英文是纯手打的!论文原文的summarizing and paraphrasing。可能会出现难以避免的拼写错误和语法错误,若有发现欢迎评论指正!文章偏向于笔记,谨慎食用
目录
2.2.2. Motivations behind employing Transformers in brain science
2.3. Fundamentals of Transformer
2.3.2. Scaled dot-product attention
2.3.5. Transformer architecture
2.4. Transformer in neuroimage analysis
2.4.1. Overview of neuroimage data
2.4.2. Applications of Transformer models
2.5. Transformer in network neuroscience analysis
2.5.1. Overview of network neuroscience
2.5.2. Applications of Transformer models
2.6. Transformer in spatiotemporal sequence analysis
2.6.1. Overview of spatiotemporal sequence data
2.6.2. Applications of Transformer models
2.7.1. Intrinsic interpretability
2.7.2. Post-hoc interpretability
2.8. Discussion and conclusions
2.8.1. Limitations and future research directions
1. 省流版
1.1. 心得
(1)好长的篇幅...
(2)拿这么多篇幅介绍transformer吗...
(3)虽然是介绍了很多东西不错,但是是不是有点太百科了
(4)为什么每一节介绍了那么多变体最后又回归Transformer本身的缺点啊?难道变体没有尝试去解决吗?为什么每一个Limitation都要提到计算成本和计算效率啊不会重复吗
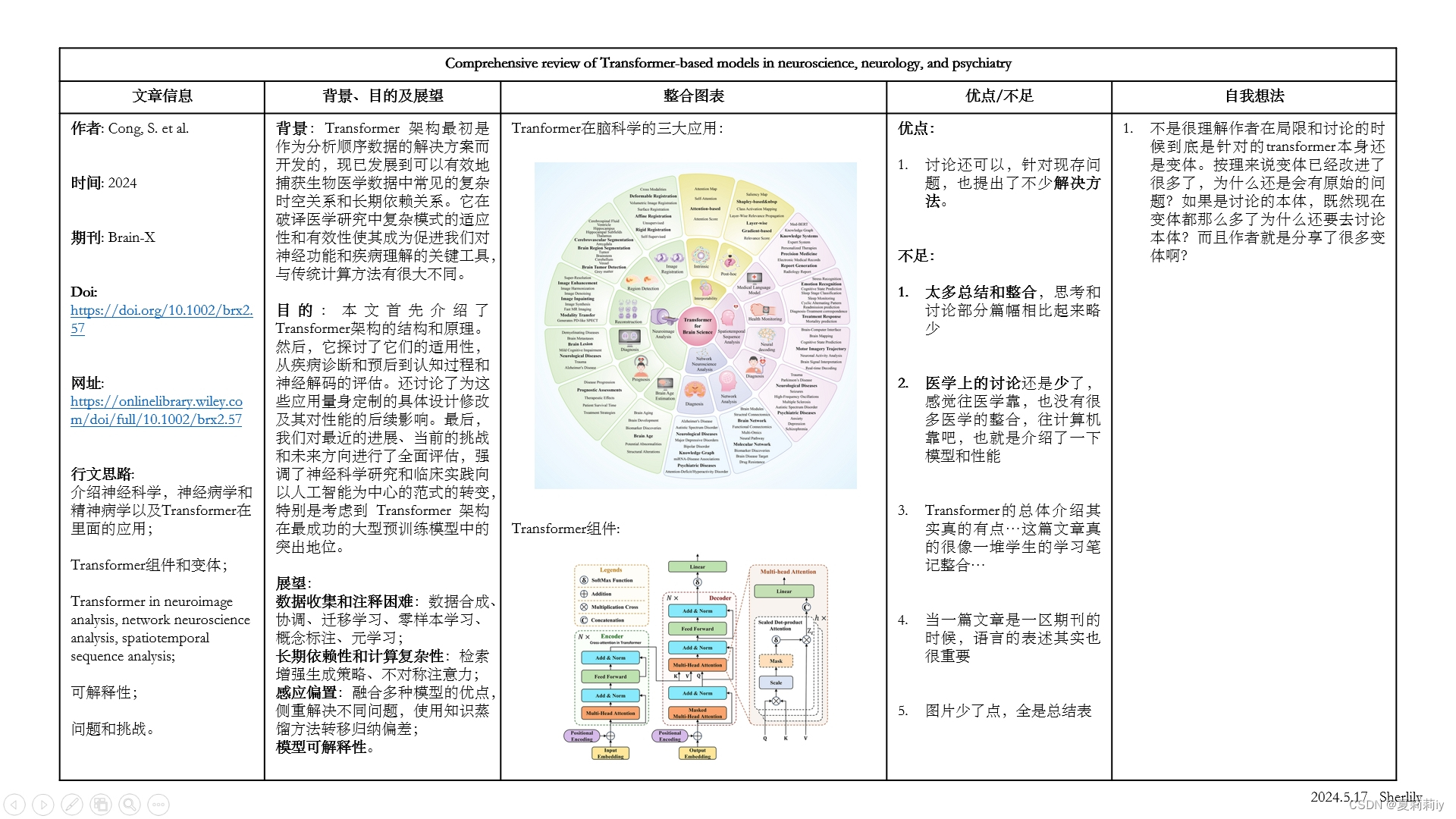
1.2. 论文总结图
2. 论文逐段精读
2.1. Abstract
①This review clarifies "the growing impact of Transformer-based models in the fields of neuroscience, neurology, and psychiatry"
②Transformer was designed for sequential data originally, but can transfer to "capture complex spatiotemporal relationships and long-range dependencies" in biomedical field
③"This review serves as an informative reference for" ...
