讲完上面两部分,我就来到真正的激光雷达数据处理的模块了。剩下有三部分,除imageProjection订阅了IMU源数据、Lidar源数据、ImuPreintegration发过来的odom(里程计数据)之外,就只通过自定义的消息体cloud_info 串联整个激光雷达处理到定位的所有模块(最后的MapOptimization还接收了GPS 源数据、回环检测数据,做因子图优化),先把系统topic 数据流图搬过来,能更加清晰的理解这个模块。
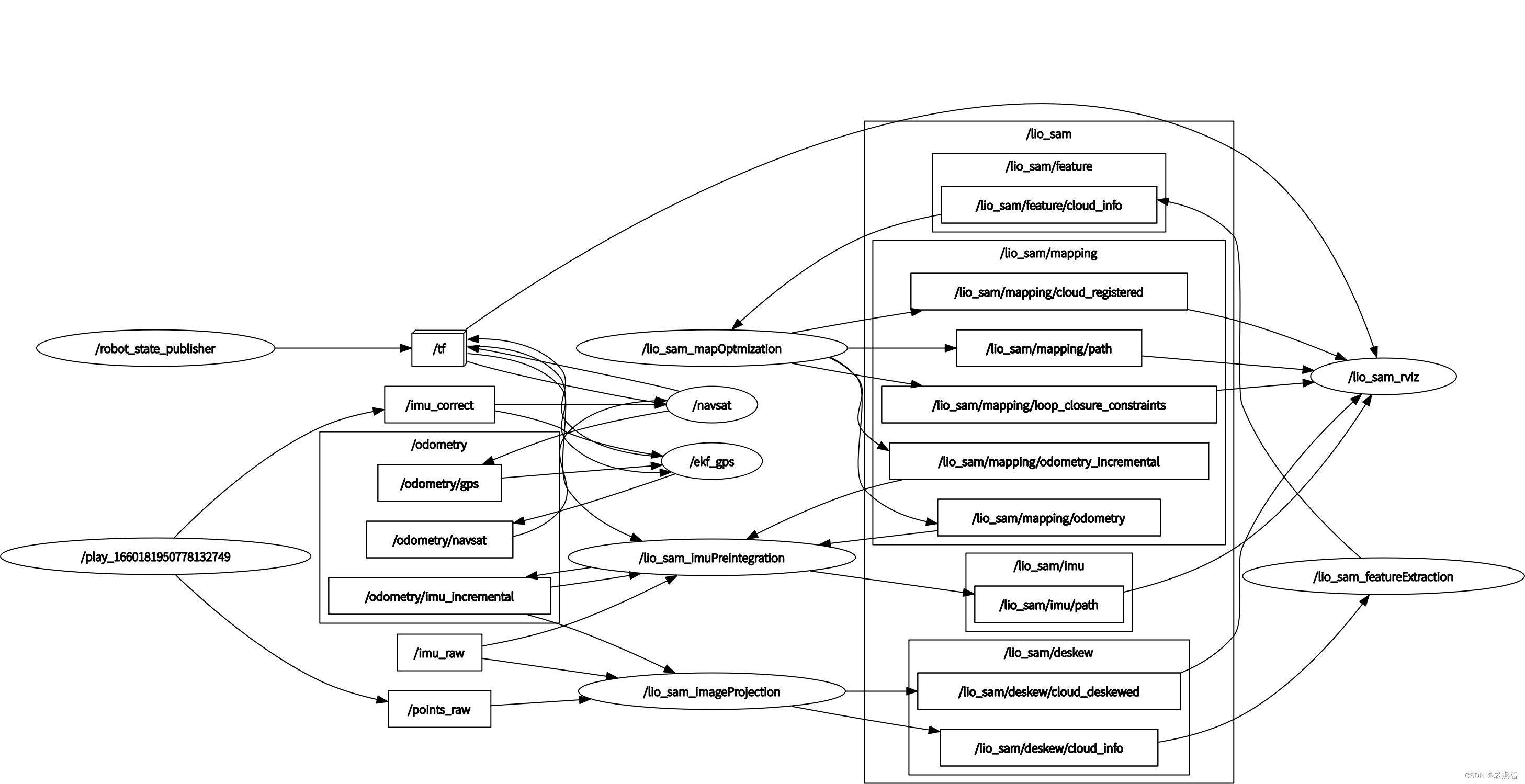
图2.ros topic 发布与订阅关系图关系图(还是叫图2,因为是同一个图)
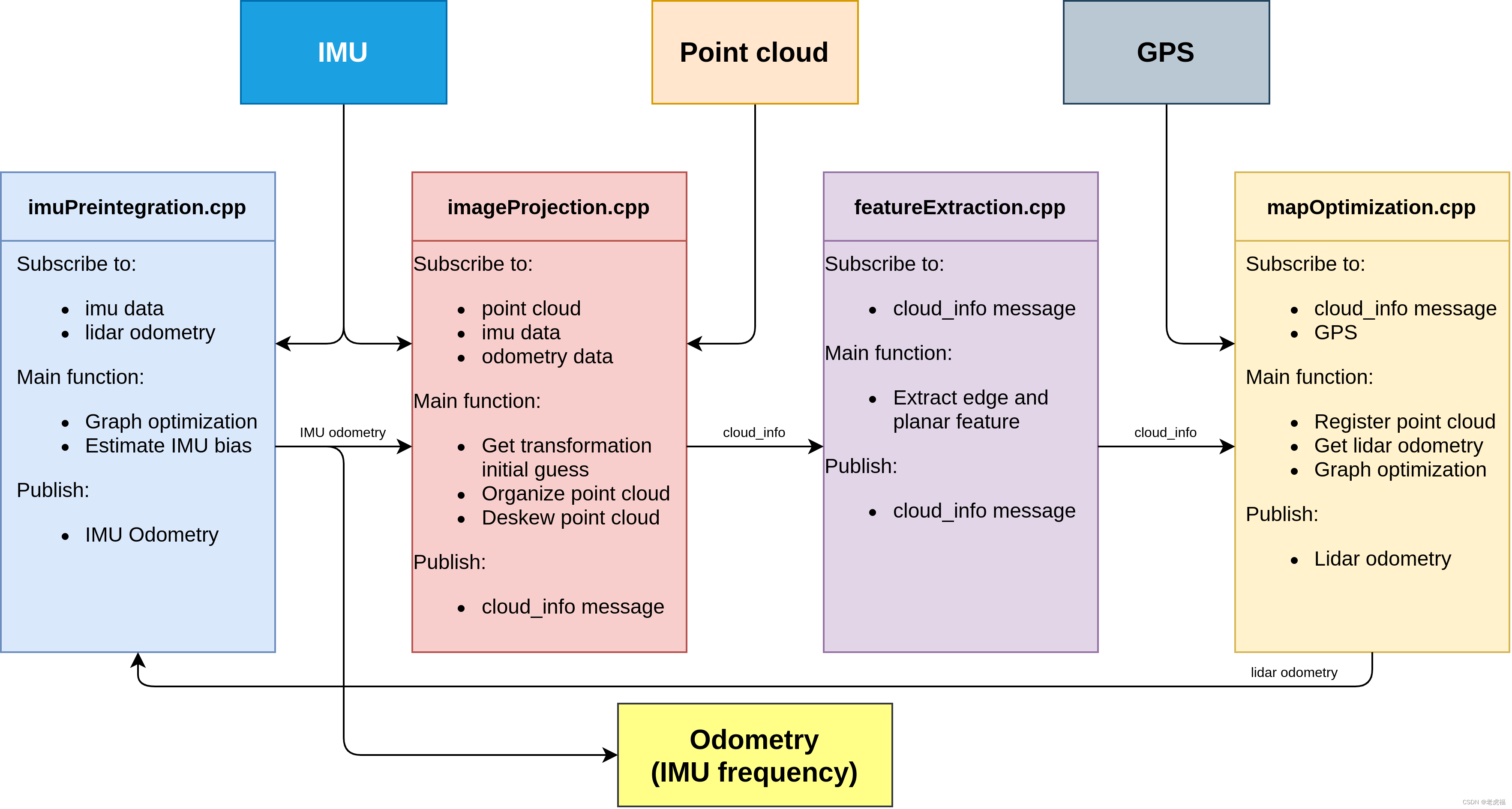
图1.代码架构图(数据流图) 分析真正的代码之前,需要先看cloud_info这个消息体的定义。
| 变量名 | 类型 | 注释 | 备注 |
| header | Header | ros 消息头 | - |
| startRingIndex | int32[] | 整形数组,在整个数据结构中,激光点云数据拉平保存在一维数组中,这个数组保存了每一线雷达的第一个数据在这个点云数组中的起始位置 | - |
| endRingIndex | int32[] | 这个数组保存了每一线雷达的最后一个数据在这个点云数组中的位置索引 | - |
| pointColInd | int32[] | # point column index in range image 这里保存的是该点云数据在二维映射图像中的列数索引 | - |
| pointRange | float32[] | # point range 点云数据对应的深度 | - |
| imuAvailable | int64 | 标记IMU 数据可用 | - |
| odomAvailable | int64 | 标记imuPreintegration发来的odom 数据可用 | - |
| imuRollInit | float32 | 保存了当帧点云起始时刻的roll角度 | - |
| imuPitchInit | float32 | 保存了当帧点云起始时刻的pitch角度 | - |
| imuYawInit | float32 | 保存了当帧点云起始时刻的yaw角度 | - |
| Initial guess from imu pre-integration | - | ||
| initialGuessX | float32 | 保存了当帧点云起始时刻的位姿信息,要给mapOptimization 作位姿初始化用 | - |
| initialGuessY | float32 | 保存了当帧点云起始时刻的位姿信息,要给mapOptimization 作位姿初始化用 | - |
| initialGuessZ | float32 | 保存了当帧点云起始时刻的位姿信息,要给mapOptimization 作位姿初始化用 | - |
| initialGuessRoll | float32 | 保存了当帧点云起始时刻的位姿信息,要给mapOptimization 作位姿初始化用 | - |
| initialGuessPitch | float32 | 保存了当帧点云起始时刻的位姿信息,要给mapOptimization 作位姿初始化用 | - |
| initialGuessYaw | float32 | 保存了当帧点云起始时刻的位姿信息,要给mapOptimization 作位姿初始化用 | - |
| Point cloud messages | - | ||
| cloud_deskewed | sensor_msgs/PointCloud2 | original cloud deskewed 经过去畸变处理的点云数据,封装在这个数据结构中,传递到下个环节环节中去 | - |
| cloud_corner | sensor_msgs/PointCloud2 | # extracted corner feature 角点点云数据,这个字段是在featureExtraction模块中填充,传递给mapOptimization模块 | - |
| cloud_surface | sensor_msgs/PointCloud2 | # extracted surface feature 平面点云数据,这个字段是在featureExtraction模块中填充,传递给mapOptimization模块 | - |
| 3rd party messages | - | ||
| key_frame_cloud | sensor_msgs/PointCloud2 | 待定 | - |
| key_frame_color | sensor_msgs/PointCloud2 | 待定 | - |
| key_frame_poses | sensor_msgs/PointCloud2 | 待定 | - |
| key_frame_map | sensor_msgs/PointCloud2 | 待定 | - |
imageProjection
先看成员列表:
| 变量名 | 类型 | 注释 | 备注 |
| imuLock | std::mutex | imu 数据队列的锁互斥量 | - |
| odoLock | std::mutex | odom 数据队列的锁互斥量 | - |
| subLaserCloud | ros::Subscriber | 订阅 "points_raw" Lidar 源数据 | - |
| pubLaserCloud | ros::Publisher | 这个玩意 没有用?? | - |
