由于tensorflow可能与本地python环境冲突,使用jupyter进行操作。
jupyter执行以下命令安装相关环境:
conda create -n tf_env
conda activate tf_env
pip install tensorflow -i https://pypi.mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/simple
pip install keras -i https://pypi.mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/simple
测试数据集百度网盘密码dmp4
将文件解压后可以看到如下目录:
创建相关目录:
import tensorflow as tf
import keras
import os, shutil
# 原始目录所在的路径
original_dataset_dir = 'C:\\Cat_And_Dog\\kaggle\\train\\'
# 数据集分类后的目录
base_dir = 'C:\\Cat_And_Dog\\kaggle\\cats_and_dogs_small'
os.mkdir(base_dir)
# # 训练、验证、测试数据集的目录
train_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, 'train')
os.mkdir(train_dir)
validation_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, 'validation')
os.mkdir(validation_dir)
test_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, 'test')
os.mkdir(test_dir)
# 猫训练图片所在目录
train_cats_dir = os.path.join(train_dir, 'cats')
os.mkdir(train_cats_dir)
# 狗训练图片所在目录
train_dogs_dir = os.path.join(train_dir, 'dogs')
os.mkdir(train_dogs_dir)
# 猫验证图片所在目录
validation_cats_dir = os.path.join(validation_dir, 'cats')
os.mkdir(validation_cats_dir)
# 狗验证数据集所在目录
validation_dogs_dir = os.path.join(validation_dir, 'dogs')
os.mkdir(validation_dogs_dir)
# 猫测试数据集所在目录
test_cats_dir = os.path.join(test_dir, 'cats')
os.mkdir(test_cats_dir)
# 狗测试数据集所在目录
test_dogs_dir = os.path.join(test_dir, 'dogs')
os.mkdir(test_dogs_dir)
移动对应文件:
# 将前1000张猫图像复制到train_cats_dir
fnames = ['cat.{}.jpg'.format(i) for i in range(1000)]
for fname in fnames:
src = os.path.join(original_dataset_dir, fname)
dst = os.path.join(train_cats_dir, fname)
shutil.copyfile(src, dst)
# 将下500张猫图像复制到validation_cats_dir
fnames = ['cat.{}.jpg'.format(i) for i in range(1000, 1500)]
for fname in fnames:
src = os.path.join(original_dataset_dir, fname)
dst = os.path.join(validation_cats_dir, fname)
shutil.copyfile(src, dst)
# 将下500张猫图像复制到test_cats_dir
fnames = ['cat.{}.jpg'.format(i) for i in range(1500, 2000)]
for fname in fnames:
src = os.path.join(original_dataset_dir, fname)
dst = os.path.join(test_cats_dir, fname)
shutil.copyfile(src, dst)
# 将前1000张狗图像复制到train_dogs_dir
fnames = ['dog.{}.jpg'.format(i) for i in range(1000)]
for fname in fnames:
src = os.path.join(original_dataset_dir, fname)
dst = os.path.join(train_dogs_dir, fname)
shutil.copyfile(src, dst)
# 将下500张狗图像复制到validation_dogs_dir
fnames = ['dog.{}.jpg'.format(i) for i in range(1000, 1500)]
for fname in fnames:
src = os.path.join(original_dataset_dir, fname)
dst = os.path.join(validation_dogs_dir, fname)
shutil.copyfile(src, dst)
# 将下500张狗图像复制到test_dogs_dir
fnames = ['dog.{}.jpg'.format(i) for i in range(1500, 2000)]
for fname in fnames:
src = os.path.join(original_dataset_dir, fname)
dst = os.path.join(test_dogs_dir, fname)
shutil.copyfile(src, dst)
#输出数据集对应目录下图片数量
打印每个目录图片数量:
print('total training cat images:', len(os.listdir(train_cats_dir)))
print('total training dog images:', len(os.listdir(train_dogs_dir)))
print('total validation cat images:', len(os.listdir(validation_cats_dir)))
print('total validation dog images:', len(os.listdir(validation_dogs_dir)))
print('total test cat images:', len(os.listdir(test_cats_dir)))
print('total test dog images:', len(os.listdir(test_dogs_dir)))


