
rtemis 是一个集机器学习与可视化于一体的 R 包,用于各种高级机器学习研究和应用。整体而言,该软件有三个目标:
-
「应用数据科学」:使高级数据分析高效且易于使用
-
「机器学习研究」:提供一个平台以开发和测试新颖的机器学习算法
-
「教育」:通过提供简明的案例、代码和可视化,使机器学习概念易于理解
比较有特点的是,rtemis 为数据处理、监督学习和聚类提供了大量算法的通用函数接口。小编在官网中看到的包装功能确实也多:
-
预处理
-
保持完整样本:可以选择仅保留没有缺失数据的样本。
-
移除常量特征:删除所有值都相同的列。
-
移除重复样本:删除重复的行。
-
根据缺失数据比例移除样本或特征:根据缺失数据的阈值删除样本或特征。
-
数据类型转换:将整数、逻辑值和字符变量转换为因子、数字或其他类型。
-
数值变量的分箱:将数值变量根据区间或分位数进行分箱处理。
-
处理缺失值:生成指示缺失数据的新布尔列,并选择多种方法进行缺失值插补。
-
数据缩放和中心化:对列进行标准化处理。
-
独热编码:将因子变量进行独热编码。
-
-
重采样
-
bootstrap:标准自助法,即带放回的随机抽样。
-
strat.sub:分层样本抽样。
-
strat.boot:先进行分层子样本抽样,然后随机复制一些训练样本以达到原始长度或指定长度。
-
kfold:k折交叉验证。
-
loocv:留一交叉验证。
-
-
无监督学习
-
聚类
-
分解 / 降维
-
-
监督学习
-
回归与分类
-
自动调参与测试
-
实验记录
-
集成法
-
提升法
-
RuleFit 算法
-
类别不平衡数据的处理
-
集成模型
-
叠加树模型
-
线性叠加树模型
-
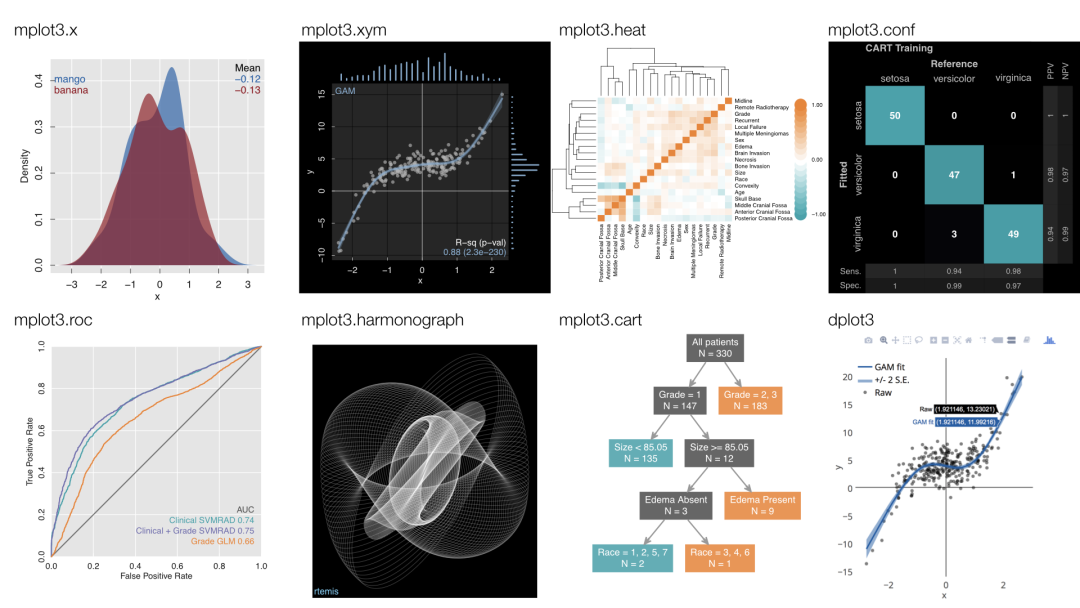
在本文中,仅仅展示如何使用 rtemis 快速进行分类与回归,更多个性化的内容大家可以参照下方的「官方文档」:
-
https://rtemis.lambdamd.org/
0. R包下载
用户可以通过以下代码安装或者引用:
# 从GitHub上安装该包
remotes::install_github("egenn/rtemis")
# 其它潜在的依赖包
install.packages("mlbench")
install.packages("pROC")
install.packages("PRROC")
install.packages("progressr")
install.packages("future.apply")
1. 回归模型
① 生成用于回归的模拟数据框dat:
x <- rnormmat(500, 5, seed = 2019)
y <- x %*% rnorm(5) + rnorm(500)
dat <- data.frame(x, y)
# check 函数用于检查数据集的整体概况
check_data(dat)
