1. 背景
提高一个系统的performance,有两种办法:
1) 不断提高一个core的performance
手段就是不断提高freq,减小Vt,这样都会在增加power(dynamic,leakage)
2) 增加processor的个数
arm的big-little processor cluster采用的就是第二个办法,通过Power Gating和DVFS也尽量的减小了功耗。但是multiprocessor的另一个问题就是cache coherence的问题。
2. cluster内部
针对cluster内部,arm采用MPCore multi-core coherency technology
1) 实现了一个基于MESI的cache coherency protocol,并且,增加了一些feature,
direct cache-to-cache copy of clean data,direct cache-to-cache move of dirty data in cluster。不需要写回main memory。
2) 还包括一个模块SCU(Snoop Control Unit),保存所有的L1 data cache tag,作为一个directory,来减少broad-cast的总线带宽浪费,
3) MPCore technology,支持一个可选的ACP(Accelerator Coherency port),accelerator可以读写processor cluster内部的cache,但是processor 不能拿到accelerator的cache,也无法保证和其cache的一致性。
3. cluster之间
多个cluster之间,可以通过AMBA4的ACE protocal(AXI Coherency Extensions)来实现。
1) ACE和ACE-lite,引入了system-level coherency,cache maintenance,DVM(distributed virtual memory),barrier transaction support。
2) ACE本身是支持5状态的MOESI cache coherency model的,master可以支持MESI,MOESI,MEI等,都兼容,
3) ACE需要与指定的system interconnect一起使用,来处理所有shared transaction,interconnect在拿到master发送的transaction时,可能会speculative reads,或者等待snoop resp,interconnect可能包含一个directory,snoop filter,或者broadcast snoop到所有的master,
4) ACE支持的system level coherency,是指所有的master,包括GPU,DMA,dissimilar CPU。
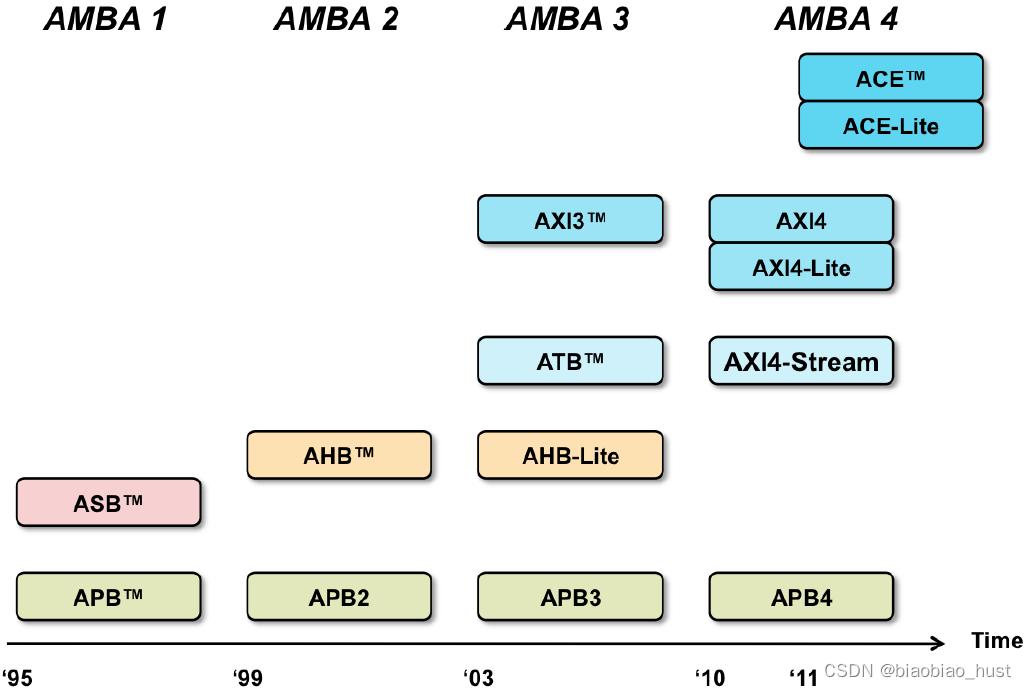
4. AMBA发展路线
1) AXI4支持了long burst,不在支持write interleaving;
2) AXI4-stream,是专为大批量数据传播的应用,是一个point-to-point 协议,没有了address channel,只有data channel;
3) AXI4-Lite,是一个简化版的AXI4,主要用在需要apb的peripheral中,做升级。
4.1 Software-Based Coherency Approach
cache的coherency也可以在software中解决,在之前的single processor,just small L1 cache中;但是,目前的SoC中,都是multiprocessor,并且有L2,L3等cache,还有其他的cache master,GPU等。用软件实现的可能性已经很小,难度太大,性能也很低。
4.2 Hardware-Based Coherency Approaches
1) Snooping cache coherency protocols,所有的master都“listening in”所有的shared-data transactions,
