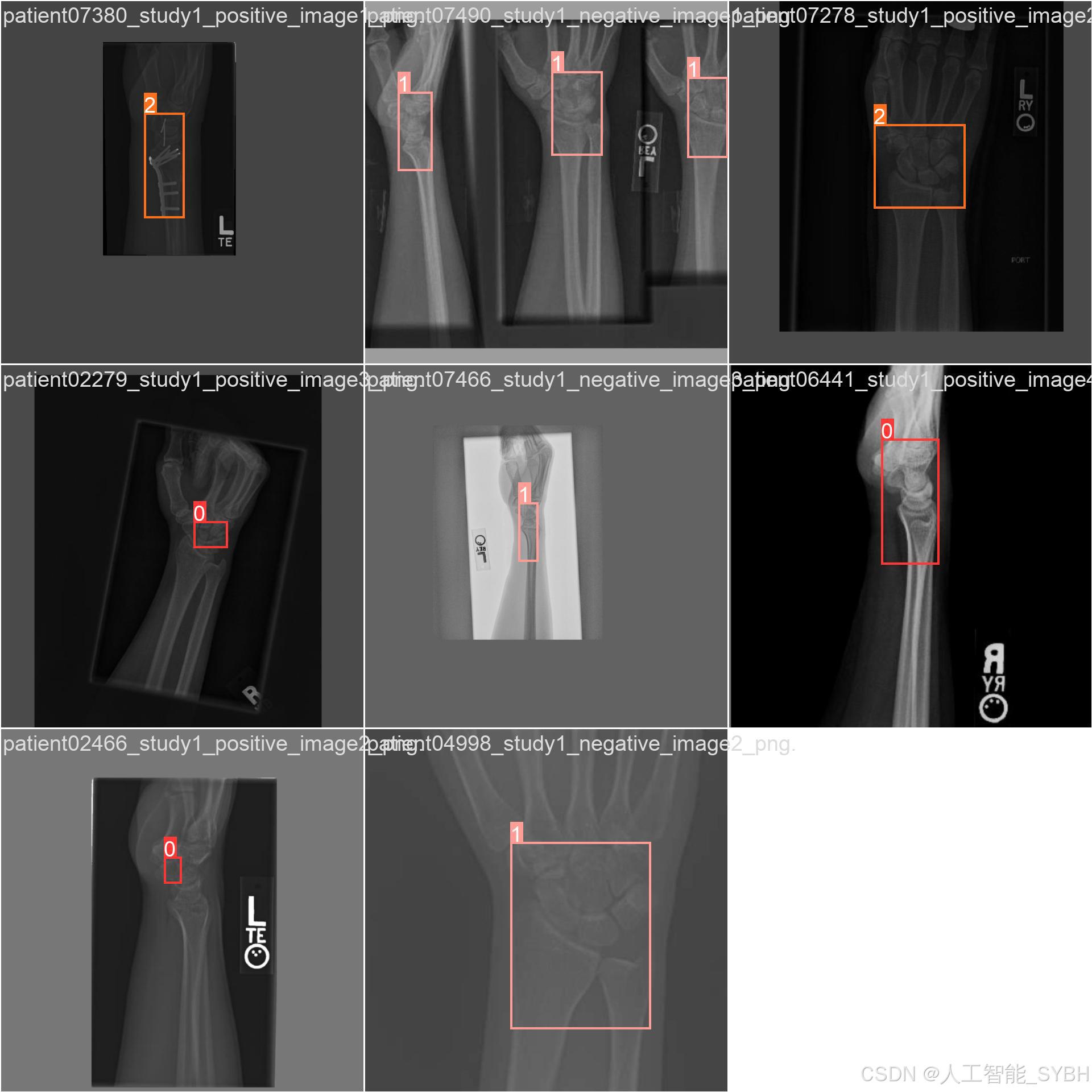
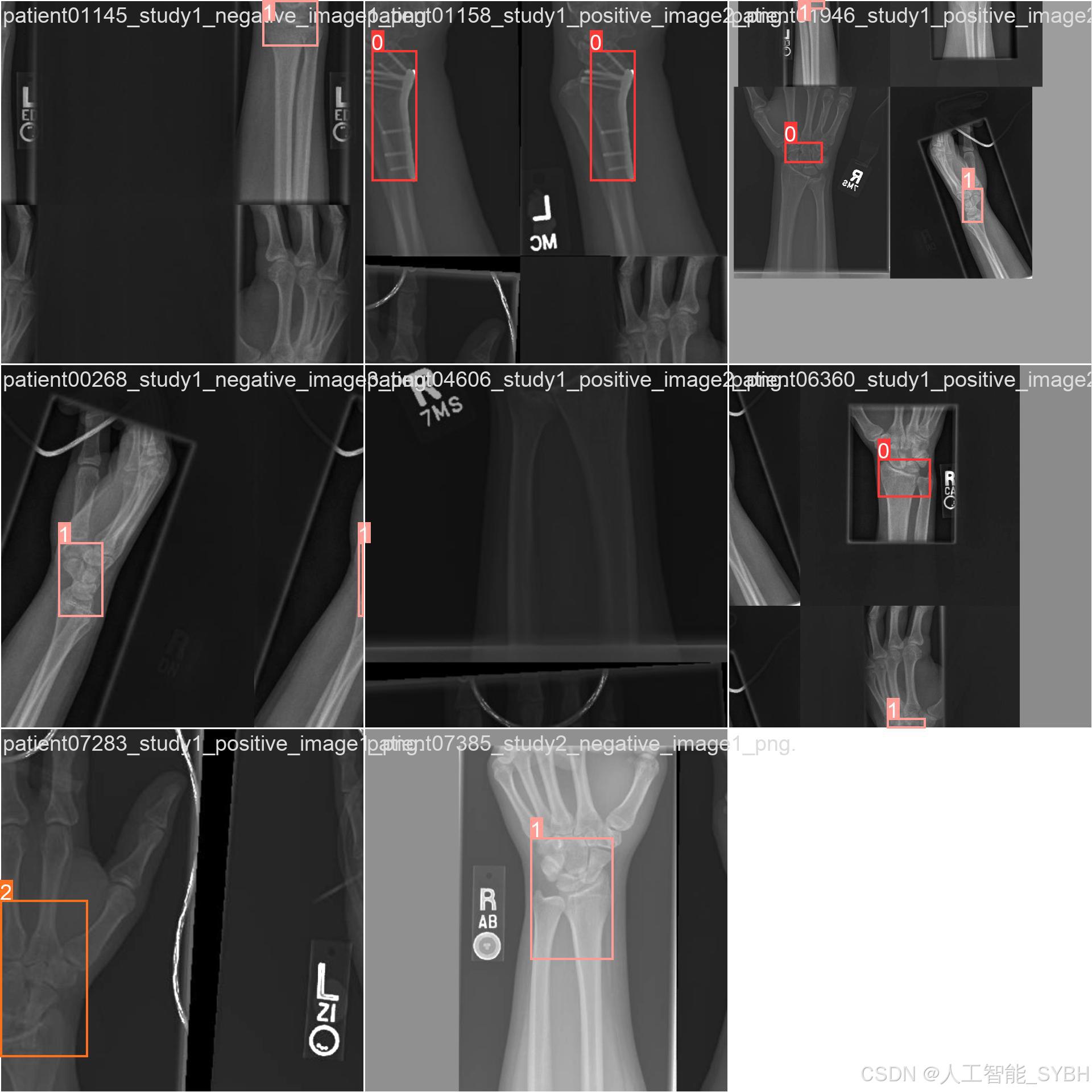
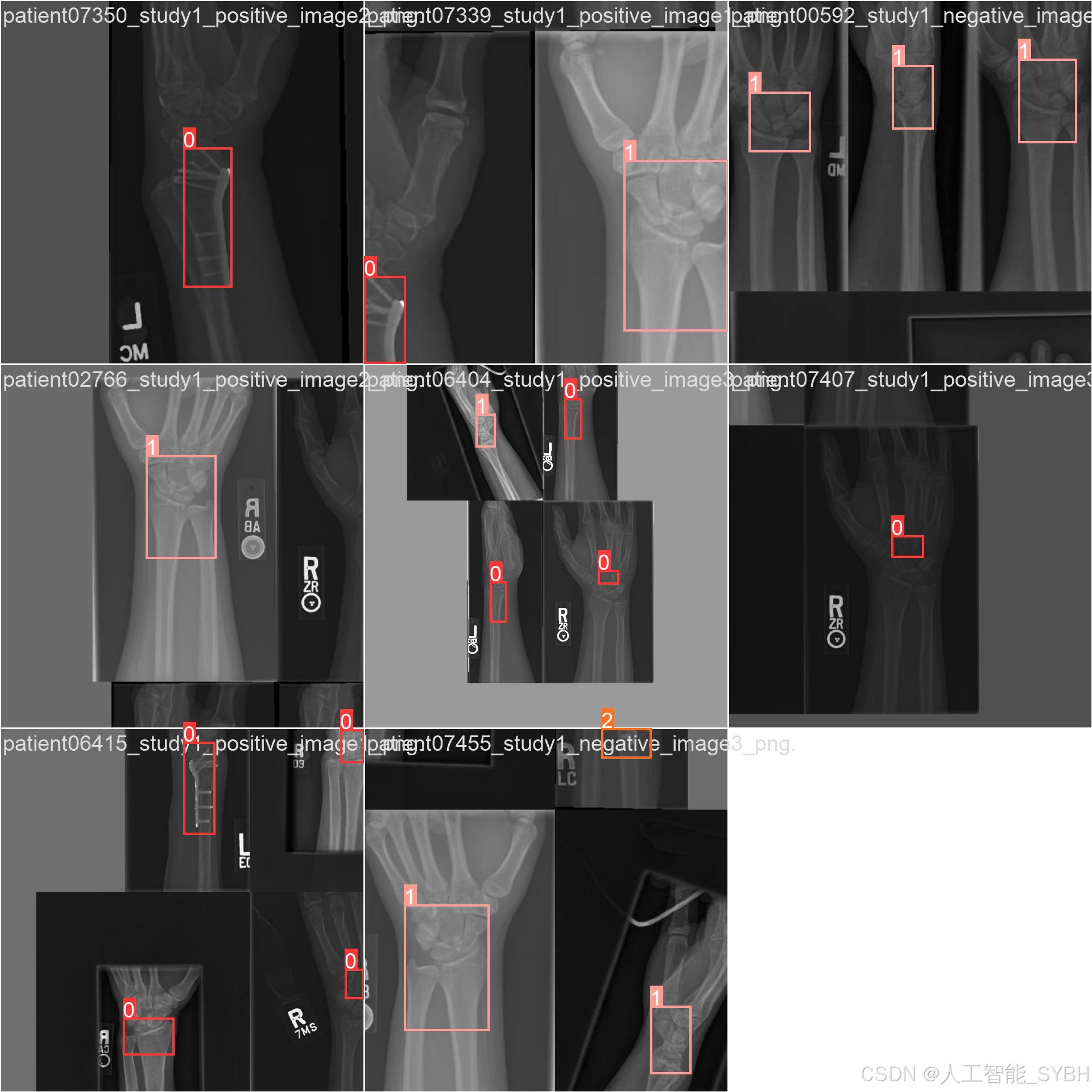
三、数据集介绍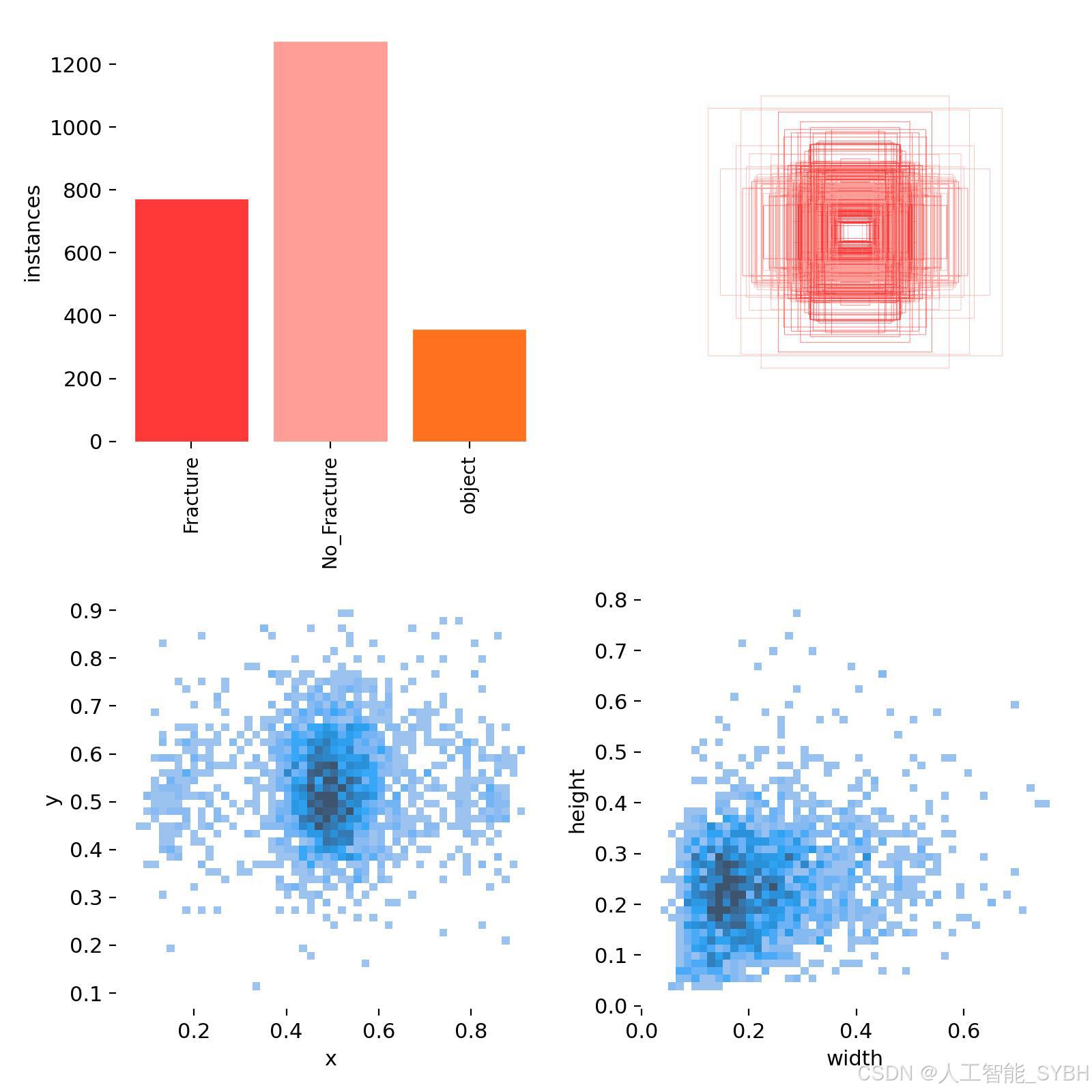
数据集概述:
本项目的数据集包含三类标签:Fracture(骨折)、No_Fracture(无骨折)、object(其他物体或干扰)。数据集分为训练集、验证集和测试集,具体数量如下:
-
训练集:2108张图像
-
验证集:602张图像
-
测试集:301张图像
数据集结构:
数据集中的每张图像都经过标注,标注信息包括:
-
类别标签:Fracture、No_Fracture、object
-
边界框坐标:骨折区域的位置信息(x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max)
数据来源:
数据集来源于公开的医学影像数据库或合作医院提供的匿名化影像数据。所有数据均经过专业医生的标注和审核,确保标注的准确性。
数据预处理:
-
图像增强:为了提升模型的泛化能力,对训练集进行了数据增强操作,包括随机旋转、翻转、缩放、亮度调整等。
-
归一化:将所有图像归一化到相同的尺寸(如640x640),以适应YOLOv10的输入要求。
-
标注格式转换:将标注信息转换为YOLOv10所需的格式(类别索引、归一化的边界框坐标)。
数据集特点:
-
类别平衡:数据集中Fracture、No_Fracture、object三类样本数量相对平衡,避免模型训练时的类别偏差。
-
多样性:数据集包含不同部位(如手臂、腿部、脊柱等)的骨折影像,涵盖了多种骨折类型。
-
高质量标注:所有标注均由专业医生完成,确保标注的准确性和可靠性。
数据集划分:
-
训练集:用于训练YOLOv10模型,优化模型参数。
-
验证集:用于调整超参数和评估模型在训练过程中的表现,防止过拟合。
-
测试集:用于最终评估模型的性能,确保模型在未见数据上的泛化能力。



数据集配置文件data.yaml
train: .\datasets\images\train
val: .\datasets\images\val
test: .\datasets\images\test
# Classes
nc: 6
# class names
names: [ 'hand-raising', 'reading', 'writing','using phone', 'bowing the head', 'leaning over the table']数据集制作流程
-
标注数据:使用标注工具(如LabelImg、CVAT等)对图像中的目标进行标注。每个目标需要标出边界框,并且标注类别。
-
转换格式:将标注的数据转换为YOLO格式。YOLO标注格式为每行:
<object-class> <x_center> <y_center> <width> <height>,这些坐标是相对于图像尺寸的比例。 -
分割数据集:将数据集分为训练集、验证集和测试集,通常的比例是80%训练集、10%验证集和10%测试集。