# dat: A data.table with 500 rows and 6 columns
# Data types
# * 6 numeric features
# * 0 integer features
# * 0 factors
# * 0 character features
# * 0 date features
# Issues
# * 0 constant features
# * 0 duplicate cases
# * 0 missing values
# Recommendations
# * Everything looks good
# 最后简单看一下dat
head(dat)
# X1 X2 X3 X4 X5 y
#1 0.7385227 -0.5201603 1.63030574 1.9567386 -0.7911291 3.9721257
#2 -0.5147605 0.5388431 0.47104282 0.8373285 0.8610578 -1.7725552
#3 -1.6401813 0.2251481 -0.73062473 -0.6192940 1.1604909 -3.3698612
#4 0.9160368 -1.5559318 -0.05606844 0.4602711 -0.9290626 5.1083103
#5 -1.2674820 -0.2355507 0.71840950 -0.9094905 -1.1453902 -2.8096872
#6 0.7382478 1.1090225 0.80076099 1.1155501 1.5148726 -0.3089569
dat的行代表样本,列X1-X5分别代表不同的特征变量,列y代表用于回归的目标变量(因变量)。同样的,对于自己的数据也是按照类似的格式准备。
② 重新采样,生成训练集与测试集列表res:
res <- resample(dat,
resampler = "strat.sub", # 选用分层抽样。
stratify.var = y, # 用于分层的指定变量
strat.n.bins = 4, # 将分层变量划分为3个区间,确保每个区间的数据在训练集和测试集中都能存在,使得测试集的结果更为可信
train.p = 0.75, # 每层中随机选取75%的样本作为新的数据集
n.resamples = 10 # 需要生成的重采样数据集数量
)
这里使用的是默认参数resampler = "strat.sub"进行分层抽样,其原理根据指定的分层变量(stratify.var参数,这里是y)将数据集分成多个组(层),在每个层内按照指定的比例(train.p=0.75)随机抽取样本,产生新的队列。n.resamples设置为10,意味着将分别抽样10次,总共生成10个新的队列,并以列表res返回抽样对列的行索引。
# 简单看一下res,每个Subsample_*对应不同的索引,可以用于提取指定的抽样数据集
str(res)
