文章目录
一、原理

论文地址:MobileNetV4 - Universal Models for the Mobile Ecosystem
官方代码: MobileNetV4代码仓库
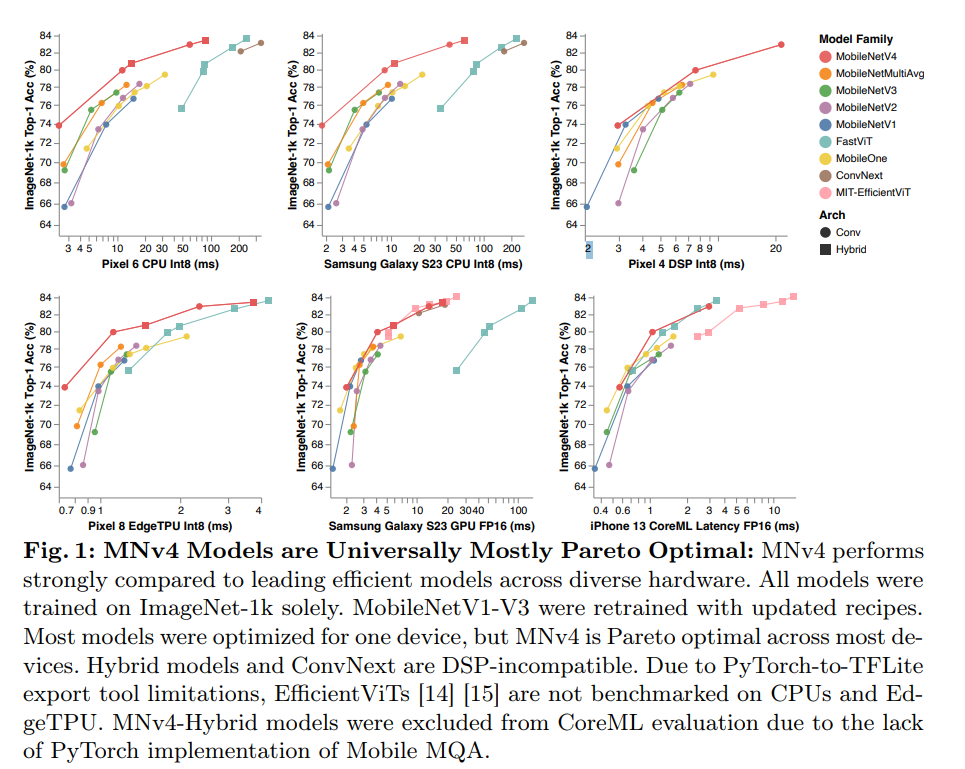
MobileNetV4(MNv4) 是最新一代的MobileNet,其核心原理在于实现了跨各种移动设备的高效性能,旨在优化各种移动设备的性能。它通过整合多种先进技术,如通用反转瓶颈(UIB)、针对移动设备优化的注意力机制(Mobile MQA),以及先进的架构搜索方法(NAS),实现了在不同硬件上的高效运行,成功打造出一系列在移动设备上表现最优的模型,兼顾计算效率和精度,实现了在多种硬件平台上的帕累托最优性能。
1)通用反转瓶颈(UIB),本文利用的机制:
MobileNetV4引入了一种名为通用反转瓶颈(UIB)的新架构组件。UIB是一个灵活的架构单元,融合了反转瓶颈(IB)、ConvNext、前馈网络(FFN),以及新颖的额外深度(ExtraDW)变体。
2)Mobile MQA注意力机制:
为了优化移动加速器的性能,MobileNetV4设计了一个特殊的注意力模块,名为Mobile MQA。这一模块针对移动设备的计算和存储限制进行了优化,提供了高达39%的推理速度提升。
3)优化的神经架构搜索(NAS)配方:
通过改进的NAS配方,MobileNetV4能够更高效地搜索和优化网络架构,这有助于发现适合特定硬件的最优模型配置。
4)模型蒸馏技术:
引入了一种新的蒸馏技术,用以提高模型的准确性。通过这种技术,MNv4-Hybrid-Large模型在ImageNet-1K上达到了87%的准确率,并且在Pixel 8 EdgeTPU上的运行时间仅为3.8毫秒。
二、YOLOv11引入MobileNetV4模块
2.1 MobileNetV4的代码实现
注意: 需要在ultralytics安装包所在文件夹里进行修改代码,否则会报错。
1)在ultralytics/nn下新建Addmodules文件夹,并在该文件下创建mobilenetv4.py,并粘贴下面的代码。
"""
Creates a MobileNetV4 Model as defined in:
Danfeng Qin, Chas Leichner, Manolis Delakis, Marco Fornoni, Shixin Luo, Fan Yang, Weijun Wang, Colby Banbury, Chengxi Ye, Berkin Akin, Vaibhav Aggarwal, Tenghui Zhu, Daniele Moro, Andrew Howard. (2024).