-
准备标签文件:为每张图片生成一个对应的标签文件,确保标签文件与图片的命名一致。
-
调整图像尺寸:根据YOLO网络要求,统一调整所有图像的尺寸(如416x416或608x608)。
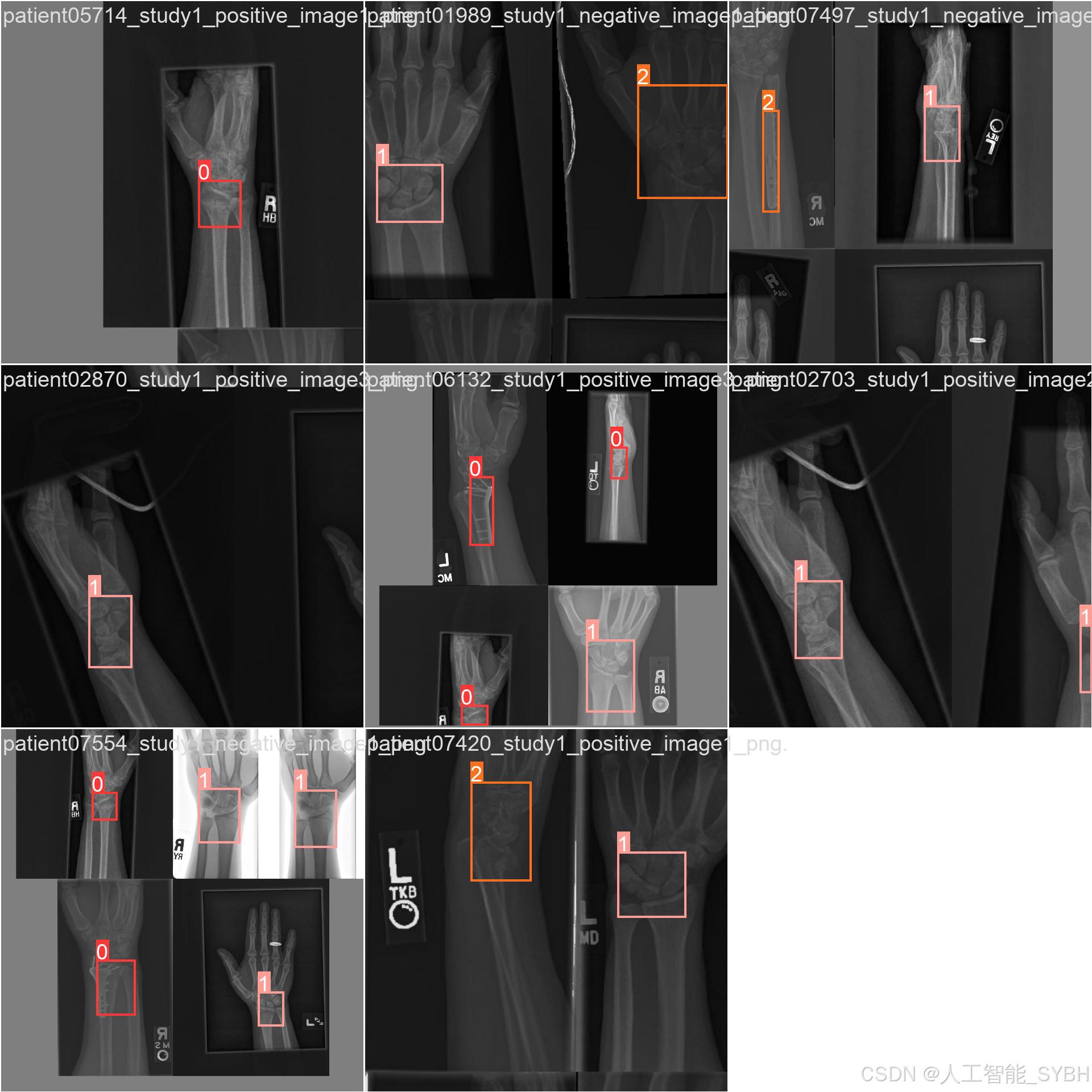
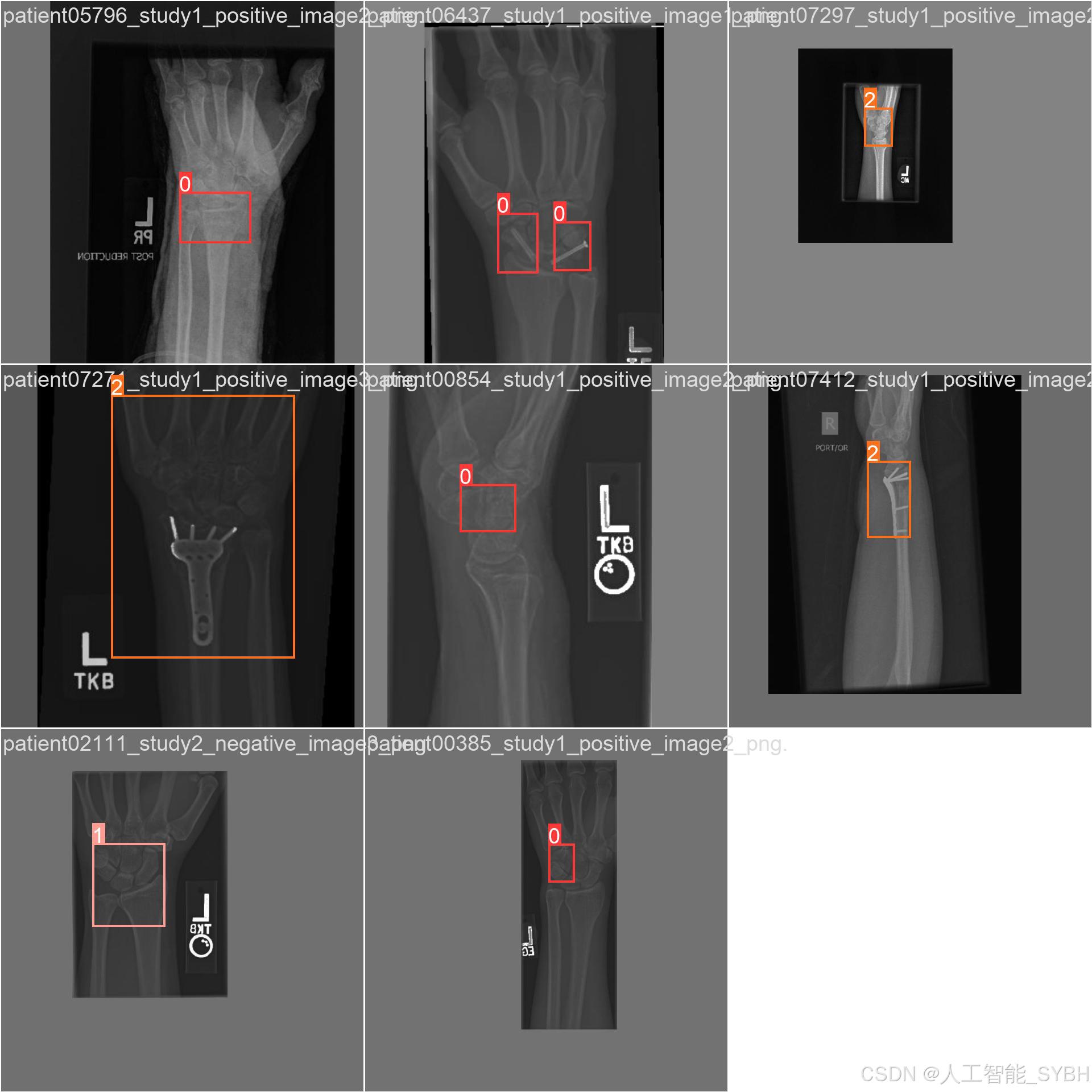
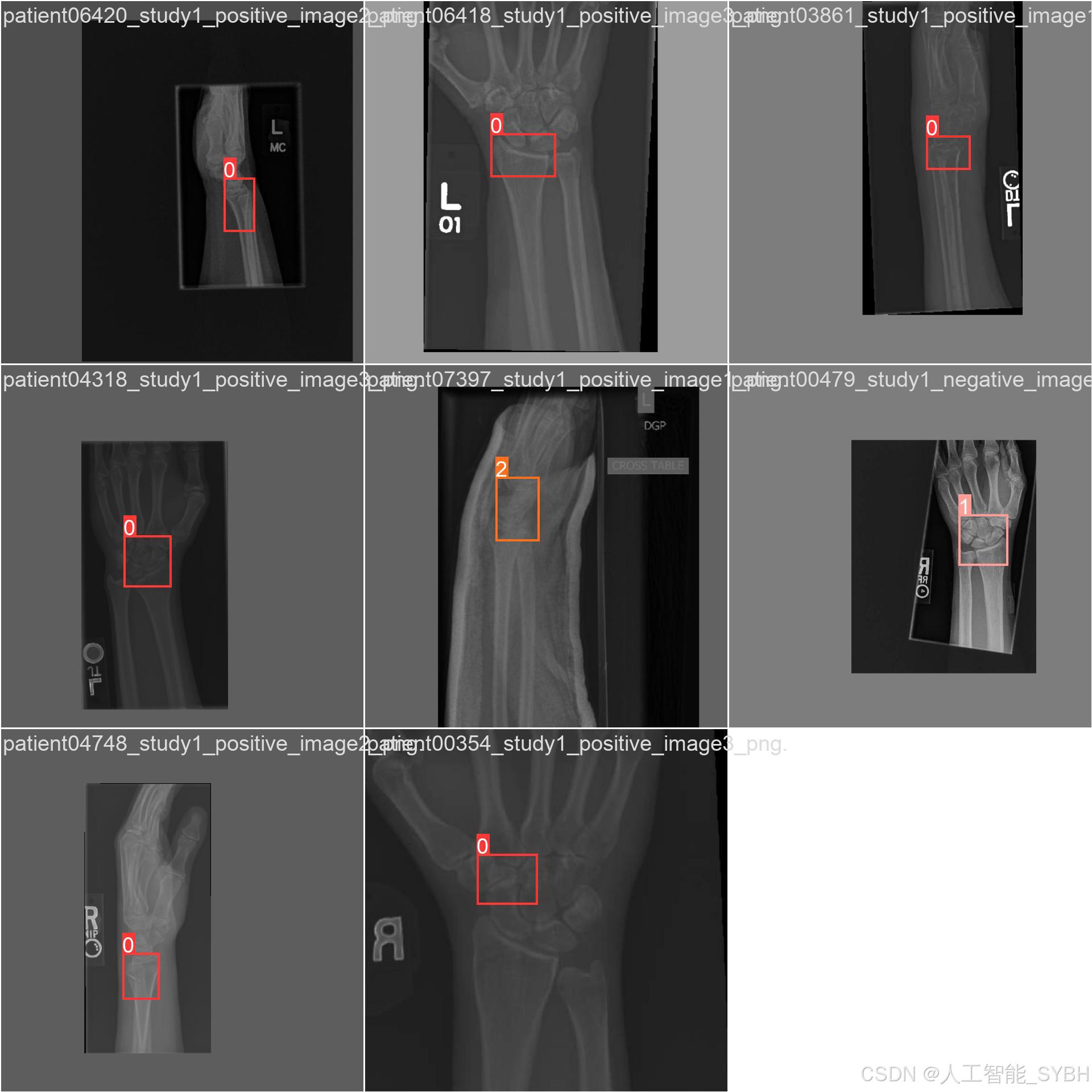
四、项目环境配置
创建虚拟环境
首先新建一个Anaconda环境,每个项目用不同的环境,这样项目中所用的依赖包互不干扰。
终端输入
conda create -n yolov10 python==3.9

激活虚拟环境
conda activate yolov10

安装cpu版本pytorch
pip install torch torchvision torchaudio

pycharm中配置anaconda


安装所需要库
pip install -r requirements.txt

五、模型训练
训练代码
from ultralytics import YOLOv10
model_path = 'yolov10s.pt'
data_path = 'datasets/data.yaml'
if __name__ == '__main__':
model = YOLOv10(model_path)
results = model.train(data=data_path,
epochs=500,
batch=64,
device='0',
workers=0,
project='runs/detect',
name='exp',
)根据实际情况更换模型 yolov10n.yaml (nano):轻量化模型,适合嵌入式设备,速度快但精度略低。 yolov10s.yaml (small):小模型,适合实时任务。 yolov10m.yaml (medium):中等大小模型,兼顾速度和精度。 yolov10b.yaml (base):基本版模型,适合大部分应用场景。 yolov10l.yaml (large):大型模型,适合对精度要求高的任务。
--batch 64:每批次64张图像。--epochs 500:训练500轮。--datasets/data.yaml:数据集配置文件。--weights yolov10s.pt:初始化模型权重,yolov10s.pt是预训练的轻量级YOLO模型。
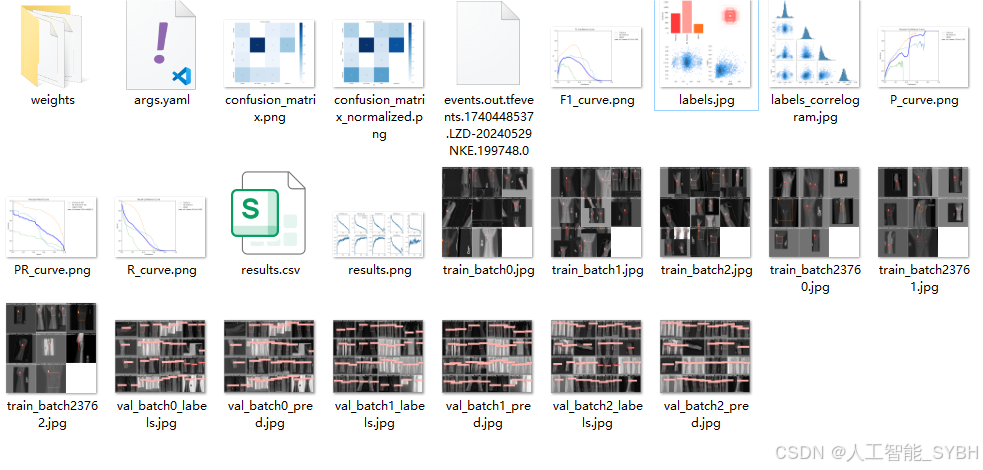
训练结果

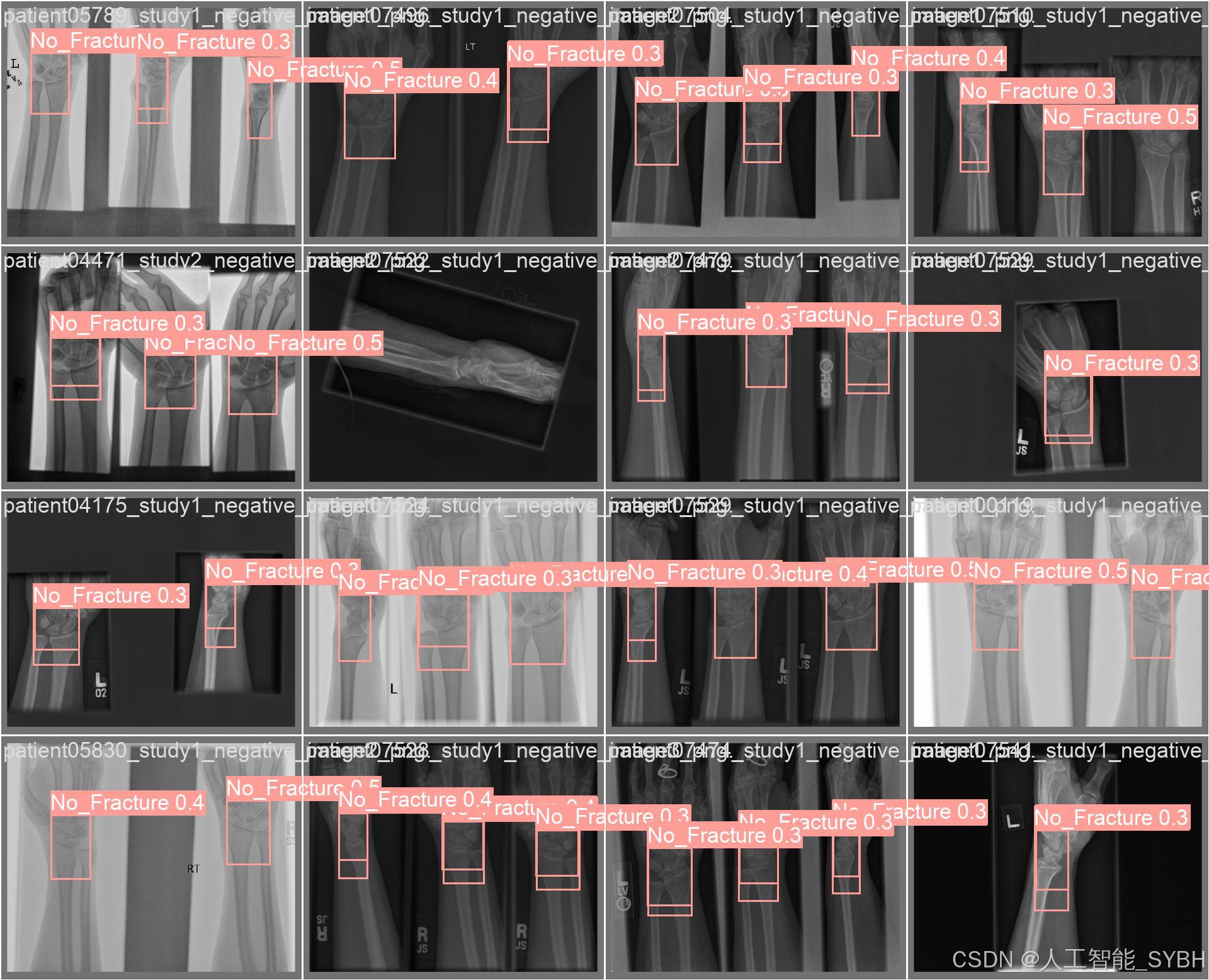


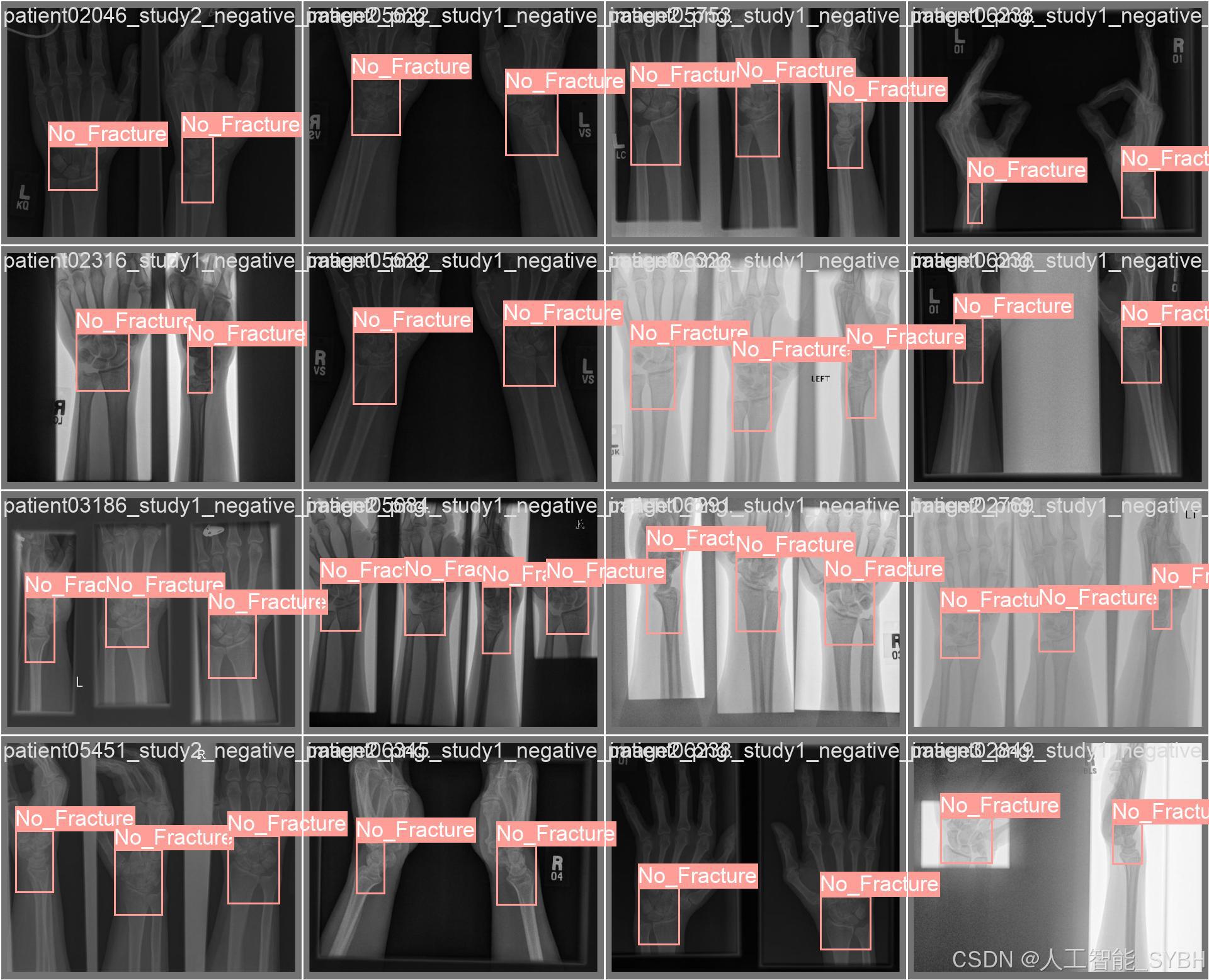
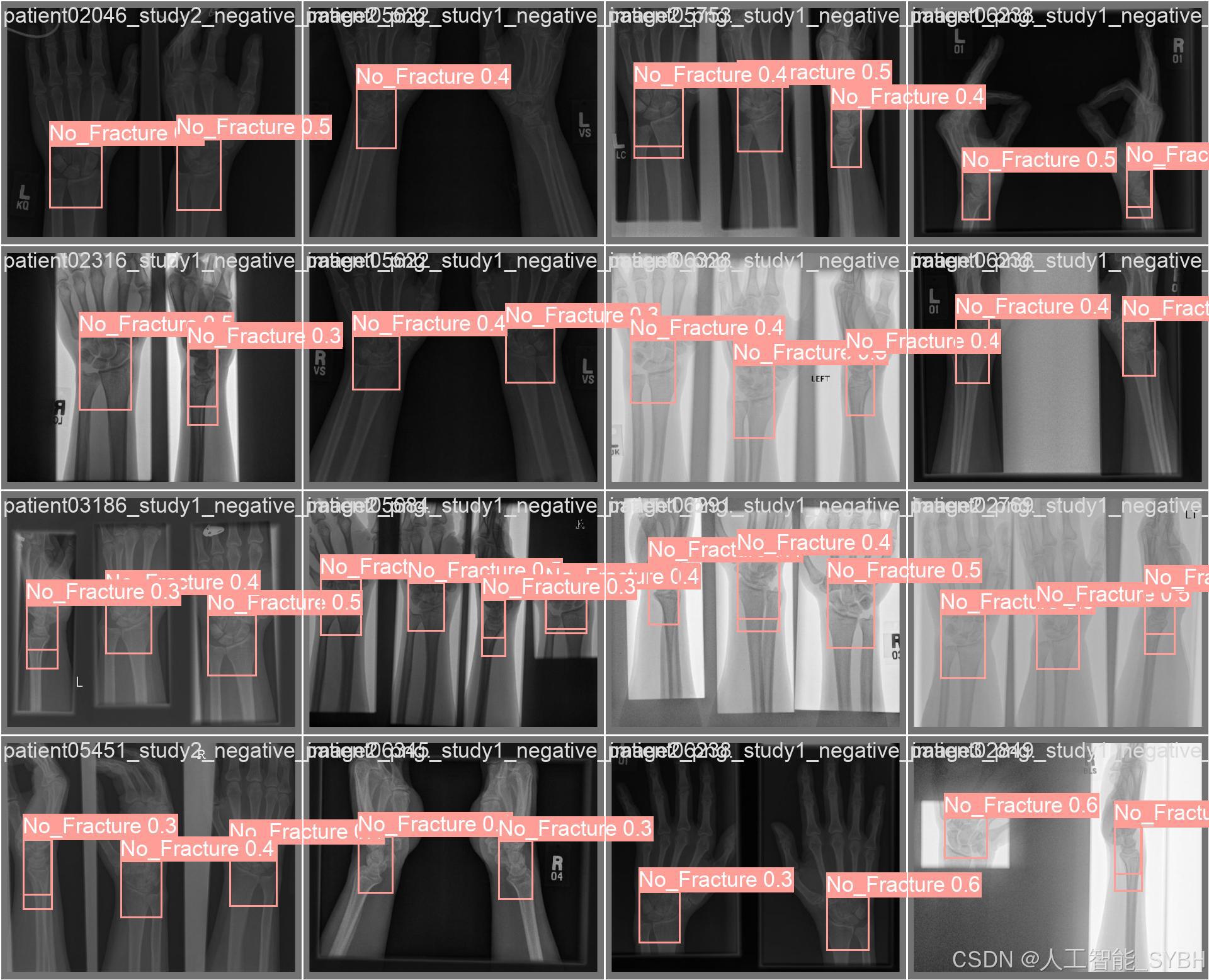
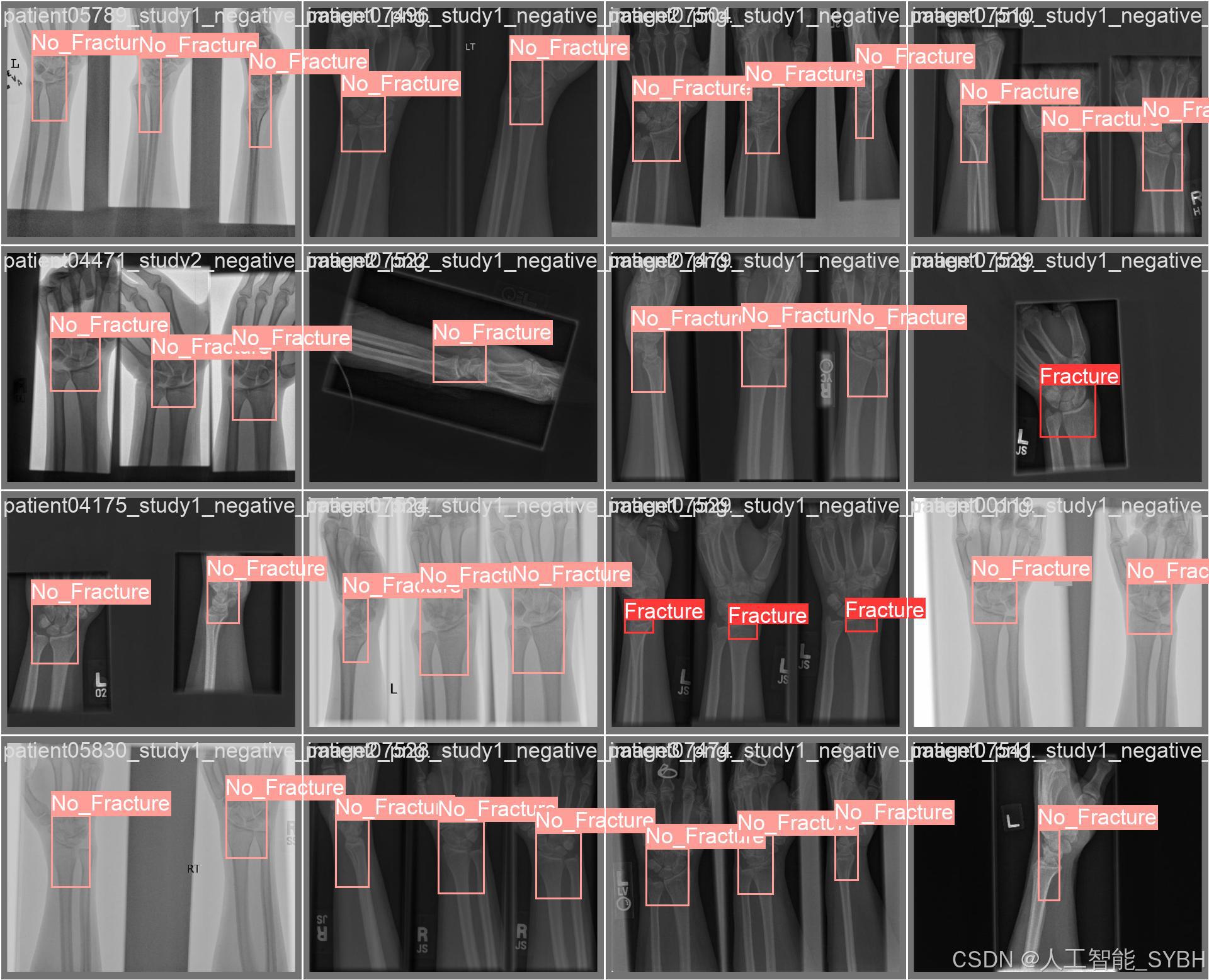
六、核心代码

import sys
import cv2
import numpy as np
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMessageBox, QFileDialog
