日期
2022-08-30
论文标题
ASpanFormer: Detector-Free Image Matching with Adaptive Span Transformer(https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.14201)
摘要
Generating robust and reliable correspondences across images is a fundamental task for a diversity of applications. To capture context at both global and local granularity, we propose ASpanFormer, a Transformer-based detector-free matcher that is built on hierarchical attention structure, adopting a novel attention operation which is capable of adjusting attention span in a self-adaptive manner. To achieve this goal, first, flow maps are regressed in each cross attention phase to locate the center of search region. Next, a sampling grid is generated around the center, whose size, instead of being empirically configured as fixed, is adaptively computed from a pixel uncertainty estimated along with the flow map. Finally, attention is computed across two images within derived regions, referred to as attention span. By these means, we are able to not only maintain long-range dependencies, but also enable fine-grained attention among pixels of high relevance that compensates essential locality and piece-wise smoothness in matching tasks. State-ofthe-art accuracy on a wide range of evaluation benchmarks validates the strong matching capability of our method.
引用信息(BibTeX格式)
@misc{chen2022aspanformer,
title={ASpanFormer: Detector-Free Image Matching with Adaptive Span Transformer},
author={Hongkai Chen and Zixin Luo and Lei Zhou and Yurun Tian and Mingmin Zhen and Tian Fang and David Mckinnon and Yanghai Tsin and Long Quan},
year={2022},
eprint={2208.14201},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV}
}
本论文解决什么问题
在sfm、vslam 中的图像匹配中,尽管像SIFT、ORB 等关键点检测算子具有很多的应用,但由于依赖关键点检测器和特征描述中的上下文丢失,这些基于检测器的匹配方法,在极端情况下(包括大视点变化和无纹理区域)会遇到困难。
同时,解决LoFTR 缺乏局部关联性的问题,为捕捉全局背景和局部细节的上下文
已有方法的优缺点
SIFT、ORB 依赖关键点检测器和特征描述中的上下文丢失,这些基于检测器的匹配方法,在极端情况下(包括大视点变化和无纹理区域)会遇到困难。
早期在无探测器匹配方面的工作通常依赖于基于相关性或成本体积的迭代卷积来发现潜在的邻域一致性。基于Transformer 被应用于特征点匹配上,如 LoFTR 利用了自注意块和交叉注意块更新交叉视图特征,其中采用Linear Transformer 替代全局全注意。但 LoFTR 中的像素标记之间缺乏精细级别的局部关联性,这可能限制其提取高度准确匹配能力。
本文采用什么方法及其优缺点
提出了一种基于 transformer 的无检测器匹配器 ASpanFormer,基于分层注意结构,采用了一种新颖的注意力模块,能够自适应地调整注意广度。为了实现这一目标,首先在每个交叉注意阶段对流图进行回归,定位搜索区域的中心。