MobileNetV4 - Universal Models for the Mobile Ecosystem
arXiv preprint arXiv:2404.10518.
"""
from typing import Any, Callable, Dict, List, Mapping, Optional, Tuple, Union
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
MNV4ConvSmall_BLOCK_SPECS = {
"conv0": {
"block_name": "convbn",
"num_blocks": 1,
"block_specs": [
[3, 32, 3, 2]
]
},
"layer1": {
"block_name": "convbn",
"num_blocks": 2,
"block_specs": [
[32, 32, 3, 2],
[32, 32, 1, 1]
]
},
"layer2": {
"block_name": "convbn",
"num_blocks": 2,
"block_specs": [
[32, 96, 3, 2],
[96, 64, 1, 1]
]
},
"layer3": {
"block_name": "uib",
"num_blocks": 6,
"block_specs": [
[64, 96, 5, 5, True, 2, 3],
[96, 96, 0, 3, True, 1, 2],
[96, 96, 0, 3, True, 1, 2],
[96, 96, 0, 3, True, 1, 2],
[96, 96, 0, 3, True, 1, 2],
[96, 96, 3, 0, True, 1, 4],
]
},
"layer4": {
"block_name": "uib",
"num_blocks": 6,
"block_specs": [
[96, 128, 3, 3, True, 2, 6],
[128, 128, 5, 5, True, 1, 4],
[128, 128, 0, 5, True, 1, 4],
[128, 128, 0, 5, True, 1, 3],
[128, 128, 0, 3, True, 1, 4],
[128, 128, 0, 3, True, 1, 4],
]
},
"layer5": {
"block_name": "convbn",
"num_blocks": 2,
"block_specs": [
[128, 960, 1, 1],
[960, 1280, 1, 1]
]
}
}
MNV4ConvMedium_BLOCK_SPECS = {
"conv0": {
"block_name": "convbn",
"num_blocks": 1,
"block_specs": [
[3, 32, 3, 2]
]
},
"layer1": {
"block_name": "fused_ib",
"num_blocks": 1,
"block_specs": [
[32, 48, 2, 4.0, True]
]
},
"layer2": {
"block_name": "uib",
"num_blocks": 2,
"block_specs": [
[48, 80, 3, 5, True, 2, 4],
[80, 80, 3, 3, True, 1, 2]
]
},
"layer3": {
"block_name": "uib",
"num_blocks": 8,
"block_specs": [
[80, 160, 3, 5, True, 2, 6],
[160, 160, 3, 3, True, 1, 4],
[160, 160, 3, 3, True, 1, 4],
[160, 160, 3, 5, True, 1, 4],
[160, 160, 3, 3, True, 1, 4],
[160, 160, 3, 0, True, 1, 4],
[160, 160, 0, 0, True, 1, 2],
[160, 160, 3, 0, True, 1, 4]
]
},
"layer4": {
"block_name": "uib",
"num_blocks": 11,
"block_specs": [
[160, 256, 5, 5, True, 2, 6],
[256, 256, 5, 5, True, 1, 4],
[256, 256, 3, 5, True, 1, 4],
[256, 256, 3, 5, True, 1, 4],
[256, 256, 0, 0, True, 1, 4],
[256, 256, 3, 0, True, 1, 4],
[256, 256, 3, 5, True, 1, 2],
[256, 256, 5, 5, True, 1, 4],
[256, 256, 0, 0, True, 1, 4],
[256, 256, 0, 0, True, 1, 4],
[256, 256, 5, 0, True, 1, 2]
]
},
"layer5": {
"block_name": "convbn",
"num_blocks": 2,
"block_specs": [
[256, 960, 1, 1],
[960, 1280, 1, 1]
]
}
}
MNV4ConvLarge_BLOCK_SPECS = {
"conv0": {
"block_name": "convbn",
"num_blocks": 1,
"block_specs": [
[3, 24, 3, 2]
]
},
"layer1": {
"block_name": "fused_ib",
"num_blocks": 1,
"block_specs": [
[24, 48, 2, 4.0, True]
]
},
"layer2": {
"block_name": "uib",
"num_blocks": 2,
"block_specs": [
[48, 96, 3, 5, True, 2, 4],
[96, 96, 3, 3, True, 1, 4]
]
},
"layer3": {
"block_name": "uib",
"num_blocks": 11,
"block_specs": [
[96, 192, 3, 5, True, 2, 4],
[192, 192, 3, 3, True, 1, 4],
[192, 192, 3, 3, True, 1, 4],
[192, 192, 3, 3, True, 1, 4],
[192, 192, 3, 5, True, 1, 4],
[192, 192, 5, 3, True, 1, 4],
[192, 192, 5, 3, True, 1, 4],
[192, 192, 5, 3, True, 1, 4],
[192, 192, 5, 3, True, 1, 4],
[192, 192, 5, 3, True, 1, 4],
[192, 192, 3, 0, True, 1, 4]
]
},
"layer4": {
"block_name": "uib",
"num_blocks": 13,
"block_specs": [
