新建一个脚本,将源码复制进去,可以直接运行。

% 基于遗传算法的栅格法机器人路径规划的MATLAB实现
clc;
clear;
% 输入数据,即栅格地图
G= [0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0;
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0;
0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0;
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0;
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0;
0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0;
0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0;
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0;
0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0;
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0;
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0;
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0;
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0;
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0;
0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0;
0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0;
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0;
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0;
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0;
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0];
p_start = 0; % 起始序号
p_end = 399; % 终止序号
NP = 200; % 种群数量
max_gen = 50; % 最大进化代数
percross = 0.8; % 交叉概率
permutate = 0.2; % 变异概率
perlenth = 1; % 路径长度比重
persmooth = 7; % 路径顺滑度比重
%init_path = [];
z = 1;
new_pop1 = {}; % 元胞类型数组,啥都可以存,类似C语言中的结构
new_pop2 = {};
[y, x] = size(G); % x = 20, y = 20,行数和列数
% 起点所在列(从左到右编号1.2.3...)
xstart = mod(p_start, x) + 1;
% 起点所在行(从上到下编号行1.2.3...)
ystart = fix(p_start / x) + 1;
% 终点所在列、行
xend = mod(p_end, x) + 1; % mod函数取余函数,前除以后取余数
yend = fix(p_end / x) + 1; % fix函数取整函数,四舍五入取整数
% 种群初始化第一步,必经节点,从起始点所在行开始往上,在每行中挑选一个自由栅格,构成必经节点
pass_num = yend - ystart + 1; % 等于地图总共的行数,表示
pop = zeros(NP, pass_num); % pop初始化置零,等于最大迭代次数*地图总行数的矩阵,表示所有可能的路径
for global1_i = 1 : NP
pop(global1_i, 1) = p_start; % 循环NP次,把起点放入pop首列
global1_j = 1;
for global_iyk = ystart+1 : yend-1 % 除去起点和终点
global1_j = global1_j + 1;
can = []; % 每一行无障碍的点组成can数组
for global_ixk = 1 : x
global_ino = (global_ixk - 1) + (global_iyk - 1) * x; % 给每个栅格编序号
if G(global_iyk, global_ixk) == 0
can = [can global_ino]; % 把无障碍的点加入can数组中
end
end
can_num = length(can); % can数组的长度
index = randi(can_num); % 产生随机的整数
pop(global1_i, global1_j) = can(index); % 每一行表示的一条路径中加入一个无障碍的点
end
pop(global1_i, end) = p_end; % 最后把终点放入pop最后一列
% 种群初始化第二步,将上述必经节点联结成无间断路径
% single_new_pop = generate_continuous_path(pop(i, :), G, x);
%@@@@@@@@@@ 将上述随机的点连接成连续路径
generate_i = 1;
single_new_pop = pop(global1_i,:); % 取pop矩阵第global1_i行而不是第generate_i行所有数据,表示取出一条路径
[~, single_path_num] = size(single_new_pop);
while generate_i ~= single_path_num
value_x_now = mod(single_new_pop(1, generate_i), x) + 1; % 当前点所在列
value_y_now = fix(single_new_pop(1, generate_i) / x) + 1; % 当前点所在行
value_x_next = mod(single_new_pop(1, generate_i + 1), x) + 1; % 下一个点所在列
value_y_next = fix(single_new_pop(1, generate_i + 1) / x) + 1; % 下一个点所在行
