什么是有号距离场(SDF)?
有号距离场(SDF)是指建立一个空间场,这个空间场中每个像素或体素记录自己与周围像素或体素的距离,如果在物体内,则距离位负,如果是在外面则记录相差的距离,在边上刚好位0
在2D上的演示如下
原图:

SDF

简而言之他是一个记录空间距离的信息。
SDF能做什么?
1.高清文字(TMP)
2.形变动画
3.序列帧动画柔和过度
4.碰撞检测
5.软阴影
6.环境遮蔽(AO)
TMP:
用过TMP的人可能会有印象,他是一个友好距离文本,他本身的图片信息记录了他的距离场。

GPU是通过插值的方式来确定中间点的信息
对于位图来说,每个像素点是RGB颜色,插值周边的值没有实际意义。(数学上面的混合)。
但对于SDF来说,每个像素点是边界的有向距离,插值后得到新增的点,SDF就是利用了插值器的特性实现了光滑放大效果。
这一步只需要记录好有号距离场的图片,然后在shader中做插值就可以了。
举个例子:
fixed4 sdf = tex2D(_SDFTextTexture, i.uv);
float distance = sdf.a;
col.a = smoothstep(_DistanceMark - _SmoothDelta, _DistanceMark + _SmoothDelta, distance);
col.rgb = lerp(fixed3(0,0,0), fixed3(1,1,1), col.a);形变动画:

这是由两个有号距离场数据组成的

然后在两个距离场纹理的采样(记得线性空间,不要进行纹理压缩)中进行简单的Lerp操作。
序列帧动画柔和过度:
他的实现原理是在有号距离场的序列帧中,多采样一帧,然后在两帧之间进行时间上的过度。