#List of 10
# $ Subsample_1 : int [1:374] 1 4 6 8 9 12 14 17 18 19 ...
# $ Subsample_2 : int [1:374] 2 3 4 5 6 8 10 11 14 15 ...
# $ Subsample_3 : int [1:374] 1 2 3 4 6 8 9 10 11 13 ...
# $ Subsample_4 : int [1:374] 1 3 4 5 6 7 8 12 14 15 ...
# $ Subsample_5 : int [1:374] 2 4 5 6 8 10 12 14 15 16 ...
# $ Subsample_6 : int [1:374] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 ...
# $ Subsample_7 : int [1:374] 3 4 5 6 7 8 10 11 12 14 ...
# $ Subsample_8 : int [1:374] 1 2 3 5 6 7 8 10 11 13 ...
# $ Subsample_9 : int [1:374] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 ...
# $ Subsample_10: int [1:374] 1 2 4 5 6 7 8 10 11 12 ...
# - attr(*, "class")= chr [1:2] "resample" "list"
# - attr(*, "N")= int 10
# - attr(*, "resampler")= chr "strat.sub"
# - attr(*, "train.p")= num 0.75
# - attr(*, "strat.n.bins")= num 4
③ 指定训练集与测试集并构建模型
# 训练集为分层采样后的第一个数据集
dat.train <- dat[res$Subsample_1, ]
# 第一个数据集分层采样剩下的数据集作为测试集
dat.test <- dat[-res$Subsample_1, ]
# 构建模型
mod <- s_GLM(dat.train, dat.test)
mod$describe()
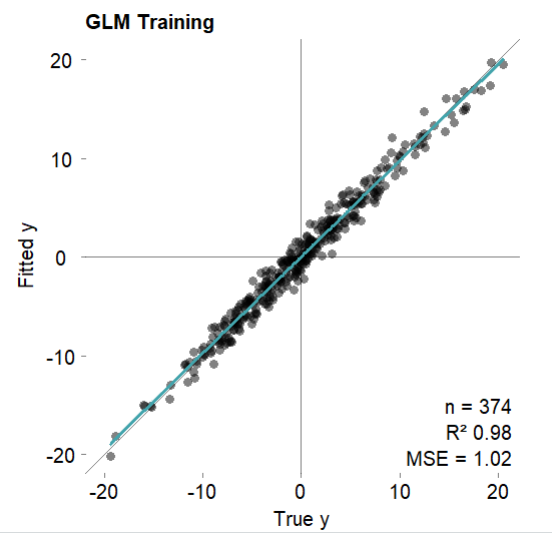
#Generalized Linear Model was used for regression.
#R-squared was 0.98 (training).
# 简单看一下常见的几个回归指标
mod$error.train # 训练集
#MSE = 1.02 (97.81%)
#RMSE = 1.01 (85.18%)
#MAE = 0.81 (84.62%)
#r = 0.99 (p = 1.3e-310)
#R sq = 0.98
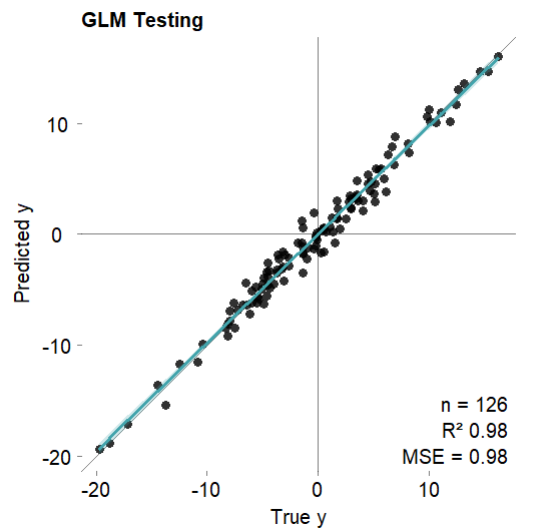
mod$error.test # 测试集
#MSE = 0.98 (97.85%)
#RMSE = 0.99 (85.35%)
#MAE = 0.76 (85.57%)
#r = 0.99 (p = 2.7e-105)
#R sq = 0.98
# 测试集上的预测结果,训练集的预测结果可以通过mod$fitted打印
mod$predicted