max_iteration = 0; % 初始化平滑路径最大迭代次数
while max(abs(value_x_next - value_x_now), abs(value_y_next - value_y_now)) ~= 1 % 判断点generate_i和generate_i+1是否连续(挨在一起),若否就插入中间点
x_insert = floor((value_x_next + value_x_now) / 2);
y_insert = floor((value_y_next + value_y_now) / 2);
if G(y_insert, x_insert) == 0 % 当插入栅格为自由栅格(不在障碍物上)时
num_insert = (x_insert - 1) + (y_insert - 1) * x; % 将栅格位置转化为序号
single_new_pop = [single_new_pop(1, 1:generate_i), num_insert, single_new_pop(1, generate_i+1:end)]; % 将栅格序号插入single数组里
else % 插入栅格为障碍物栅格(在障碍物上)时
% 往左走
if G(y_insert, x_insert - 1) == 0 && ((x_insert - 2) + (y_insert - 1) * x ~= single_new_pop(1, generate_i)) && ((x_insert - 2) + (y_insert - 1) * x ~= single_new_pop(1, generate_i+1))
x_insert = x_insert - 1;
num_insert = (x_insert - 1) + (y_insert - 1) * x; % 将栅格位置转化为序号
single_new_pop = [single_new_pop(1, 1:generate_i), num_insert, single_new_pop(1, generate_i+1:end)]; % 将栅格序号插入single数组里
% 往右走
elseif G(y_insert, x_insert + 1) == 0 && (x_insert + (y_insert - 1) * x ~= single_new_pop(1, generate_i)) && (x_insert + (y_insert - 1) * x ~= single_new_pop(1, generate_i+1))
x_insert = x_insert + 1;
num_insert = (x_insert - 1) + (y_insert - 1) * x; % 将栅格位置转化为序号
single_new_pop = [single_new_pop(1, 1:generate_i), num_insert, single_new_pop(1, generate_i+1:end)]; % 将栅格序号插入single数组里
% 向上走
elseif G(y_insert + 1, x_insert) == 0 && ((x_insert - 1) + y_insert * x ~= single_new_pop(1, generate_i)) && ((x_insert - 1) + y_insert * x ~= single_new_pop(1, generate_i+1))
y_insert = y_insert + 1;
num_insert = (x_insert - 1) + (y_insert - 1) * x; % 将栅格位置转化为序号
single_new_pop = [single_new_pop(1, 1:generate_i), num_insert, single_new_pop(1, generate_i+1:end)]; % 将栅格序号插入single数组里
% 向下走
elseif G(y_insert - 1, x_insert) == 0 && ((x_insert - 1) + (y_insert - 2) * x ~= single_new_pop(1, generate_i)) && ((x_insert - 1) + (y_insert-2) * x ~= single_new_pop(1, generate_i+1))
y_insert = y_insert - 1;
num_insert = (x_insert - 1) + (y_insert - 1) * x; % 将栅格位置转化为序号
single_new_pop = [single_new_pop(1, 1:generate_i), num_insert, single_new_pop(1, generate_i+1:end)]; % 将栅格序号插入single数组里
% 其他情况舍去此路径
else
single_new_pop = [];
break
end
end
value_x_next = x_insert;
value_y_next = y_insert;
max_iteration = max_iteration + 1;
if max_iteration > 20000 % 最多执行20000次,是为平滑路径最大迭代次数
single_new_pop = [];
break
end
end
if isempty(single_new_pop)
break
end
[~, single_path_num] = size(single_new_pop);
generate_i = generate_i + 1;
end
if ~isempty(single_new_pop)
new_pop1(z, 1) = {single_new_pop};
z = z + 1;
end
end
% 计算初始化种群的适应度
%@@@@@@@@@@ 计算路径长度
% path_value = cal_path_value(new_pop1, x);
path_value_in_pop = new_pop1;
[value_n, ~] = size(path_value_in_pop);
path_value_out_pop = zeros(1, value_n);
for value_i = 1 : value_n
path_value_single_pop = path_value_in_pop{value_i, 1};
[~, value_m] = size(path_value_single_pop);
for value_j = 1 : value_m - 1
% 点i所在列(从左到右编号1.2.3...)
value_x_now = mod(path_value_single_pop(1, value_j), x) + 1;
% 点i所在行(从上到下编号行1.2.3...)