接下来,在中心周围生成采样网格,其大小不是经验配置为固定的,而是根据与流程图一起估计的像素不确定性自适应计算。最后,在派生区域内计算两幅图像的注意力,称为注意力广度。通过这些方法,我们不仅能够保持相关系,还能够在高相关性的像素之间实现细粒度关注,从而补偿必要的局部信息。
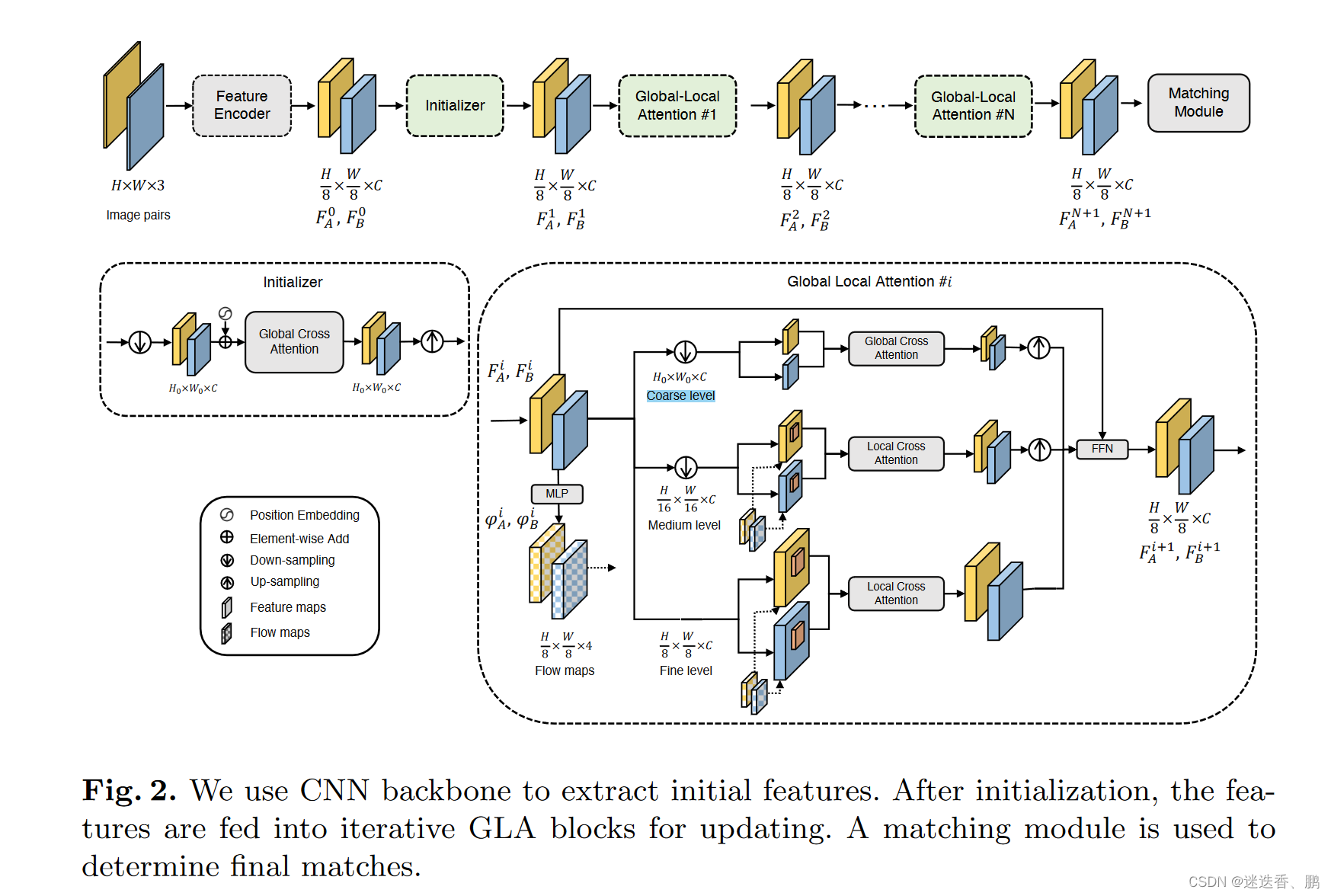
1、特征提取
使用卷积神经网络(CNN)提取1/8的下采样初始特征,由于这些特征是对每张图像进行独立处理的,因此遗漏了关键的交叉视图上下文。为了丰富上下文信息,我们将初始特性进一步馈送到 Transformer 模块中进行更新。
2、初始化
positional encoding(位置编码) 和 two-view contexts initialization(双视图上下文初始化) 两个模块 。对于Transformer网络,位置编码对于空间信息至关重要,在此,使用了 LoFTR 的 positional encoding(位置编码)。同时,在每个局部注意力模块,我们的网络需要回归一个辅助流图作为指导,这需要交叉视图上下文,因此加入了 轻量级的 global cross attention block 。
3、全局 - 局部的注意力模块(Global-Local Attention (GLA)Block)
对于每个GLA块,注意力模块在由跨行平均池化构建的3级粗到细特征金字塔上。是由3个不同特征等级的特征金字塔,由跨行平均池化。全局注意力模块在分辨率最大的下采样特征中进行,而局部注意力模块在fine level features 和medium-resolution 特征之间传递信息,最后经过FFN计算,如下式:


4、匹配
使用了LoFTR中的方案来生成最终对应关系,包括粗匹配阶段和亚像素细化阶段。