| pubExtractedCloud | ros::Publisher | 发布 去畸变的点云数据 "lio_sam/deskew/cloud_deskewed" 从图2中看,貌似只给rviz 当调试数据用 | - |
| pubLaserCloudInfo | ros::Publisher | 发布cloud_info :"lio_sam/deskew/cloud_info" 主要传递的数据结构,串联整个模块 | - |
| subImu | ros::Subscriber | 订阅 "imu_raw" IMU 源数据 | - |
| imuQueue | std::deque | IMU 源数据对应的队列 | - |
| subOdom | ros::Subscriber | 订阅"odometry/imu_incremental" 通过IMU IMU 预积分器 融合了Lidar里程计的当前时刻的里程计数据 same frequency as IMU std::deque odomQueue; // "odometry/imu_incremental" 对应的里程计的数据队列 | - |
| cloudQueue | std::deque | lidar 点云的源数据队列 | - |
| currentCloudMsg | sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 | 从队列里取出来要处理的点云 | - |
| i// 保存一帧点云 帧内时间期间 的相对于帧内第一点的数据位姿旋转变换关系,根据IMU 数据频率采集计算得来 | - | ||
| double *imuTime = new double[queueLength] | - | ||
| double *imuRotX = new double[queueLength] | - | ||
| double *imuRotY = new double[queueLength] | - | ||
| double *imuRotZ = new double[queueLength] | - | ||
| imuPointerCur | int | 遍历点云时用的 索引下标 | - |
| firstPointFlag | bool | 标记点云中的第一个点,不需要作运动畸变矫正,并且计算到 transStartInverse | - |
| transStartInverse | Eigen::Affine3f | 点云中每一线起始点的位姿变换矩阵的逆 乘以 某个点的变换矩阵 就是相对变换 | - |
| laserCloudIn | pcl::PointCloud::Ptr | 点云遍历时存放未运动畸变矫正的点云 | - |
| fullCloud | pcl::PointCloud::Ptr | 处理完后,点云存放在这里,过滤盲区点、运动畸变矫正等 | - |
| extractedCloud | pcl::PointCloud::Ptr | 与fullCloud 唯一的区别就是,fullCloud 严格按横列排序的,而extractedCloud 是紧凑无序的 | - |
| deskewFlag | int | 是否作运动畸变矫正的标志,0 无需 1 要 | - |
| rangeMat | cv::Mat | 深度图 最后赋值给cloudInfo.pointRange 传递出去 | - |
| 里程计数据 求得 lidar 起始时刻 到末尾时刻的运动增量 | - | ||
| bool odomDeskewFlag | - | ||
| float odomIncreX | - | ||
| float odomIncreY | - | ||
| float odomIncreZ | - | ||
| cloudInfo | lio_sam::cloud_info | 自定义结构,这个结构要串联整个激光点云处理模块,重点关注 | - |
| timeScanCur | double | 当帧点云起始时间戳 | - |
| timeScanEnd | double | 当帧点云末尾时间戳 | - |
| cloudHeader | std_msgs::Header | ros 消息头,主要是为了获取消息时间 | - |
| columnIdnCountVec | vector | 这个数组主要是为了计算Livox激光雷达数据的横列用到的 | - |
1.送入odomhandle,放入odomqueue中。
这里要说一下,注意两点:
第一,这个话题odometry/imu_incremental是imu里程计融合了激光里程计发送频率跟IMU 保持一致的里程计,是来自IMUPreintegration(imuPreintegration.cpp中的TransformFusion类)发布的里程计话题。它就是一个里程计数据,通过imu预积分计算优化来得到的任意时刻在世界坐标系下的位姿。
mapOptimization.cpp文件还会发布一个叫"lio_sam/mapping/odometry_incremental",它代表的是激光里程计,这里的odometry/imu_incremental融合了激光里程计发送频率跟IMU 保持一致的里程计信息。
2.原始点云数据送入cloudhandle:
3.1 点云加入cloudQueue,检查数据有效性(格式上,主要因为雷达款式不同)
3.1.1 cachePointCloud
-
- 保存Lidar 数据到队列中
-
- 转换数据结构
-
- 判断点云数据是否包含 ring 字段
-
- 判断点云数据是否包含 time 字段
-
- 设置点云开始、结束时间戳
