Hough 变换可以提取图像中的直线。但是提取的直线的精度不高。而很多场合下,我们需要精确的估计直线的参数,这时就需要进行直线拟合。
直线拟合的方法很多,比如一元线性回归就是一种最简单的直线拟合方法。但是这种方法不适合用于提取图像中的直线。因为这种算法假设每个数据点的X 坐标是准确的,Y 坐标是带有高斯噪声的。可实际上,图像中的每个数据点的XY 坐标都是带有噪声的。
下面就来讲讲适用于提取图像中直线的直线拟合算法。
一个点 <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-140">(x_i, y_i)</script> 到直线的距离用 <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-141">r_i</script> 来表示。
所谓直线拟合,就是找到一条直线,使得:
<script type="math/tex; mode=display" id="MathJax-Element-582"> \sum \rho(r_i) </script>
最小。
<script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-583">\rho(r)</script> 是距离函数。<script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-584">\rho(r)</script> 函数取不同的形式,对应不同的直线拟合方法。OpenCV 中支持 6 种不同的<script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-585">\rho(r)</script> 函数形式。分别是:
CV_DIST_L2
<script type="math/tex; mode=display" id="MathJax-Element-586"> \rho(r) = \frac{r^2}{2} </script>
这种方法是以距离平方和为拟合判据。也就是常见的最小二乘拟合算法,运行速度也最快。但是这个算法也有个很大的问题,就是当干扰点离直线较远时,一个干扰点就可能将整条拟合直线拉偏了。简单的说就是对干扰点的鲁棒性不够。所以后来又提出了其他的函数。
CV_DIST_L1
<script type="math/tex; mode=display" id="MathJax-Element-248"> \rho(r) = r </script>
CV_DIST_L12
<script type="math/tex; mode=display" id="MathJax-Element-249"> \rho(r) = 2 \left( \sqrt{1 + \frac{r^2}{2}} -1 \right ) </script>
CV_DIST_FAIR
<script type="math/tex; mode=display" id="MathJax-Element-250"> \rho(r) = C^2 \left( \frac{r}{C} - \log \left(1+\frac{r}{C}\right)\right ) </script>
其中 C = 1.3998
CV_DIST_WELSCH
<script type="math/tex; mode=display" id="MathJax-Element-251"> \rho(r) = \frac{C^2}{2} \left ( 1 - \exp\left( - \left(\frac{r}{C}\right)^2\right) \right ) </script>
其中 C = 2.9846
CV_DIST_HUBER
<script type="math/tex; mode=display" id="MathJax-Element-635"> \rho(r) =\begin{cases} \frac{r^2}{2}& if \ \ r
其中 C = 1.345
后面这 5 种函数我知道第一种,其他的不知道是怎么来的。OpenCV 的帮助文档给出了一个链接:M-estimator
但是这个页面也被墙了。
下面来说说 OpenCV 提供的直线拟合函数。函数原型如下:
void fitLine( InputArray points,
OutputArray line,
int distType,
double param,
double reps,
double aeps );- 1
distType 指定拟合函数的类型,可以取 CV_DIST_L2、CV_DIST_L1、CV_DIST_L12、CV_DIST_FAIR、CV_DIST_WELSCH、CV_DIST_HUBER。
param 就是 CV_DIST_FAIR、CV_DIST_WELSCH、CV_DIST_HUBER 公式中的C。如果取 0,则程序自动选取合适的值。
reps 表示直线到原点距离的精度,建议取 0.01。
aeps 表示直线角度的精度,建议取 0.01。
计算出的直线信息存放在 line 中,为 cv::Vec4f 类型。line[0]、line[1] 存放的是直线的方向向量。line[2]、line[3] 存放的是直线上一个点的坐标。