from PyQt5.QtCore import QThread, pyqtSignal
from ultralytics import YOLOv10
from UiMain import UiMainWindow
import time
import os
class DetectionThread(QThread):
frame_received = pyqtSignal(np.ndarray, np.ndarray, list) # 原始帧, 检测帧, 检测结果
finished_signal = pyqtSignal() # 线程完成信号
def __init__(self, model, source, conf, iou, parent=None):
super().__init__(parent)
self.model = model
self.source = source
self.conf = conf
self.iou = iou
self.running = True
def run(self):
try:
if isinstance(self.source, int) or self.source.endswith(('.mp4', '.avi', '.mov')): # 视频或摄像头
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(self.source)
while self.running and cap.isOpened():
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
break
# 保存原始帧
original_frame = frame.copy()
# 检测
results = self.model(frame, conf=self.conf, iou=self.iou)
annotated_frame = results[0].plot()
# 提取检测结果
detections = []
for result in results:
for box in result.boxes:
class_id = int(box.cls)
class_name = self.model.names[class_id]
confidence = float(box.conf)
x, y, w, h = box.xywh[0].tolist()
detections.append((class_name, confidence, x, y))
# 发送信号
self.frame_received.emit(
cv2.cvtColor(original_frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB),
cv2.cvtColor(annotated_frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB),
detections
)
# 控制帧率
time.sleep(0.03) # 约30fps