# [1] -6.9228634 13.5473120 -4.4142316 -6.4150050 -3.1899404 5.8635544 10.9276092 -3.3697528 7.3197323 4.5917325 3.8279902
# [12] -2.5436844 -8.4399966 -3.2597535 3.0558347 10.1805533 -4.5057564 -0.1087756 -0.7984958 -8.4851937 -4.8099938 -0.7611819
# [23] -0.3023645 -1.1838060 6.2697071 2.9259362 2.9894219 3.5715647 3.2065868 2.3246177 -1.1029005 -3.1490491 -7.2180310
# [34] 1.3552666 8.1584272 -2.2085630 -1.5803727 -0.7588147 1.4364268 0.6639963 5.3642140 0.3600681 -4.2238833 -18.8447897
# [45] -6.2053170 -5.6646543 -6.3526682 5.9058403 -2.9385554 -1.8897201 3.3465618 3.1953050 1.9692337 -8.0531435 0.4722245
# [56] 14.6760641 -1.6578528 11.2129667 -9.2015635 0.6143482 -2.8688158 -1.5580413 0.3452240 -19.3633269 -4.7365043 -1.7222169
# [67] -3.5001696 2.0906088 -5.5367285 16.0566618 -2.2632949 10.1779890 4.8057160 5.0095983 -3.4675440 -7.8418409 1.5149870
# [78] -1.0510093 1.2397077 7.8981605 0.1196208 -13.6210350 -2.1589314 -4.5641406 -4.9111480 -0.5444266 3.8954173 -15.3977663
# [89] -6.3044076 -5.8120357 0.2301799 -1.8128115 4.7353047 -11.5507244 2.2981759 -11.6778343 -4.4418715 4.5915911 13.0456691
#[100] 2.3961443 11.6771535 2.9362587 3.4500863 14.6597287 7.2120194 -6.8395880 -17.1198556 8.7869138 -3.8199982 -5.0879467
#[111] -3.9051859 -9.9320098 0.5141523 -6.2265527 -6.1502030 10.6211752 -1.2735560 3.0118796 3.2969205 -1.8482288 3.6860180
#[122] 0.6108124 10.0208633 5.8474645 1.4720176 0.2498226
需要注意,构建回归模型的函数s_GLM默认使用最后一列作为因变量/目标变量(其实这个函数参数超级多,感兴趣的铁子可以自行学习指定)。同时,s_GLM 既支持 线性回归 和 逻辑回归(单分类任务),也支持 多项逻辑回归(也就是多分类任务)。对于多分类任务,如果 y 有两个以上的类别,s_GLM内部使用nnet::multinom进行多项逻辑回归。
④ 可视化模型结果:
# 可视化训练集拟合结果
mod$plotFitted(theme = 'white')
# 可视化测试集拟合结果
mod$plotPredicted(theme = 'white')
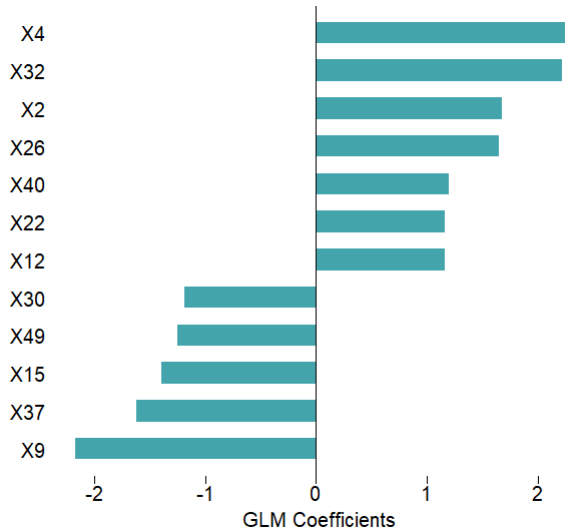
# 可视化特征重要性
mod$plotVarImp(theme = 'white')
需要注意,返回的mod是 R6 类对象。R6 对象包含属性和函数,同时支持 S3 方法,因此用户可以访问所有熟悉的 R 泛型。
2. 分类模型
① 示例数据的准备,这里使用的是mlbench的内置数据集,总共有 60 个特征与最后一列的 Class 的分类属性:
data(Sonar, package = 'mlbench')
str(Sonar)
#'data.frame': 208 obs. of 61 variables:
# $ V1 : num 0.02 0.0453 0.0262 0.01 0.0762 0.0286 0.0317 0.0519 0.0223 0.0164 ...
# $ V2 : num 0.0371 0.0523 0.0582 0.0171 0.0666 0.0453 0.0956 0.0548 0.0375 0.0173 ...
# $ V3 : num 0.0428 0.0843 0.1099 0.0623 0.0481 ...
# $ V4 : num 0.0207 0.0689 0.1083 0.0205 0.0394 ...
# $ V5 : num 0.0954 0.1183 0.0974 0.0205 0.059 ...
# $ V6 : num 0.0986 0.2583 0.228 0.0368 0.0649 ...
# $** .........................................
# $ V60 : num 0.0032 0.0044 0.0078 0.0117 0.0094 0.0062 0.0103 0.0053 0.0022 0.004 ...
# $ Class: Factor w/ 2 levels "M","R": 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 ...
# 检查一下数据
check_data(Sonar)
# Sonar: A data.table with 208 rows and 61 columns
# Data types
# * 60 numeric features
# * 0 integer features
# * 1 factor, which is not ordered
# * 0 character features
# * 0 date features
# Issues
# * 0 constant features
# * 0 duplicate cases
# * 0 missing values
# Recommendations
# * Everything looks good
② 数据重采样分组(与上面回归模型的一致):
res <- resample(Sonar)
sonar.train <- Sonar[res$Subsample_1, ]
sonar.test <- Sonar[-res$Subsample_1, ]
③ 模型的构建,s_Ranger函数是该包提供的用于构建随机森林的分类/回归模型,内部提供了多种参数(包括常见的mtry,用于自动调参的autotune等等)
mod <- s_Ranger(sonar.train, sonar.test)
# 简答看看模型的描述
mod$describe()
#Ranger Random Forest was used for classification.
#Balanced accuracy was 1 (training)and 0.83 (testing).
④ 可视化结果(基本上训练集测试集都有,命名也是具有统一规律,这边就只展示其中一张)
mod$plotPredicted(theme = 'white') # 测试集,分类性能的四格热图
mod$plotFitted(theme = 'white') # 训练集
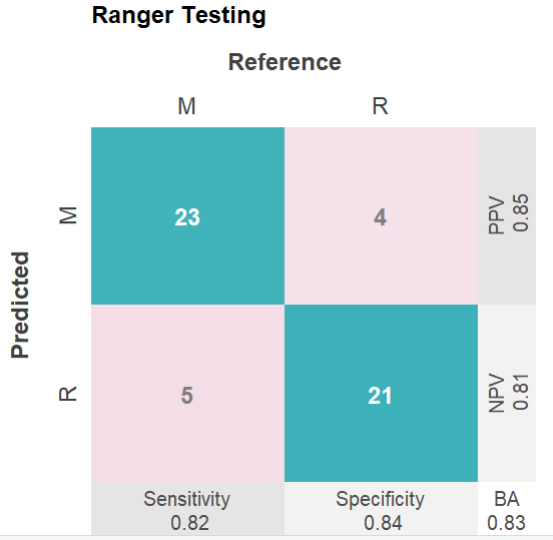
mod$plotROCpredicted(theme = 'white')# 测试集,分类性能的roc曲线
mod$plotROCfitted(theme = 'white') # 训练集
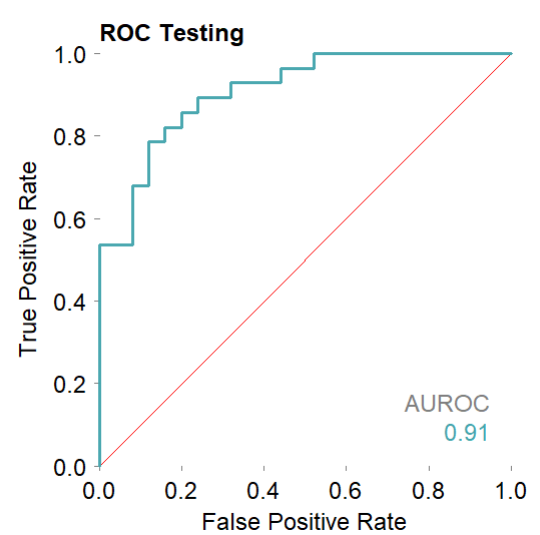
mod$plotPRpredicted(theme = 'white')# 测试集,分类性能的PR曲线