构建网络模型并查看参数:
#网络模型构建
from keras import layers
from keras import models
#keras的序贯模型
model = models.Sequential()
#卷积层,卷积核是3*3,激活函数relu
model.add(layers.Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu',
input_shape=(150, 150, 3)))
#最大池化层
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))
#卷积层,卷积核2*2,激活函数relu
model.add(layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'))
#最大池化层
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))
#卷积层,卷积核是3*3,激活函数relu
model.add(layers.Conv2D(128, (3, 3), activation='relu'))
#最大池化层
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))
#卷积层,卷积核是3*3,激活函数relu
model.add(layers.Conv2D(128, (3, 3), activation='relu'))
#最大池化层
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))
#flatten层,用于将多维的输入一维化,用于卷积层和全连接层的过渡
model.add(layers.Flatten())
#全连接,激活函数relu
model.add(layers.Dense(512, activation='relu'))
#全连接,激活函数sigmoid
model.add(layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
#输出模型各层的参数状况
model.summary()

配置训练方法,将训练和验证的图片,调整为150*150。
from keras import optimizers
model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy',
optimizer=optimizers.RMSprop(lr=1e-4),
metrics=['acc'])
from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
# 所有图像将按1/255重新缩放
train_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255)
test_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255)
train_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_directory(
# 这是目标目录
train_dir,
# 所有图像将调整为150x150
target_size=(150, 150),
batch_size=20,
# 因为我们使用二元交叉熵损失,我们需要二元标签
class_mode='binary')
validation_generator = test_datagen.flow_from_directory(
validation_dir,
target_size=(150, 150),
batch_size=20,
class_mode='binary')
from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
# 所有图像将按1/255重新缩放
train_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255)
test_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255)
train_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_directory(
# 这是目标目录
train_dir,
# 所有图像将调整为150x150
target_size=(150, 150),
batch_size=20,
# 因为我们使用二元交叉熵损失,我们需要二元标签
class_mode='binary')
validation_generator = test_datagen.flow_from_directory(
validation_dir,
target_size=(150, 150),
batch_size=20,
class_mode='binary')

for data_batch, labels_batch in train_generator:
print('data batch shape:', data_batch.shape)
print('labels batch shape:', labels_batch.shape)
break

保存训练得到的的模型(这个挺费时间的)
#模型训练过程
history = model.fit_generator(
train_generator,
steps_per_epoch=100,
epochs=30,
validation_data=validation_generator,
validation_steps=50)
#保存训练得到的的模型
model.save('C:\\Cat_And_Dog\\kaggle\\cats_and_dogs_small_1.h5')

可视化
#对于模型进行评估,查看预测的准确性
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
acc = history.history['acc']
val_acc = history.history['val_acc']
loss = history.history['loss']
val_loss = history.history['val_loss']
epochs = range(len(acc))
plt.plot(epochs, acc, 'bo', label='Training acc')
plt.plot(epochs, val_acc, 'b', label='Validation acc')
plt.title('Training and validation accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.figure()
plt.plot(epochs, loss, 'bo', label='Training loss')
plt.plot(epochs, val_loss, 'b', label='Validation loss')
plt.title('Training and validation loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()

