文章目录
前言
interface是UVM验证过程中的一个重要的组件,主要起到连接测试用例与DUT的作用,具有简化代码,易于修改等特点。本文主要介绍interface中的modport和clocking的用法。
1 modport和clocking的介绍
modport和clocking都是interface组件中的块,主要用于对信号进行分组和同步采样。
1.1 modport
modport主要用于将接口中的信号进行分组,同时指定输入输出属性。
modprot的参数列表可以是port,也可以是clocking
interface i2;
wire a, b, c, d;
modport master (input a, b, output c, d);
modport slave (output a, b, input c, d);
endinterface
在上面例子中,modport将信号分为master和slave两组,并分别指定了其输入输出方向。
1.2 clocking
clocking时钟模块主要用于信号的同步和采样。
clocking skew决定了信号从时钟事件到采样或驱动的时间单位是多少。
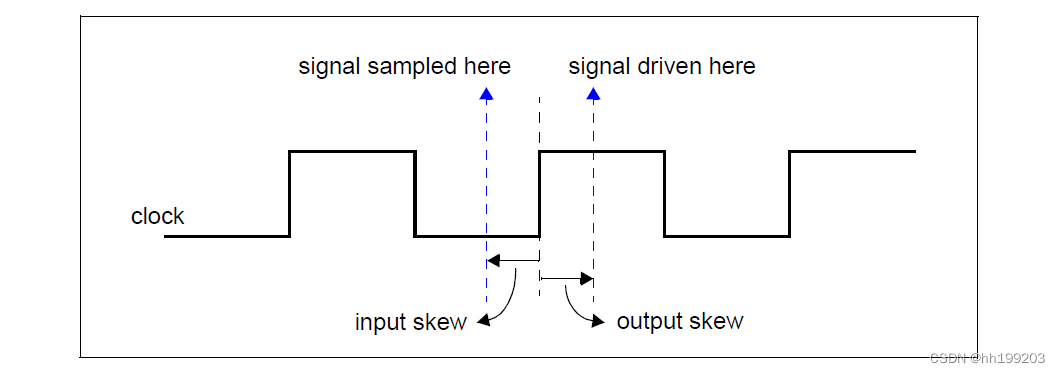
clocking bus @(posedge clock1);
default input #10ns output #2ns;
input data, ready, enable = top.mem1.enable;
output negedge ack;
input #1step addr;
endclocking
在上面的例子中,第一行声明了一个称为总线的时钟块,它将在信号clock1的正边缘上被计时。第二行指定在默认情况下,时钟块中的所有信号都将使用10ns的输入倾斜和2ns的输出倾斜。下一行将三个输入信号添加到时钟块中:data、ready和enable;最后一个信号指的是分层信号top.mem1.enable。第四行将信号ack添加到时钟块中,并覆盖默认输出倾斜,使ack被驱动在时钟的负边缘上。最后一行添加信号addr并覆盖默认的输入倾斜,以便addr在时钟的正边缘前一步被采样。
1.3 modport和clock之间的关系
interface A_Bus( input bit clk );
wire req, gnt;
wire [7:0] addr, data;
clocking sb @(posedge clk);
input gnt;
output req, addr;
inout data;
endclocking
modport STB ( clocking sb ); // synchronous testbench modport
endinterface
在上面例子中,主要演示clocking时钟块作为modport参数的用法。
从上面的例子中可以看出,modport介于interface和clocking之间,主要用于对信号进行分组,指定信号的输入输出方向,而clocking则是作用于信号的更底层,主要用于信号时序相关的控制,例如采样、同步等,当然clocking也可以指定信号的输入输出方向。(这么来看,modport好像没啥作用,modport能做的,clocking都能做。)
2 interface实战
下面主要演示一下interface在实际工程中的应用。
2.1 interface的例化
这里主要演示一个interface的具体实现。包含mst和mon两个clocking时钟块,分别用于driver和monitor组件的使用。另外一个dut的modport块,用于连接dut。
host_io.sv
`ifndef HOST_IO__SV
`define HOST_IO__SV
interface host_io(input logic clk);
logic wr_n, rd_n;
wire [15:0] address;
wire [15:0] data;
clocking mst @(posedge clk);
inout data;
output address;
output wr_n;
output rd_n;
endclocking
clocking mon @(posedge clk);
input data;
inout address;
input wr_n;
input rd_n;
endclocking
modport dut(input wr_n, rd_n, inout data, address);
endinterface: host_io
`endif
2.2 interface在验证组件中的应用
这里主要演示interface在driver、monitor以及agent中的应用。
2.2.1 driver
利用uvm_config_db的get函数获取interface的句柄。
host_driver.sv
class host_driver extends uvm_driver #(host_data);
`uvm_component_utils(host_driver)
virtual host_io vif;
function new(string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
`uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH);
endfunction: new
virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
`uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH);
uvm_config_db#(virtual host_io)::get(this, "", "vif", vif);
endfunction: build_phase
virtual function void end_of_elaboration_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.end_of_elaboration_phase(phase);
`uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH);
if (vif == null) begin
`uvm_fatal("CFGERR", "Interface for host driver not set");
end
endfunction: end_of_elaboration_phase
virtual task run_phase(uvm_phase phase);
`uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH);
forever begin
seq_item_port.get_next_item(req);
`uvm_info("RUN", { "Before process\n", req.sprint() }, UVM_FULL);
data_rw(req);
rsp = host_data::type_id::create("rsp", this);
rsp.set_id_info(req);
`uvm_info("RUN", { "After process\n", req.sprint() }, UVM_FULL);
seq_item_port.item_done();
end
endtask: run_phase
virtual task data_rw(host_data req);
`uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH);
if (req.addr inside {['h4000:'h4fff]}) begin // emulating RAM access
case(req.kind)
UVM_READ, UVM_BURST_READ: begin
vif.rd_n <= '0;
vif.address <= req.addr;
@(vif.mst);
req.data = vif.mst.data;
vif.rd_n <= '1;
vif.address <= 'z;
end
UVM_WRITE, UVM_BURST_WRITE: begin
vif.wr_n <= '0;
vif.data <= req.data;
vif.address <= req.addr;
@(vif.mst);
vif.wr_n <= '1;
vif.data <= 'z;
vif.address <= 'z;
end