[192, 512, 5, 5, True, 2, 4],
[512, 512, 5, 5, True, 1, 4],
[512, 512, 5, 5, True, 1, 4],
[512, 512, 5, 5, True, 1, 4],
[512, 512, 5, 0, True, 1, 4],
[512, 512, 5, 3, True, 1, 4],
[512, 512, 5, 0, True, 1, 4],
[512, 512, 5, 0, True, 1, 4],
[512, 512, 5, 3, True, 1, 4],
[512, 512, 5, 5, True, 1, 4],
[512, 512, 5, 0, True, 1, 4],
[512, 512, 5, 0, True, 1, 4],
[512, 512, 5, 0, True, 1, 4]
]
},
"layer5": {
"block_name": "convbn",
"num_blocks": 2,
"block_specs": [
[512, 960, 1, 1],
[960, 1280, 1, 1]
]
}
}
MNV4HybridConvMedium_BLOCK_SPECS = {
}
MNV4HybridConvLarge_BLOCK_SPECS = {
}
MODEL_SPECS = {
"MobileNetV4ConvSmall": MNV4ConvSmall_BLOCK_SPECS,
"MobileNetV4ConvMedium": MNV4ConvMedium_BLOCK_SPECS,
"MobileNetV4ConvLarge": MNV4ConvLarge_BLOCK_SPECS,
"MobileNetV4HybridMedium": MNV4HybridConvMedium_BLOCK_SPECS,
"MobileNetV4HybridLarge": MNV4HybridConvLarge_BLOCK_SPECS,
}
def make_divisible(
value: float,
divisor: int,
min_value: Optional[float] = None,
round_down_protect: bool = True,
) -> int:
"""
This function is copied from here
"https://github.com/tensorflow/models/blob/master/official/vision/modeling/layers/nn_layers.py"
This is to ensure that all layers have channels that are divisible by 8.
Args:
value: A `float` of original value.
divisor: An `int` of the divisor that need to be checked upon.
min_value: A `float` of minimum value threshold.
round_down_protect: A `bool` indicating whether round down more than 10%
will be allowed.
Returns:
The adjusted value in `int` that is divisible against divisor.
"""
if min_value is None:
min_value = divisor
new_value = max(min_value, int(value + divisor / 2) // divisor * divisor)
# Make sure that round down does not go down by more than 10%.
if round_down_protect and new_value < 0.9 * value:
new_value += divisor
return int(new_value)
def conv_2d(inp, oup, kernel_size=3, stride=1, groups=1, bias=False, norm=True, act=True):
conv = nn.Sequential()
padding = (kernel_size - 1) // 2
conv.add_module('conv', nn.Conv2d(inp, oup, kernel_size, stride, padding, bias=bias, groups=groups))
if norm:
conv.add_module('BatchNorm2d', nn.BatchNorm2d(oup))
if act:
conv.add_module('Activation', nn.ReLU6())
return conv
class InvertedResidual(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inp, oup, stride, expand_ratio, act=False):
super(InvertedResidual, self).__init__()
self.stride = stride
assert stride in [1, 2]
hidden_dim = int(round(inp * expand_ratio))
self.block = nn.Sequential()
if expand_ratio != 1:
self.block.add_module('exp_1x1', conv_2d(inp, hidden_dim, kernel_size=1, stride=1))
self.block.add_module('conv_3x3', conv_2d(hidden_dim, hidden_dim, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, groups=hidden_dim))
self.block.add_module('red_1x1', conv_2d(hidden_dim, oup, kernel_size=1, stride=1, act=act))
self.use_res_connect = self.stride == 1 and inp == oup
def forward(self, x):
if self.use_res_connect:
return x + self.block(x)
else:
return self.block(x)
class UniversalInvertedBottleneckBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
inp,
oup,
start_dw_kernel_size,
middle_dw_kernel_size,
middle_dw_downsample,
stride,
expand_ratio
):
super().__init__()