利用图像生成器定义一些常见的图像变换,增强图像中的有用信息。
#该部分代码及以后的代码,用于替代基准模型中分类后面的代码(执行代码前,需要先将之前分类的目录删掉,重写生成分类,否则,会发生错误)
from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
rotation_range=40,
width_shift_range=0.2,
height_shift_range=0.2,
shear_range=0.2,
zoom_range=0.2,
horizontal_flip=True,
fill_mode='nearest')
查看图像
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# This is module with image preprocessing utilities
from keras.utils import image_utils
fnames = [os.path.join(train_cats_dir, fname) for fname in os.listdir(train_cats_dir)]
# We pick one image to "augment"
img_path = fnames[3]
# Read the image and resize it
img = image_utils.load_img(img_path, target_size=(150, 150))
# Convert it to a Numpy array with shape (150, 150, 3)
x =image_utils.img_to_array(img)
# Reshape it to (1, 150, 150, 3)
x = x.reshape((1,) + x.shape)
# The .flow() command below generates batches of randomly transformed images.
# It will loop indefinitely, so we need to `break` the loop at some point!
i = 0
for batch in datagen.flow(x, batch_size=1):
plt.figure(i)
imgplot = plt.imshow(image_utils.array_to_img(batch[0]))
i += 1
if i % 4 == 0:
break
plt.show()

网络模型增加一层dropout
#网络模型构建
from keras import layers
from keras import models
#keras的序贯模型
model = models.Sequential()
#卷积层,卷积核是3*3,激活函数relu
model.add(layers.Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu',
input_shape=(150, 150, 3)))
#最大池化层
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))
#卷积层,卷积核2*2,激活函数relu
model.add(layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'))
#最大池化层
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))
#卷积层,卷积核是3*3,激活函数relu
model.add(layers.Conv2D(128, (3, 3), activation='relu'))
#最大池化层
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))
#卷积层,卷积核是3*3,激活函数relu
model.add(layers.Conv2D(128, (3, 3), activation='relu'))
#最大池化层
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))
#flatten层,用于将多维的输入一维化,用于卷积层和全连接层的过渡
model.add(layers.Flatten())
#退出层
model.add(layers.Dropout(0.5))
#全连接,激活函数relu
model.add(layers.Dense(512, activation='relu'))
#全连接,激活函数sigmoid
model.add(layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
#输出模型各层的参数状况
model.summary()
from keras import optimizers
model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy',
optimizer=optimizers.RMSprop(lr=1e-4),
metrics=['acc'])

训练模型
train_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
rescale=1./255,
rotation_range=40,
width_shift_range=0.2,
height_shift_range=0.2,
shear_range=0.2,
zoom_range=0.2,
horizontal_flip=True,)
# Note that the validation data should not be augmented!
test_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255)
train_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_directory(
# This is the target directory
train_dir,
# All images will be resized to 150x150
target_size=(150, 150),
batch_size=32,
# Since we use binary_crossentropy loss, we need binary labels
class_mode='binary')
validation_generator = test_datagen.flow_from_directory(
validation_dir,
target_size=(150, 150),
batch_size=32,
class_mode='binary')
history = model.fit(
train_generator,
steps_per_epoch=40,
epochs=40,
validation_data=validation_generator,
validation_steps=50)
model.save('C:\\Cat_And_Dog\\kaggle\\cats_and_dogs_small_2.h5')
可视化
acc = history.history['acc']
val_acc = history.history['val_acc']
loss = history.history['loss']
val_loss = history.history['val_loss']
epochs = range(len(acc))
plt.plot(epochs, acc, 'bo', label='Training acc')
plt.plot(epochs, val_acc, 'b', label='Validation acc')
plt.title('Training and validation accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.figure()
plt.plot(epochs, loss, 'bo', label='Training loss')
plt.plot(epochs, val_loss, 'b', label='Validation loss')
plt.title('Training and validation loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()


