Box2d::HasOverlap(const Box2d &box)
最近看apollo的一些common函数,对于Box2d::HasOverlap函数仔细画了图研究了一下,根据前人的文章,用自己的习惯重新整理了一下。
矩形Box2d
是指世界坐标系下的一个矩形,其中IsPointIn、IsPointOnBoundary、DistanceTo(point)的计算都是先转成AABox2d的格式进行比较的(从绝对坐标系转到矩形坐标系),转个坐标系即可。
该函数主要是判断矩形是否与其他矩形相交
完整的函数代码如下:
bool Box2d::HasOverlap(const Box2d &box) const
{
if (box.max_x() < min_x() || box.min_x() > max_x() || box.max_y() < min_y() ||
box.min_y() > max_y())
{
return false;
}
const double shift_x = box.center_x() - center_.x();
const double shift_y = box.center_y() - center_.y();
const double dx1 = cos_heading_ * half_length_;
const double dy1 = sin_heading_ * half_length_;
const double dx2 = sin_heading_ * half_width_;
const double dy2 = -cos_heading_ * half_width_;
const double dx3 = box.cos_heading() * box.half_length();
const double dy3 = box.sin_heading() * box.half_length();
const double dx4 = box.sin_heading() * box.half_width();
const double dy4 = -box.cos_heading() * box.half_width();
return std::abs(shift_x * cos_heading_ + shift_y * sin_heading_) <=