3.2 deskewinfo: 分别收集IMU 数据和Odom中的在Lidar 数据帧内的期间内的位姿数据 3.2.1 imuDeskewInfo:遍历激光帧,从imuqueue中找当前激光帧前0.01s开始,当前帧后0.01s结束,找到最近的一个imu数据,把它的原始角度数据,作为cloudInfo.imuRollInit等变量。 这个函数主要是收集 Lidar 点云数据的开始时间到结束时间之间的IMU数据,用作点云运动畸变矫正用
-
- 提取lidar最早时刻的 IMU 的Roll Pitch Yaw 作为该点云数据的开始时刻的坐标方向
-
- 收集最开始时刻到Lidar 数据的最后时刻,相对于第一时刻(点云开始时刻)的旋转角
- 其中第一个数据相对于第1个时刻的旋转角为0 然后往下递推
- 旋转角 = 上一时刻旋转角 + 角速度 * 时间
3.2.2 odomDeskewInfo:遍历imu里程计的odomqueue队列,剔除当前0.01s之前的数据,找到第一个大于当前激光帧的数据,然后用里程计数据来初始化雷达,也是填充角度,不过这次填充的是cloudInfo.initialGuessRoll等变量,位置也会被填充到initialGuessX里。
-
- 通过里程计数据求得Lidar 数据帧内 起始时刻的位姿,并保存到cloud_info中,传给MapOptimization中
-
- 通过里程计数据求得Lidar 数据帧内 末尾时刻的位姿
-
- 通过1和2 求得 末尾时刻相对起始时刻的变换矩阵 ,并求得相关标量的增量
注意:cloudInfo.initialGuessRoll和cloudInfo.imuRollInit,这些东西都是角度数据,带Guess的为imu里程计提供的数据,imuRollInit这种为imu原始数据。如果有合适的,分别会填充cloudInfo.odomAvailable和cloudInfo.imuAvailable变量为true,代表这块的数据可用。这些会被用在mapOptimization.cpp的updateInitGuess函数,给激光里程计做一个初始化,然后在这个初始化的基础上进行非线性优化。
3.3 projectPointCloud:
3.3.1 获取点云中的每一个点,投影图像。
3.3.2 去畸变。假设一帧激光数据,是在一个很小的时间段内获取的,但是由于这段时间内,激光雷达可能处于运动状态,那么就可能导致运动畸变。这里就要用到了3.2.1中提到的imuRotX等玩意,根据imu的运动信息,把这段时间内依次接收的每个点统一投影到初始时刻,去除运动畸变。
3.4 CloudExtraction:
-
- 过滤一些盲区数据
-
- 跳线过滤压缩点云
-
- 计算点云中的点的列索引
-
- 点云运动畸变矫正
-
- 点云深度计算
pcl::cloudPoint2 里面保存的点云是一维的。 既然是一维数组,16线的点都弄到一维数组里,那就比较麻烦。虽然说这里要弄一个深度投影图像,但是其实进程之间传输的并不是这个深度投影图像,而是自定义的cloudinfo形式的数据。
实际上是想把有效的数据记录进来,例如空值不要,每根线前5个和后5个也不要……那这样16线的数据混到一维组里就分不清了,所以要记录下每根扫瞄线起始点在1维数组中的索引startRingIndex,结束点的索引endRingIndex,在原始图像中的列数pointColInd,距离值pointRange。然后把有效激光点,放到extractedCloud中。
3.5 publishClouds:
把extractedCloud发布出去,/lio_sam/deskew/cloud_deskewed,这个只有点云信息。
然后再把这些点,赋值到cloudInfo.cloud_deskewed中,把整个的cloudInfo发布出去,名字就叫“lio_sam/deskew/cloud_info",这个就是作者自己定义的特殊的msg。
void imuHandler(const sensor_msgs::Imu::ConstPtr& imuMsg)
{
// 对IMU 数据做数据矫正,使得IMU 的坐标系方向与Lidar坐标系方向保持一致,这样IMU 与 Lidar 的外参仅差一个平移变换
sensor_msgs::Imu thisImu = imuConverter(*imuMsg);
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock1(imuLock);
// IMU 的数据频率比较高,进来时先保留在队列中,然后等Lidar 数据进来时,按Lidar的数据周期处理数据
imuQueue.push_back(thisImu);
// debug IMU data
// cout << std::setprecision(6);
// cout << "IMU acc: " << endl;
// cout << "x: " << thisImu.linear_acceleration.x <<
// ", y: " << thisImu.linear_acceleration.y <<
// ", z: " << thisImu.linear_acceleration.z << endl;
// cout << "IMU gyro: " << endl;
// cout << "x: " << thisImu.angular_velocity.x <<
// ", y: " << thisImu.angular_velocity.y <<
// ", z: " << thisImu.angular_velocity.z << endl;
// double imuRoll, imuPitch, imuYaw;
// tf::Quaternion orientation;
// tf::quaternionMsgToTF(thisImu.orientation, orientation);
