Synchronous HDLC framing involves decoding a continuous bit stream of data to look for bit patterns that indicate the beginning and end of frames (packets). Seeing exactly 6 consecutive 1s (i.e., 01111110) is a "flag" that indicate frame boundaries. To avoid the data stream from accidentally containing "flags", the sender inserts a zero after every 5 consecutive 1s which the receiver must detect and discard. We also need to signal an error if there are 7 or more consecutive 1s.
Create a finite state machine to recognize these three sequences:
- 0111110: Signal a bit needs to be discarded (disc).
- 01111110: Flag the beginning/end of a frame (flag).
- 01111111...: Error (7 or more 1s) (err).
When the FSM is reset, it should be in a state that behaves as though the previous input were 0.
Here are some example sequences that illustrate the desired operation.
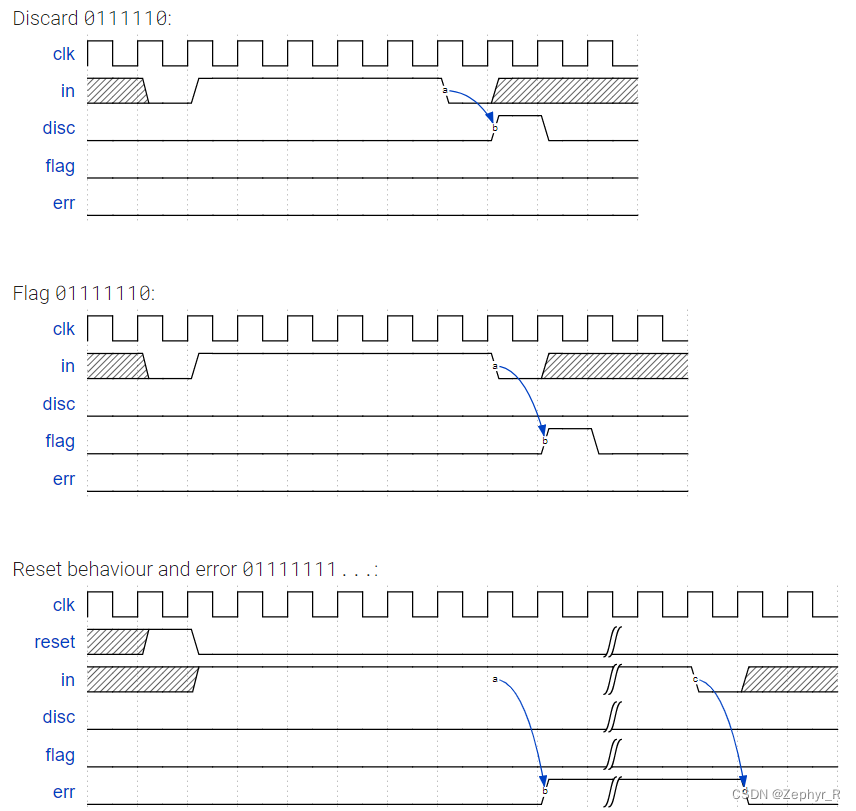
Implement this state machine.
//Fsm hdlc
module top_module(
input clk,
input reset, // Synchronous reset
input in,
output disc,
output flag,
output err);
reg[3:0]state,next_state;
reg[2:0]count_1;
wire n1;
parameter idle=4'd0, s0=4'd1, s1=4'd2, s2=4'd3, s3=4'd4, s4=4'd5, s5=4'd6, s6=4'd7; //idle代表从未检测到0的特殊情况,s0代表前一个数据为0,也可能有多个零,s1代表检测到0后跟了一个1,以此类推
parameter error=4'd8, discard=4'd9, fg=4'd10;
always @(*)
begin
case(state)
idle: next_state = (in ? (n1 ? error : idle): s0); //idle状态用于判断数据中从来没有0的情况
s0 : next_state = (in ? s1 : s0); //其余状态若不是达成err、disc、flag状态时,出现0则跳回s0,不会回到idle
s1 : next_state = (in ? s2 : s0);
s2 : next_state = (in ? s3 : s0);
s3 : next_state = (in ? s4 : s0);
s4 : next_state = (in ? s5 : s0);
s5 : next_state = (in ? s6 : discard);
s6 : next_state = (in ? error : fg);
error : next_state = (in ? error : s0); //因为是连续检测,discard与fg状态时已经有一个0了,所以in为1时直接跳到s1,为零则跳至s0
discard : next_state = (in ? s1 : s0);
fg : next_state = (in ? s1 : s0);
endcase
end
//用于在整个数据未出现0的情况下检测连续1数目的模块
always @(posedge clk)
begin
if((~in)|reset)
count_1 <= 3'd0;
else
count_1 <= (count_1==3'd7 ? 3'd7 : count_1+1'b1);
end
assign n1=(count_1==3'd7 ? 1'b1 : 1'b0); //1的数量达到七个后,输出n1信号,使下个状态进入error
always @(posedge clk)
begin
if(reset)
state <= s0;
else
state <= next_state;
end
assign disc = (state==discard) ;
assign flag = (state==fg) ;
assign err = (state==error) ;
endmodule






















 763
763











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