value_y_now = fix(path_value_single_pop(1, value_j) / x) + 1;
% 点i+1所在列、行
value_x_next = mod(path_value_single_pop(1, value_j + 1), x) + 1;
value_y_next = fix(path_value_single_pop(1, value_j + 1) / x) + 1;
if abs(value_x_now - value_x_next) + abs(value_y_now - value_y_next) == 1
path_value_out_pop(1, value_i) = path_value_out_pop(1, value_i) + 1;
else
path_value_out_pop(1, value_i) = path_value_out_pop(1, value_i) + sqrt(2);
end
end
end
path_value = path_value_out_pop;
%@@@@@@@@@@ 计算路径平滑度
%path_smooth = cal_path_smooth(new_pop1, x);
path_smooth_in_pop = new_pop1;
[smooth_n, ~] = size(path_smooth_in_pop);
path_smooth_out_pop = zeros(1, smooth_n);
for smooth_i = 1 : smooth_n
path_smooth_single_pop = path_smooth_in_pop{smooth_i, 1};
[~, smooth_m] = size(path_smooth_single_pop);
for smooth_j = 1 : smooth_m - 2
% 点i所在列(从左到右编号1.2.3...)
smooth_x_now = mod(path_smooth_single_pop(1, smooth_j), x) + 1;
% 点i所在行(从上到下编号行1.2.3...)
smooth_y_now = fix(path_smooth_single_pop(1, smooth_j) / x) + 1;
% 点i+1所在列、行
% smooth_x_next1 = mod(path_smooth_single_pop(1, smooth_j + 1), x) + 1;
% smooth_y_next1 = fix(path_smooth_single_pop(1, smooth_j + 1) / x) + 1;
% 点i+2所在列、行
smooth_x_next2 = mod(path_smooth_single_pop(1, smooth_j + 2), x) + 1;
smooth_y_next2 = fix(path_smooth_single_pop(1, smooth_j + 2) / x) + 1;
smooth_c2 = (smooth_x_now - smooth_x_next2)^2 + (smooth_y_now - smooth_y_next2)^2;
if smooth_c2 < 8 && smooth_c2 > 4
path_smooth_out_pop(1, smooth_i) = path_smooth_out_pop(1, smooth_i) + 5;
elseif smooth_c2 <= 4 && smooth_c2 > 1
path_smooth_out_pop(1, smooth_i) = path_smooth_out_pop(1, smooth_i) + 30;
elseif smooth_c2 <= 1
path_smooth_out_pop(1, smooth_i) = path_smooth_out_pop(1, smooth_i) + 5000;
end
end
end
path_smooth = path_smooth_out_pop;
% 由路径平滑度与长度计算路径适应度函数
fit_value = perlenth .* path_value .^ -1 + persmooth .* path_smooth .^ -1;
mean_path_value = zeros(1, max_gen);
min_path_value = zeros(1, max_gen);
% 循环迭代操作(体现遗传算法的优越性)
for global2_i = 1 : max_gen
%@@@@@@@@@@ 选择操作
% new_pop2 = selection(new_pop1, fit_value);
select_in_pop = new_pop1;
select_out_pop = cell(length(new_pop1),1); % 建立一个元胞数组,啥都可以存
[select_px, ~] = size(select_in_pop);
total_fit = sum(fit_value);
p_fit_value = fit_value / total_fit;
p_fit_value = cumsum(p_fit_value); % 概率求和排序
% 随机数从小到大排列
select_ms = sort(rand(select_px, 1));
fitin = 1;
newin = 1;
while newin <= select_px
if(select_ms(newin)) < p_fit_value(fitin)
select_out_pop{newin, 1} = select_in_pop{fitin, 1};
newin = newin+1;
else
fitin = fitin+1;
end
end
new_pop2 = select_out_pop;
%@@@@@@@@@@ 交叉操作
% new_pop2 = crossover(new_pop2, percross);
cross_in_pop = new_pop2;
cross_out_pop = cell(length(new_pop1),1);
[cross_px,~] = size(cross_in_pop);
parity = mod(cross_px, 2);% 判断路径点数是奇数或偶数
for cross_i = 1:2:cross_px-1
singal_now_pop = cross_in_pop{cross_i, 1};
singal_next_pop = cross_in_pop{cross_i+1, 1};
[lia, lib] = ismember(singal_now_pop, singal_next_pop);
[~, cross_n] = find(lia == 1);
[~, cross_m] = size(cross_n);
if (rand < percross) && (cross_m >= 3)
% 生成一个2-m-1之间的随机数
cross_r = round(rand(1,1)*(cross_m-3)) +2;