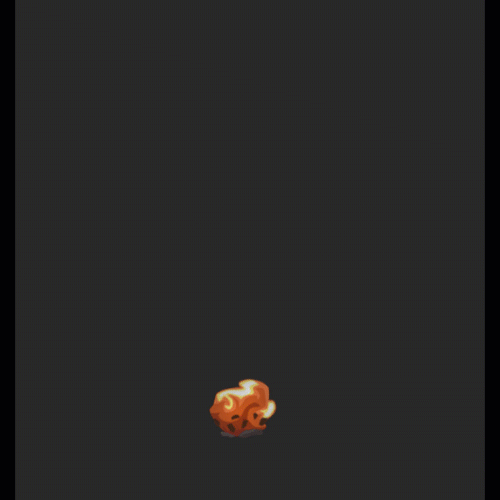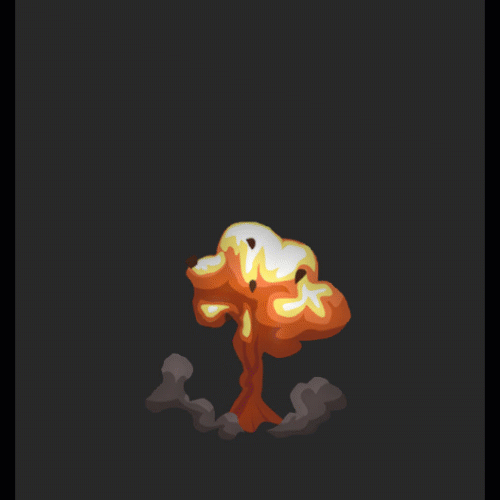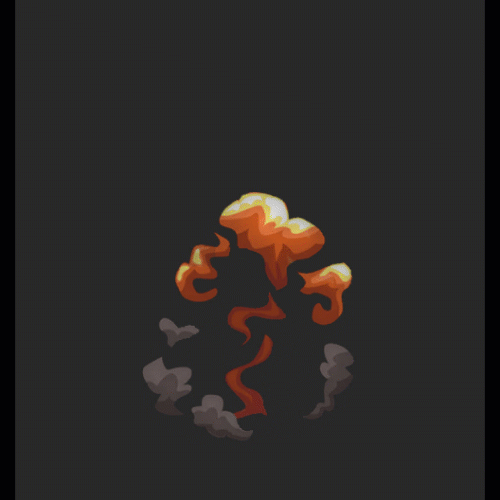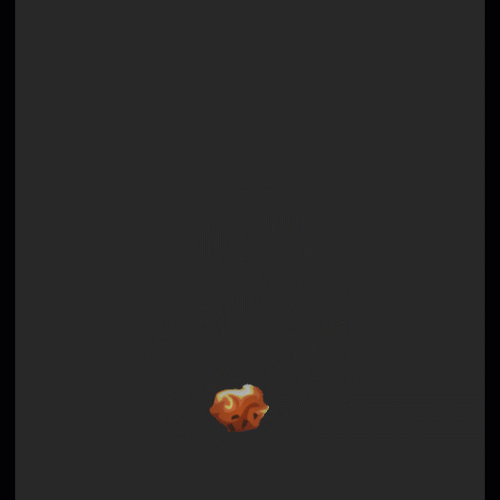
碰撞检测:
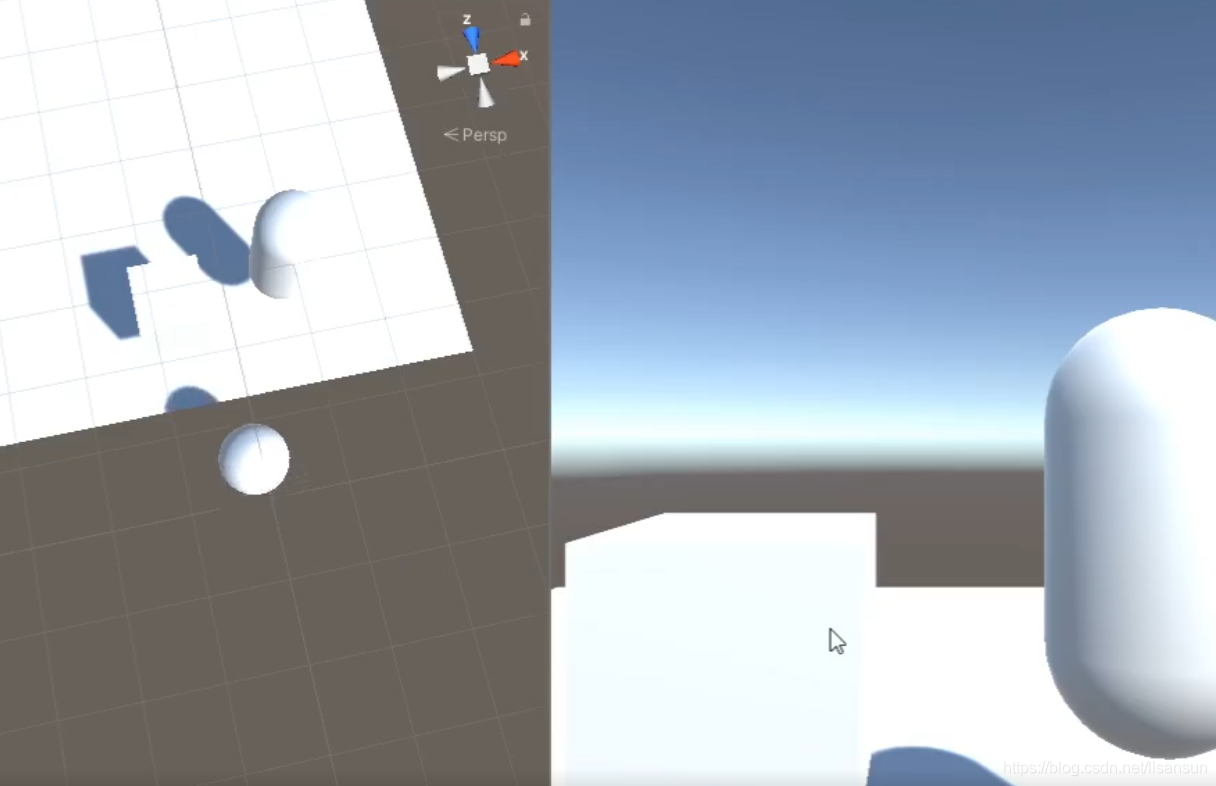
这个的实现过程可以详细说一下:
首先建立有号距离场:
for (int i = -half; i < half; i++)
{
for (int j = -half; j < half; j++)
{
for (int k = -half; k < half; k++)
{
bool isContinue = false;
for (int q = 0; q < SDFCollider.Length; q++)
{
Vector3 origin = new Vector3(i, j, k);
Vector3Int vector = new Vector3Int(Mathf.RoundToInt(i * floatToIntNum), Mathf.RoundToInt(j * floatToIntNum), Mathf.RoundToInt(k * floatToIntNum));
Vector3 dir = (SDFCollider[q].transform.position - origin).normalized;
Ray ray = new Ray(origin, dir);
if (Physics.Raycast(ray, 1f))
{
SubSDF(new Vector3(i, j, k), SDFCollider);
isContinue = true;
continue;
}
AddSDFData(vector, ray);
}
if (isContinue)
{
continue;
}
}
}
}这里的做法是在-half到half之间,根据SDFCollider所有collider的中心为方向,发射射线检测是否有撞到对象表面,如果没有则记录距离。(注意这里ijk是用int来执行增加的,也就相当于说我这里是用1为一个体素来步进的)。
如果有撞到表面,则表示这里有碰撞体,需要细化碰撞体,我这里是在SubSDF中继续检测更细的距离场。
private void SubSDF(Vector3 startVector, Transform[] trans)
{
float interval = 0.1f;
for (float i = startVector.x-1; i <= startVector.x + 1; i+= interval)
{
for (float j = startVector.y-1; j <= startVector.y + 1; j += interval)
{
for (float k = startVector.z-1; k <= startVector.z + 1; k += interval)
{
bool isContinue = false;
for (int q = 0; q < trans.Length; q++)
{
Vector3 origin = new Vector3(i, j, k);
Vector3Int vector = new Vector3Int(Mathf.RoundToInt(i * floatToIntNum), Mathf.RoundToInt(j * floatToIntNum), Mathf.RoundToInt(k * floatToIntNum));
Vector3 dir = (trans[q].transform.position - origin).normalized;
Ray ray = new Ray(origin, dir);
if (Physics.Raycast(ray, (interval + 0.1f)))
{
AddSDF(vector, -1);
isContinue = true;
continue;
}
AddSDFData(vector, ray);
}
if (isContinue)
{
continue;
}
}
}
}
}在SubSDF中我会以0.1的间隔为单位去步进找碰撞点,如果有碰撞点就AddSDFData加入到sdf数据里面。
这里用到了树的数据结构,相当于没有碰撞数据就以1为步进,如果有碰撞数据则说明在这1米内有碰撞体,则细化到0.1米为单位步进。
如果可视化的看这些有号距离场覆盖的边界则可以看到类似这样的情况
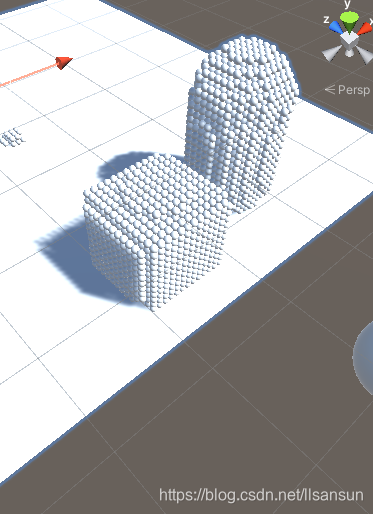
有号距离场检测:
检测有两种方式:
第一种是比较简单的根据碰撞体的数量,遍历然后拿他们的中心跟当前点的中心的位置相减为方向,然后在这里步进,如果步进的这个距离有距离场数据,并且他的值为小于0的,则说明他碰撞到边缘了,不让他走过去。
for (int i = 0; i < SDFCreator.SDFCollider.Length; i++)
{
Vector3 radius = (SDFCreator.SDFCollider[i].transform.position - this.transform.position).normalized * 0.4f;
Vector3 newPos = this.transform.position;
Vector3 circle = newPos + radius;
Vector3Int vector = new Vector3Int(Mathf.RoundToInt(circle.x * SDFCreator.floatToIntNum), Mathf.RoundToInt(circle.y * SDFCreator.floatToIntNum), Mathf.RoundToInt(circle.z * SDFCreator.floatToIntNum));
if (SDFCreator.mSDFValue.ContainsKey(vector))
{
//Debug.Log("distance:" + SDFCreator.mSDFValue[vector]);
if (SDFCreator.mSDFValue[vector] < 0)
{
//Debug.LogError("hit");
this.transform.position -= pos;
break;
//Vector3 normalDir =
}
}
}第二种就比较复杂,是增对比较多碰撞体的情况下比较适用,但是也会增加额外的内存。也就是用八叉树记录当前有号距离场在的区域。
具体判断就是一层一层的往下走,直到最小单元都有碰撞数据了说明就是碰撞上了。
创建场和移动的代码是:
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class SDFCreator : MonoBehaviour
{
public static Dictionary<Vector3Int, float> mSDFValue = new Dictionary<Vector3Int, float>();
public int TotalNum = 50;
public const float floatToIntNum = 10.0f;
public static Transform[] SDFCollider;
// Start is called before the first frame update
void Start()
{
CreateSDF();
//ShowSDF();
RemoveCollider();
}
private void AddSDF(Vector3Int vector, float value)
{
if (mSDFValue.ContainsKey(vector))
{
if (value < mSDFValue[vector])
{
mSDFValue[vector] = value;
}
}
else
{
mSDFValue.Add(vector, value);
}
}
private void ShowSDF()
{
