Python+OpenCV:傅里叶变换(Fourier Transform)
####################################################################################################
# 图像傅里叶变换(Image Fourier Transform)
def lmc_cv_image_fourier_transform():
"""
函数功能: 图像傅里叶变换(Image Fourier Transform)。
"""
# Fourier Transform in Numpy
image = lmc_cv.imread('D:/99-Research/Python/Image/messi.jpg', flags=lmc_cv.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
fft_image = np.fft.fft2(image)
fft_shift_image = np.fft.fftshift(fft_image)
magnitude_spectrum = 20 * np.log(np.abs(fft_shift_image))
pyplot.figure('Fourier Transform in Numpy')
pyplot.subplot(1, 2, 1)
pyplot.imshow(image, cmap='gray')
pyplot.title('Original Image')
pyplot.xticks([])
pyplot.yticks([])
pyplot.subplot(1, 2, 2)
pyplot.imshow(magnitude_spectrum, cmap='gray')
pyplot.title('Magnitude Spectrum')
pyplot.xticks([])
pyplot.yticks([])
pyplot.show()
# high pass filtering and reconstruct the image in Numpy
rows, cols = image.shape
crow, ccol = rows // 2, cols // 2
fft_shift_image[crow - 30:crow + 31, ccol - 30:ccol + 31] = 0
fft_ishift = np.fft.ifftshift(fft_shift_image)
inverse_image_complex = np.fft.ifft2(fft_ishift)
inverse_image_real = np.real(inverse_image_complex)
pyplot.figure('HPF Fourier Transform in Numpy')
pyplot.subplot(1, 3, 1)
pyplot.imshow(image, cmap='gray')
pyplot.title('Original Image')
pyplot.xticks([])
pyplot.yticks([])
pyplot.subplot(1, 3, 2)
pyplot.imshow(inverse_image_real, cmap='gray')
pyplot.title('Image after HPF')
pyplot.xticks([])
pyplot.yticks([])
pyplot.subplot(1, 3, 3)
pyplot.imshow(inverse_image_real)
pyplot.title('High Pass Filtering Image')
pyplot.xticks([])
pyplot.yticks([])
pyplot.show()
# Fourier Transform in OpenCV
dft_image = lmc_cv.dft(np.float32(image), flags=lmc_cv.DFT_COMPLEX_OUTPUT)
dft_shift_image = np.fft.fftshift(dft_image)
magnitude_spectrum = 20 * np.log(lmc_cv.magnitude(dft_shift_image[:, :, 0], dft_shift_image[:, :, 1]))
pyplot.figure('Fourier Transform in OpenCV')
pyplot.subplot(1, 2, 1)
pyplot.imshow(image, cmap='gray')
pyplot.title('Original Image')
pyplot.xticks([])
pyplot.yticks([])
pyplot.subplot(1, 2, 2)
