序:
上一节我们安装好了MPU6050的三方库,这一节我们尝试使用该库通过esp32将IMU模块驱动起来。
参考资料:小鱼——使用开源库驱动IMU
一、使用开源库驱动IMU
1. MPU6050介绍
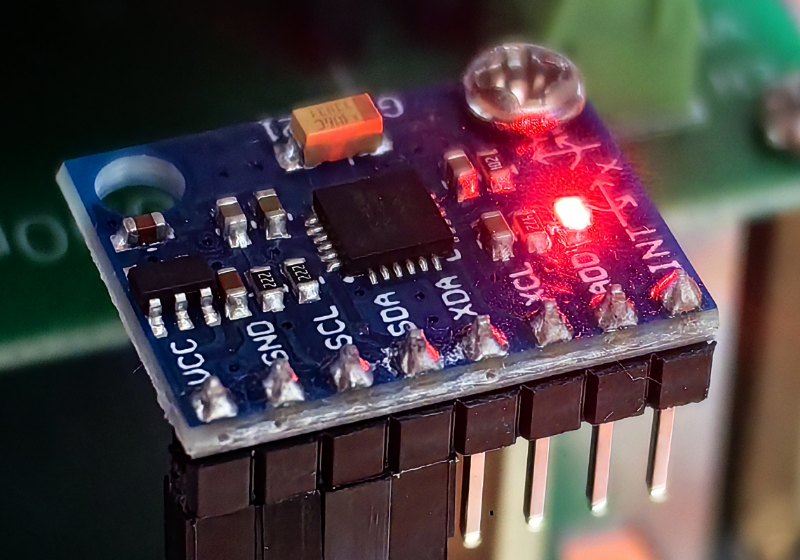
首先我们了解下MPU6050模块,从外观看,长这个样子

MPU6050 为全球首例集成六轴传感器的运动处理组件,内置了运动融合引擎,用于手持和桌面的应用程序、游戏控制器、体感遥控以及其他消费电子设备。它内置一个三轴 MEMS 陀螺仪、一个三轴 MEMS 加速度计、一个数字运动处理引擎(DMP)以及用于第三方的数字传感器接口的辅助 I2C 端口(常用于扩展磁力计)。当辅助 I2C 端口连接到一个三轴磁力计,MPU6050 能提供一个完整的九轴融合输出到其主 I2C 端口。
在板子上是这样的
2. 调用开源库驱动
新建工程example06_mpu6050
2.1 添加依赖
修改platformio.ini
[env:esp32doit-devkit-v1]
platform = espressif32
board = esp32doit-devkit-v1
framework = arduino
monitor_speed = 115200
lib_deps =
https://mirror.ghproxy.com/https://github.com/rfetick/MPU6050_light.git
2.2 样例程序
复制到main.cpp中
/* Get all possible data from MPU6050
* Accelerometer values are given as multiple of the gravity [1g = 9.81 m/s²]
* Gyro values are given in deg/s
* Angles are given in degrees
* Note that X and Y are tilt angles and not pitch/roll.
*
* License: MIT
*/
#include "Wire.h"
#include <MPU6050_light.h>
MPU6050 mpu(Wire);
unsigned long timer = 0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
Wire.begin();
byte status = mpu.begin();
Serial.print(F("MPU6050 status: "));
Serial.println(status);
while(status!=0){ } // stop everything if could not connect to MPU6050
Serial.println(F("Calculating offsets, do not move MPU6050"));
delay(1000);
mpu.calcOffsets(true,true); // gyro and accelero
Serial.println("Done!\n");
}
void loop() {
mpu.update();