crossover_index1 = cross_n(1, cross_r);
crossover_index2 = lib(crossover_index1);
cross_out_pop{cross_i, 1} = [singal_now_pop(1:crossover_index1), singal_next_pop(crossover_index2+1:end)];
cross_out_pop{cross_i+1, 1} = [singal_next_pop(1:crossover_index2), singal_now_pop(crossover_index1+1:end)];
else
cross_out_pop{cross_i, 1} =singal_now_pop;
cross_out_pop{cross_i+1, 1} = singal_next_pop;
end
if parity == 1
cross_out_pop{cross_px, 1} = cross_in_pop{cross_px, 1};
end
end
new_pop2 = cross_out_pop;
%@@@@@@@@@@ 变异操作
% new_pop2 = mutation(new_pop2, permutate, G, x);
mutate_in_pop = new_pop2;
mutate_out_pop = cell(length(new_pop1),1);
[mutate_px, ~] = size(mutate_in_pop);
for mutate_i = 1:mutate_px
% 初始化最大迭代次数
mutate_max = 0;
mutate_single_new_pop = mutate_in_pop{mutate_i, 1};
[~, mutate_m] = size(mutate_single_new_pop);
% single_new_pop_slice初始化
mutate_single_new_pop_slice = [];
if(rand < permutate) % rand随机一个0-1的四位小数
while isempty(mutate_single_new_pop_slice)
% 生成2-(m-1)的两个随机数,并排序
mutate_mpoint = sort(round(rand(1,2)*(mutate_m-3)) + [2 2]);
mutate_single_new_pop_slice = [mutate_single_new_pop(mutate_mpoint(1, 1)-1) mutate_single_new_pop(mutate_mpoint(1, 2)+1)];
%@@@@@@@@@@ 将上述必经节点联结成无间断路径
% mutate_single_new_pop_slice = generate_continuous_path(mutate_single_new_pop_slice, G, x);
% mutate_generate_in_pop = mutate_single_new_pop_slice;
mutate_generate_out_pop = mutate_single_new_pop_slice;
mutate_generate_i = 1;
[~, mutate_single_path_num] = size(mutate_generate_out_pop);
while mutate_generate_i ~= mutate_single_path_num
mutate_x_now = mod(mutate_generate_out_pop(1, mutate_generate_i), x) + 1; % 当前点所在列
mutate_y_now = fix(mutate_generate_out_pop(1, mutate_generate_i) / x) + 1; % 当前点所在行
mutate_x_next = mod(mutate_generate_out_pop(1, mutate_generate_i + 1), x) + 1; % 下一个点所在列
mutate_y_next = fix(mutate_generate_out_pop(1, mutate_generate_i + 1) / x) + 1; % 下一个点所在行
mutate_max_iteration = 0; % 初始化平滑路径最大迭代次数
while max(abs(mutate_x_next - mutate_x_now), abs(mutate_y_next - mutate_y_now)) ~= 1 % 判断点generate_i和generate_i+1是否连续(挨在一起),若否就插入中间点
mutate_x_insert = floor((mutate_x_next + mutate_x_now) / 2);
mutate_y_insert = floor((mutate_y_next + mutate_y_now) / 2);
if G(mutate_y_insert, mutate_x_insert) == 0 % 当插入栅格为自由栅格(不在障碍物上)时
mutate_num_insert = (mutate_x_insert - 1) + (mutate_y_insert - 1) * x; % 将栅格位置转化为序号
mutate_generate_out_pop = [mutate_generate_out_pop(1, 1:mutate_generate_i), mutate_num_insert, mutate_generate_out_pop(1, mutate_generate_i+1:end)]; % 将栅格序号插入single数组里
else % 插入栅格为障碍物栅格(在障碍物上)时
% 往左走
if G(mutate_y_insert, mutate_x_insert - 1) == 0 && ((mutate_x_insert - 2) + (mutate_y_insert - 1) * x ~= mutate_generate_out_pop(1, mutate_generate_i)) && ((mutate_x_insert - 2) + (mutate_y_insert - 1) * x ~= mutate_generate_out_pop(1, mutate_generate_i+1))
mutate_x_insert = mutate_x_insert - 1;
mutate_num_insert = (mutate_x_insert - 1) + (mutate_y_insert - 1) * x; % 将栅格位置转化为序号
mutate_generate_out_pop = [mutate_generate_out_pop(1, 1:mutate_generate_i), mutate_num_insert, mutate_generate_out_pop(1, mutate_generate_i+1:end)]; % 将栅格序号插入single数组里
% 往右走