foreach(var sdf in mSDFValue)
{
if (sdf.Value < 0)
{
GameObject go = GameObject.CreatePrimitive(PrimitiveType.Sphere);
Component.Destroy(go.GetComponent<Collider>());
go.transform.SetParent(this.transform);
go.transform.position = new Vector3((float)sdf.Key.x / floatToIntNum, (float)sdf.Key.y / floatToIntNum, (float)sdf.Key.z / floatToIntNum);
go.transform.localScale = new Vector3(0.1f, 0.1f, 0.1f);
}
}
}
private void SubSDF(Vector3 startVector, Transform[] trans)
{
float interval = 0.1f;
for (float i = startVector.x-1; i <= startVector.x + 1; i+= interval)
{
for (float j = startVector.y-1; j <= startVector.y + 1; j += interval)
{
for (float k = startVector.z-1; k <= startVector.z + 1; k += interval)
{
bool isContinue = false;
for (int q = 0; q < trans.Length; q++)
{
Vector3 origin = new Vector3(i, j, k);
Vector3Int vector = new Vector3Int(Mathf.RoundToInt(i * floatToIntNum), Mathf.RoundToInt(j * floatToIntNum), Mathf.RoundToInt(k * floatToIntNum));
Vector3 dir = (trans[q].transform.position - origin).normalized;
Ray ray = new Ray(origin, dir);
if (Physics.Raycast(ray, (interval + 0.1f)))
{
AddSDF(vector, -1);
isContinue = true;
continue;
}
AddSDFData(vector, ray);
}
if (isContinue)
{
continue;
}
}
}
}
}
private void AddSDFData(Vector3Int vector, Ray ray)
{
RaycastHit[] hits = Physics.RaycastAll(ray);
if (hits.Length > 0)
{
float minDistance = 10000;
foreach (var hit in hits)
{
minDistance = Mathf.Min(hit.distance, minDistance);
}
AddSDF(vector, minDistance);
}
}
public void CreateSDF()
{
SDFCollider = this.GetComponentsInChildren<Transform>();
int half = TotalNum / 2;
for (int i = -half; i < half; i++)
{
for (int j = -half; j < half; j++)
{
for (int k = -half; k < half; k++)
{
bool isContinue = false;
for (int q = 0; q < SDFCollider.Length; q++)
{
Vector3 origin = new Vector3(i, j, k);
Vector3Int vector = new Vector3Int(Mathf.RoundToInt(i * floatToIntNum), Mathf.RoundToInt(j * floatToIntNum), Mathf.RoundToInt(k * floatToIntNum));
Vector3 dir = (SDFCollider[q].transform.position - origin).normalized;
Ray ray = new Ray(origin, dir);
if (Physics.Raycast(ray, 1f))
{
SubSDF(new Vector3(i, j, k), SDFCollider);
isContinue = true;
continue;
}
AddSDFData(vector, ray);
}
if (isContinue)
{
continue;
}
}
}
}
}
private void RemoveCollider()
{
foreach (var c in SDFCollider)
{
Component.Destroy(c.GetComponent<Rigidbody>());
Component.Destroy(c.GetComponent<Collider>());
}
}
private void Update()
{
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.Space))
{
OCTree();
}
}
public struct ocTree
{
public Vector3 startPos;
public float Len;
}
private void OCTree()
{
int half = TotalNum / 2;
CreateOCTree(-half, 0, -half, 0, -half, 0, half, 1);
}
private Dictionary<int, List<ocTree>> mOCTrees = new Dictionary<int, List<ocTree>>();
private void CreateOCTree(float left, float right, float top, float bottom, float front, float back, float len, int index, bool isAddIndex = true)
{
int nextIndex = index;
if (isAddIndex)
{
nextIndex = index + 1;
}
if (nextIndex >= 10000)
{
return;
}
ocTree lefttopfront = new ocTree();
lefttopfront.startPos = new Vector3(left, top, front);
lefttopfront.Len = len;
ocTree lefttopback = new ocTree();
lefttopback.startPos = new Vector3(left, top, back);
lefttopback.Len = len;
ocTree leftbottomfront = new ocTree();
leftbottomfront.startPos = new Vector3(left, bottom, front);
leftbottomfront.Len = len;
ocTree leftbottomback = new ocTree();
leftbottomback.startPos = new Vector3(left, bottom, back);
leftbottomback.Len = len;
ocTree righttopfront = new ocTree();
righttopfront.startPos = new Vector3(right, top, front);