if(millis() - timer > 1000){ // print data every second
Serial.print(F("TEMPERATURE: "));Serial.println(mpu.getTemp());
Serial.print(F("ACCELERO X: "));Serial.print(mpu.getAccX());
Serial.print("\tY: ");Serial.print(mpu.getAccY());
Serial.print("\tZ: ");Serial.println(mpu.getAccZ());
Serial.print(F("GYRO X: "));Serial.print(mpu.getGyroX());
Serial.print("\tY: ");Serial.print(mpu.getGyroY());
Serial.print("\tZ: ");Serial.println(mpu.getGyroZ());
Serial.print(F("ACC ANGLE X: "));Serial.print(mpu.getAccAngleX());
Serial.print("\tY: ");Serial.println(mpu.getAccAngleY());
Serial.print(F("ANGLE X: "));Serial.print(mpu.getAngleX());
Serial.print("\tY: ");Serial.print(mpu.getAngleY());
Serial.print("\tZ: ");Serial.println(mpu.getAngleZ());
Serial.println(F("=====================================================\n"));
timer = millis();
}
}
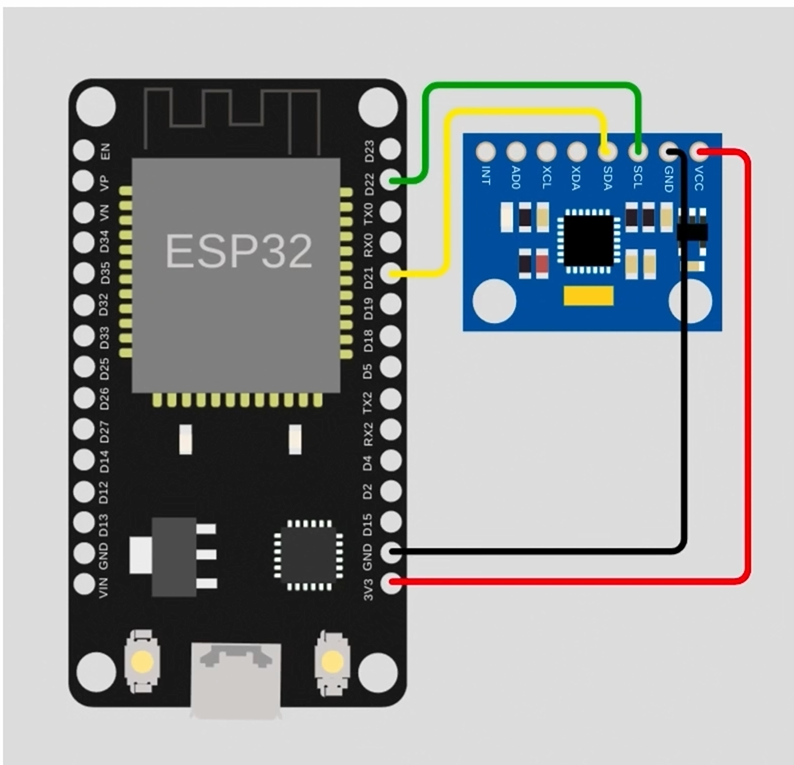
2.3 接线方法
如图所示
2.4 修改代码
- 修改波特率 9600->115200
- 修改IO地址 Wire.begin();->Wire.begin(21, 22);
#include "Wire.h" // 导入I2C相关头文件
#include <MPU6050_light.h> // 导入MPU6050库
MPU6050 mpu(Wire); // 新建MPU6050对象mpu
unsigned long timer = 0;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(115200);
Wire.begin(21, 22); // 初始化I2C,设置sda引脚为GPIO21,SCL引脚为GPIO22
byte status = mpu.begin(); // 检测IMU模块状态
Serial.print(F("MPU6050 status: "));
Serial.println(status);
while (status != 0)
{
} // stop everything if could not connect to MPU6050