# Starting depthwise conv.
self.start_dw_kernel_size = start_dw_kernel_size
if self.start_dw_kernel_size:
stride_ = stride if not middle_dw_downsample else 1
self._start_dw_ = conv_2d(inp, inp, kernel_size=start_dw_kernel_size, stride=stride_, groups=inp, act=False)
# Expansion with 1x1 convs.
expand_filters = make_divisible(inp * expand_ratio, 8)
self._expand_conv = conv_2d(inp, expand_filters, kernel_size=1)
# Middle depthwise conv.
self.middle_dw_kernel_size = middle_dw_kernel_size
if self.middle_dw_kernel_size:
stride_ = stride if middle_dw_downsample else 1
self._middle_dw = conv_2d(expand_filters, expand_filters, kernel_size=middle_dw_kernel_size, stride=stride_, groups=expand_filters)
# Projection with 1x1 convs.
self._proj_conv = conv_2d(expand_filters, oup, kernel_size=1, stride=1, act=False)
# Ending depthwise conv.
# this not used
# _end_dw_kernel_size = 0
# self._end_dw = conv_2d(oup, oup, kernel_size=_end_dw_kernel_size, stride=stride, groups=inp, act=False)
def forward(self, x):
if self.start_dw_kernel_size:
x = self._start_dw_(x)
# print("_start_dw_", x.shape)
x = self._expand_conv(x)
# print("_expand_conv", x.shape)
if self.middle_dw_kernel_size:
x = self._middle_dw(x)
# print("_middle_dw", x.shape)
x = self._proj_conv(x)
# print("_proj_conv", x.shape)
return x
def build_blocks(layer_spec):
if not layer_spec.get('block_name'):
return nn.Sequential()
block_names = layer_spec['block_name']
layers = nn.Sequential()
if block_names == "convbn":
schema_ = ['inp', 'oup', 'kernel_size', 'stride']
args = {}
for i in range(layer_spec['num_blocks']):
args = dict(zip(schema_, layer_spec['block_specs'][i]))
layers.add_module(f"convbn_{i}", conv_2d(**args))
elif block_names == "uib":
schema_ = ['inp', 'oup', 'start_dw_kernel_size', 'middle_dw_kernel_size', 'middle_dw_downsample', 'stride', 'expand_ratio']
args = {}
for i in range(layer_spec['num_blocks']):
args = dict(zip(schema_, layer_spec['block_specs'][i]))
layers.add_module(f"uib_{i}", UniversalInvertedBottleneckBlock(**args))
elif block_names == "fused_ib":
schema_ = ['inp', 'oup', 'stride', 'expand_ratio', 'act']
args = {}
for i in range(layer_spec['num_blocks']):
args = dict(zip(schema_, layer_spec['block_specs'][i]))
layers.add_module(f"fused_ib_{i}", InvertedResidual(**args))
else:
raise NotImplementedError
return layers
class MobileNetV4(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, model):
# MobileNetV4ConvSmall MobileNetV4ConvMedium MobileNetV4ConvLarge
# MobileNetV4HybridMedium MobileNetV4HybridLarge
"""Params to initiate MobilenNetV4
Args:
model : support 5 types of models as indicated in
"https://github.com/tensorflow/models/blob/master/official/vision/modeling/backbones/mobilenet.py"
"""
super().__init__()
assert model in MODEL_SPECS.keys()
self.model = model
self.spec = MODEL_SPECS[self.model]
# conv0
self.conv0 = build_blocks(self.spec['conv0'])
# layer1
self.layer1 = build_blocks(self.spec['layer1'])
# layer2
self.layer2 = build_blocks(self.spec['layer2'])
# layer3
self.layer3 = build_blocks(self.spec['layer3'])
# layer4
self.layer4 = build_blocks(self.spec['layer4'])
# layer5
self.layer5 = build_blocks(self.spec['layer5'])
self.features = nn.ModuleList([self.conv0, self.layer1, self.layer2, self.layer3, self.layer4, self.layer5])
self.channel = [i.size(1) for i in self.forward(torch.randn(1, 3, 640, 640))]
def forward(self, x):
input_size = x.size(2)
scale = [4, 8, 16, 32]
features = [None, None, None, None]
for f in self.features:
x = f(x)
if input_size // x.size(2) in scale:
features[scale.index(input_size // x.size(2))] = x
return features
def MobileNetV4ConvSmall():
model = MobileNetV4('MobileNetV4ConvSmall')
return model
def MobileNetV4ConvMedium():
model = MobileNetV4('MobileNetV4ConvMedium')
return model
def MobileNetV4ConvLarge():
model = MobileNetV4('MobileNetV4ConvLarge')
return model
def MobileNetV4HybridMedium():
model = MobileNetV4('MobileNetV4HybridMedium')
return model
def MobileNetV4HybridLarge():
model = MobileNetV4('MobileNetV4HybridLarge')
return model
2)添加完MobileNetV4代码后,在ultralytics/nn/Addmodules/__init__.py文件中引用
from .MobileNetV4 import *

2.2 修改ultralytics/nn/tasks.py文件
from .Extramodule import *
1)在tasks.py找到parse_model函数(ctrl+f 可以直接搜索parse_model位置),分别添加:
backbone=False
t=m

2)添加主干代码
elif m in {MobileNetV4ConvLarge, MobileNetV4ConvSmall,MobileNetV4ConvMedium, MobileNetV4HybridMedium, MobileNetV4HybridLarge
}:
m = m(*args)
c2 = m.width_list
backbone = True
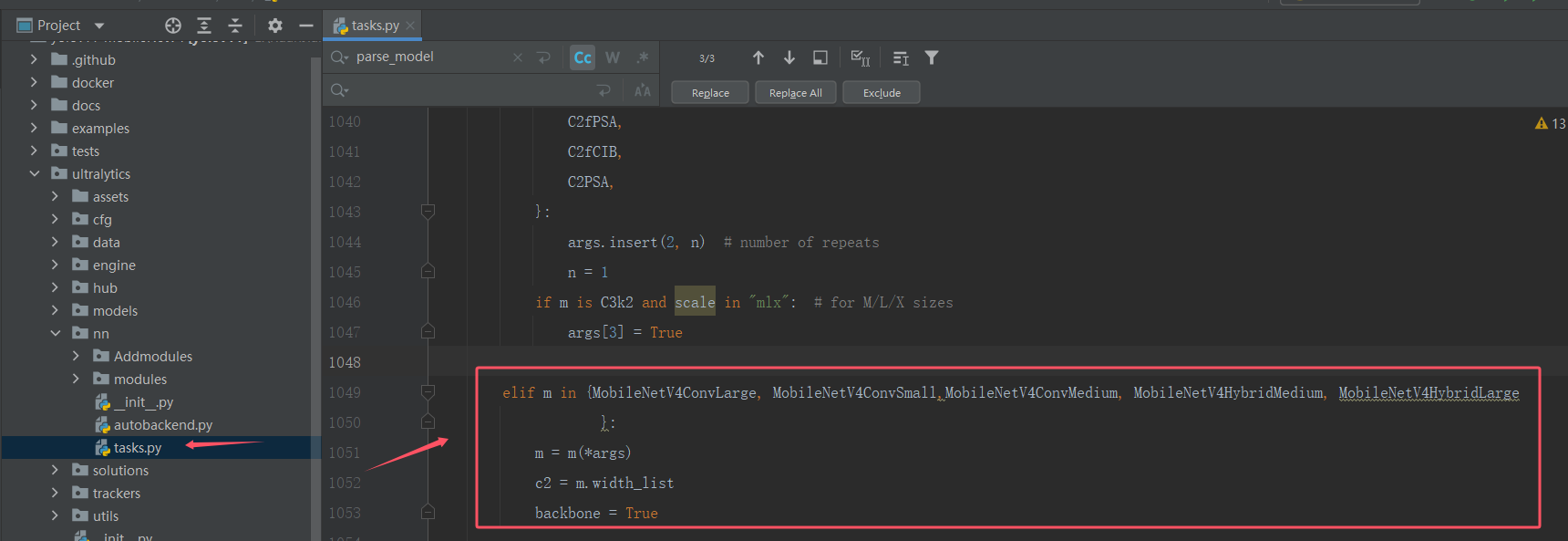
3)将elif m is AIFI 到parse_model函数的结尾:以下的代码全部替换下方代码
elif m is AIFI:
args = [ch[f], *args]
elif m in {HGStem, HGBlock}:
c1, cm, c2 = ch[f], args[0], args[1]
args = [c1, cm, c2, *args[2:]]
if m is HGBlock:
args.insert(4, n) # number of repeats
n = 1
elif m is ResNetLayer:
c2 = args[1] if args[3] else args[1] * 4
elif m is nn.BatchNorm2d:
args = [ch[f]]
elif m is Concat:
c2 = sum(ch[x] for x in f)
elif m in {Detect, WorldDetect, Segment, Pose, OBB, ImagePoolingAttn, v10Detect}:
args.append([ch[x] for x in f])
if m is Segment:
args[2] = make_divisible(min(args[2], max_channels) * width, 8)
elif m is RTDETRDecoder: # special case, channels arg must be passed in index 1