5、损失函数
分别为coarse matches loss 、fine-level loss 和 flow estimation loss,coarse matches loss 是通过使用数据集中的深度和相机姿态的重投影误差得到的,fine-level loss 是求出的坐标与 ground truth 之间的二范数, flow estimation loss 是最小化每个估计分布的对数似然
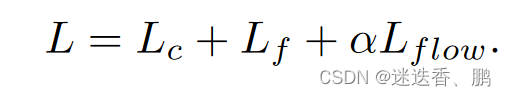
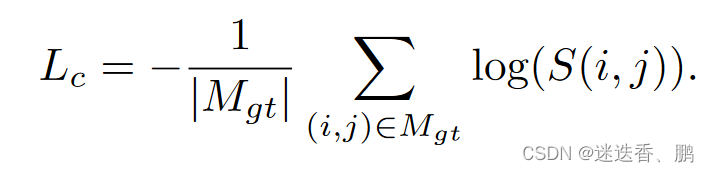
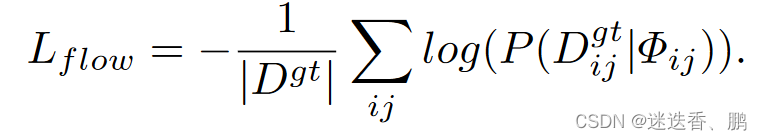
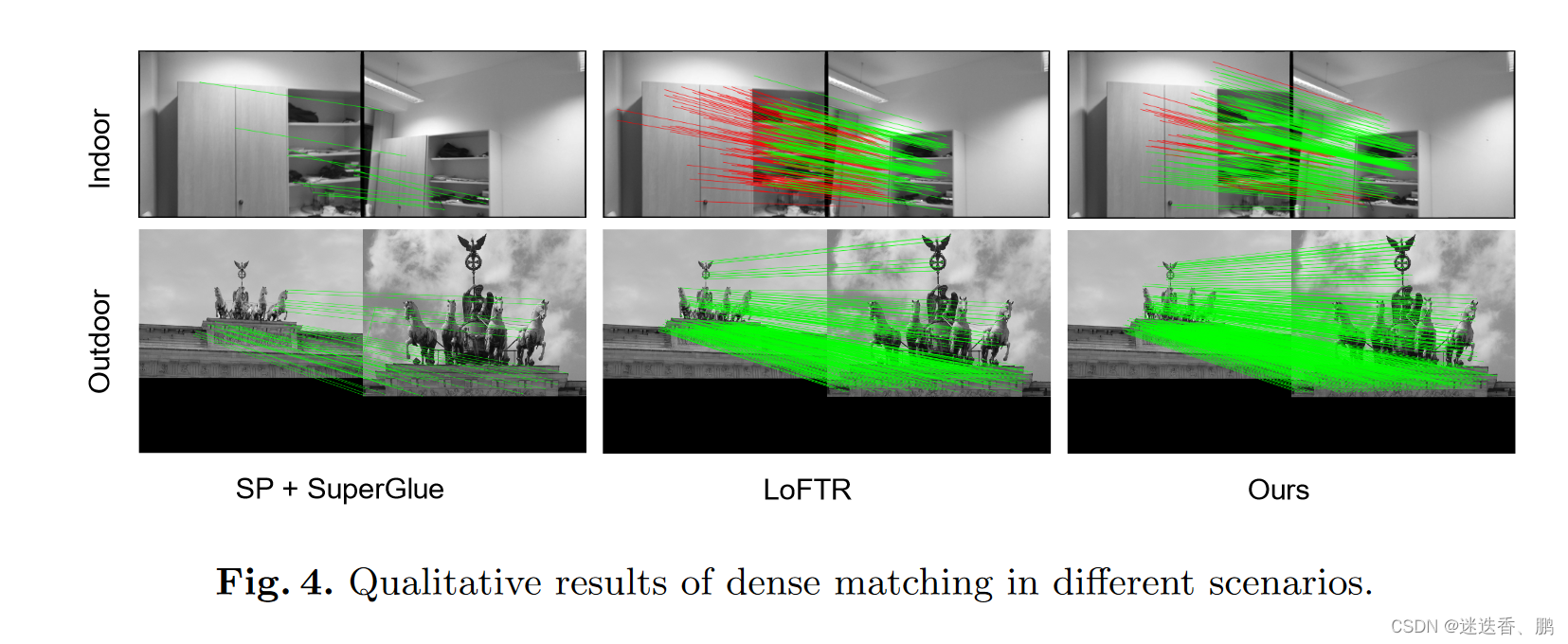
使用的数据集和性能度量
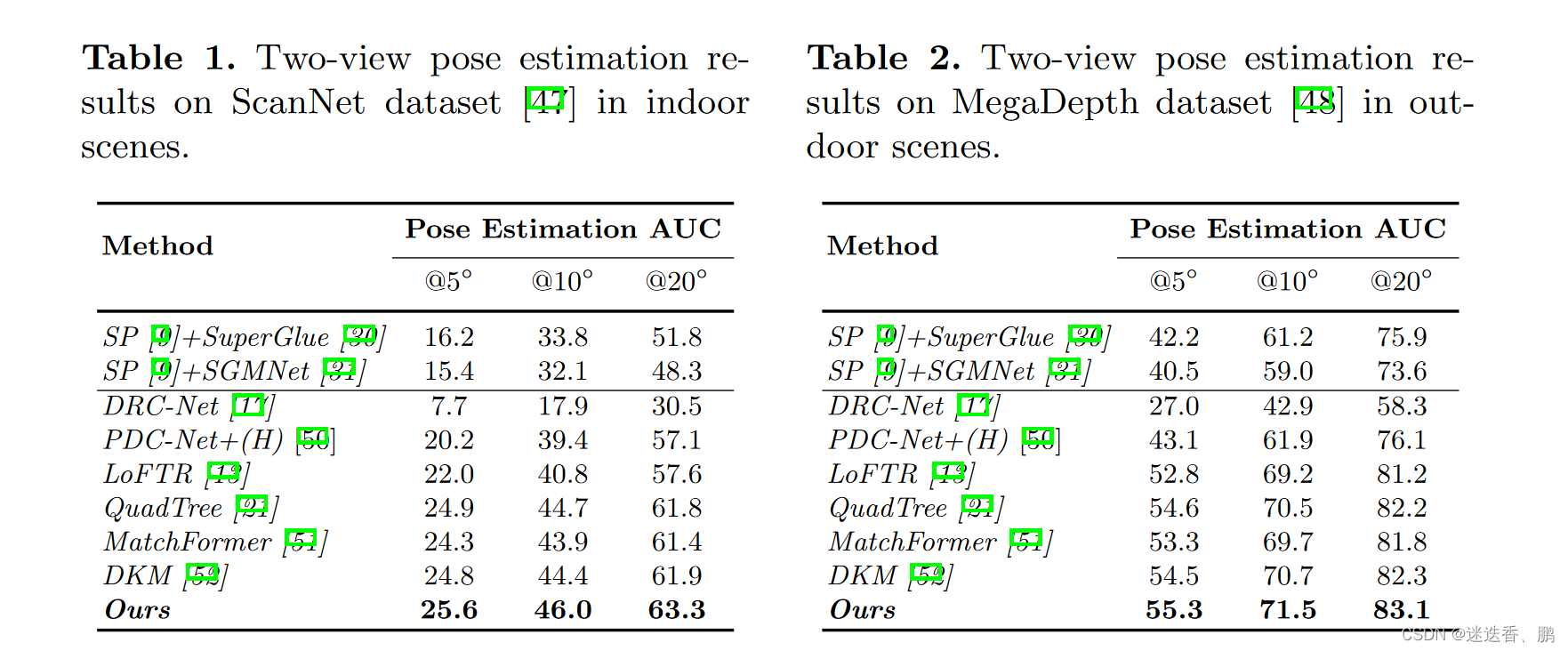
ScanNet dataset 和 MegaDepth分别测试了室内和室外环境下的结果,在多个误差阈值下,用AUC测量姿态精度

YFCC100M
Image Matching Challenge(IMC)
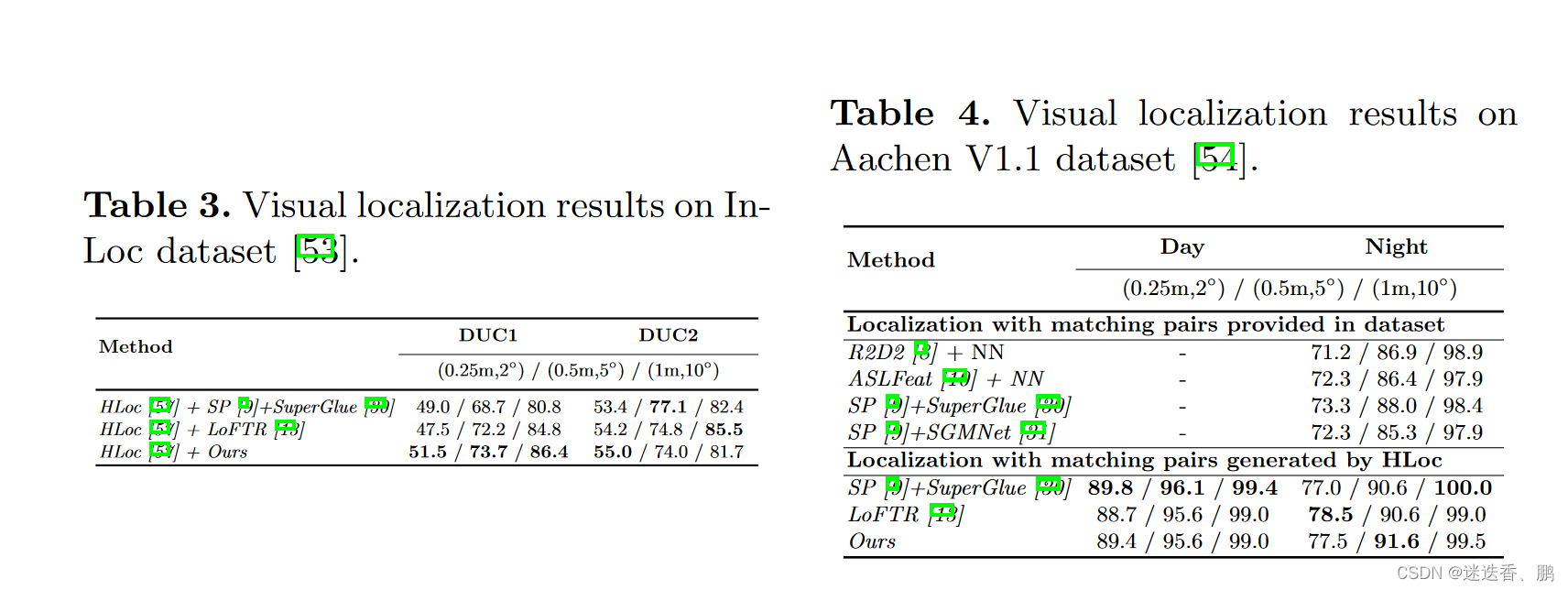
同时,用到视觉定位上进行比较结果
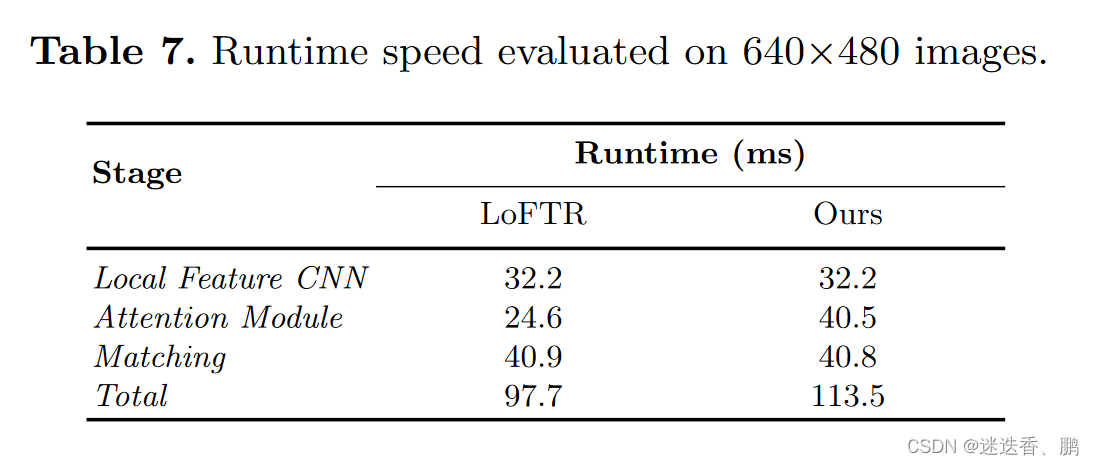
建图运行时间对比

























 2604
2604











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