cap.release()
else: # 图片
frame = cv2.imread(self.source)
if frame is not None:
original_frame = frame.copy()
results = self.model(frame, conf=self.conf, iou=self.iou)
annotated_frame = results[0].plot()
# 提取检测结果
detections = []
for result in results:
for box in result.boxes:
class_id = int(box.cls)
class_name = self.model.names[class_id]
confidence = float(box.conf)
x, y, w, h = box.xywh[0].tolist()
detections.append((class_name, confidence, x, y))
self.frame_received.emit(
cv2.cvtColor(original_frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB),
cv2.cvtColor(annotated_frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB),
detections
)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Detection error: {e}")
finally:
self.finished_signal.emit()
def stop(self):
self.running = False
class MainWindow(UiMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
# 初始化模型
self.model = None
self.detection_thread = None
self.current_image = None
self.current_result = None
self.video_writer = None
self.is_camera_running = False
self.is_video_running = False
self.last_detection_result = None # 新增:保存最后一次检测结果
# 连接按钮信号
self.image_btn.clicked.connect(self.detect_image)
self.video_btn.clicked.connect(self.detect_video)
self.camera_btn.clicked.connect(self.detect_camera)
self.stop_btn.clicked.connect(self.stop_detection)
self.save_btn.clicked.connect(self.save_result)