// tf::Matrix3x3(orientation).getRPY(imuRoll, imuPitch, imuYaw);
// cout << "IMU roll pitch yaw: " << endl;
// cout << "roll: " << imuRoll << ", pitch: " << imuPitch << ", yaw: " << imuYaw << endl << endl;
}
void odometryHandler(const nav_msgs::Odometry::ConstPtr& odometryMsg)
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock2(odoLock);
// 融合里程计的数据频率与IMU 的数据频率相同,进来时先保留在队列中,然后等Lidar 数据进来时,按Lidar的数据周期处理数据
odomQueue.push_back(*odometryMsg);
}
/**
* Lidar 数据的回调函数 主要逻辑都放在这里
* */
void cloudHandler(const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2ConstPtr& laserCloudMsg)
{
/** 这个函数1. 保存Lidar 数据到队列中
* 2. 转换数据结构
* 3. 判断点云数据是否包含 ring 字段
* 4. 判断点云数据是否包含 time 字段
* 5. 设置点云开始、结束时间戳
* */
if (!cachePointCloud(laserCloudMsg))
return;
/**
* 分别收集IMU 数据和Odom中的在Lidar 数据帧内的期间内的位姿数据
* */
if (!deskewInfo())
return;
projectPointCloud();
cloudExtraction();
publishClouds();
resetParameters();
}
/** 这个函数1. 保存Lidar 数据到队列中
* 2. 转换数据结构
* 3. 判断点云数据是否包含 ring 字段
* 4. 判断点云数据是否包含 time 字段
* 5. 设置点云开始、结束时间戳
* */
bool cachePointCloud(const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2ConstPtr& laserCloudMsg)
{
// Lidar 数据存进队列末尾
// cache point cloud
cloudQueue.push_back(*laserCloudMsg);
if (cloudQueue.size() <= 2)
return false;
// 取出最久的一帧点云数据
// convert cloud
currentCloudMsg = std::move(cloudQueue.front());
// 取出之后就pop掉
cloudQueue.pop_front();
// 该系统支持 VELODYNE、LIVOX、OUSTER 三款激光雷达,但是OUSTER 数据需要转成VELODYNE 格式
if (sensor == SensorType::VELODYNE || sensor == SensorType::LIVOX)
{
pcl::moveFromROSMsg(currentCloudMsg, *laserCloudIn);
}
else if (sensor == SensorType::OUSTER)
{
// Convert to Velodyne format
pcl::moveFromROSMsg(currentCloudMsg, *tmpOusterCloudIn);
laserCloudIn->points.resize(tmpOusterCloudIn->size());
laserCloudIn->is_dense = tmpOusterCloudIn->is_dense;
for (size_t i = 0; i < tmpOusterCloudIn->size(); i++)
{
auto &src = tmpOusterCloudIn->points[i];
auto &dst = laserCloudIn->points[i];
dst.x = src.x;
dst.y = src.y;
dst.z = src.z;
dst.intensity = src.intensity;
dst.ring = src.ring;
dst.time = src.t * 1e-9f;
}
}
else
{
ROS_ERROR_STREAM("Unknown sensor type: " << int(sensor));
ros::shutdown();
}
// get timestamp
cloudHeader = currentCloudMsg.header;
// 当前帧的开始时间戳
timeScanCur = cloudHeader.stamp.toSec();
// 当前帧最后数据的时间戳
timeScanEnd = timeScanCur + laserCloudIn->points.back().time;
// check dense flag
if (laserCloudIn->is_dense == false)
{
ROS_ERROR("Point cloud is not in dense format, please remove NaN points first!");
ros::shutdown();
}