decipher vt.破译;辨认(难认、难解的东西) v.破译 n.密电(或密信)的译文
2.2. Introduction
2.2.1. Background
①Transformers can be used to analyse brain structure and functional connectivity (FC) with irregular grid and interval
②Used in specific neuroscience, neurology, and psychiatry...
throughput n.吞吐量;(某一时期内的)生产量,接待人数
2.2.2. Motivations behind employing Transformers in brain science
①Transformer is able to caputure long term dependency
②It can be also added in pre-training and fine-tuning
2.2.3. Objective and scope
①They specifically analyse how Transformer used in diffferent type of data
②They provide interpretability of Transformer
③Applicable fields of Transformer (in neuroscience, neurology, and psychiatry):
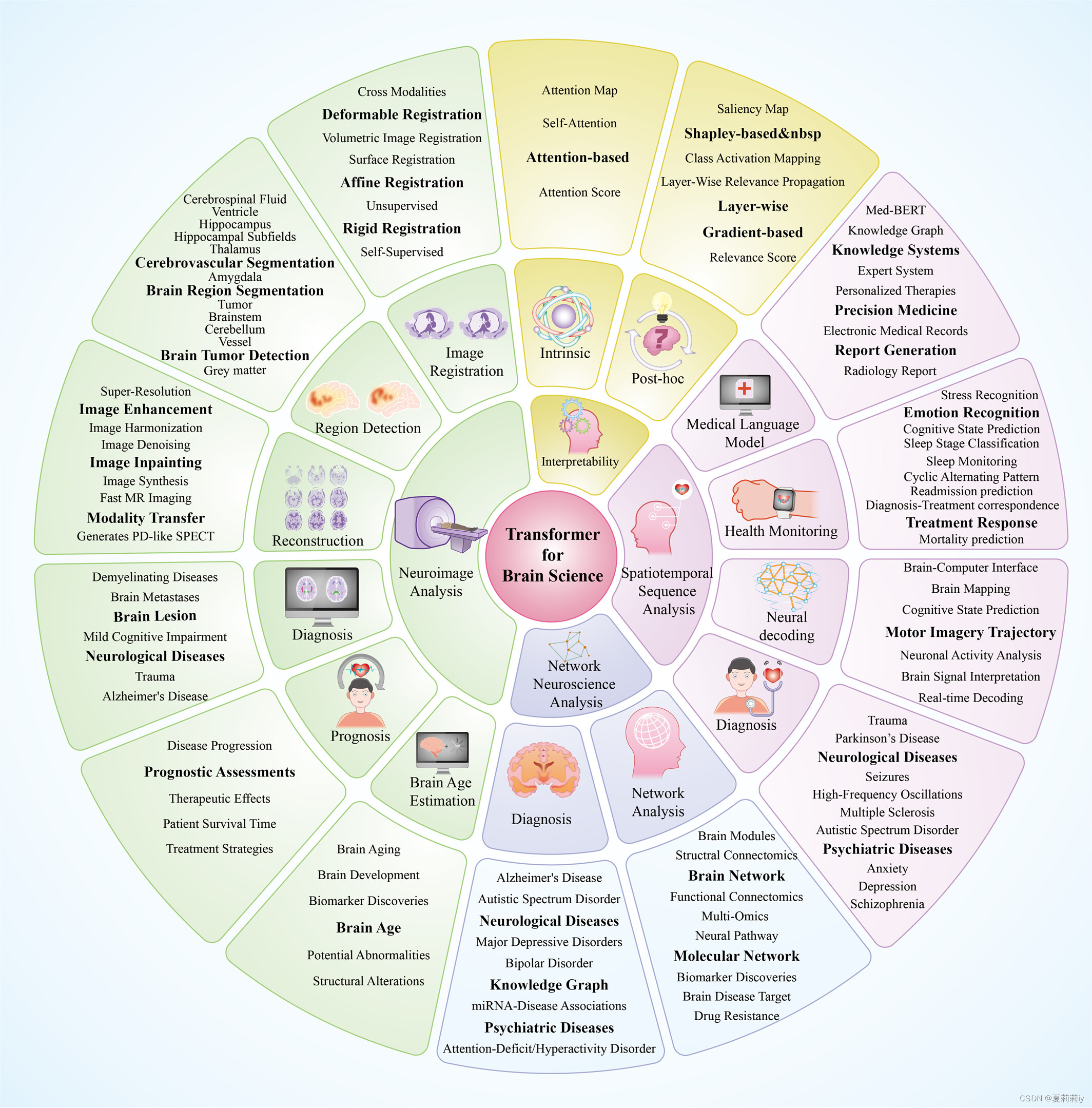
nuance n.细微的差别;(意义、声音、颜色、感情等方面的)细微差别
2.3. Fundamentals of Transformer
2.3.1. Attention mechanisms
①Introducing attention mechanism and Transformer
2.3.2. Scaled dot-product attention
①Scaled dot-product attention (SDA), the part of Transformer:
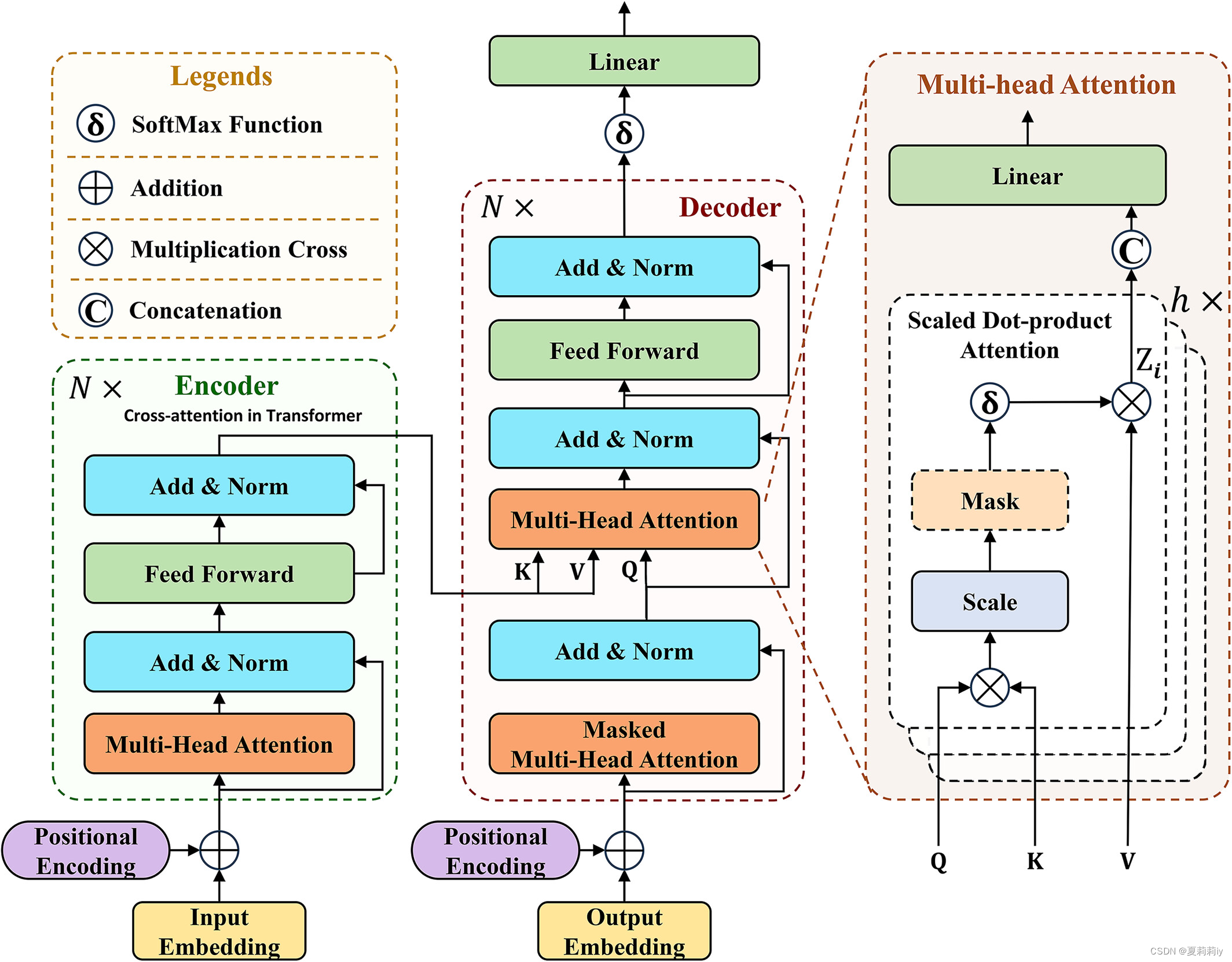
②Introducing their functions