如果直线用 <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-846">y = k x + b</script> 来表示,那么 k = line[1]/line[0],b = line[3] - k * line[2]。
如果直线用 <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-847">\rho = x \cos \theta+ y \sin \theta</script> 来表示, 那么 <script type="math/tex" id="MathJax-Element-848">\theta = \arctan k + \frac{\pi}{2} </script>
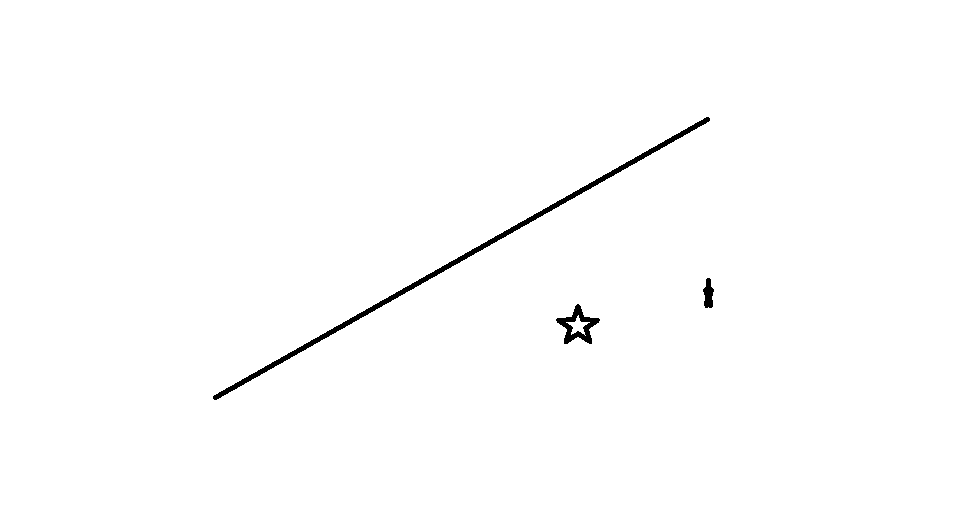
下面是个测试图像:
图像中有一条直线和一些干扰图案。
下面的代码可以从图像中提取出需要的坐标点。
std::vector<cv::Point> getPoints(cv::Mat &image, int value)
{
int nl = image.rows; // number of lines
int nc = image.cols * image.channels();
std::vector<cv::Point> points;
for (int j = 0; j < nl; j++)
{
uchar* data = image.ptr<uchar>(j);
for (int i = 0; i < nc; i++)
{
if(data[i] == value)
{
points.push_back(cv::Point(i, j));
}
}
}
return points;
}下面的代码可以在图中画一条直线。
void drawLine(cv::Mat &image, double theta, double rho, cv::Scalar color)
{
if (theta < PI/4. || theta > 3.*PI/4.)// ~vertical line
{
cv::Point pt1(rho/cos(theta), 0);
cv::Point pt2((rho - image.rows * sin(theta))/cos(theta), image.rows);
cv::line( image, pt1, pt2, cv::Scalar(255), 1);
}
else
{
cv::Point pt1(0, rho/sin(theta));
cv::Point pt2(image.cols, (rho - image.cols * cos(theta))/sin(theta));
cv::line(image, pt1, pt2, color, 1);
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
下面的代码是程序的主体。
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QCoreApplication a(argc, argv);
cv::Mat image = imread("c:\\line_test.png", cv::IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
std::vector<cv::Point> points = getPoints(image, 0);
cv::Vec4f line;
cv::fitLine(points,
line,
CV_DIST_HUBER ,
0,
0.01,
0.01);
double cos_theta = line[0];
double sin_theta = line[1];
double x0 = line[2], y0 = line[3];
double phi = atan2(sin_theta, cos_theta) + PI / 2.0;
double rho = y0 * cos_theta - x0 * sin_theta;
std::cout << "phi = " << phi / PI * 180 << std::endl;
std::cout << "rho = " << rho << std::endl;
drawLine(image, phi, rho, cv::Scalar(0));
double k = sin_theta / cos_theta;
double b = y0 - k * x0;
double x = 0;
double y = k * x + b;
std::cout << k << std::endl;
std::cout << b << std::endl;
//cv::line(image, Point(x0,y0), Point(x,y), cv::Scalar(255), 1);
imshow("", image);
return a.exec();
}
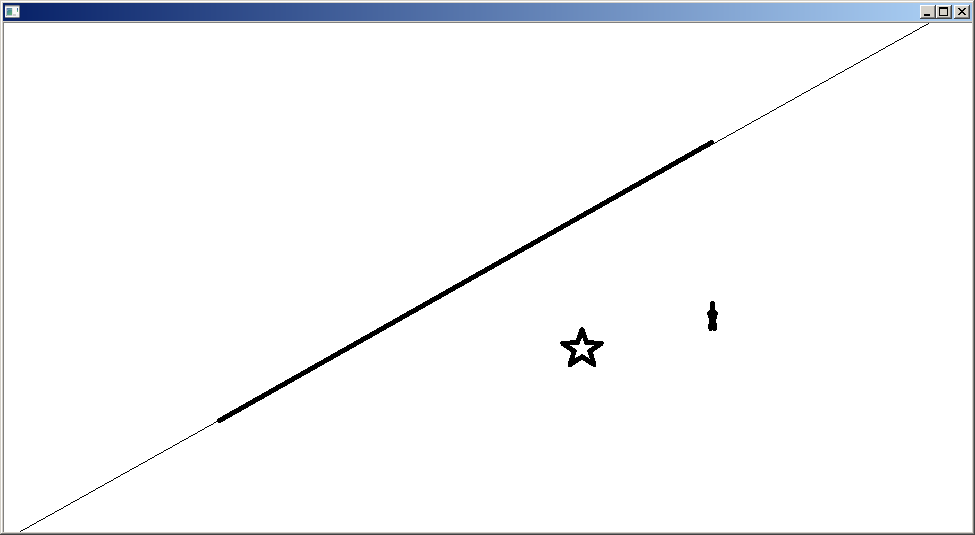
如果直线拟合类型选择 CV_DIST_L2。那么效果就没这么好了。代码不贴了,就贴个结果。






















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