pyplot.imshow(magnitude_spectrum, cmap='gray')
pyplot.title('Magnitude Spectrum')
pyplot.xticks([])
pyplot.yticks([])
pyplot.show()
# low pass filtering and reconstruct the image in OpenCV
rows, cols = image.shape
crow, ccol = rows // 2, cols // 2
# create a mask first, center square is 1, remaining all zeros
mask = np.zeros((rows, cols, 2), np.uint8)
mask[crow - 30:crow + 30, ccol - 30:ccol + 30] = 1
# apply mask and inverse DFT
fft_shift_image = dft_shift_image * mask
fft_ishift = np.fft.ifftshift(fft_shift_image)
inverse_image = lmc_cv.idft(fft_ishift)
inverse_image = lmc_cv.magnitude(inverse_image[:, :, 0], inverse_image[:, :, 1])
pyplot.figure('LPF Fourier Transform in OpenCV')
pyplot.subplot(1, 2, 1)
pyplot.imshow(image, cmap='gray')
pyplot.title('Original Image')
pyplot.xticks([])
pyplot.yticks([])
pyplot.subplot(1, 2, 2)
pyplot.imshow(inverse_image, cmap='gray')
pyplot.title('Low Pass Filtering Image')
pyplot.xticks([])
pyplot.yticks([])
pyplot.show()
# Performance Optimization of DFT
print("{} {}".format(rows, cols))
nrows = lmc_cv.getOptimalDFTSize(rows)
ncols = lmc_cv.getOptimalDFTSize(cols)
print("{} {}".format(nrows, ncols))
# pad zeros method 1
new_image = np.zeros((nrows, ncols))
new_image[:rows, :cols] = image
# pad zeros method 2
right = ncols - cols
bottom = nrows - rows
bordertype = lmc_cv.BORDER_CONSTANT # just to avoid line breakup in PDF file
new_image = lmc_cv.copyMakeBorder(image, 0, bottom, 0, right, bordertype, value=0)
# calculate the DFT performance comparison of Numpy function
number = 1000
start_time = time.time()
for i in range(number):
np.fft.fft2(image)
print(f"{number} loops, best of {(time.time() - start_time) / number} ms per loop")
start_time = time.time()
for i in range(number):
np.fft.fft2(image, [nrows, ncols])
print(f"{number} loops, best of {(time.time() - start_time) / number} ms per loop")
# calculate the DFT performance comparison of OpenCV function
start_time = time.time()
for i in range(number):
lmc_cv.dft(np.float32(image), flags=lmc_cv.DFT_COMPLEX_OUTPUT)
print(f"{number} loops, best of {(time.time() - start_time) / number} ms per loop")