elseif G(mutate_y_insert, mutate_x_insert + 1) == 0 && (mutate_x_insert + (mutate_y_insert - 1) * x ~= mutate_generate_out_pop(1, mutate_generate_i)) && (mutate_x_insert + (mutate_y_insert - 1) * x ~= mutate_generate_out_pop(1, mutate_generate_i+1))
mutate_x_insert = mutate_x_insert + 1;
mutate_num_insert = (mutate_x_insert - 1) + (mutate_y_insert - 1) * x; % 将栅格位置转化为序号
mutate_generate_out_pop = [mutate_generate_out_pop(1, 1:mutate_generate_i), mutate_num_insert, mutate_generate_out_pop(1, mutate_generate_i+1:end)]; % 将栅格序号插入single数组里
% 向上走
elseif G(mutate_y_insert + 1, mutate_x_insert) == 0 && ((mutate_x_insert - 1) + mutate_y_insert * x ~= mutate_single_new_pop(1, mutate_generate_i)) && ((mutate_x_insert - 1) + mutate_y_insert * x ~= mutate_generate_out_pop(1, mutate_generate_i+1))
mutate_y_insert = mutate_y_insert + 1;
mutate_num_insert = (mutate_x_insert - 1) + (mutate_y_insert - 1) * x; % 将栅格位置转化为序号
mutate_generate_out_pop = [mutate_generate_out_pop(1, 1:mutate_generate_i), mutate_num_insert, mutate_generate_out_pop(1, mutate_generate_i+1:end)]; % 将栅格序号插入single数组里
% 向下走
elseif G(mutate_y_insert - 1, mutate_x_insert) == 0 && ((mutate_x_insert - 1) + (mutate_y_insert - 2) * x ~= mutate_generate_out_pop(1, mutate_generate_i)) && ((mutate_x_insert - 1) + (mutate_y_insert-2) * x ~= mutate_generate_out_pop(1, mutate_generate_i+1))
mutate_y_insert = mutate_y_insert - 1;
mutate_num_insert = (mutate_x_insert - 1) + (mutate_y_insert - 1) * x; % 将栅格位置转化为序号
mutate_generate_out_pop = [mutate_generate_out_pop(1, 1:mutate_generate_i), mutate_num_insert, mutate_generate_out_pop(1, mutate_generate_i+1:end)]; % 将栅格序号插入single数组里
% 其他情况舍去此路径
else
mutate_generate_out_pop = [];
break
end
end
mutate_x_next = mutate_x_insert;
mutate_y_next = mutate_y_insert;
mutate_max_iteration = mutate_max_iteration + 1;
if mutate_max_iteration > 20000 % 最多执行20000次,是为平滑路径最大迭代次数
mutate_generate_out_pop = [];
break
end
end
if isempty(mutate_generate_out_pop)
break
end
[~, mutate_single_path_num] = size(mutate_generate_out_pop);
mutate_generate_i = mutate_generate_i + 1;
end
mutate_single_new_pop_slice = mutate_generate_out_pop;
% @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
mutate_max = mutate_max + 1;
if mutate_max >= 100000
break
end
end
if mutate_max >= 100000
mutate_out_pop{mutate_i, 1} = mutate_in_pop{mutate_i, 1};
else
mutate_out_pop{mutate_i, 1} = [mutate_single_new_pop(1, 1:mutate_mpoint(1, 1)-1), mutate_single_new_pop_slice(2:end-1), mutate_single_new_pop(1, mutate_mpoint(1, 2)+1:mutate_m)];
end
% single_new_pop_slice再次初始化
mutate_single_new_pop_slice = [];
else
mutate_out_pop{mutate_i, 1} = mutate_in_pop{mutate_i, 1};
end
end
new_pop2 = mutate_out_pop;
% 更新种群
new_pop1 = new_pop2;
% 计算适应度值
%@@@@@@@@@@ 计算路径长度
% path_value = cal_path_value(new_pop1, x);
path2_value_in_pop = new_pop1;
[value2_n, ~] = size(path2_value_in_pop);
path2_value_out_pop = zeros(1,value2_n);
for value2_i = 1 : value2_n
path2_value_single_pop = path2_value_in_pop{value2_i, 1};
[~, value2_m] = size(path2_value_single_pop);
for value2_j = 1 : value2_m - 1
% 点i所在列(从左到右编号1.2.3...)