Serial.println(F("Calculating offsets, do not move MPU6050"));
delay(1000);
mpu.calcOffsets(true, true); // gyro and accelero 校准
Serial.println("Done!\n");
}
void loop()
{
mpu.update();
if (millis() - timer > 1000)
{ // print data every second
Serial.print(F("TEMPERATURE: "));
Serial.println(mpu.getTemp()); // 温度
Serial.print(F("ACCELERO X: "));
Serial.print(mpu.getAccX()); // X轴加速度
Serial.print("\tY: ");
Serial.print(mpu.getAccY()); // Y轴加速度
Serial.print("\tZ: ");
Serial.println(mpu.getAccZ()); // Z轴加速度
Serial.print(F("GYRO X: "));
Serial.print(mpu.getGyroX()); // X轴 角速度
Serial.print("\tY: ");
Serial.print(mpu.getGyroY()); // Y轴 角速度
Serial.print("\tZ: ");
Serial.println(mpu.getGyroZ()); // Z轴 角速度
Serial.print(F("ACC ANGLE X: "));
Serial.print(mpu.getAccAngleX()); // X轴角加速度
Serial.print("\tY: ");
Serial.println(mpu.getAccAngleY()); // Y轴角加速度
Serial.print(F("ANGLE X: "));
Serial.print(mpu.getAngleX()); // X角度
Serial.print("\tY: ");
Serial.print(mpu.getAngleY()); // Y角度
Serial.print("\tZ: ");
Serial.println(mpu.getAngleZ()); // Z角度
Serial.println(F("=====================================================\n"));
timer = millis();
}
}
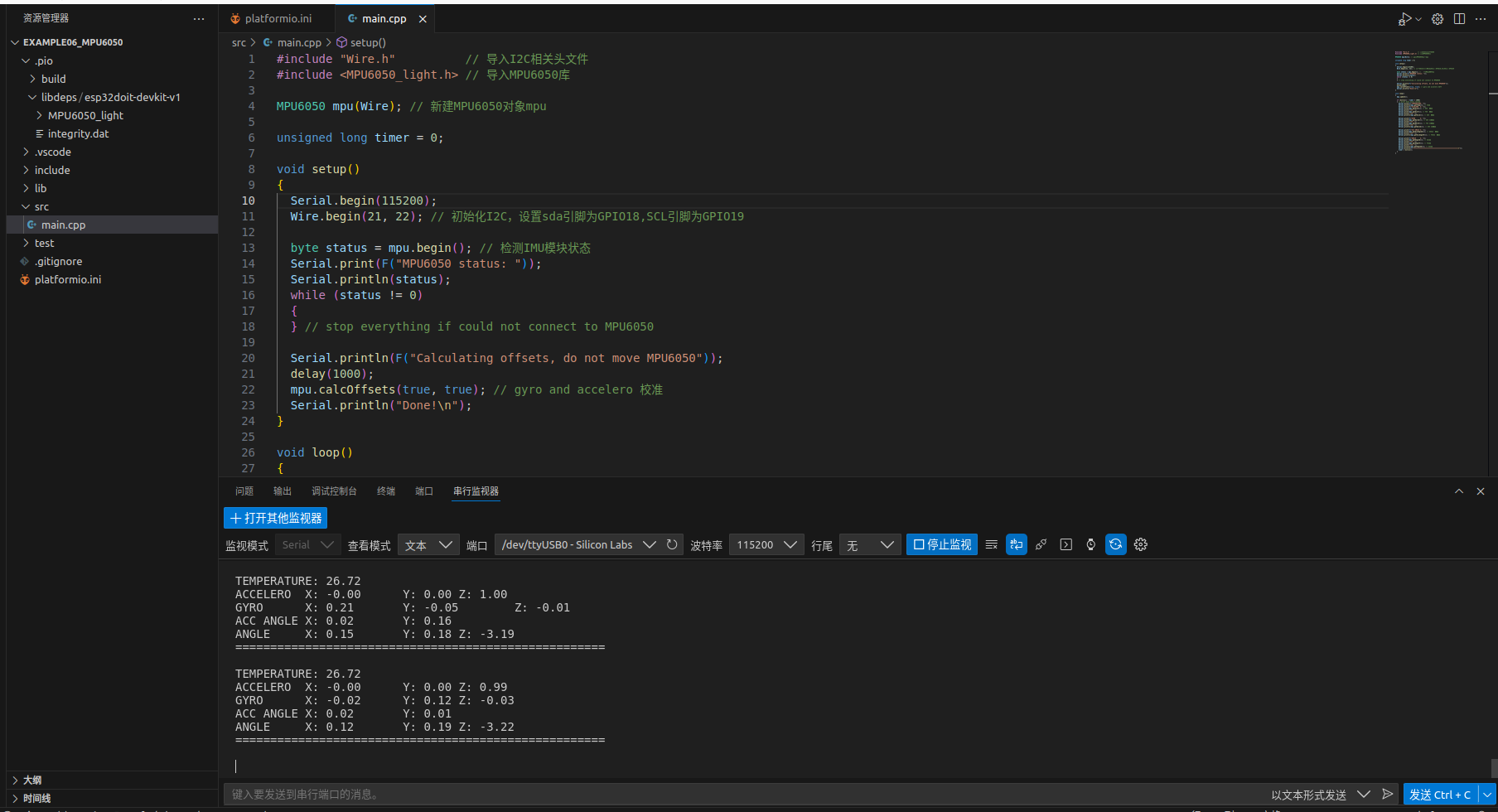
3. 编译测试
保存代码,编译下载到开发板。打开串口监视器,查看结果。
二、学会面向对象编程-封装IMU驱动
说明:在本章练习编写c++代码,建议跟着视频【ROS2硬件控制】13A.3.学会面向对象编程-封装IMU驱动(上)一步一步敲一遍,是有用的,但还没有全部理解,故暂时空下。
文档链接:学会面向对象编程-封装IMU驱动

























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