read,addr输入,所有的processor检查自己的cache中,是否有该addr,有的话,直接返回ack,不再访问memory;
write,addr输入,所有的processor检查自己的cache中,是否有该addr,需要invalid掉。
这种方式的coherency tranffic是比较大的,N(N-1),因为需要broadcast到所有的processor中,在processor越来越大时,效率会越来越小。
2) Directory-based cache coherency protocols:
系统中,有一个single directory,保存系统中cache line的list,这样,master发出一个transaction,首先查找该directory,然后directed cache coherency traffic到某些master中,减小coherency traffic。
最好的情况下,traffic是2N,最差的情况下是N*(N-1+1),因为还需要首先检查directory。这种方式,需要一块很大的on-chip RAM,如果放在off-chip,又增加了系统的latency。实际应用中,可以做些优化,比如Snoop based system,可以加些snoop filters,来减小coherency traffic。
4.3 ACE
ACE对于snoop和directory-based的方式,甚至其他的hybrid类型的protocol都是支持的:

在现有的channel中,增加了新的信号:
ARSNOOP和AWSNOOP,表示对shareable transactions的snoop transactions;
ARBAR和AWBAR,用来表示barrier signal;

4.4 ACE-LITE
ACE-Lite,在AXI的基础上增加了新的signals,却没有增加新的channels。
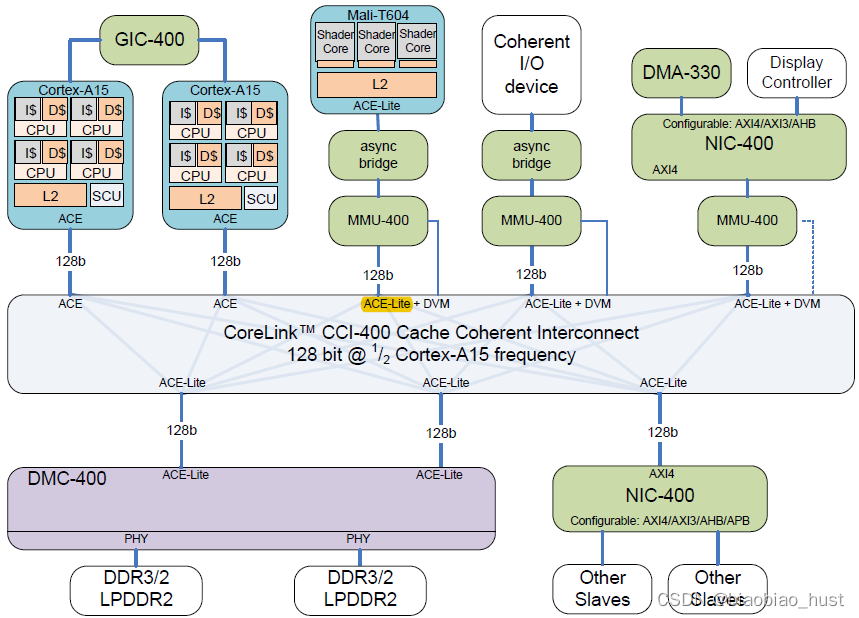
ACE-Lite master主要用来snoop其他的ACE-compliment master,但是themselves并不能被snooped。以CCI400的interconnect,为例,支持两个clusters CPU,三个ACE-lite I/O coherent master:
ACE引入了很多new transactions,一般可以根据memory attribute,进行分组。
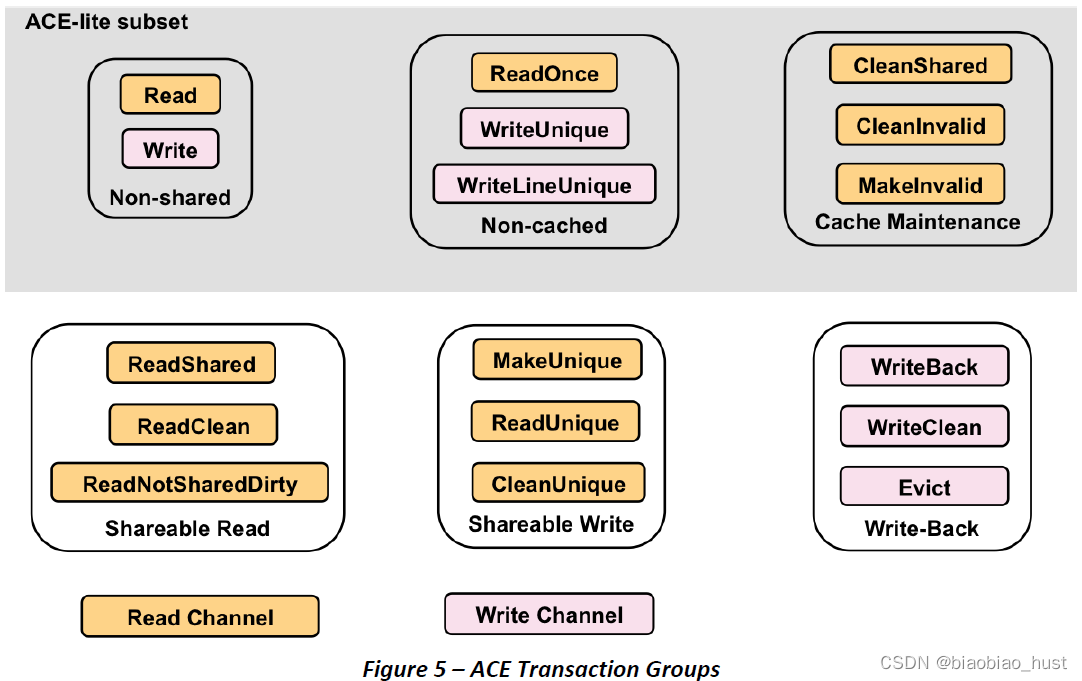
ACE-Lite I/O Coherency,ACE-Lite Master可以实现,Non-shared,Non-cached,Cache Maintenance transaction,三种group的transaction,实现了uncached masters来snoop ACE coherent master,比如Gigabit Ethernet 直接读写cached data shared with CPU。
DVM(Distributed Virtual Memory),用来保证MMU内部TLB的一致性,支持TLB Invalidation,Brach Predictor,Instruction cache Invalidation。
5. cache coherence基础
cache coherence设计的主要目的是,在multicore的系统中,多个caches的表现与sing-core system相同。
cache coherence的define,可以描述为,多个memory copy,允许single-writer-multiple-reader(SWMR),在某个logic time中,只存在最多一个core写A,或者多个cores read A。
coherence的granularities,一般是按照cache line的大小来定义。必须在写操作之后禁止对同一地址的读操作,直到所有的cache都发反馈信号(ack),表示该cache已经invalid或者update。
