转自四元数、欧拉角、旋转矩阵之间互相转换C++源码
还可参考
Creating a rotation matrix with pitch, yaw, roll using Eigen
Finding roll, pitch yaw from 3X3 rotation matrix with Eigen
1、源码
- #include <iostream>
- #include <Eigen/Eigen>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <Eigen/Geometry>
- #include <Eigen/Core>
- #include <vector>
- #include <math.h>
- using namespace std;
- using namespace Eigen;
- Eigen::Quaterniond euler2Quaternion(const double roll, const double pitch, const double yaw)
- {
- Eigen::AngleAxisd rollAngle(roll, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitZ());
- Eigen::AngleAxisd yawAngle(yaw, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitY());
- Eigen::AngleAxisd pitchAngle(pitch, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitX());
- Eigen::Quaterniond q = rollAngle yawAngle pitchAngle;
- cout << “Euler2Quaternion result is:” <<endl;
- cout << ”x = ” << q.x() <<endl;
- cout << ”y = ” << q.y() <<endl;
- cout << ”z = ” << q.z() <<endl;
- cout << ”w = ” << q.w() <<endl<<endl;
- return q;
- }
- Eigen::Vector3d Quaterniond2Euler(const double x,const double y,const double z,const double w)
- {
- Eigen::Quaterniond q;
- q.x() = x;
- q.y() = y;
- q.z() = z;
- q.w() = w;
- Eigen::Vector3d euler = q.toRotationMatrix().eulerAngles(2, 1, 0);
- cout << “Quaterniond2Euler result is:” <<endl;
- cout << ”x = ”<< euler[2] << endl ;
- cout << ”y = ”<< euler[1] << endl ;
- cout << ”z = ”<< euler[0] << endl << endl;
- }
- Eigen::Matrix3d Quaternion2RotationMatrix(const double x,const double y,const double z,const double w)
- {
- Eigen::Quaterniond q;
- q.x() = x;
- q.y() = y;
- q.z() = z;
- q.w() = w;
- Eigen::Matrix3d R = q.normalized().toRotationMatrix();
- cout << “Quaternion2RotationMatrix result is:” <<endl;
- cout << ”R = ” << endl << R << endl<< endl;
- return R;
- }
- Eigen::Quaterniond rotationMatrix2Quaterniond(Eigen::Matrix3d R)
- {
- Eigen::Quaterniond q = Eigen::Quaterniond(R);
- q.normalize();
- cout << “RotationMatrix2Quaterniond result is:” <<endl;
- cout << ”x = ” << q.x() <<endl;
- cout << ”y = ” << q.y() <<endl;
- cout << ”z = ” << q.z() <<endl;
- cout << ”w = ” << q.w() <<endl<<endl;
- return q;
- }
- Eigen::Matrix3d euler2RotationMatrix(const double roll, const double pitch, const double yaw)
- {
- Eigen::AngleAxisd rollAngle(roll, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitZ());
- Eigen::AngleAxisd yawAngle(yaw, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitY());
- Eigen::AngleAxisd pitchAngle(pitch, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitX());
- Eigen::Quaterniond q = rollAngle yawAngle pitchAngle;
- Eigen::Matrix3d R = q.matrix();
- cout << “Euler2RotationMatrix result is:” <<endl;
- cout << ”R = ” << endl << R << endl<<endl;
- return R;
- }
- Eigen::Vector3d RotationMatrix2euler(Eigen::Matrix3d R)
- {
- Eigen::Matrix3d m;
- m = R;
- Eigen::Vector3d euler = m.eulerAngles(0, 1, 2);
- cout << “RotationMatrix2euler result is:” << endl;
- cout << ”x = ”<< euler[2] << endl ;
- cout << ”y = ”<< euler[1] << endl ;
- cout << ”z = ”<< euler[0] << endl << endl;
- return euler;
- }
- int main(int argc, char **argv)
- {
- //this is euler2Quaternion transform function,please input your euler angle//
- euler2Quaternion(0,0,0);
- //this is Quaternion2Euler transform function,please input your euler angle//
- Quaterniond2Euler(0,0,0,1);
- //this is Quaternion2RotationMatrix transform function,please input your Quaternion parameter//
- Quaternion2RotationMatrix(0,0,0,1);
- //this is rotationMatrix2Euler transform function,please input your RotationMatrix parameter like following//
- Eigen::Vector3d x_axiz,y_axiz,z_axiz;
- x_axiz << 1,0,0;
- y_axiz << 0,1,0;
- z_axiz << 0,0,1;
- Eigen::Matrix3d R;
- R << x_axiz,y_axiz,z_axiz;
- rotationMatrix2Quaterniond(R);
- //this is euler2RotationMatrix transform function,please input your euler angle for the function parameter//
- euler2RotationMatrix(0,0,0);
- //this is RotationMatrix2euler transform function,please input your euler angle for the function parameter//
- RotationMatrix2euler(R);
- cout << “All transform is done!” << endl;
- }
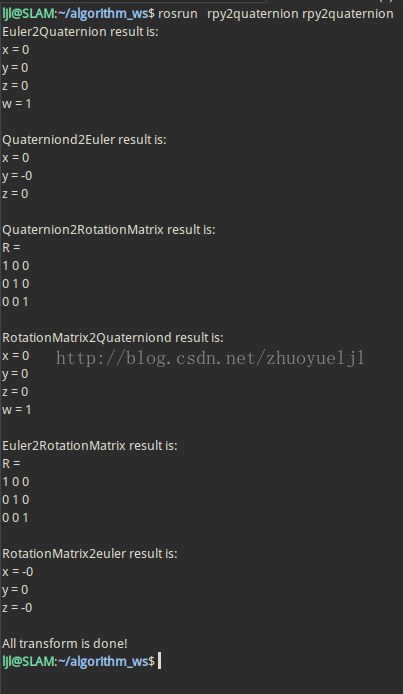
2、测试结果






















 1912
1912











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