2.3.3. Multi-head attention
①Briefly introducing multi-head attention (MHA)
2.3.4. Cross-attention
①Cross attention is able to capture the cross sequence information
②The second MHA lyaer in denoder block is the cross attention module
2.3.5. Transformer architecture
(1)Encoder
(2)Decoder
(3)Embedding
(4)Positional encoding
①Positional encoding for information in different dimension :
(5)Layer normalization
①Especially for sequences with different lengths, normalization method calculates the mean and variance along with the feature dimension
(6)Masked multi-head attention
①When Transformer predicts, it relies on the previous data but can not see the subsequent data
2.3.6. Transformer variants
①Introducing the variants of Transformer, Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT), Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT), DEtection TRansformer (DETR), Vision Transformer (ViT), Data-efficient image Transformers (DeiT), Swin Transformer, Segment Anything Model (SAM), Graph Transformer Networks (GTNs), Efficient Transformers
2.4. Transformer in neuroimage analysis
2.4.1. Overview of neuroimage data
①Computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), positron emission tomography (PET), and single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) can obtain the neuroimage, which represents the brain structure
2.4.2. Applications of Transformer models
(1)Region detection
①Models used for region detection, such as brain tissues, abnormal anatomical structures, and lesions:
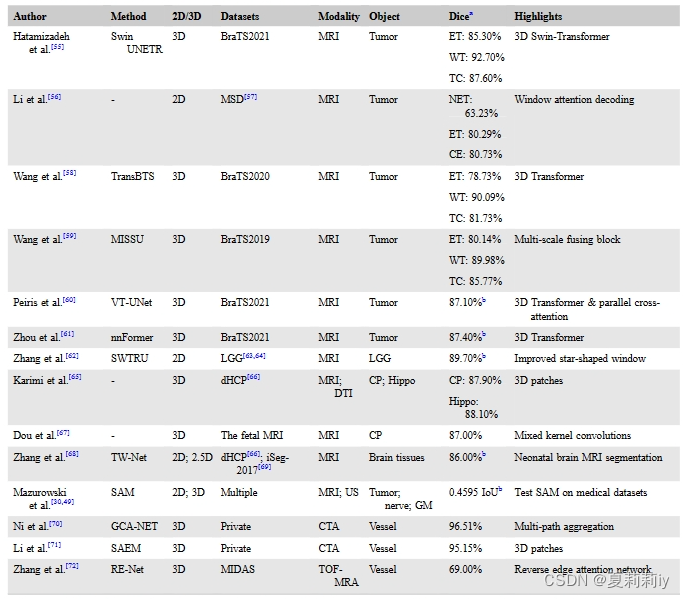
②作者居然找得到2020年全球癌症登记结果,“1930 万例新发癌症病例,其中包括 308,102 例与大脑和神经系统相关的病例”
③Then listing some variants for detecting cancer
④Introducing some models applied in cortical and subcortical region segmentation and intracranial vessel segmentation
neonatal adj.新生儿的 intracranial n. 颅内;颅内段
(2)Image reconstruction
①Transformer based models appied for image reconstruction:

②Introducing Transformer variants used in image denosing and super resolution of image enhancement, image inpainting, modality transfer, and image harmonization