start_time = time.time()
for i in range(number):
lmc_cv.dft(np.float32(new_image), flags=lmc_cv.DFT_COMPLEX_OUTPUT)
print(f"{number} loops, best of {(time.time() - start_time) / number} ms per loop")
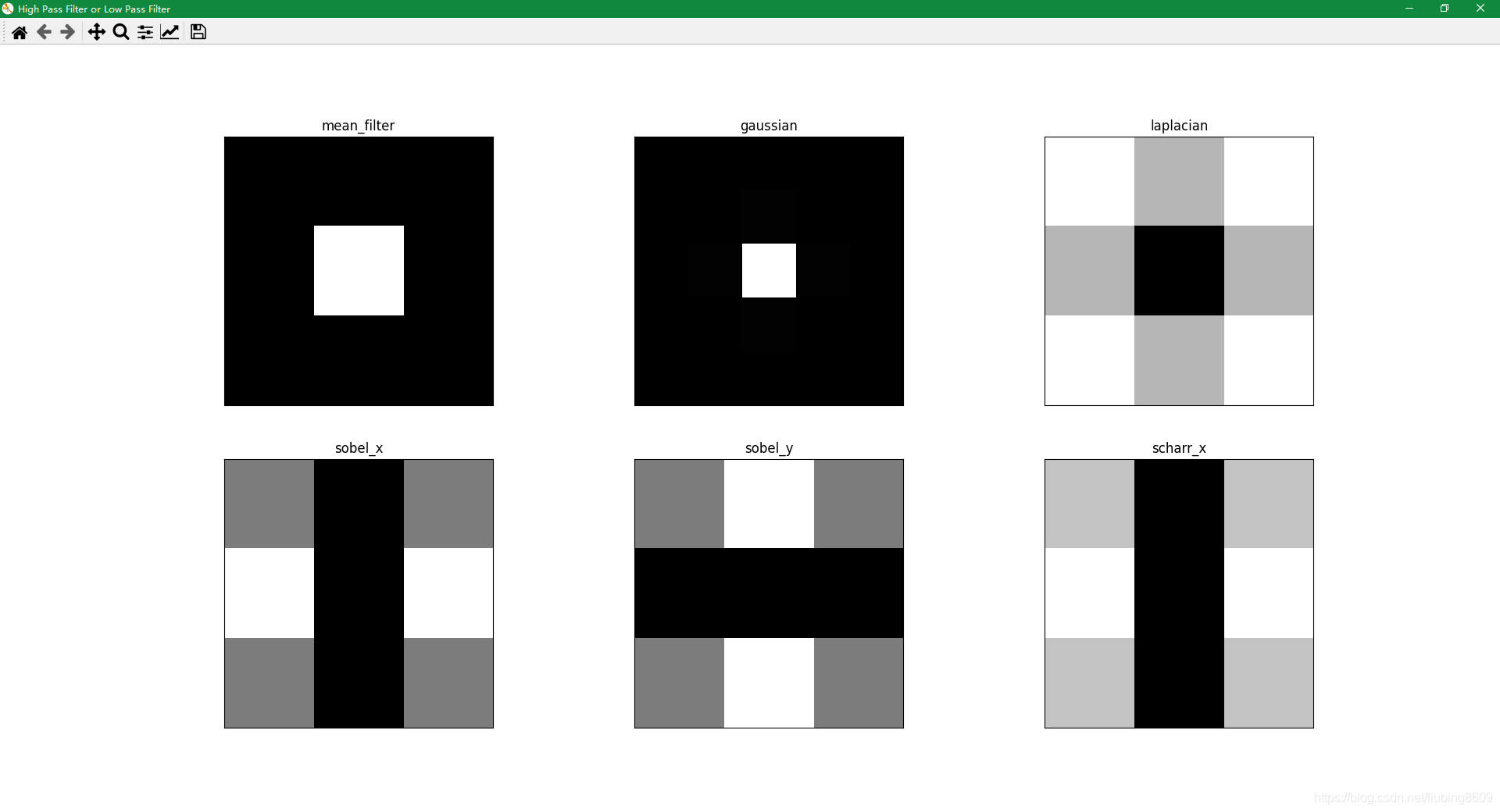
# High Pass Filter or Low Pass Filter
# simple averaging filter without scaling parameter
mean_filter = np.ones((3, 3))
# creating a gaussian filter
x = lmc_cv.getGaussianKernel(5, 10)
gaussian = x * x.T
# different edge detecting filters
# scharr in x-direction
scharr = np.array([[-3, 0, 3],
[-10, 0, 10],
[-3, 0, 3]])
# sobel in x direction
sobel_x = np.array([[-1, 0, 1],
[-2, 0, 2],
[-1, 0, 1]])
# sobel in y direction
sobel_y = np.array([[-1, -2, -1],
[0, 0, 0],
[1, 2, 1]])
# laplacian
laplacian = np.array([[0, 1, 0],
[1, -4, 1],
[0, 1, 0]])
filters = [mean_filter, gaussian, laplacian, sobel_x, sobel_y, scharr]
filter_name = ['mean_filter', 'gaussian', 'laplacian', 'sobel_x', 'sobel_y', 'scharr_x']
fft_filters = [np.fft.fft2(x) for x in filters]
fft_shift = [np.fft.fftshift(y) for y in fft_filters]
magnitude_spectrum = [20 * np.log(np.abs(z) + 1.00) for z in fft_shift]
pyplot.figure('High Pass Filter or Low Pass Filter')
for i in range(6):
pyplot.subplot(2, 3, i + 1)
pyplot.imshow(magnitude_spectrum[i], cmap='gray')
pyplot.title(filter_name[i])
pyplot.xticks([])
pyplot.yticks([])
pyplot.show()
# 根据用户输入保存图像
if ord("q") == (lmc_cv.waitKey(0) & 0xFF):
# 销毁窗口
pyplot.close('all')
return



Performance Optimization of DFT
581 739
600 750
calculate the DFT performance comparison of Numpy function:
1000 loops, best of 0.057367880821228026 ms per loop
1000 loops, best of 0.022089494943618775 ms per loop
calculate the DFT performance comparison of OpenCV function:
1000 loops, best of 0.010666451215744019 ms per loop
1000 loops, best of 0.005198104381561279 ms per loop










 本文详细介绍了如何使用Python的OpenCV库进行图像傅里叶变换,包括numpy和OpenCV两种方式的操作,展示了高通、低通滤波的应用,并比较了DFT性能。此外,还探讨了不同滤波器和优化DFT的方法。
本文详细介绍了如何使用Python的OpenCV库进行图像傅里叶变换,包括numpy和OpenCV两种方式的操作,展示了高通、低通滤波的应用,并比较了DFT性能。此外,还探讨了不同滤波器和优化DFT的方法。
















 3万+
3万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








