- point-wise MLP,仅仅是对每个点表征,对局部结构信息整合能力太弱 --> PointNet++的改进:sampling和grouping整合局部邻域
- global feature直接由max pooling获得,无论是对分类还是对分割任务,都会造成巨大的信息损失 --> PointNet++的改进:hierarchical feature learning framework,通过多个set abstraction逐级降采样,获得不同规模不同层次的local-global feature
- 分割任务的全局特征global feature是直接复制与local feature拼接,生成discriminative feature能力有限 --> PointNet++的改进:分割任务设计了encoder-decoder结构,先降采样再上采样,使用skip connection将对应层的local-global feature拼接
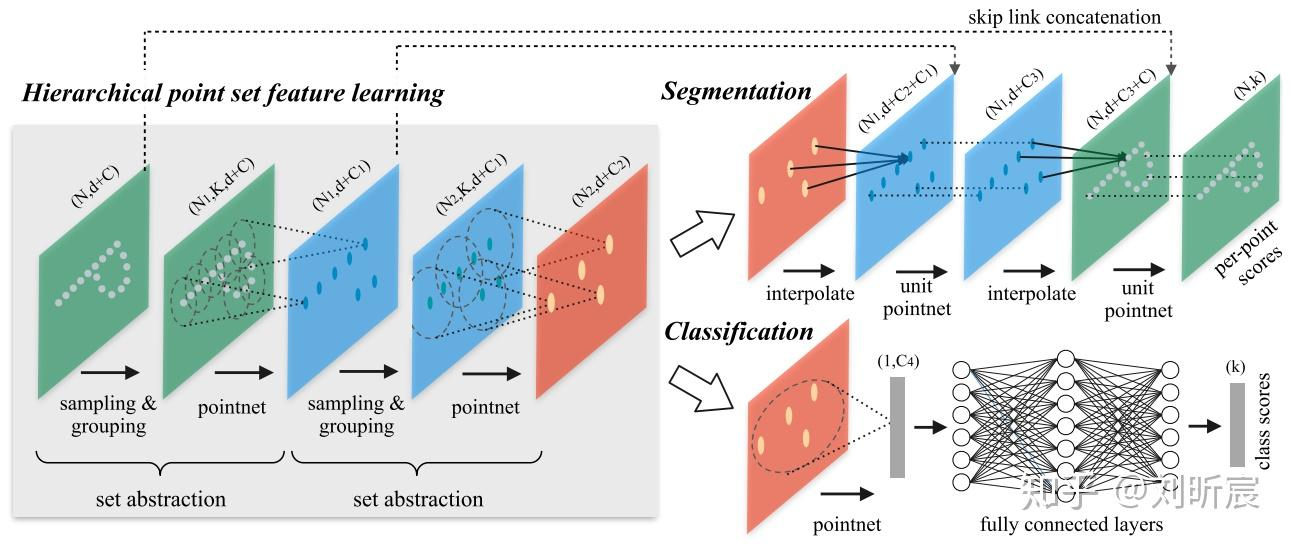
PointNet++的网络大体是encoder-decoder结构
encoder为降采样过程,通过多个set abstraction结构实现多层次的降采样,得到不同规模的point-wise feature,最后一个set abstraction输出可以认为是global feature。其中set abstraction由sampling,grouping,pointnet三个模块构成。
decoder根据分类和分割应用,又有所不同。分类任务decoder比较简单,不介绍了。分割任务decoder为上采样过程,通过反向插值和skip connection实现在上采样的同时,还能够获得local+global的point-wise feature,使得最终的表征能够discriminative
因此在往下看之前,我们最好带着2个问题:
- PointNet++降采样过程是怎么实现的?/PointNet++是如何表征global feature的?(关注set abstraction, sampling layer, grouping layer, pointnet layer)
- PointNet++用于分割任务的上采样过程是怎么实现的?/PointNet++是如何表征用于分割任务的point-wise feature的?(关注反向插值,skip connection)
2.1 encoder
在PointNet的基础上增加了hierarchical feature learning framework的结构。这种多层次的结构由set abstraction层组成。
在每一个层次的set abstraction,点集都会被处理和抽象,而产生一个规模更小的点集,可以理解成是一个降采样表征过程,可参考上图左半部分。
set abstraction由三个部分构成(代码贴在下面):
def pointnet_sa_module(xyz, points, npoint, radius, nsample, mlp, mlp2, group_all, is_training, bn_decay, scope, bn=True, pooling='max', knn=False, use_xyz=True, use_nchw=False):
''' PointNet Set Abstraction (SA) Module
Input:
xyz: (batch_size, ndataset, 3) TF tensor
points: (batch_size, ndataset, channel) TF tensor
npoint: int32 -- #points sampled in farthest point sampling
radius: float32 -- search radius in local region
nsample: int32 -- how many points in each local region
mlp: list of int32 -- output size for MLP on each point
mlp2: list of int32 -- output size for MLP on each region
group_all: bool -- group all points into one PC if set true, OVERRIDE
npoint, radius and nsample settings
use_xyz: bool, if True concat XYZ with local point features, otherwise just use point features
use_nchw: bool, if True, use NCHW data format for conv2d, which is usually faster than NHWC format
Return:
new_xyz: (batch_size, npoint, 3) TF tensor
new_points: (batch_size, npoint, mlp[-1] or mlp2[-1]) TF tensor
idx: (batch_size, npoint, nsample) int32 -- indices for local regions
'''
data_format = 'NCHW' if use_nchw else 'NHWC'
with tf.variable_scope(scope) as sc:
# Sample and Grouping
if group_all:
nsample = xyz.get_shape()[1].value
new_xyz, new_points, idx, grouped_xyz = sample_and_group_all(xyz, points, use_xyz)
else:
new_xyz, new_points, idx, grouped_xyz = sample_and_group(npoint, radius, nsample, xyz, points, knn, use_xyz)
# Point Feature Embedding
if use_nchw: new_points = tf.transpose(new_points, [0,3,1,2])
for i, num_out_channel in enumerate(mlp):
new_points = tf_util.conv2d(new_points, num_out_channel, [1,1],
padding='VALID', stride=[1,1],
bn=bn, is_training=is_training,
scope='conv%d'%(i), bn_decay=bn_decay,





 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 8895
8895

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