在memory system中,cache controller负责issue coherence req和received coherence rsp,
memory controller负责,received coherence req和issue coherence rsp,两者之间通过interconnect来连接。

coherence protocol有两种,snooping和directory,transactions/action不同,但是stable state是相同的。
5.1 stable states
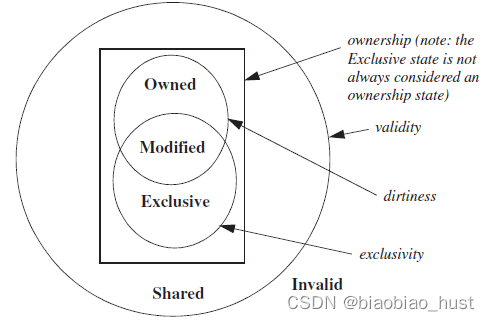
很多的coherence protocol都是MOESI model的子集,
M(Modified),表明一个cache line是valid,exclusive,owned,可能还是dirty的。
S(Shared),表明一个cache line是valid,但是不是exclusive,不是dirty,不是owned的。
I(Invalid),表明一个cache line是invalid,或者说是不可读写的,
MSI是最基本的protocol status,还有两个可扩展的status,O和E,
O(Owned),表明cache line是valid,owned,但是不是exclusive,而且可能是dirty的,在main memory中的data很可能是stale的。
E(Exclusive),表明cache line是valid,exclusive,并且是clean的。
5.2 由cache controller发出的common transaction
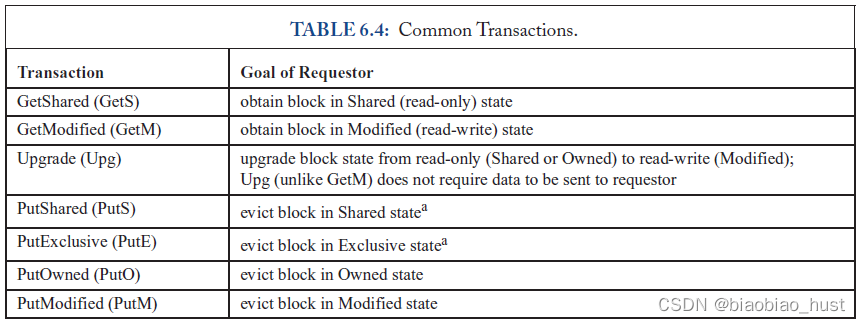
5.3 common core对cache controller的req
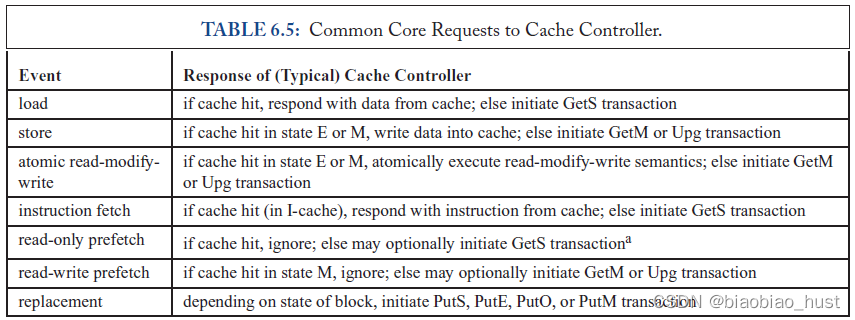
5.4 snooping protocol
snooping protocol,broadcasting a req message到所有的coherence controller,这些req到每个core的order是可以不定的。看具体interconnect的实现。
directory protocol,unicast该req到具体的cache controller或者memory controller。
snooping结构简单,但是不易scale to large numbers of core,
directory,可以scale到large num of core,但是增加了每笔coherence req的lantency。
5.5 write cache line
当一个core write cache line时,该coherence protocol作何动作,可以分为invalidation/update两种,与snooping和directory无关。
invalidation,当core发出write cache line的操作时,其他cache copy都被更新为invalid。
update,当core发出write cache line的操作时,其他cache copy都被update为最新的值。
实际中update用的很少,因为update的操作,相对还是比较占用bus的bandwidth,而且这种方式会将memory consistency model复杂化,因为原子操作中,如果出现多个cache更新该cache中的数据,情况会很复杂。
6. Cache和MMU之间的结构
按照工作原理来分,cache有physical index physical tagged, virtual index virtual tagged, physical index virtual tagged等几种工作方式。
1) physical index physical tagged
优点:cache仅仅针对物理地址进行操作,简单粗暴,而且不会有歧义。