VGG19实现猫狗分类
from keras.applications import VGG19
conv_base = VGG19(weights = 'imagenet',include_top = False,input_shape=(150, 150, 3))
conv_base.summary()
训练模型
import os
import numpy as np
from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
# 数据集分类后的目录
base_dir = 'E:\\Cat_And_Dog\\kaggle\\cats_and_dogs_small'
train_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, 'train')
validation_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, 'validation')
test_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, 'test')
datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale = 1. / 255)
batch_size = 20
def extract_features(directory, sample_count):
features = np.zeros(shape = (sample_count, 4, 4, 512))
labels = np.zeros(shape = (sample_count))
generator = datagen.flow_from_directory(directory, target_size = (150, 150),
batch_size = batch_size,
class_mode = 'binary')
i = 0
for inputs_batch, labels_batch in generator:
#把图片输入VGG16卷积层,让它把图片信息抽取出来
features_batch = conv_base.predict(inputs_batch)
#feature_batch 是 4*4*512结构
features[i * batch_size : (i + 1)*batch_size] = features_batch
labels[i * batch_size : (i+1)*batch_size] = labels_batch
i += 1
if i * batch_size >= sample_count :
#for in 在generator上的循环是无止境的,因此我们必须主动break掉
break
return features , labels
#extract_features 返回数据格式为(samples, 4, 4, 512)
train_features, train_labels = extract_features(train_dir, 2000)
validation_features, validation_labels = extract_features(validation_dir, 1000)
test_features, test_labels = extract_features(test_dir, 1000)
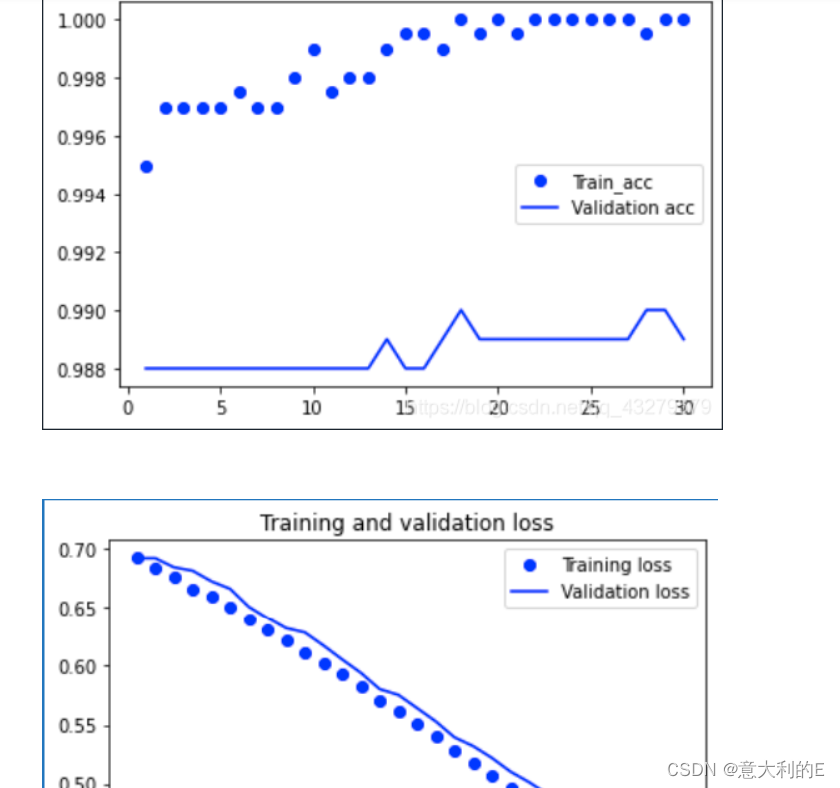
可视化
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
acc = history.history['acc']
val_acc = history.history['val_acc']
loss = history.history['loss']
val_loss = history.history['val_loss']
epochs = range(1, len(acc) + 1)
plt.plot(epochs, acc, 'bo', label = 'Train_acc')
plt.plot(epochs, val_acc, 'b', label = 'Validation acc')
plt.title('Trainning and validation accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.figure()
plt.plot(epochs, loss, 'bo', label = 'Training loss')
plt.plot(epochs, val_loss, 'b', label = 'Validation loss')
plt.title('Training and validation loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()





















 1008
1008











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