args.insert(1, [ch[x] for x in f])
elif m is CBLinear:
c2 = args[0]
c1 = ch[f]
args = [c1, c2, *args[1:]]
elif m is CBFuse:
c2 = ch[f[-1]]
else:
c2 = ch[f]
if isinstance(c2, list):
m_ = m
m_.backbone = True
else:
m_ = nn.Sequential(*(m(*args) for _ in range(n))) if n > 1 else m(*args) # module
t = str(m)[8:-2].replace('__main__.', '') # module type
m.np = sum(x.numel() for x in m_.parameters()) # number params
m_.i, m_.f, m_.type = i + 4 if backbone else i, f, t # attach index, 'from' index, type
if verbose:
LOGGER.info(f'{i:>3}{str(f):>20}{n_:>3}{m.np:10.0f} {t:<45}{str(args):<30}') # print
save.extend(
x % (i + 4 if backbone else i) for x in ([f] if isinstance(f, int) else f) if x != -1) # append to savelist
layers.append(m_)
if i == 0:
ch = []
if isinstance(c2, list):
ch.extend(c2)
if len(c2) != 5:
ch.insert(0, 0)
else:
ch.append(c2)
return nn.Sequential(*layers), sorted(save)
4)在tasks.py找到_predict_once函数,替换为:
def _predict_once(self, x, profile=False, visualize=False, embed=None):
"""
Perform a forward pass through the network.
Args:
x (torch.Tensor): The input tensor to the model.
profile (bool): Print the computation time of each layer if True, defaults to False.
visualize (bool): Save the feature maps of the model if True, defaults to False.
embed (list, optional): A list of feature vectors/embeddings to return.
Returns:
(torch.Tensor): The last output of the model.
"""
y, dt, embeddings = [], [], [] # outputs
for m in self.model:
if m.f != -1: # if not from previous layer
x = y[m.f] if isinstance(m.f, int) else [x if j == -1 else y[j] for j in m.f] # from earlier layers
if profile:
self._profile_one_layer(m, x, dt)
if hasattr(m, 'backbone'):
x = m(x)
if len(x) != 5: # 0 - 5
x.insert(0, None)
for index, i in enumerate(x):
if index in self.save:
y.append(i)
else:
y.append(None)
x = x[-1] # 最后一个输出传给下一层
else:
x = m(x) # run
y.append(x if m.i in self.save else None) # save output
if visualize:
feature_visualization(x, m.type, m.i, save_dir=visualize)
if embed and m.i in embed:
embeddings.append(nn.functional.adaptive_avg_pool2d(x, (1, 1)).squeeze(-1).squeeze(-1)) # flatten
if m.i == max(embed):
return torch.unbind(torch.cat(embeddings, 1), dim=0)
return x
5)在ultralytics/models/yolo/detect/train.py里找到build_dataset函数,替换为:
def build_dataset(self, img_path, mode="train", batch=None):
"""
Build YOLO Dataset.
Args:
img_path (str): Path to the folder containing images.
mode (str): `train` mode or `val` mode, users are able to customize different augmentations for each mode.
batch (int, optional): Size of batches, this is for `rect`. Defaults to None.