seamlessly adv.无缝的;无缝;无缝地;天衣无缝地
(3)Image registration
①Models used for neuroimage registration:
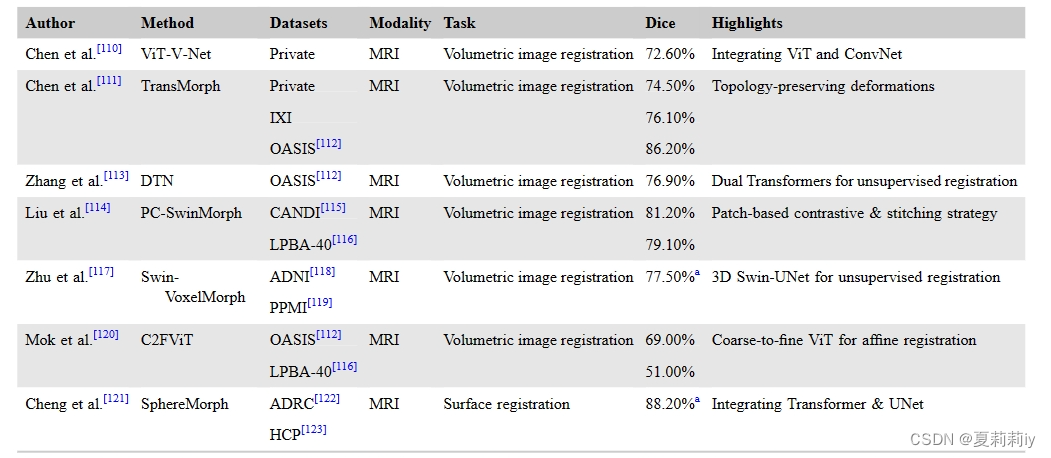
affine adj.亲合的;仿射的;拟似的;远交的 n.姻亲
(4)Diagnosis
①Transformer based model applied in disease diagosis:
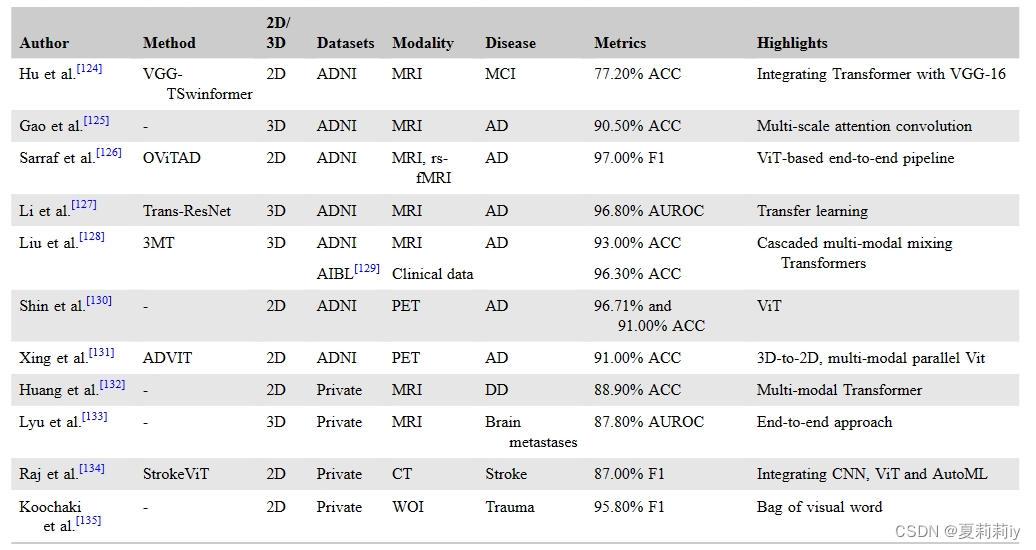
(5)Prognostic assessments
①Some models are used for assess the outcome
(6)Brain age estimation
①....
2.4.3. Current limitations
①⭐Transformers cannot analyse the inherent spatial and temporal biases(这样写也太奇怪了,毕竟作者没定义如何使用transformer,是用在时间上还是空间上还是都用。就片面地说什么偏差啥的也有点太vague了吧。不敢苟同喔,其实我觉得都可以解决的)
②Transformer mostly analyses gloabal information rather than local
③Computing costs
intensified v.(使)加强,增强,加剧 adj.加强的
2.5. Transformer in network neuroscience analysis
2.5.1. Overview of network neuroscience
①They introduced Transformer searching the relationship between neural entities and functional systems
2.5.2. Applications of Transformer models
(1)Diagnosis
①Transformer in brain desease diagnosis(表是倒着的,我就不截图了)
(2)Network analysis
①Introducing models.........