// 检查数据是否有ring 字段,ring 表示该点云数据点所在的线数,没有标明ring 的点云数据 在该系统中失效
// check ring channel
static int ringFlag = 0;
if (ringFlag == 0)
{
ringFlag = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)currentCloudMsg.fields.size(); ++i)
{
if (currentCloudMsg.fields[i].name == "ring")
{
ringFlag = 1;
break;
}
}
if (ringFlag == -1)
{
ROS_ERROR("Point cloud ring channel not available, please configure your point cloud data!");
ros::shutdown();
}
}
// 检查点云数据是否有time 字段
// check point time
if (deskewFlag == 0)
{
deskewFlag = -1;
for (auto &field : currentCloudMsg.fields)
{
if (field.name == "time" || field.name == "t")
{
deskewFlag = 1;
break;
}
}
if (deskewFlag == -1)
ROS_WARN("Point cloud timestamp not available, deskew function disabled, system will drift significantly!");
}
return true;
}
/**
* 分别收集IMU 数据和Odom中的在Lidar 数据帧内的期间内的位姿数据
* */
bool deskewInfo()
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock1(imuLock);
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock2(odoLock);
// make sure IMU data available for the scan
if (imuQueue.empty() || imuQueue.front().header.stamp.toSec() > timeScanCur || imuQueue.back().header.stamp.toSec() < timeScanEnd)
{
ROS_DEBUG("Waiting for IMU data ...");
return false;
}
/***
* 这个函数主要是收集 Lidar 点云数据的开始时间到结束时间之间的IMU数据,用作点云运动畸变矫正用
* 1. 提取lidar最早时刻的 IMU 的Roll Pitch Yaw 作为该点云数据的开始时刻的坐标方向
* 2. 收集最开始时刻到Lidar 数据的最后时刻,相对于第一时刻(点云开始时刻)的旋转角
* 其中第一个数据相对于第1个时刻的旋转角为0 然后往下递推
* 旋转角 = 上一时刻旋转角 + 角速度 * 时间
* */
imuDeskewInfo();
/**这个函数 1. 通过里程计数据求得Lidar 数据帧内 起始时刻的位姿,并保存到cloud_info中,传给MapOptimization中
* 2. 通过里程计数据求得Lidar 数据帧内 末尾时刻的位姿
* 3. 通过1和2 求得 末尾时刻相对起始时刻的变换矩阵 ,并求得相关标量的增量
* */
odomDeskewInfo();
return true;
}
/***
* 这个函数主要是收集 Lidar 点云数据的开始时间到结束时间之间的IMU数据,用作点云运动畸变矫正用
* 1. 提取lidar最早时刻的 IMU 的Roll Pitch Yaw 作为该点云数据的开始时刻的坐标方向
* 2. 收集最开始时刻到Lidar 数据的最后时刻,相对于第一时刻(点云开始时刻)的旋转角
* 其中第一个数据相对于第1个时刻的旋转角为0 然后往下递推
* 旋转角 = 上一时刻旋转角 + 角速度 * 时间
* */
void imuDeskewInfo()
{
cloudInfo.imuAvailable = false;
// pop 掉比 lidar 时间戳小0.01 的IMU数据
while (!imuQueue.empty())
{
if (imuQueue.front().header.stamp.toSec() < timeScanCur - 0.01)
imuQueue.pop_front();
else
break;
}
if (imuQueue.empty())
return;
imuPointerCur = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)imuQueue.size(); ++i)
{
sensor_msgs::Imu thisImuMsg = imuQueue[i];
double currentImuTime = thisImuMsg.header.stamp.toSec();
// get roll, pitch, and yaw estimation for this scan
if (currentImuTime <= timeScanCur)
// 在9 轴 IMU 数据中提取 Roll pitch yaw 数据
imuRPY2rosRPY(&thisImuMsg, &cloudInfo.imuRollInit, &cloudInfo.imuPitchInit, &cloudInfo.imuYawInit);