"""
gs = max(int(de_parallel(self.model).stride.max() if self.model else 0), 32)
return build_yolo_dataset(self.args, img_path, batch, self.data, mode=mode, rect=False, stride=gs)
三、新建MobileNetV4.yaml文件
新建一个ultralytics/cfg/models/11/MobileNetV4.yaml文件
# Ultralytics YOLOv11, AGPL-3.0 license
# YOLO11 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolo11n.yaml' will call yolo11.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
n: [0.50, 0.25, 1024] # summary: 319 layers, 2624080 parameters, 2624064 gradients, 6.6 GFLOPs
s: [0.50, 0.50, 1024] # summary: 319 layers, 9458752 parameters, 9458736 gradients, 21.7 GFLOPs
m: [0.50, 1.00, 512] # summary: 409 layers, 20114688 parameters, 20114672 gradients, 68.5 GFLOPs
l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # summary: 631 layers, 25372160 parameters, 25372144 gradients, 87.6 GFLOPs
x: [1.00, 1.50, 512] # summary: 631 layers, 56966176 parameters, 56966160 gradients, 196.0 GFLOPs
# 0-P1/2
# 1-P2/4
# 2-P3/8
# 3-P4/16
# 4-P5/32
# YOLO11n backbone
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, MobileNetV4ConvSmall, []] # 4
- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 5
- [-1, 2, C2PSA, [1024]] # 6
# YOLO11n head
head:
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]]
- [[-1, 3], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- [-1, 2, C3k2, [512, False]] # 9
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]]
- [[-1, 2], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
- [-1, 2, C3k2, [256, False]] # 12 (P3/8-small)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 9], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
- [-1, 2, C3k2, [512, False]] # 15 (P4/16-medium)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
- [-1, 2, C3k2, [1024, True]] # 18 (P5/32-large)
- [[12, 15, 18], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
四、模型训练
创建一个train.py文件
# 模型配置文件,此处以 s 为例,只需要写 yolo11s.yaml ,yolo11.yaml 会自动定位为 yolo11s 模型
# 如果写成yolo11m.yaml ,yolo11.yaml 会自动定位为 yolo11m 模型
model_yaml_path = r"ultralytics/cfg/models/11/MobileNetV4-2.yaml"
# 数据集配置文件
data_yaml_path = r'dataSet/waste-dataset/waste-classification.yaml'
# 预训练模型
pre_model_name = 'yolo11l.pt'
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
from ultralytics import YOLO
if __name__ == '__main__':
model = YOLO(model_yaml_path)
# 如何切换模型版本, 上面的ymal文件可以改为 yolo11s.yaml就是使用的11s,
# 类似某个改进的yaml文件名称为yolov11-XXX.yaml那么如果想使用其它版本就把上面的名称改为yolov11l-XXX.yaml即可(改的是上面YOLO中间的名字不是配置文件的)!
model.load(pre_model_name) # 是否加载预训练权重
model.train(data = data_yaml_path,
# 如果大家任务是其它的'ultralytics/cfg/default.yaml'找到这里修改task可以改成detect, segment, classify, pose
cache = False,
imgsz = 640,
epochs = 200,
single_cls = False, # 是否是单类别检测
batch = 64,
close_mosaic = 0,
workers = 8,
device = '0',
optimizer = 'SGD', # using SGD 优化器 默认为auto建议大家使用固定的.