# 初始化模型
self.load_model()
def load_model(self):
try:
model_name = self.model_combo.currentText()
self.model = YOLOv10(f"{model_name}.pt") # 自动下载或加载本地模型
self.update_status(f"模型 {model_name} 加载成功")
except Exception as e:
QMessageBox.critical(self, "错误", f"模型加载失败: {str(e)}")
self.update_status("模型加载失败")
def detect_image(self):
if self.detection_thread and self.detection_thread.isRunning():
QMessageBox.warning(self, "警告", "请先停止当前检测任务")
return
file_path, _ = QFileDialog.getOpenFileName(
self, "选择图片", "", "图片文件 (*.jpg *.jpeg *.png *.bmp)")
if file_path:
self.clear_results()
self.current_image = cv2.imread(file_path)
self.current_image = cv2.cvtColor(self.current_image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
self.display_image(self.original_image_label, self.current_image)
# 创建检测线程
conf = self.confidence_spinbox.value()
iou = self.iou_spinbox.value()
self.detection_thread = DetectionThread(self.model, file_path, conf, iou)
self.detection_thread.frame_received.connect(self.on_frame_received)
self.detection_thread.finished_signal.connect(self.on_detection_finished)
self.detection_thread.start()
self.update_status(f"正在检测图片: {os.path.basename(file_path)}")
def detect_video(self):
if self.detection_thread and self.detection_thread.isRunning():
QMessageBox.warning(self, "警告", "请先停止当前检测任务")
return
file_path, _ = QFileDialog.getOpenFileName(