if (currentImuTime > timeScanEnd + 0.01)
break;
// 开始的那个时间点 用0 填充
if (imuPointerCur == 0){
imuRotX[0] = 0;
imuRotY[0] = 0;
imuRotZ[0] = 0;
imuTime[0] = currentImuTime;
++imuPointerCur;
continue;
}
// 提取IMU 数据的角速度
// get angular velocity
double angular_x, angular_y, angular_z;
imuAngular2rosAngular(&thisImuMsg, &angular_x, &angular_y, &angular_z);
// 然后递增的计算往后的IMU 的旋转角
// 旋转角 = 上一时刻旋转角 + 角速度 * 时间
// integrate rotation
double timeDiff = currentImuTime - imuTime[imuPointerCur-1];
imuRotX[imuPointerCur] = imuRotX[imuPointerCur-1] + angular_x * timeDiff;
imuRotY[imuPointerCur] = imuRotY[imuPointerCur-1] + angular_y * timeDiff;
imuRotZ[imuPointerCur] = imuRotZ[imuPointerCur-1] + angular_z * timeDiff;
imuTime[imuPointerCur] = currentImuTime;
++imuPointerCur;
}
--imuPointerCur;
if (imuPointerCur <= 0)
return;
cloudInfo.imuAvailable = true; // IMU 旋转角可用
}
/**这个函数 1. 通过里程计数据求得Lidar 数据帧内 起始时刻的位姿,并保存到cloud_info中,传给MapOptimization中
* 2. 通过里程计数据求得Lidar 数据帧内 末尾时刻的位姿
* 3. 通过1和2 求得 末尾时刻相对起始时刻的变换矩阵 ,并求得相关标量的增量
* */
void odomDeskewInfo()
{
cloudInfo.odomAvailable = false;
while (!odomQueue.empty())
{ // 去除 Lidar 时间开始时刻0.01秒以前的数据
if (odomQueue.front().header.stamp.toSec() < timeScanCur - 0.01)
odomQueue.pop_front();
else
break;
}
if (odomQueue.empty())
return;
// 如果 里程计队列里没有比Lidar 时间更小的数据,返回,证明Odom用于点云运动畸变修正的数据不可用
if (odomQueue.front().header.stamp.toSec() > timeScanCur)
return;
// startOdomMsg 时刻刚刚好大于或者等于 lidar 时刻,由于IMU Odom 的频率远高于Lidar 周期,startOdomMsg的时刻比较接近Lidar 的起始时刻
// get start odometry at the beinning of the scan
nav_msgs::Odometry startOdomMsg;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)odomQueue.size(); ++i)
{
startOdomMsg = odomQueue[i];
if (ROS_TIME(&startOdomMsg) < timeScanCur)
continue;
else
break;
}
tf::Quaternion orientation;
tf::quaternionMsgToTF(startOdomMsg.pose.pose.orientation, orientation);
double roll, pitch, yaw;
tf::Matrix3x3(orientation).getRPY(roll, pitch, yaw);
// 对应着 Lidar 数据帧起始时刻的位姿
// Initial guess used in mapOptimization
cloudInfo.initialGuessX = startOdomMsg.pose.pose.position.x;
cloudInfo.initialGuessY = startOdomMsg.pose.pose.position.y;
cloudInfo.initialGuessZ = startOdomMsg.pose.pose.position.z;
cloudInfo.initialGuessRoll = roll;
cloudInfo.initialGuessPitch = pitch;
cloudInfo.initialGuessYaw = yaw;
cloudInfo.odomAvailable = true;
// get end odometry at the end of the scan
odomDeskewFlag = false;
if (odomQueue.back().header.stamp.toSec() < timeScanEnd)
return;