# resume=, # 续训的话这里填写True, yaml文件的地方改为lats.pt的地址,需要注意的是如果你设置训练200轮次模型训练了200轮次是没有办法进行续训的.
amp = True, # 如果出现训练损失为Nan可以关闭amp
project = 'runs/train',
name = 'exp',
)
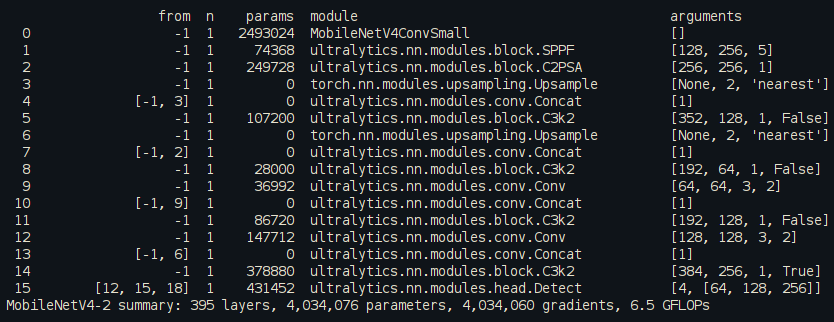
我们可以看到GFLOPs下降了许多
- Params (M): 这代表模型的参数量,单位是百万(Million)。参数量是指模型中所有权重和偏置的总数,通常用来衡量模型的大小和复杂度。参数量越小,模型越轻量,但可能在性能上有所牺牲。
- FLOPs (G):这代表模型的浮点运算次数,单位是十亿(Giga),即模型在进行一次前向传播时需要执行的浮点运算的总数。FLOPs可以用来衡量算法或模型的计算复杂度,对于硬件资源有限的环境,低FLOPs的模型可能更适合部署。
- Size (M): 这代表模型文件的大小,单位是兆字节(Megabyte)。模型文件大小包括了模型的参数和可能的二进制信息等,对于模型部署来说,较小的模型文件大小有利于减少存储和传输的开销。
- Frames Per Second( FPS): 模型每秒能够检测的帧数,指明了模型的检测速度,其计算公式为:1000 / 一张图片处理时间(单位为ms)。
- 实时性标准:对于大多数实际应用,特别是视频监控和实时视频处理,FPS至少要达到视频本身的帧率。例如,对于30帧/秒的视频,YOLO的FPS应该不低于30。
- 高质量实时性:为了更好的用户体验和减少延迟,FPS通常会希望更高,例如45或60帧/秒,尤其是在对延迟敏感的应用中(如直播或在线视频游戏)。
**训练结果:**YOLOv11s summary: 157 layers, 7020913 parameters, 0 gradients, 15.8 GFLOPs(M),即YOLOv11s模型有7.02百万(7.02 M)个参数。
训练结果: Speed: 0.6ms pre-process, 6.6ms inference, 2.8ms NMS perimage at shape (16, 3, 640, 640)
给定的处理时间包括三个部分:
预处理(pre-process): 0.6毫秒(ms)
推理(inference): 6.6毫秒(ms)
非极大值抑制(NMS): 2.8毫秒(ms)
FPS=1000/(0.6+6.6+2.8)=100
所以,这个模型的处理速度大约是每秒100帧(FPS),这意味着模型可以在一秒钟内处理100张图片。
五、目标检测系列文章
- YOLOv5s网络模型讲解(一看就会)
- 生活垃圾数据集(YOLO版)
- YOLOv5如何训练自己的数据集
- 双向控制舵机(树莓派版)
- 树莓派部署YOLOv5目标检测(详细篇)
- YOLO_Tracking 实践 (环境搭建 & 案例测试)
- 目标检测:数据集划分 & XML数据集转YOLO标签
- DeepSort行人车辆识别系统(实现目标检测+跟踪+统计)
- YOLOv5参数大全(parse_opt篇)
- YOLOv5改进(一)-- 轻量化YOLOv5s模型
- YOLOv5改进(二)-- 目标检测优化点(添加小目标头检测)
- YOLOv5改进(三)-- 引进Focaler-IoU损失函数
- YOLOv5改进(四)–轻量化模型ShuffleNetv2
- YOLOv5改进(五)-- 轻量化模型MobileNetv3
- YOLOv5改进(六)–引入YOLOv8中C2F模块
- YOLOv5改进(七)–改进损失函数EIoU、Alpha-IoU、SIoU、Focal-EIOU
- YOLOv5改进(八)–引入Soft-NMS非极大值抑制
- YOLOv5改进(九)–引入BiFPN模块
- 基于YOLOv10的车辆统计跟踪与车速计算应用
- 初探 YOLOv8(训练参数解析)
- YOLOv8不同模型对比和onnx部署详解
- 如何利用YOLOv8训练自己的数据集 && 3种加载模型场景讲解
- YOLOv8改进(一)-- 轻量化模型ShuffleNetV2
- 如何使用Labelimg查看已经标注好的YOLO数据集标注情况
- YOLOv5、YOLOv6、YOLOv7、YOLOv8、YOLOv9、YOLOv10、YOLOv11、YOLOv12的网络结构图
- YOLOv5改进(十)-- 轻量化模型MobileNetv4
























 1911
1911

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