std::abs(dx3 * cos_heading_ + dy3 * sin_heading_) +
std::abs(dx4 * cos_heading_ + dy4 * sin_heading_) +
half_length_ &&
std::abs(shift_x * sin_heading_ - shift_y * cos_heading_) <=
std::abs(dx3 * sin_heading_ - dy3 * cos_heading_) +
std::abs(dx4 * sin_heading_ - dy4 * cos_heading_) +
half_width_ &&
std::abs(shift_x * box.cos_heading() + shift_y * box.sin_heading()) <=
std::abs(dx1 * box.cos_heading() + dy1 * box.sin_heading()) +
std::abs(dx2 * box.cos_heading() + dy2 * box.sin_heading()) +
box.half_length() &&
std::abs(shift_x * box.sin_heading() - shift_y * box.cos_heading()) <=
std::abs(dx1 * box.sin_heading() - dy1 * box.cos_heading()) +
std::abs(dx2 * box.sin_heading() - dy2 * box.cos_heading()) +
box.half_width();
}
判断相交主要是分成几个模块进行判断。下面这部分是粗检测。
if (box.max_x() < min_x() || box.min_x() > max_x() || box.max_y() < min_y() ||
box.min_y() > max_y())
{
return false;
}
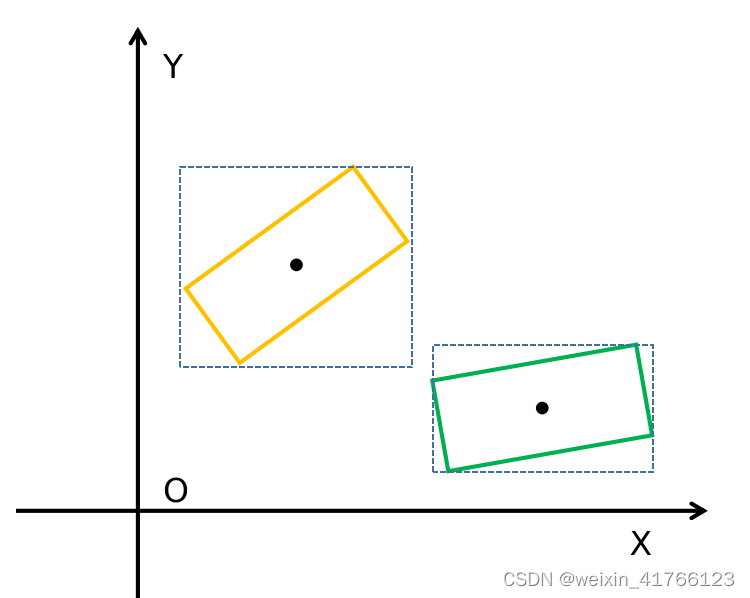
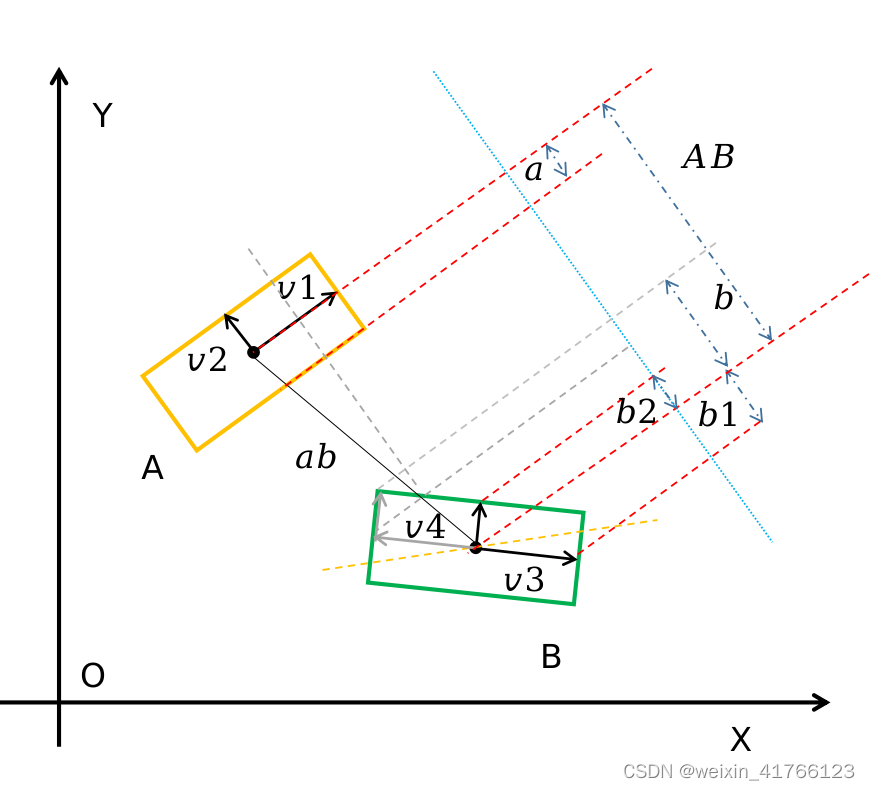