// endOdomMsg 获取 lidar 数据帧内的最后一时刻的位姿,有了最开始时刻的位姿和最后一时刻的位姿,就可以根据点云时间戳线性插值,修正点云运动畸变
nav_msgs::Odometry endOdomMsg;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)odomQueue.size(); ++i)
{
endOdomMsg = odomQueue[i];
if (ROS_TIME(&endOdomMsg) < timeScanEnd)
continue;
else
break;
}
if (int(round(startOdomMsg.pose.covariance[0])) != int(round(endOdomMsg.pose.covariance[0])))
return;
Eigen::Affine3f transBegin = pcl::getTransformation(startOdomMsg.pose.pose.position.x, startOdomMsg.pose.pose.position.y, startOdomMsg.pose.pose.position.z, roll, pitch, yaw);
tf::quaternionMsgToTF(endOdomMsg.pose.pose.orientation, orientation);
tf::Matrix3x3(orientation).getRPY(roll, pitch, yaw);
Eigen::Affine3f transEnd = pcl::getTransformation(endOdomMsg.pose.pose.position.x, endOdomMsg.pose.pose.position.y, endOdomMsg.pose.pose.position.z, roll, pitch, yaw);
// 末尾时刻相对于起始时刻的变换矩阵
Eigen::Affine3f transBt = transBegin.inverse() * transEnd;
// 转换成 增量
float rollIncre, pitchIncre, yawIncre;
pcl::getTranslationAndEulerAngles(transBt, odomIncreX, odomIncreY, odomIncreZ, rollIncre, pitchIncre, yawIncre);
odomDeskewFlag = true;
}
/**
* 根据激光点云的时间戳,在 imuRotX imuRotY imuRotZ 列表中按线形插值的方式寻找该时刻相对于点云起始时刻的旋转
* */
void findRotation(double pointTime, float *rotXCur, float *rotYCur, float *rotZCur)
{
*rotXCur = 0; *rotYCur = 0; *rotZCur = 0;
int imuPointerFront = 0;
while (imuPointerFront < imuPointerCur)
{
if (pointTime < imuTime[imuPointerFront])
break;
++imuPointerFront;
}
if (pointTime > imuTime[imuPointerFront] || imuPointerFront == 0)
{
*rotXCur = imuRotX[imuPointerFront];
*rotYCur = imuRotY[imuPointerFront];
*rotZCur = imuRotZ[imuPointerFront];
} else {
int imuPointerBack = imuPointerFront - 1;
double ratioFront = (pointTime - imuTime[imuPointerBack]) / (imuTime[imuPointerFront] - imuTime[imuPointerBack]);
double ratioBack = (imuTime[imuPointerFront] - pointTime) / (imuTime[imuPointerFront] - imuTime[imuPointerBack]);
*rotXCur = imuRotX[imuPointerFront] * ratioFront + imuRotX[imuPointerBack] * ratioBack;
*rotYCur = imuRotY[imuPointerFront] * ratioFront + imuRotY[imuPointerBack] * ratioBack;
*rotZCur = imuRotZ[imuPointerFront] * ratioFront + imuRotZ[imuPointerBack] * ratioBack;
}
}
/**
* 本来也是根据激光点云的时间戳按线性插值法找位移的,但是下面注释说了,如果系统运动的很慢,位移的运动畸变矫正意义不大,所以作者就没有做
* */
void findPosition(double relTime, float *posXCur, float *posYCur, float *posZCur)
{
*posXCur = 0; *posYCur = 0; *posZCur = 0;
// If the sensor moves relatively slow, like walking speed, positional deskew seems to have little benefits. Thus code below is commented.