mod$plotPRfitted(theme = 'white') # 训练集

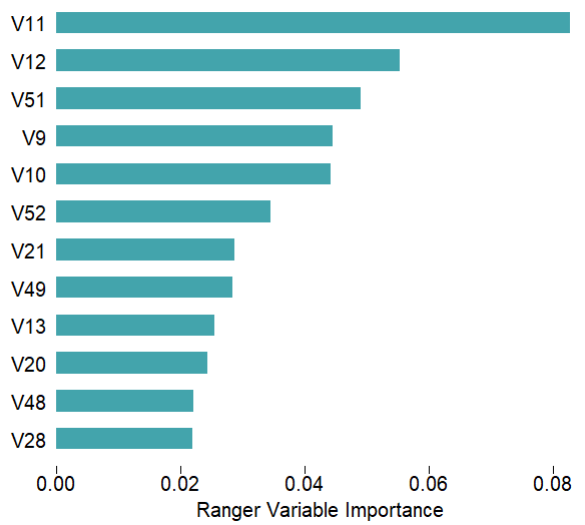
mod$plotVarImp(theme = 'white')# 特征重要性
三. 可视化主题
① 配色系列,rtpalette函数提供了多种可供选择的配色系列:
rtpalette()
#[1] "ucsfCol" "pennCol" "imperialCol" "stanfordCol" "ucdCol"
#[6] "berkeleyCol" "ucscCol" "ucmercedCol" "ucsbCol" "uclaCol"
#[11] "ucrColor" "uciCol" "ucsdCol" "californiaCol" "scrippsCol"
#[16] "caltechCol" "cmuCol" "princetonCol" "columbiaCol" "yaleCol"
#[21] "brownCol" "cornellCol" "hmsCol" "dartmouthCol" "usfCol"
#[26] "uwCol" "jhuCol" "nyuCol" "washuCol" "chicagoCol"
#[31] "pennstateCol" "msuCol" "michiganCol" "iowaCol" "texasCol"
#[36] "techCol" "jeffersonCol" "hawaiiCol" "nihCol" "torontoCol"
#[41] "mcgillCol" "uclCol" "oxfordCol" "nhsCol" "ethCol"
#[46] "rwthCol" "firefoxCol" "mozillaCol" "appleCol" "googleCol"
#[51] "amazonCol" "microsoftCol" "pantoneBalancingAct" "pantoneWellspring" "pantoneAmusements"
#[56] "grays" "rtCol1" "rtCol3"
简单给各位铁子看看:
previewcolor(rtpalette("imperialCol"), "Imperial", bg = "white")

previewcolor(rtpalette("ucsfCol"), "UCSF", bg = "white")
具体使用的时候可以指定参数palette:
mplot3_x(iris, palette = "google", theme = 'white')
② 主题,可选的主题包括以下几种:
-
white
-
whitegrid
-
whiteigrid
-
black
-
blackgrid
-
blackigrid
-
darkgray
-
darkgraygrid
-
darkgrayigrid
-
lightgraygrid
-
mediumgraygrid
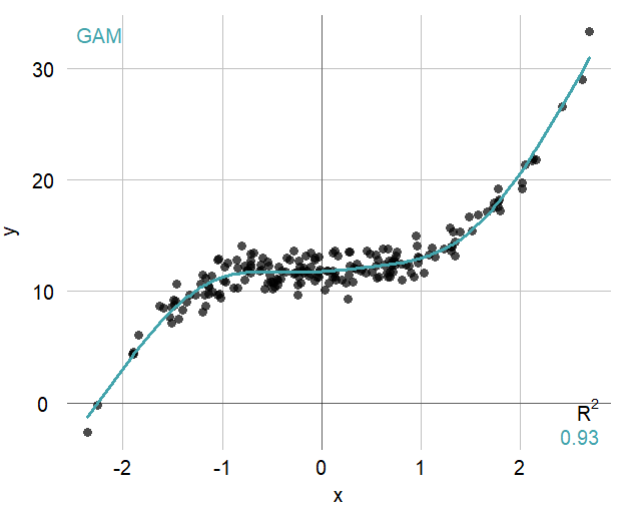
具体使用的时候指定theme参数即可:
set.seed = 2019
x <- rnorm(200)
y <- x^3 + 12 + rnorm(200)
mplot3_xy(x, y, theme = 'whitegrid', fit = 'gam')
传统的机器学习 R 包确实不少
但今天分享的有一些特点
首先是大量可供选择的算法
封装的不错,参数很多
简便易行
其次是提供建模前的预处理方法
最后是兼顾数据可视化
就分享到这





















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