value2_x_now = mod(path2_value_single_pop(1, value2_j), x) + 1;
% 点i所在行(从上到下编号行1.2.3...)
value2_y_now = fix(path2_value_single_pop(1, value2_j) / x) + 1;
% 点i+1所在列、行
value_x_next = mod(path2_value_single_pop(1, value2_j + 1), x) + 1;
value_y_next = fix(path2_value_single_pop(1, value2_j + 1) / x) + 1;
if abs(value2_x_now - value_x_next) + abs(value2_y_now - value_y_next) == 1
path2_value_out_pop(1, value2_i) = path2_value_out_pop(1, value2_i) + 1;
else
path2_value_out_pop(1, value2_i) = path2_value_out_pop(1, value2_i) + sqrt(2);
end
end
end
path_value = path2_value_out_pop;
%@@@@@@@@@@ 计算路径平滑度
% path_smooth = cal_path_smooth(new_pop1, x);
path2_smooth_in_pop = new_pop1;
[smooth2_n, ~] = size(path2_smooth_in_pop);
path2_smooth_out_pop = zeros(1,smooth2_n);
for smooth2_i = 1 : smooth2_n
path2_smooth_single_pop = path2_smooth_in_pop{smooth2_i, 1};
[~, smooth2_m] = size(path2_smooth_single_pop);
for smooth2_j = 1 : smooth2_m - 2
% 点i所在列(从左到右编号1.2.3...)
smooth2_x_now = mod(path2_smooth_single_pop(1, smooth2_j), x) + 1;
% 点i所在行(从上到下编号行1.2.3...)
smooth2_y_now = fix(path2_smooth_single_pop(1, smooth2_j) / x) + 1;
% 点i+1所在列、行
% smooth2_x_next1 = mod(path2_smooth_single_pop(1, smooth2_j + 1), x) + 1;
% smooth2_y_next1 = fix(path2_smooth_single_pop(1, smooth2_j + 1) / x) + 1;
% 点i+2所在列、行
smooth2_x_next2 = mod(path2_smooth_single_pop(1, smooth2_j + 2), x) + 1;
smooth2_y_next2 = fix(path2_smooth_single_pop(1, smooth2_j + 2) / x) + 1;
%path_smooth(1, i) = path_smooth(1, i) + abs(atan(abs(x_now - x_next1)/abs(y_now - y_next1))-atan(abs(x_next2 - x_next1)/abs(y_next2 - y_next1)));
%a2 = (x_now - x_next1)^2 + (y_now - y_next1)^2;
%b2 = (x_next2 - x_next1)^2 + (y_next2 - y_next1)^2;
c2 = (smooth2_x_now - smooth2_x_next2)^2 + (smooth2_y_now - smooth2_y_next2)^2;
%angle = (a2 + c2 - b2) / (2 * sqrt(a2) * sqrt(c2));