righttopfront.Len = len;
ocTree righttopback = new ocTree();
righttopback.startPos = new Vector3(right, top, back);
righttopback.Len = len;
ocTree rightbottomfront = new ocTree();
rightbottomfront.startPos = new Vector3(right, bottom, front);
rightbottomfront.Len = len;
ocTree rightbottomback = new ocTree();
rightbottomback.startPos = new Vector3(right, bottom, back);
rightbottomback.Len = len;
List<ocTree> trees = new List<ocTree>();
trees.Add(lefttopfront);
trees.Add(lefttopback);
trees.Add(leftbottomfront);
trees.Add(leftbottomback);
trees.Add(righttopfront);
trees.Add(righttopback);
trees.Add(rightbottomfront);
trees.Add(rightbottomback);
mOCTrees.Add(index, trees);
for (int j = 0; j < trees.Count; j++)
{
Vector3Int vectorStart = new Vector3Int(Mathf.RoundToInt(trees[j].startPos.x * floatToIntNum),
Mathf.RoundToInt(trees[j].startPos.y * floatToIntNum),
Mathf.RoundToInt(trees[j].startPos.z * floatToIntNum));
Vector3Int vectorEnd = new Vector3Int(Mathf.RoundToInt((trees[j].startPos.x + trees[j].Len) * floatToIntNum),
Mathf.RoundToInt((trees[j].startPos.y + trees[j].Len) * floatToIntNum),
Mathf.RoundToInt((trees[j].startPos.z + trees[j].Len) * floatToIntNum));
SubTrees(vectorStart, vectorEnd, nextIndex, trees[j], j);
}
}
private void SubTrees(Vector3Int vectorStart, Vector3Int vectorEnd, int nextIndex, ocTree tree, int nextIndex2)
{
for (int ii = vectorStart.x; ii < vectorEnd.x; ii++)
{
for (int jj = vectorStart.y; jj < vectorEnd.y; jj++)
{
for (int kk = vectorStart.z; kk < vectorEnd.z; kk++)
{
Vector3Int searchPos = new Vector3Int(ii, jj, kk);
if (mSDFValue.ContainsKey(searchPos) && mSDFValue[searchPos] < 0)
{
int cIndex = nextIndex * 10 + (nextIndex2 + 1);
float clen = tree.Len / 2;
float cleft = tree.startPos.x;
float cright = cleft + clen;
float ctop = tree.startPos.y;
float cbottom = ctop + clen;
float cfront = tree.startPos.z;
float cback = cfront + clen;
CreateOCTree(cleft, cright, ctop, cbottom, cfront, cback, clen, cIndex, false);
return;
}
}
}
}
}
}using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class Move : MonoBehaviour
{
public float _speed = 2f;
// Start is called before the first frame update
void Start()
{
}
// Update is called once per frame
void Update()
{
Vector3 pos = Vector3.zero;
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.A))
{
pos.x -= Time.deltaTime * _speed;
}
else if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.D))
{
pos.x += Time.deltaTime * _speed;
}
else if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.W))
{
pos.z += Time.deltaTime * _speed;
}
else if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.S))
{
pos.z -= Time.deltaTime * _speed;
}
CheckHit(pos);
}
private void CheckHit(Vector3 pos)
{
this.transform.position += pos;
if (SDFCreator.SDFCollider == null)
{
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < SDFCreator.SDFCollider.Length; i++)
{
Vector3 radius = (SDFCreator.SDFCollider[i].transform.position - this.transform.position).normalized * 0.4f;
Vector3 newPos = this.transform.position;
Vector3 circle = newPos + radius;
Vector3Int vector = new Vector3Int(Mathf.RoundToInt(circle.x * SDFCreator.floatToIntNum), Mathf.RoundToInt(circle.y * SDFCreator.floatToIntNum), Mathf.RoundToInt(circle.z * SDFCreator.floatToIntNum));
if (SDFCreator.mSDFValue.ContainsKey(vector))
{
//Debug.Log("distance:" + SDFCreator.mSDFValue[vector]);
if (SDFCreator.mSDFValue[vector] < 0)
{
//Debug.LogError("hit");
this.transform.position -= pos;
break;
//Vector3 normalDir =
}
}
}
}
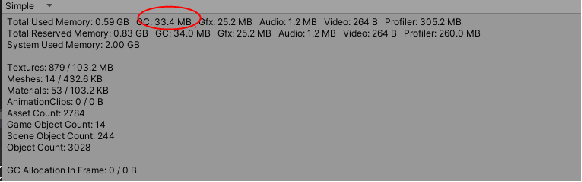
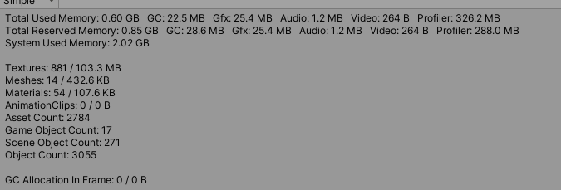
}cpu消耗对比:
有号距离场:

碰撞检测消耗

内存:
有号距离场消耗:
碰撞检测消耗:
软阴影:
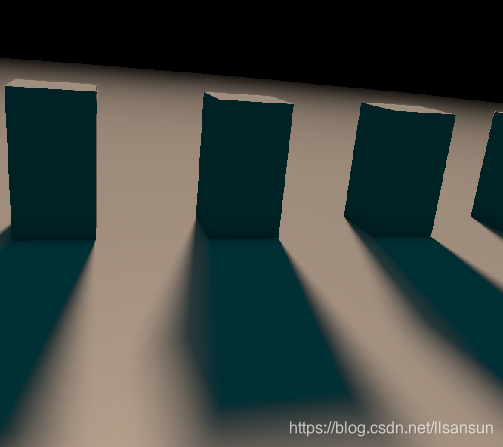
这个是用一个光线步进创建地板和方块的方式来演示。
参考:https://www.shadertoy.com/view/lsKcDD
实现的步骤是:
1.从摄像机角度出发(通过旋转及位置偏移后),对每个像素都步进直线方向,如果步进的方向能找到有号距离场的对象,则进行下一步。这里说明下他找了两个实时距离场,一个是地板,地板的距离场比较好确定,就是一个高度,如果在这个高度上就是说明是地板。另一个是盒子box,box的判断方式是先abs(p)让他从6个象限转到3个正向的象限,因为box是对称的。然后减去他的长宽高
float3 d = abs(p) - b;如果d都为负数,说明这个点在box内,则min(max(d.x, max(d.y, d.z)), 0.0)=0,length(max(d, 0.0))也为0.如果有一个不为负数则有距离。
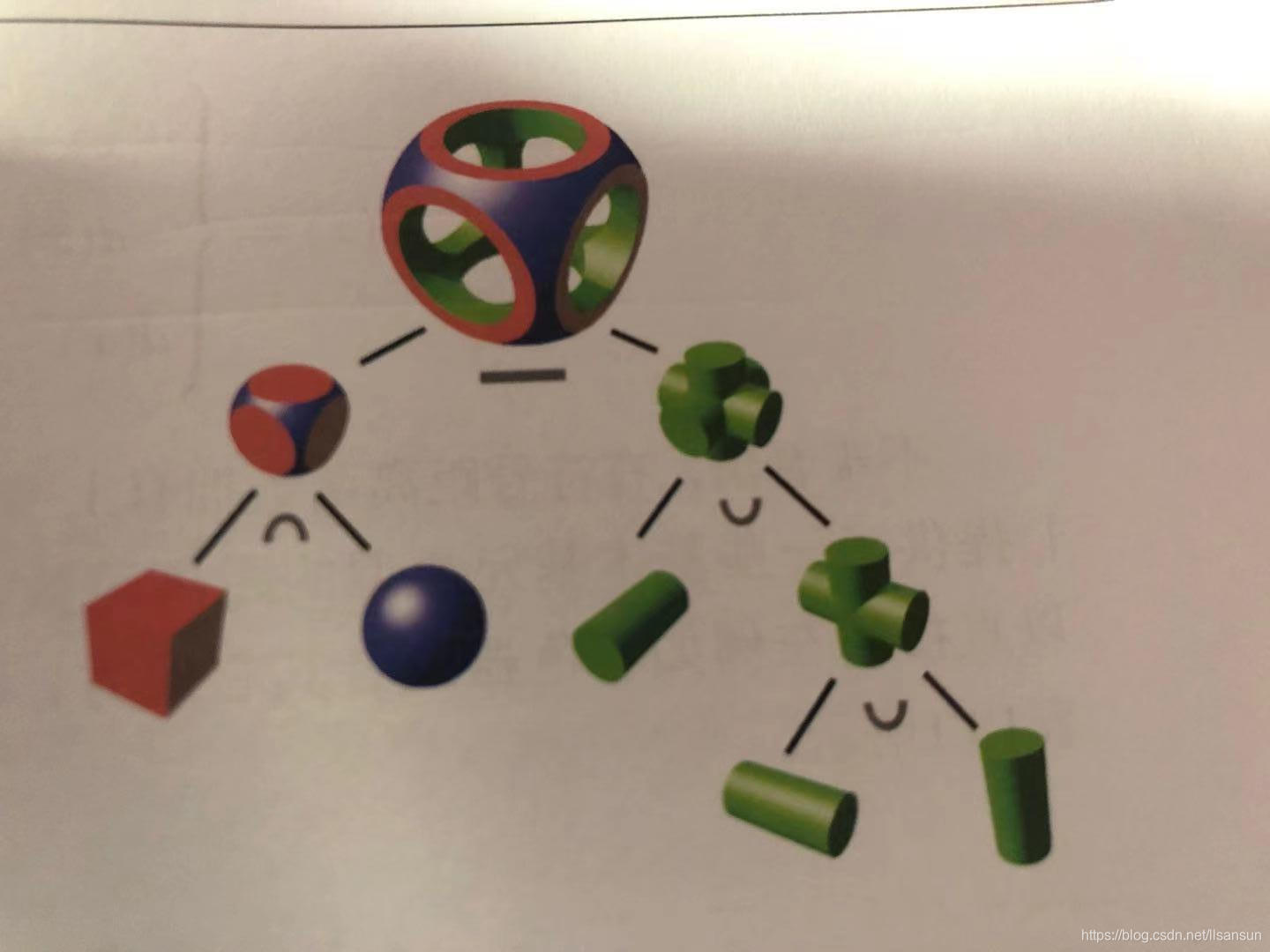
有号距离场判断是否有碰到物体是可以这样表述:
1.f(x)=min(f1(x),f2(x))表示在区域f1(x)和f2(x)内部的联合。
2.f(x)=max(f1(x),f2(x))表示区域f1(x)和f2(x)内部的相交。
3.f1(x)的补集可以定义为f(x)=-f1(x)
4.f(x)=max(f1(x),-f2(x))表示从区域f1(x)内部减去区域f2(x)的内部。
然后多个物体间的结合可以形成想要的形状,比如
然后如圆球的表示可以为:

float sdSphere(float3 p, float s)
{
return length(p) - s;
}圆环的表示可以为:

float sdTorus(float3 p, float2 t)
{
float2 q = float2(length(p.xz) - t.x, p.y);
return length(q) - t.y;
}2.如果有碰撞的物体,则直接半径到这个距离t内找到他的法线(这也是有号距离场的优点,他不像普通的光线步进,每次都固定的步长,他这个是精确的指导下一个碰撞的点在哪里,所以半径能很容易确定)。
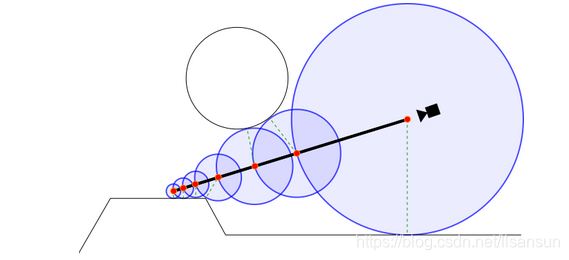
法线的获取是构建四个点 k0 = {1,-1,-1}, k1 = {-1,-1,1}, k2 = {-1,1,-1} and k3 = {1,1,1}. 其实就是构建了一个锥形,当前p点在锥形的中心部分,然后对四个点做偏移。最终就可求出当前的P的的斜率。
vec3 calcNormal( in vec3 pos )
{
vec2 e = vec2(1.0,-1.0)*0.5773*0.0005;
return normalize( e.xyy*map( pos + e.xyy ).x +
e.yyx*map( pos + e.yyx ).x +
e.yxy*map( pos + e.yxy ).x +
e.xxx*map( pos + e.xxx ).x );
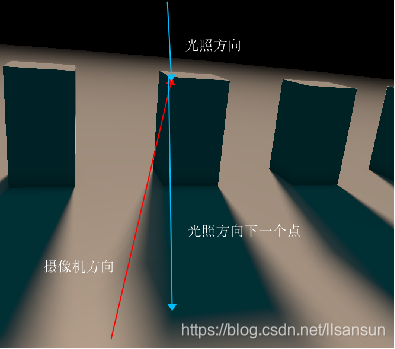
}3.然后关键是计算阴影:
计算阴影是找到当前摄像机步进来的点然后研光照方向找下一个点,这个点就是我们的阴影点了。
4.最后就是他要呈现软阴影,就得有一些虚化的效果,这里用的是s*s*(3.0-2.0*s)的公式,他的意义是3次方的衰减,用这个公式的原理是要得到f(0)=0,f(1)=1,f(0.5)=0.5的值。
5.然后还有一步是要计算AO,这里计算ao是沿着法线方向上找最近的物体。比如地面和物体相近,则法线方向找的下个点就是地面的点,自然可以得出d,那么久能算出他的ao。根据他们的距离来确定一个ao颜色深度大小。
其他都是比较普通的方式:
完整代码:
//
// Testing Sebastian Aaltonen's soft shadow improvement
//
// The technique is based on estimating a better closest point in ray
// at each step by triangulating from the previous march step.
//
// More info about the technique at slide 39 of this presentation:
// https://www.dropbox.com/s/s9tzmyj0wqkymmz/Claybook_Simulation_Raytracing_GDC18.pptx?dl=0
//
// Traditional technique: http://iquilezles.org/www/articles/rmshadows/rmshadows.htm
//
// Go to lines 54 to compare both.
// make this 1 is your machine is too slow
#define AA 1
float3 _Light;
//------------------------------------------------------------------
float sdPlane(float3 p)
{
return p.y;
}
float sdBox(float3 p, float3 b)
{
float3 d = abs(p) - b;//abs(p)将6个象限转为3个想象(全为正数),减去b就是减去他的长宽高
//如果d都为负数,说明这个点在box内,则min(max(d.x, max(d.y, d.z)), 0.0)=0,length(max(d, 0.0))也为0.
//如果有一个不为负数则有距离
return min(max(d.x, max(d.y, d.z)), 0.0) + length(max(d, 0.0));
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------
//通过距离场来确定步进的位置是地板还是box
float map(in float3 pos)
{
float3 qos = float3(frac(pos.x + 0.5) - 0.5, pos.yz);//这里通过frac取余的方式可以根据x轴分割出多个
return min(sdPlane(pos.xyz - float3(0.0, 0.00, 0.0)),
sdBox(qos.xyz - float3(0.0, 0.25, 0.0), float3(0.2, 0.5, 0.2)));
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------
//ro是当前的点,rd是灯光方向
float calcSoftshadow(in float3 ro, in float3 rd, in float mint, in float tmax, int tech)
{
float res = 1.0;
float t = mint;
float ph = 1e10; // big, such that y = 0 on the first iteration
for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++)
{
float h = map(ro + rd * t);
// traditional tech
if (tech == 0)
{
//传统方式是用10*位置的距离除上一次位置距离
res = min(res, 10.0*h / t);
}
// improved tech
else
{
// use this if you are getting artifact on the first iteration, or unroll the
// first iteration out of the loop
//float y = (i==0) ? 0.0 : h*h/(2.0*ph);
float y = h * h / (2.0*ph);
float d = sqrt(h*h - y * y);
res = min(res, 10.0*d / max(0.0, t - y));
ph = h;
}
t += h;//使路长到了h这么远之后再步进,才能找到灯光方向过来的当前位置的rd方向的投影位置
if (res<0.0001 || t>tmax) break;
}
res = clamp(res, 0.0, 1.0);
return res * res*(3.0 - 2.0*res);//这里输出的就是3次方的衰减,用这个公式的原理是要得到f(0)=0,f(1)=1,f(0.5)=0.5的值
}
//上下左右距离场步进的方式找到点,然后相加并有权重得到他的中心的法线信息
float3 calcNormal(in float3 pos)
{
//我们构建四个点 k0 = {1,-1,-1}, k1 = {-1,-1,1}, k2 = {-1,1,-1} and k3 = {1,1,1}. 其实就是构建了一个锥形,当前p点在锥形的中心部分,然后对四个点做偏移。最终就可求出当前的P的的斜率。
float2 e = float2(1.0, -1.0)*0.5773*0.0005;
return normalize(e.xyy*map(pos + e.xyy) +
e.yyx*map(pos + e.yyx) +