2.5.3. Current limitations
①It is hard to handle multimodal and heterogeneous structure
②Limit interpretability
2.6. Transformer in spatiotemporal sequence analysis
2.6.1. Overview of spatiotemporal sequence data
2.6.2. Applications of Transformer models
(1)Diagnosis
①Transformer in temporal disease diagnosis:
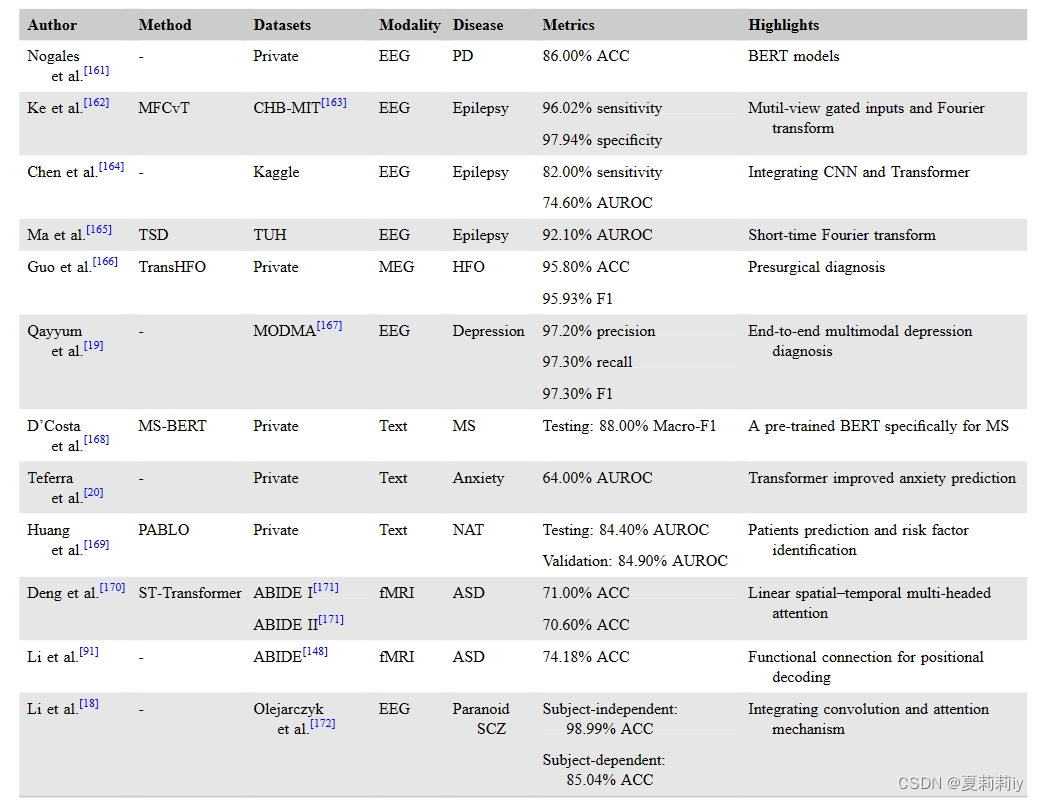
(2)Neural decoding
①Transformer in neural decoding:
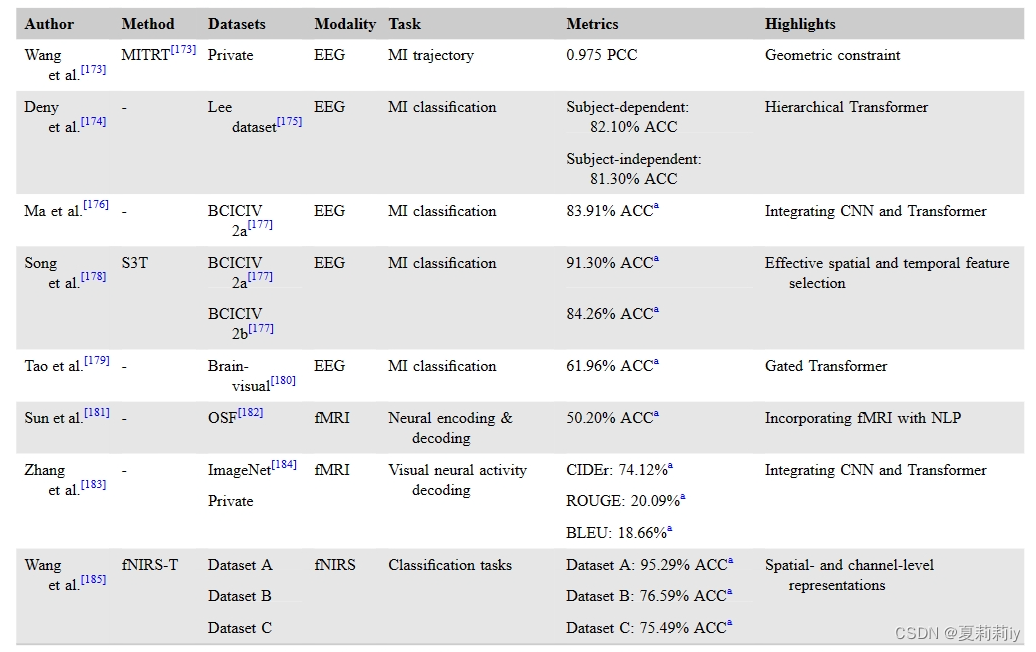
(3)Health monitoring
①Transformer in health monitorning:
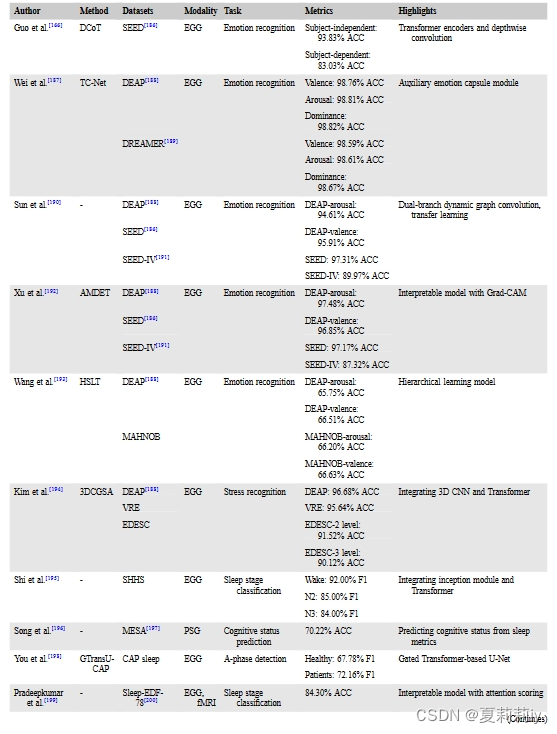
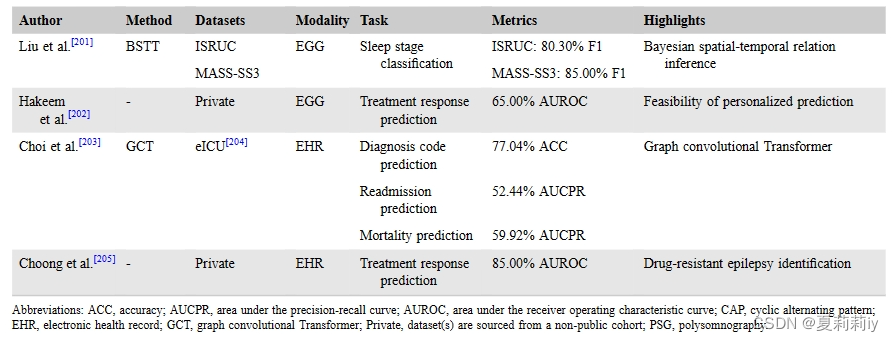
②They further go with emotion recognition, sleep monitoring, and treatment response
apnea n.呼吸暂停;窒息
(4)Medical reports generation and knowledge systems
①Transformer in auto medical report generation:
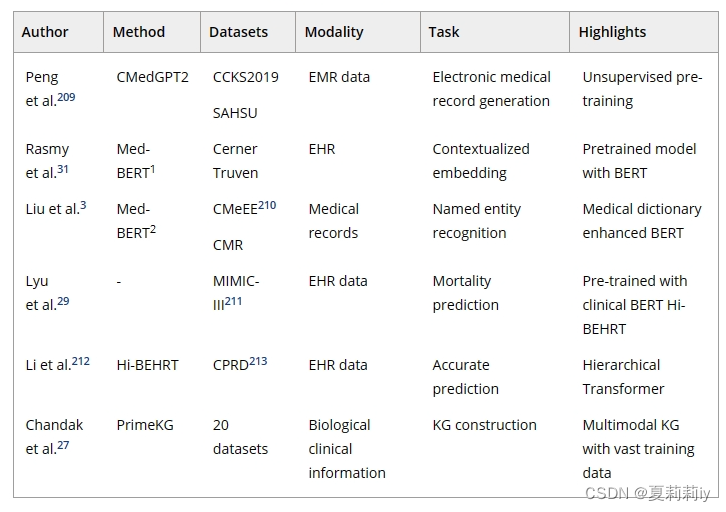
synergy n.协同作用;协同增效作用(人或公司共同协作所产生的效果优于各自单独行动的效果)
2.6.3. Current limitations
①Again, low computing efficiency
②⭐Lack of the long term dependency representations and efficiencies
③Field overlaping in neurological and psychiatric disorders may bring challenge
2.7. Interpretability
2.7.1. Intrinsic interpretability
(1)Attention-based feature importance analysis