self, "选择视频", "", "视频文件 (*.mp4 *.avi *.mov)")
if file_path:
self.clear_results()
self.is_video_running = True
# 初始化视频写入器
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(file_path)
frame_width = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
frame_height = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
fps = cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)
cap.release()
# 创建保存路径
save_dir = "results"
os.makedirs(save_dir, exist_ok=True)
timestamp = time.strftime("%Y%m%d_%H%M%S")
save_path = os.path.join(save_dir, f"result_{timestamp}.mp4")
fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'mp4v')
self.video_writer = cv2.VideoWriter(save_path, fourcc, fps, (frame_width, frame_height))
# 创建检测线程
conf = self.confidence_spinbox.value()
iou = self.iou_spinbox.value()
self.detection_thread = DetectionThread(self.model, file_path, conf, iou)
self.detection_thread.frame_received.connect(self.on_frame_received)
self.detection_thread.finished_signal.connect(self.on_detection_finished)
self.detection_thread.start()
self.update_status(f"正在检测视频: {os.path.basename(file_path)}")
def detect_camera(self):
if self.detection_thread and self.detection_thread.isRunning():
QMessageBox.warning(self, "警告", "请先停止当前检测任务")
return
self.clear_results()
self.is_camera_running = True
# 创建检测线程 (默认使用摄像头0)
conf = self.confidence_spinbox.value()
iou = self.iou_spinbox.value()