// if (cloudInfo.odomAvailable == false || odomDeskewFlag == false)
// return;
// float ratio = relTime / (timeScanEnd - timeScanCur);
// *posXCur = ratio * odomIncreX;
// *posYCur = ratio * odomIncreY;
// *posZCur = ratio * odomIncreZ;
}
/**
* 对点云中的某个点进行运动畸变矫正,统一把点云映射到以点云起始时刻的位姿坐标系下
* */
PointType deskewPoint(PointType *point, double relTime)
{
if (deskewFlag == -1 || cloudInfo.imuAvailable == false)
return *point;
double pointTime = timeScanCur + relTime;
float rotXCur, rotYCur, rotZCur;
findRotation(pointTime, &rotXCur, &rotYCur, &rotZCur);
float posXCur, posYCur, posZCur;
findPosition(relTime, &posXCur, &posYCur, &posZCur);
if (firstPointFlag == true)
{
transStartInverse = (pcl::getTransformation(posXCur, posYCur, posZCur, rotXCur, rotYCur, rotZCur)).inverse();
firstPointFlag = false;
}
// transform points to start
Eigen::Affine3f transFinal = pcl::getTransformation(posXCur, posYCur, posZCur, rotXCur, rotYCur, rotZCur);
Eigen::Affine3f transBt = transStartInverse * transFinal;
PointType newPoint;
// newpoint = transBt * [point|1]^T
newPoint.x = transBt(0,0) * point->x + transBt(0,1) * point->y + transBt(0,2) * point->z + transBt(0,3);
newPoint.y = transBt(1,0) * point->x + transBt(1,1) * point->y + transBt(1,2) * point->z + transBt(1,3);
newPoint.z = transBt(2,0) * point->x + transBt(2,1) * point->y + transBt(2,2) * point->z + transBt(2,3);
newPoint.intensity = point->intensity;
return newPoint;
}
/**
* 1. 过滤一些盲区数据
* 2. 跳线过滤压缩点云
* 3. 计算点云中的点的列索引
* 4. 点云运动畸变矫正
* 5. 点云深度计算
* */
void projectPointCloud()
{
int cloudSize = laserCloudIn->points.size();
// range image projection
for (int i = 0; i < cloudSize; ++i)
{
PointType thisPoint;
thisPoint.x = laserCloudIn->points[i].x;
thisPoint.y = laserCloudIn->points[i].y;
thisPoint.z = laserCloudIn->points[i].z;
thisPoint.intensity = laserCloudIn->points[i].intensity;
// 计算点云的距离,过滤掉属于盲区的点云
float range = pointDistance(thisPoint);
if (range < lidarMinRange || range > lidarMaxRange)
continue;
int rowIdn = laserCloudIn->points[i].ring;
if (rowIdn < 0 || rowIdn >= N_SCAN)
continue;
// downsampleRate 这个字段是用来滤波的压缩数据,downsampleRate =2 时 128线 ->64线
if (rowIdn % downsampleRate != 0)
continue;
int columnIdn = -1;
if (sensor == SensorType::VELODYNE || sensor == SensorType::OUSTER)
{ // 计算该点的水平夹角,
float horizonAngle = atan2(thisPoint.x, thisPoint.y) * 180 / M_PI;
//Horizon_SCAN=1800,每格0.2度
static float ang_res_x = 360.0/float(Horizon_SCAN);
//horizonAngle 为[-180,180],horizonAngle -90 为[-270,90],-round 为[-90,270], /ang_res_x 为[-450,1350]
//+Horizon_SCAN/2为[450,2250]
// 即把horizonAngle从[-180,180]映射到[450,2250]
columnIdn = -round((horizonAngle-90.0)/ang_res_x) + Horizon_SCAN/2;
//大于1800,则减去1800,相当于把1801~2250映射到1~450
//先把columnIdn从horizonAngle:(-PI,PI]转换到columnIdn:[H/4,5H/4],
//然后判断columnIdn大小,把H到5H/4的部分切下来,补到0~H/4的部分。
//将它的范围转换到了[0,H] (H:Horizon_SCAN)。
//这样就把扫描开始的地方角度为0与角度为360的连在了一起,非常巧妙。
//如果前方是x,左侧是y,那么正后方左边是180,右边是-180。
if (columnIdn >= Horizon_SCAN)
columnIdn -= Horizon_SCAN;
}
else if (sensor == SensorType::LIVOX)
{
columnIdn = columnIdnCountVec[rowIdn];
columnIdnCountVec[rowIdn] += 1;
}
if (columnIdn < 0 || columnIdn >= Horizon_SCAN)
continue;
if (rangeMat.at<float>(rowIdn, columnIdn) != FLT_MAX)
continue;
thisPoint = deskewPoint(&thisPoint, laserCloudIn->points[i].time);
rangeMat.at<float>(rowIdn, columnIdn) = range;
int index = columnIdn + rowIdn * Horizon_SCAN;
fullCloud->points[index] = thisPoint;
}
}
void cloudExtraction()
{
int count = 0;
// extract segmented cloud for lidar odometry
for (int i = 0; i < N_SCAN; ++i)
{
cloudInfo.startRingIndex[i] = count - 1 + 5;
for (int j = 0; j < Horizon_SCAN; ++j)
{
if (rangeMat.at<float>(i,j) != FLT_MAX)
{
// mark the points' column index for marking occlusion later
cloudInfo.pointColInd[count] = j;
// save range info
cloudInfo.pointRange[count] = rangeMat.at<float>(i,j);
// save extracted cloud
extractedCloud->push_back(fullCloud->points[j + i*Horizon_SCAN]);
// size of extracted cloud
++count;
}
}
cloudInfo.endRingIndex[i] = count -1 - 5;
}
}
void publishClouds()
{
cloudInfo.header = cloudHeader;
cloudInfo.cloud_deskewed = publishCloud(pubExtractedCloud, extractedCloud, cloudHeader.stamp, lidarFrame);
pubLaserCloudInfo.publish(cloudInfo);
}























 9383
9383











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