e.yxy*map(pos + e.yxy) +
e.xxx*map(pos + e.xxx));
}
//ro是摄像机位置,rd是步进方向
float castRay(in float3 ro, in float3 rd)
{
float tmin = 1.0;
float tmax = 20.0;
#if 1
// bounding volume
float tp1 = (0.0 - ro.y) / rd.y; if (tp1 > 0.0) tmax = min(tmax, tp1);
float tp2 = (1.0 - ro.y) / rd.y; if (tp2 > 0.0) {
if (ro.y > 1.0) tmin = max(tmin, tp2);
else tmax = min(tmax, tp2);
}
#endif
//这里首先以0.0005的半径为起步来步进,找到每次rd方向的和plane和box的最小距离,作为下个步进的大小。不断的步进到超过范围
float t = tmin;
for (int i = 0; i < 64; i++)
{
float precis = 0.0005*t;
float res = map(ro + rd * t);
if (res<precis || t>tmax) break;//res<precis说明当前点在物体内部,停止步进
t += res;
}
if (t > tmax) t = -1.0;
return t;
}
float calcAO(in float3 pos, in float3 nor)
{
float occ = 0.0;
float sca = 1.0;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
float h = 0.001 + 0.15*float(i) / 4.0;
float d = map(pos + h * nor);//法线方向上找最近的物体。比如地面和物体相近,则法线方向找的下个点就是地面的点,自然可以得出d,那么久能算出他的ao。
occ += (h - d)*sca;//根据他们的距离来确定一个ao颜色深度大小
sca *= 0.95;//深度大小递减
}
return clamp(1.0 - 1.5*occ, 0.0, 1.0);
}
//ro是摄像机位置,rd是步进方向
float3 render(in float3 ro, in float3 rd, in int tech)
{
float3 col = float3(0,0,0);
float t = castRay(ro, rd);//有了距离场sdplane和sdbox,可以大范围步进到指定点得到t为这个方向的距离
if (t > -0.5)
{
float3 pos = ro + t * rd;//摄像机方向步进
float3 nor = calcNormal(pos);
// material
float3 mate = float3(0.3,0.3,0.3);
// key light
//float3 lig = normalize(float3(-0.1, 0.3, 0.6));
float3 hal = normalize(_Light - rd);
//漫反射以及他的阴影,阴影用步进得到光线方向上的下一个投影到的点就是阴影点,然后用3次方的衰减让他成为软阴影
float dif = clamp(dot(nor, _Light), 0.0, 1.0) *
calcSoftshadow(pos, _Light, 0.01, 3.0, tech);//摄像机方向步进的点然后看光照方向的阴影
//高光
float spe = pow(clamp(dot(nor, hal), 0.0, 1.0), 16.0)*
dif *
(0.04 + 0.96*pow(clamp(1.0 + dot(hal, rd), 0.0, 1.0), 5.0));
//颜色为材质本身颜色跟漫反射以及软阴影结合
col = mate * 4.0*dif*float3(1.00, 0.70, 0.5);
//再加上高光
col += 12.0*spe*float3(1.00, 0.70, 0.5);
// ambient light
float occ = calcAO(pos, nor);
float amb = clamp(0.5 + 0.5*nor.y, 0.0, 1.0);
col += mate * amb*occ*float3(0.0, 0.08, 0.1);
// fog
col *= exp(-0.0005*t*t*t);
}
return col;
}
float3x3 setCamera(in float3 ro, in float3 ta, float cr)
{
float3 cw = normalize(ta - ro);//摄像机外一点与摄像机得到的方向,这个就是其中一个轴
float3 cp = float3(sin(cr), cos(cr), 0.0);//摄像机旋转角度
float3 cu = normalize(cross(cw, cp));//叉乘后得到摄像机一个轴
float3 cv = normalize(cross(cu, cw));//通过另一个叉乘得到另一个轴。
return float3x3(cu, cv, cw);//摄像机的坐标(xyz轴)
}
void mainImage(out float4 fragColor, in float2 fragCoord, in float2 iResolution)
{
// camera
float iTime = _Time.y;
float an = 12.0 - sin(0.1*iTime);
float3 ro = float3(3.0*cos(0.1*an), 1, -3.0*sin(0.1*an));//摄像机位置
float3 ta = float3(0.0, 2, 0.0);//外面的一点,决定摄像机的坐标系
// camera-to-world transformation
float3x3 ca = setCamera(ro, ta, 0.0);
int tech = (frac(iTime / 2.0) > 0.5) ? 1 : 0;
float3 tot = float3(0,0,0);
#if AA>1
for (int m = 0; m < AA; m++)
for (int n = 0; n < AA; n++)
{
// pixel coordinates
float2 o = float2(float(m), float(n)) / float(AA) - 0.5;
float2 p = (-iResolution.xy + 2.0*(fragCoord + o)) / iResolution.y;
#else
float2 p = (-iResolution.xy + 2.0*fragCoord) / iResolution.y;//(-iResolution.xy + 2.0*fragCoord)是把相机设置到-1到1,然后除iResolution.y相当于乘以一个屏幕大小
#endif
// ray direction
float3 rd = mul(ca, normalize(float3(p.xy, 2.0)));//屏幕空间的坐标转到摄像机空间
// render
float3 col = render(ro, rd, tech);
// gamma
col = pow(col, 0.4545);//pow(col, float3(0.4545));
tot += col;
#if AA>1
}
tot /= float(AA*AA);
#endif
fragColor = float4(tot, 1.0);
}环境遮蔽(AO)
什么是环境遮蔽(AO)
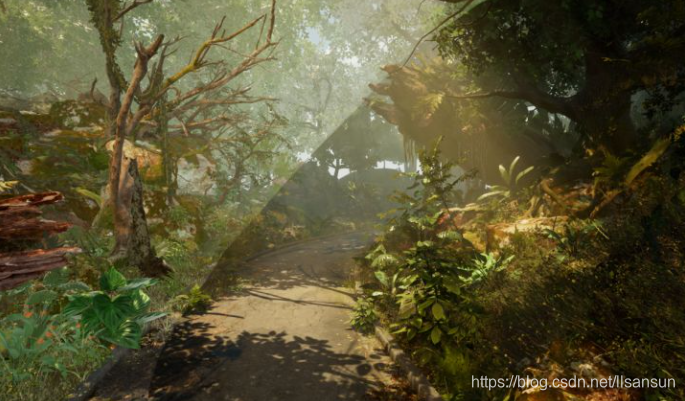