AABB检测用于粗检测,根据自车和障碍物的box角点构建两个长宽分别平行于坐标轴的box,查看这两个box(两个虚线box表示)是否有交集,可以直接根据新构建的box的角点的坐标值来判断。如下图所示,通过这种方式可以粗略检测到A、B有碰撞,但是是否真的有碰撞还需要通过OBB进一步检测。
第二部分是分离轴定理进行检测。
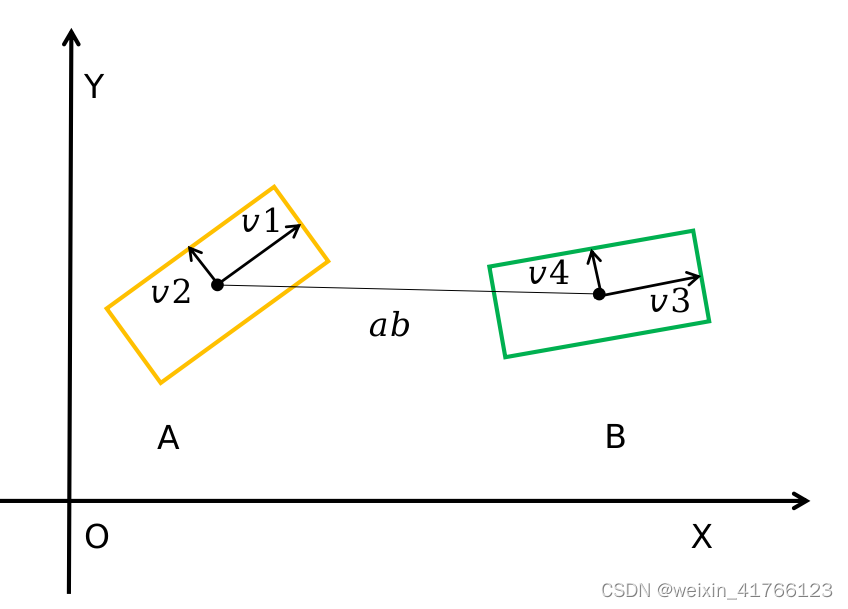
首先是构造了几个向量:
const double shift_x = box.center_x() - center_.x();
const double shift_y = box.center_y() - center_.y();
const double dx1 = cos_heading_ * half_length_;
const double dy1 = sin_heading_ * half_length_;
const double dx2 = sin_heading_ * half_width_;
const double dy2 = -cos_heading_ * half_width_;
const double dx3 = box.cos_heading() * box.half_length();
const double dy3 = box.sin_heading() * box.half_length();
const double dx4 = box.sin_heading() * box.half_width();
const double dy4 = -box.cos_heading() * box.half_width();
其中:
shift_x,shift_f是向量
a
b
⃗
\vec{ab}
ab。
dx1,dy1是向量
v
1
⃗
\vec{v_1}
v1。
dx2,dy2是向量
v
2
⃗
\vec{v_2}
v2。
dx3,dy3是向量
v
3
⃗
\vec{v_3}
v3。
dx4,dxy4是向量
v
4
⃗
\vec{v_4}
v4。
如下图所示。
接着看下面这行代码:
std::abs(shift_x * cos_heading_ + shift_y * sin_heading_) <=