default: begin `uvm_fatal("REGERR", $sformatf("%p is not a valid Register Command", req.kind)); end
endcase
end else begin // emulating register access
case(req.kind)
UVM_READ, UVM_BURST_READ: begin
vif.rd_n <= '0;
vif.address <= req.addr;
@(vif.mst);
req.data = vif.mst.data;
vif.rd_n <= '1;
vif.address <= 'z;
end
UVM_WRITE, UVM_BURST_WRITE: begin
vif.wr_n <= '0;
vif.data <= req.data;
vif.address <= req.addr;
@(vif.mst);
vif.wr_n <= '1;
vif.data <= 'z;
vif.address <= 'z;
end
default: begin `uvm_fatal("REGERR", $sformatf("%p is not a valid Register Command", req.kind)); end
endcase
end
endtask: data_rw
endclass: host_driver
2.2.2 monitor
利用uvm_config_db的get函数直接获取interface。
host_monitor.sv
class host_monitor extends uvm_monitor;
uvm_analysis_port #(host_data) analysis_port;
virtual host_io vif;
host_data tr;
`uvm_component_utils(host_monitor)
function new(string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
`uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH);
endfunction: new
virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
`uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH);
uvm_config_db#(virtual host_io)::get(this, "", "vif", vif);
analysis_port = new("analysis_port", this);
endfunction: build_phase
virtual function void end_of_elaboration_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.end_of_elaboration_phase(phase);
`uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH);
if (vif == null) begin
`uvm_fatal("CFGERR", "Interface for host monitor not set");
end
endfunction: end_of_elaboration_phase
virtual task run_phase(uvm_phase phase);
`uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH);
forever begin
tr = host_data::type_id::create("tr", this);
data_detect(tr);
`uvm_info("HOST_MON", {"\n", tr.sprint()}, UVM_HIGH);
analysis_port.write(tr);
end
endtask: run_phase
virtual task data_detect(host_data tr);
`uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH);
fork
begin
fork
wr_detect();
rd_detect();
join_any
disable fork;
end
join
endtask: data_detect
virtual task wr_detect();
@(vif.mon);
wait(vif.mon.wr_n == 0);
tr.addr = vif.mon.address;
tr.data = vif.mon.data;
tr.kind = UVM_WRITE;
`uvm_info("GOT_WRITE", {"\n", tr.sprint()}, UVM_FULL);
endtask: wr_detect
virtual task rd_detect();
@(vif.mon);
wait(vif.mon.rd_n == 0);
tr.addr = vif.mon.address;
tr.data = vif.mon.data;
tr.kind = UVM_READ;
`uvm_info("GOT_READ", {"\n", tr.sprint()}, UVM_FULL);
endtask: rd_detect
endclass: host_monitor
2.2.3 agent
在host_agent中,利用uvm_config_db的get函数获取interface,再利用uvm_config_db的set函数,将interface传递给底层的driver和monitor组件。
host_agent.sv
class host_agent extends uvm_agent;
typedef uvm_sequencer #(host_data) host_sequencer;
uvm_analysis_port #(host_data) analysis_port;
virtual host_io vif;
host_sequencer sqr;
host_driver drv;
host_monitor mon;
`uvm_component_utils(host_agent)
function new(string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
`uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH);
endfunction: new
virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
`uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH);
uvm_config_db#(virtual host_io)::get(this, "", "vif", vif);
uvm_config_db#(virtual host_io)::set(this, "*", "vif", vif);
if (is_active == UVM_ACTIVE) begin
sqr = host_sequencer::type_id::create("sqr", this);
drv = host_driver::type_id::create("drv", this);
end
mon = host_monitor::type_id::create("mon", this);
analysis_port = new("analysis_port", this);
endfunction: build_phase
virtual function void connect_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.connect_phase(phase);
`uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH);
if (is_active == UVM_ACTIVE) begin
drv.seq_item_port.connect(sqr.seq_item_export);
end
mon.analysis_port.connect(this.analysis_port);
endfunction: connect_phase