左边的效果是没有ao的,可以看到他的立体感是比较差的,一些应该光照难以照到的位置都是亮的。而右边戴上AO后,他的间接光效果就比较立体了。AO也是全局光照中很重要的一个组成模块。市面上有很多ao的做法,比如贴图ao,ssao,hbao,gtao,dfao等。
而其中dfao就是集成在UE中的基于有号距离场的ao效果。
dfao的优点是:
Dfao通过距离场产生比一般实时屏幕空间ao更加精确的ao效果,
能提供环境光镜面反射的遮挡效果,能提高画面实时效果又不产生太大消耗。
缺点:
Dfao不适合太过精细的物体投影,因为构建dfao大多数时候是物体的一个拟合;
遮蔽效果有时候会覆盖物的光泽;不适合pc以外的主机;会与其他透明效果产生
冲突等等。

他的建场方式:
UE用暴力建场的方法,就是直接迭代32*32*32个点,然后在每个点上向周围发射一大堆光线,然后保存交到的最小距离,作为距离场在这个点上的值。
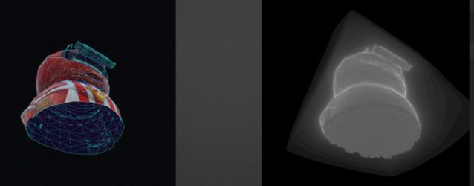

而搜索方面可以用一个kd树来加快搜索速度:
在三维空间中,他是一个根据xyz三个轴来分割所有物体的一个树状结构,他的优势是可以快速找到近邻的物体,他的搜索方式是首先找到树种临近的分叉中的物体,然后再以要找的对象和到这个物体的位置为半径搜索这个半径内的物体是否有更近的。这是因为最近的物体有可能并不在自己这个树的这边,而是在另一边。所以需要这个半径范围再找一遍。
以上就是了解到和自己也实践的一些关于有号距离场的知识,如有问题欢迎指出。











 有号距离场(SDF)是一种在游戏开发中用于表示物体边界和进行碰撞检测、动画、阴影和环境遮蔽的技术。它通过记录每个像素或体素到物体表面的距离,实现平滑放大、形变动画和序列帧过渡。SDF在碰撞检测中,通过射线检测和步进找到碰撞点,提供精确的碰撞信息。此外,SDF还用于生成软阴影和环境遮蔽,提升图形质量。尽管SDF有较高的CPU和内存消耗,但其精确性和效率使其在某些场景中优于传统方法。
有号距离场(SDF)是一种在游戏开发中用于表示物体边界和进行碰撞检测、动画、阴影和环境遮蔽的技术。它通过记录每个像素或体素到物体表面的距离,实现平滑放大、形变动画和序列帧过渡。SDF在碰撞检测中,通过射线检测和步进找到碰撞点,提供精确的碰撞信息。此外,SDF还用于生成软阴影和环境遮蔽,提升图形质量。尽管SDF有较高的CPU和内存消耗,但其精确性和效率使其在某些场景中优于传统方法。
















 2294
2294

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