std::abs(dx3 * cos_heading_ + dy3 * sin_heading_) +
std::abs(dx4 * cos_heading_ + dy4 * sin_heading_) +
half_length_
std::abs(shift_x * cos_heading_ + shift_y * sin_heading_)就是指向量
a
b
⃗
\vec{ab}
ab在中轴线上的投影,其值为AB,我们以相离和相交的两种图展示,如下图所示。std::abs(dx3 * cos_heading_ + dy3 * sin_heading_)是向量
v
3
⃗
\vec{v_3}
v3在中轴上的投影为b1,std::abs(dx4 * cos_heading_ + dy4 * sin_heading_)是指
v
4
⃗
\vec{v_4}
v4的投影为b2,half_length_是指向量
v
1
⃗
\vec{v_1}
v1在中轴线上的投影a,向量
v
2
⃗
\vec{v_2}
v2在中轴线上的投影为零,可不计入。
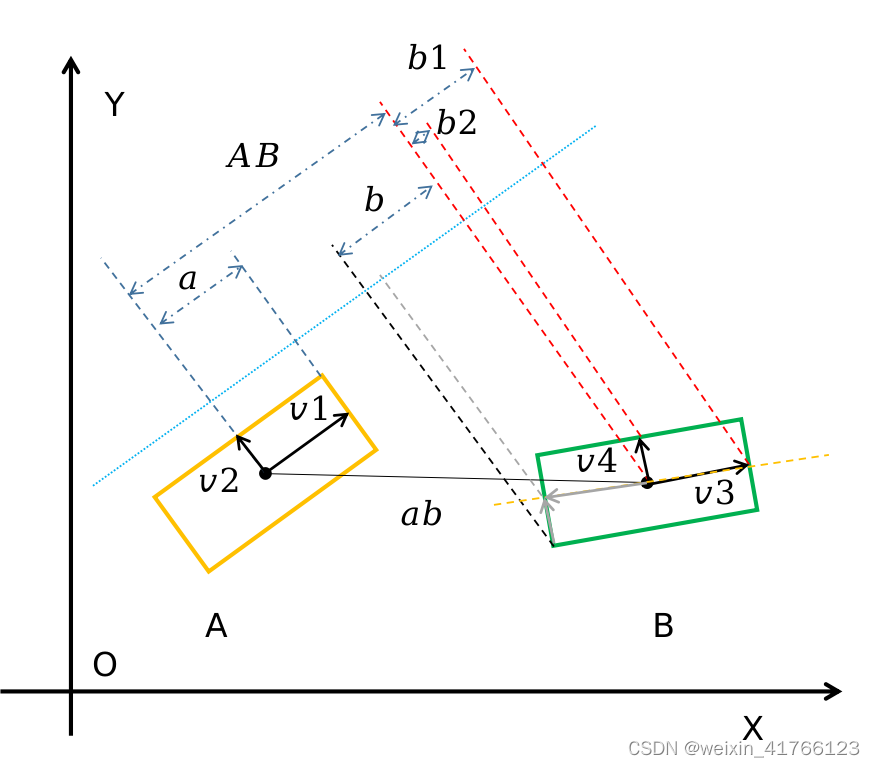
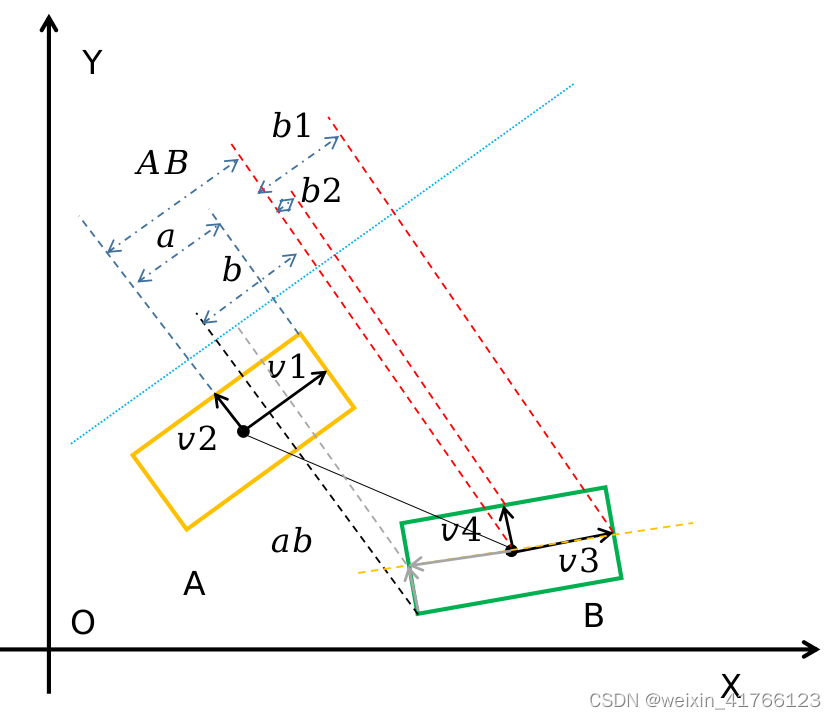
如果AB<=a+b那么就会出现上面相交的情况,如果大于就是图1相离的情况。
同理下面的这段代码是指
std::abs(shift_x * sin_heading_ - shift_y * cos_heading_) <=
std::abs(dx3 * sin_heading_ - dy3 * cos_heading_) +
std::abs(dx4 * sin_heading_ - dy4 * cos_heading_) +
half_width_
再向A矩形的横轴上进行投影
再往后就是计算往B纵轴上的投影,横轴上的投影,如果几面的投影都相交那么两个矩形就一定相交了。
主要参考的是这篇博客:
百度Apollo规划算法——OBB障碍物检测代码解析
主要用作个人学习、查询使用。
如有侵权,请联系删除。
























 1961
1961











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