if c2 < 8 && c2 > 4
path2_smooth_out_pop(1, smooth2_i) = path2_smooth_out_pop(1, smooth2_i) + 5;
elseif c2 <= 4 && c2 > 1
path2_smooth_out_pop(1, smooth2_i) = path2_smooth_out_pop(1, smooth2_i) + 30;
elseif c2 <= 1
path2_smooth_out_pop(1, smooth2_i) = path2_smooth_out_pop(1, smooth2_i) + 5000;
end
end
end
path_smooth = path2_smooth_out_pop;
fit_value = perlenth .* path_value .^ -1 + persmooth .* path_smooth .^ -1;
mean_path_value(1, global2_i) = mean(path_value);
[~, global_m] = max(fit_value);
min_path_value(1, global2_i) = path_value(1, global_m);
end
% 画每次迭代平均路径长度和最优路径长度图
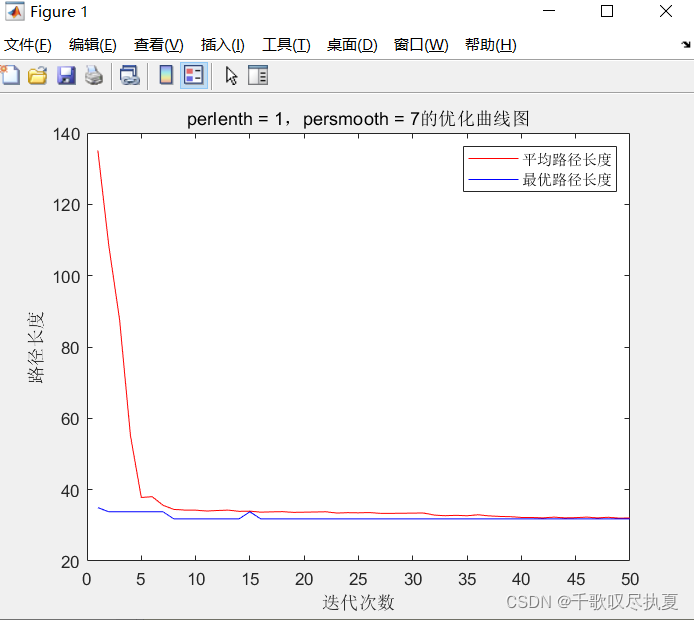
figure(1)
plot(1:max_gen, mean_path_value, 'r')
hold on;
title(['perlenth = ', num2str(perlenth)', ',persmooth = ',num2str(persmooth)','的优化曲线图']);
xlabel('迭代次数');
ylabel('路径长度');
plot(1:max_gen, min_path_value, 'b')
legend('平均路径长度', '最优路径长度');
min_path_value(1, end)
% 在地图上画路径
[~, min_index] = max(fit_value);
min_path = new_pop1{min_index, 1};
figure(2)
hold on;
title(['perlenth = ', num2str(perlenth)', ',persmooth = ',num2str(persmooth)','遗传算法机器人运动轨迹']);
xlabel('坐标x');
ylabel('坐标y');
%@@@@@@@@@@ DrawMap(G);
draw_b = G;
draw_b(end+1,end+1) = 0;
colormap([1 1 1;0 0 0]); % 创建颜色
pcolor(0.5:size(G,2) + 0.5, 0.5:size(G,1) + 0.5, draw_b); % 赋予栅格颜色
set(gca, 'XTick', 1:size(G,1), 'YTick', 1:size(G,2)); % 设置坐标
axis image xy; % 沿每个坐标轴使用相同的数据单位,保持一致
[~, min_path_num] = size(min_path);
for draw_i = 1:min_path_num
% 路径点所在列(从左到右编号1.2.3...)
x_min_path(1, draw_i) = mod(min_path(1, draw_i), x) + 1;
% 路径点所在行(从上到下编号行1.2.3...)
y_min_path(1, draw_i) = fix(min_path(1, draw_i) / x) + 1;
end
hold on;
plot(x_min_path, y_min_path, 'r')
不眠者科技:一个大学生竞赛平台。欢迎关注一起学习,关注后,可添加千歌微信,邀请你进大学生竞赛交流群(人数超200,只能邀请,没办法扫码,所以这里就没放群码了)
























 5776
5776











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