①Intrinsic interpretability of Transformer: different importance between different input location
②Introducing some relevant models
2.7.2. Post-hoc interpretability
(1)Shapley-based feature importance analysis
(2)Gradient-based feature importance analysis
(3)Layer-wise feature importance analysis
2.8. Discussion and conclusions
2.8.1. Limitations and future research directions
①Data collection and annotation difficulties: "而数据合成等技术93和协调82为增强数据和跨不同领域进行调整提供了潜在的解决方案,但它们可能会受到生物医学数据固有的复杂性和可变性的限制。迁移学习127和零样本学习,105尽管它们在利用现有数据集方面具有优势,但由于数据分布的差异和专业临床领域的样本量小,它们往往面临困难。为了提高标注效率,概念标注233是一个不断发展的研究课题,旨在有效地对数据进行分类并自动生成标签。此外,元学习234, 235策略使模型能够快速适应新的数据类型和任务,从而在泛化功能方面提供有希望的改进。"
②Long-term dependency and computational complexity
③Inductive biases: combining different models to achieve multi-aspect learning
④Model Interpretability: lack of noise filtering ability
2.8.2. Conclusions
They elucidate Transformers in neuroscience, neurology, and psychiatry
3. 知识补充
3.1. Shapley Value
Shapley值(Shapley Value)是合作博弈论中的一个核心概念,由经济学家劳埃德·S·沙普利(Lloyd S. Shapley)于1953年提出。它用于衡量在合作博弈中,各个参与者对合作所创造的价值的贡献程度。
在合作博弈中,参与者通过合作形成联盟,并通过合作产生一定的效益或收益。Shapley值的主要思想是,一个参与者的贡献应该由他在所有可能的联盟中的边际贡献来衡量。这里的边际贡献是指当一个参与者加入或离开一个联盟时,对整个联盟价值的变化。