virtual function void end_of_elaboration_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.end_of_elaboration_phase(phase);
`uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH);
if (vif == null) begin
`uvm_fatal("CFGERR", "Interface for host agent not set");
end
endfunction: end_of_elaboration_phase
endclass: host_agent
2.3 interface在dut顶层的连接
在dut的顶层,将interface的接口与dut连接。
module router_test_top;
parameter simulation_cycle = 100 ;
bit SystemClock;
host_io host_if(SystemClock);
reset_io reset_if(SystemClock);
router dut(.clk(SystemClock),
.reset_n(reset_if.dut.reset_n),
.address(host_if.dut.address),
.wr_n(host_if.dut.wr_n),
.rd_n(host_if.dut.rd_n),
.data(host_if.dut.data));
initial begin
$fsdbDumpvars;
forever #(simulation_cycle/2) SystemClock = ~SystemClock ;
end
endmodule
2.4 interface在testbench顶层的连接
在testbench的顶层。利用uvm_resource_db将interface传递下去。
test.sv
program automatic test;
import uvm_pkg::*;
import router_test_pkg::*;
initial begin
uvm_resource_db#(virtual reset_io)::set("reset_vif", "", router_test_top.reset_if);
//
// Store the host interface in the resource database.
//
uvm_resource_db#(virtual host_io)::set("host_vif", "", router_test_top.host_if);
run_test();
end
endprogram
在test_base的build_phase中,利用uvm_resource_db的read_by_type得到interface,再利用uvm_config_db的set函数,将interface传递给底层的组件。
test_base.sv
class test_base extends uvm_test;
`uvm_component_utils(test_base)
router_env env;
virtual reset_io reset_vif;
virtual host_io host_vif
function new(string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
`uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH);
endfunction: new
virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
`uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH);
env = router_env::type_id::create("env", this);
uvm_resource_db#(virtual reset_io)::read_by_type("reset_vif", reset_vif, this);
uvm_config_db#(virtual reset_io)::set(this, "env.r_agt", "vif", reset_vif);
// The test is responsible for picking it up and configure the agent with the interface.
uvm_resource_db#(virtual host_io)::read_by_type("host_vif", host_vif, this);
uvm_config_db#(virtual host_io)::set(this, "env.h_agt", "vif", host_vif);
endfunction: build_phase
virtual function void final_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.final_phase(phase);
`uvm_info("TRACE", $sformatf("%m"), UVM_HIGH);
if (uvm_report_enabled(UVM_DEBUG, UVM_INFO, "TOPOLOGY")) begin
uvm_root::get().print_topology();
end
if (uvm_report_enabled(UVM_DEBUG, UVM_INFO, "FACTORY")) begin
uvm_factory::get().print();
end
endfunction: final_phase
endclass: test_base
3 interconnect
reg_define.svh
`define DMA_REG_MAX_ADDR_WIDTH 32
`define DMA_REG_MAX_DATA_WIDTH 32
reg_if.sv
`include "reg_define.svh"
interface reg_if (
input clk,
input rst_n
);
// interface pins
logic [`DMA_REG_MAX_ADDR_WIDTH-1:0] address; // 地址信号
logic req;
logic write_enable; // 写使能信号
logic [`DMA_REG_MAX_DATA_WIDTH-1:0] write_data; // 写数据
logic [`DMA_REG_MAX_DATA_WIDTH-1:0] read_data; // 读数据
clocking drv_ck @(posedge clk);
default input #1step output #1ps;
input read_data;
output address, req, write_enable, write_data;
endclocking : drv_ck
clocking mon_ck @(posedge clk);
default input #1step;
input address, req, write_enable, write_data, read_data;
endclocking : mon_ck
//modport dut_mp(input read_data, output address, req, write_enable, write_data);
// debug signals
endinterface
tb.sv
// interfaces
clk_rst_if clk_rst_if(.clk(clk), .rst_n(rst_n));
reg_if dma_reg_if(.clk(clk), .rst_n(rst_n));
// dut
dma dut (
.clk_i (clk ),
.reset_n (rst_n ),
.address (dma_reg_if.address),
.req (dma_reg_if.req),
.write_enable (dma_reg_if.write_enable),
.write_data (dma_reg_if.write_data),
.read_data (dma_reg_if.read_data)
);
总结
本主要总结了modport和clocking的基本用法,同时实战演示了interface的用法,以及在uvm环境中的传递方式。























 3662
3662











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