self.detection_thread = DetectionThread(self.model, 0, conf, iou)
self.detection_thread.frame_received.connect(self.on_frame_received)
self.detection_thread.finished_signal.connect(self.on_detection_finished)
self.detection_thread.start()
self.update_status("正在从摄像头检测...")
def stop_detection(self):
if self.detection_thread and self.detection_thread.isRunning():
self.detection_thread.stop()
self.detection_thread.quit()
self.detection_thread.wait()
if self.video_writer:
self.video_writer.release()
self.video_writer = None
self.is_camera_running = False
self.is_video_running = False
self.update_status("检测已停止")
def on_frame_received(self, original_frame, result_frame, detections):
# 更新原始图像和结果图像
self.display_image(self.original_image_label, original_frame)
self.display_image(self.result_image_label, result_frame)
# 保存当前结果帧用于后续保存
self.last_detection_result = result_frame # 新增:保存检测结果
# 更新表格
self.clear_results()
for class_name, confidence, x, y in detections:
self.add_detection_result(class_name, confidence, x, y)
# 保存视频帧
if self.video_writer:
self.video_writer.write(cv2.cvtColor(result_frame, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR))
def on_detection_finished(self):
if self.video_writer:
self.video_writer.release()
self.video_writer = None
self.update_status("视频检测完成,结果已保存")
elif self.is_camera_running:
self.update_status("摄像头检测已停止")
else:
self.update_status("图片检测完成")