缺陷:在多进程操作系统中,每个进程指令和代码都是以虚拟地址的方式存在,cpu发出的memory access的指令都是以虚拟地址的方式发出,所以对于每一个memory access的操作,都要先等待MMU将虚拟地址翻译为物理地址,这样还是增加了操作的latency。
2) virtual index virtual tagged
优点:是纯粹用虚拟地址来寻址,
缺陷:由于多个virtual address可以对应一个physical address,每一行数据在原有tag的基础上都要将进程标识加上以区分多个进程之间的相同地址,而在处理共享内存时,共享内存在不同的进程中的虚拟地址不相同,如何同步是个问题。结构太复杂。
3) virtual index physical tagged
该方式现在使用的比较多,virtual index的含义是当cpu发出一个地址请求之后,低位地址去和cache中的index匹配(低位一般都是页内偏移地址,virtual address与physical address低位部分相同),physical tagged是指虚拟地址的高位地址去和mmu中的页表匹配以拿到页的物理地址,这样virtual index的匹配操作和smmu的转换操作可以并行工作。
ARM MPCore的cache结构,L1 Cache一般放在processor里边,可以分为L1 data cache,L1 instruction cache。(8KByte----64KByte)
L1 instruction cache,不但能做instuction caching,还可以做Dynamic branch prediction,一些使用PC作为目的寄存器的操作,BXJ指令,Return from Exception的指令,不会做prediction;多是2-way set associative结构,64byte cache line。
L1 data cache,是一块physically indexed physically tagged cache,内部包括一个internal exclusive monitor,用来存放当前有效的exclusive访问的列表,可以直接返回EXOkay,可以产生ACE transaction和CHI transaction,多是4-way set associative结构,64byte cache line。
L2 cache包括一个集成好的SCU(连接到一个cluster内的4个cores),一个L2 Cache,(128KByte------2MB)。SCU中包含L1 Data cache tags来做4个core之间的coherency,L2 cache中不支持snoop hardware操作,来保证cache之间的coherency,可以配置选择ACE或者CHI连接到main memory
Physically index, Physically tagged cache,8ways-----16ways。SCU支持direct cache-to-cache transfer,dirty cache lines to be moved between cores,内建tags filter,来发送指定的coherent requests。







 本文探讨了提高系统性能的两种策略,重点介绍了ARM的MPCore架构,包括其采用的MPCore多核一致性技术、基于MESI的缓存一致性协议、ACE协议在系统级一致性中的作用以及AMBA4的发展路线。同时分析了软件和硬件实现缓存一致性的方式,以及MMU与缓存之间的结构设计。
本文探讨了提高系统性能的两种策略,重点介绍了ARM的MPCore架构,包括其采用的MPCore多核一致性技术、基于MESI的缓存一致性协议、ACE协议在系统级一致性中的作用以及AMBA4的发展路线。同时分析了软件和硬件实现缓存一致性的方式,以及MMU与缓存之间的结构设计。














 248
248











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