计算Shapley值的方法基于排列组合的思想,对所有可能的联盟进行考虑。然后,对所有可能的排列进行平均,得到每个参与者的Shapley值。具体地,假设有n个参与者,第i个参与者的Shapley值计算公式为:
φi(v) = ∑s∈Si ω(|s|)[v(s) - v(s{i})]
其中,Si是包含参与者i的所有可能联盟集合,ω(|s|)是联盟s的权重(通常与联盟的大小有关),v(s)是联盟s的总效用,v(s{i})是去掉参与者i后联盟s的总效用。
Shapley值分解法在实际应用中被广泛用于解释和评估预测模型的输出,以及分析协作多智能体系统的分配机制等。例如,在社交网络中,Shapley值分解法可以用来解释恶意用户产生的影响、优化社交网络中的影响传播等。然而,Shapley值分解法也存在一些问题,如过度依赖基础模型的质量等。
总的来说,Shapley值是一个用于衡量合作博弈中参与者贡献程度的重要工具,具有广泛的应用前景。
3.2. Zero-Shot Learning
零样本学习(Zero-Shot Learning,ZSL)是机器学习中的一种策略,其目标是使模型能够理解并识别它在训练阶段未曾遇到过的类别。零样本学习涉及的主要数据包括已知类(模型训练时用到的带类别标签的)和未知类(模型测试、训练时不知道类别标签的)。辅助信息,如对已知类和未知类数据的描述、语义属性、词嵌入等信息,充当了已知类和未知类之间的桥梁。
零样本学习的核心思想是利用另一个模型的现有知识,以获得新类别的有意义的表示。它使用语义嵌入或基于属性的学习,以有意义的方式利用先前的知识,提供已知类别和未知类别之间关系的高级理解。语义嵌入是单词、短语或文档的向量表示,它们在连续向量空间中捕捉了它们之间的潜在含义和关系。这些嵌入通常是使用无监督学习算法生成的,如Word2Vec、GloVe或BERT。
零样本学习的应用非常广泛,包括但不限于计算机视觉、自然语言处理和语音识别等领域。例如,在图像识别领域,零样本学习可以帮助AI系统学习如何识别新的物体;在自然语言处理领域,零样本学习可以帮助AI系统学习处理从未见过的词汇和语法结构;在语音识别领域,零样本学习可以帮助AI系统学习识别从未听过的语音。
4. Reference List
Cong, S. et al. (2024) 'Comprehensive review of Transformer-based models in neuroscience, neurology, and psychiatry', Brain-X, 2(2): https://doi.org/10.1002/brx2.57






















 3904
3904

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