def save_result(self):
if not hasattr(self, 'last_detection_result') or self.last_detection_result is None:
QMessageBox.warning(self, "警告", "没有可保存的检测结果")
return
save_dir = "results"
os.makedirs(save_dir, exist_ok=True)
timestamp = time.strftime("%Y%m%d_%H%M%S")
if self.is_camera_running or self.is_video_running:
# 保存当前帧为图片
save_path = os.path.join(save_dir, f"snapshot_{timestamp}.jpg")
cv2.imwrite(save_path, cv2.cvtColor(self.last_detection_result, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR))
self.update_status(f"截图已保存: {save_path}")
else:
# 保存图片检测结果
save_path = os.path.join(save_dir, f"result_{timestamp}.jpg")
cv2.imwrite(save_path, cv2.cvtColor(self.last_detection_result, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR))
self.update_status(f"检测结果已保存: {save_path}")
def closeEvent(self, event):
self.stop_detection()
event.accept()
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
# 设置应用程序样式
app.setStyle("Fusion")
# 创建并显示主窗口
window = MainWindow()
window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())七、项目源码(视频下方简介内)
完整全部资源文件(包括测试图片、视频,py文件,训练数据集、训练代码、界面代码等),这里已打包上传至博主的平台,见可参考博客与视频,已将所有涉及的文件同时打包到里面,点击即可运行,完整文件截图如下:

基于深度学习YOLOv10的骨折检测系统(YOLOv10+YOLO数据集+UI界面+Python项目源码+模型)_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
基于深度学习YOLOv10的骨折检测系统(YOLOv10+YOLO数据集+UI界面+Python项目源码+模型)

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










