主要内容
(1)torch7的安装
(2)torch7的hello-world入门
(3)对抗生成网络torch-gan
......
(1)torch7的安装(centos7测试)
LuaJIT方法安装:
git clone https://github.com/torch/distro.git --recursive
cd torch; bash install-deps;
./install.sh
source ~/.bashrc
Lua5.2方法安装:
git clone https://github.com/torch/distro.git --recursive
cd torch
./clean.sh
TORCH_LUA_VERSION=LUA52 ./install.sh
luarocks install image
luarocks list
luarocks install hdf5
luarocks install matio
luarocks install optnet
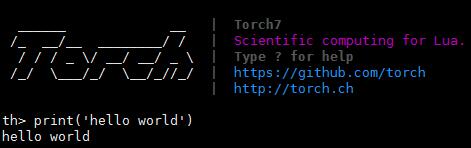
测试安装环境:
th
print('hello world')
自己安装时遇到的问题,没有检测到libmatio.so.2
进入自己的torchroot/install/lib下面发现没有这个动态链接库,
解决方式,源码安装,
下载matio源码包,https://sourceforge.net/projects/matio/,注意要下载的是matio-1.5.2这个版本。
unzip matio-1.5.2.zip
cd matio-1.5.2
./configure
make -j8
make check
make install
#此时会安装在/usr/local/lib下面,
cp /usr/local/lib/libmatio* torchroot/install/lib
问题解决,matio.so.2可以检测到了。
(2)torch7的hello-world入门
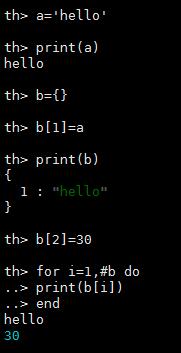
字符串(strings),数字(numbers),tables(表)
a = 'hello'
print(a)
b = {}
b[1] = a
print(b)
b[2] = 30
for i=1,#b do -- the # operator is the length operator in Lua
print(b[i])
end
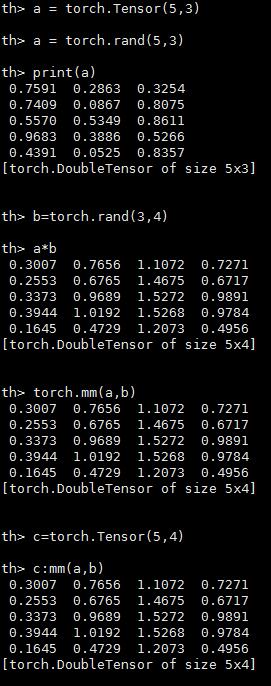
张量(Tensors)
a = torch.Tensor(5,3) -- construct a 5x3 matrix, uninitialized
a = torch.rand(5,3)
print(a)
b=torch.rand(3,4) -- matrix-matrix multiplication: syntax 1
a*b-- matrix-matrix multiplication: syntax 2
torch.mm(a,b)-- matrix-matrix multiplication: syntax 3
c=torch.Tensor(5,4)
c:mm(a,b) -- store the result of a*b in c
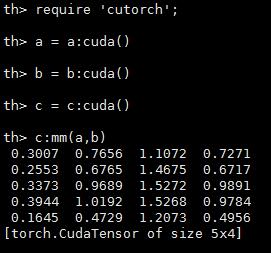
CUDA张量(CUDA Tensors)
require 'cutorch';
a = a:cuda()
b = b:cuda()
c = c:cuda()
c:mm(a,b) -- done on GPU
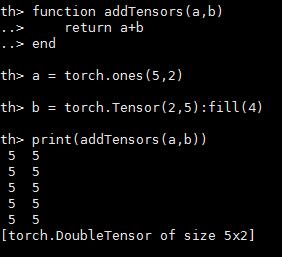
张量相加
function addTensors(a,b)
return a+b
end
a = torch.ones(5,2)
b = torch.Tensor(2,5):fill(4)
print(addTensors(a,b))
神经网络(Neural Networks)
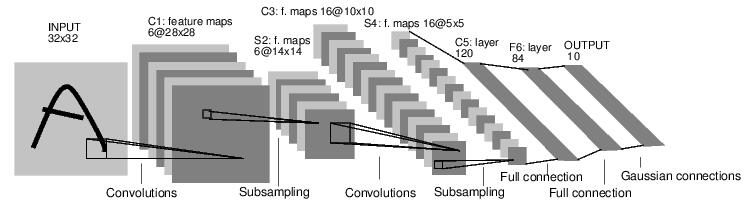
lenet5的网络结构图如下,
torch的神经网络支持线性,级联,并行三种连接方式。这里我们的lenet5采用线性的方式。
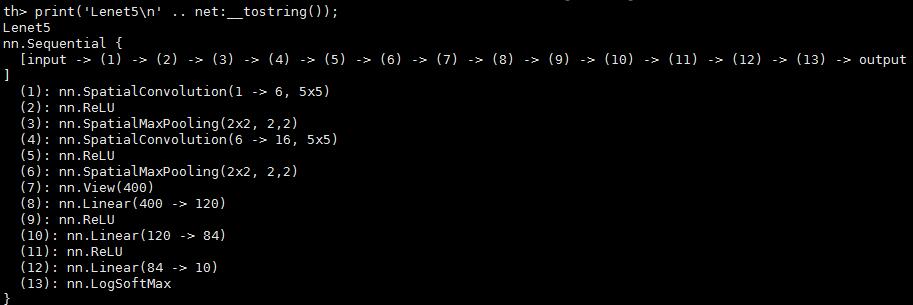
require 'nn';
net = nn.Sequential()
net:add(nn.SpatialConvolution(1, 6, 5, 5)) -- 1 input image channel, 6 output channels, 5x5 convolution kernel
net:add(nn.ReLU()) -- non-linearity
net:add(nn.SpatialMaxPooling(2,2,2,2)) -- A max-pooling operation that looks at 2x2 windows and finds the max.
net:add(nn.SpatialConvolution(6, 16, 5, 5))
net:add(nn.ReLU()) -- non-linearity
net:add(nn.SpatialMaxPooling(2,2,2,2))
net:add(nn.View(16*5*5)) -- reshapes from a 3D tensor of 16x5x5 into 1D tensor of 16*5*5
net:add(nn.Linear(16*5*5, 120)) -- fully connected layer (matrix multiplication between input and weights)
net:add(nn.ReLU()) -- non-linearity
net:add(nn.Linear(120, 84))
net:add(nn.ReLU()) -- non-linearity
net:add(nn.Linear(84, 10)) -- 10 is the number of outputs of the network (in this case, 10 digits)
net:add(nn.LogSoftMax())
print('Lenet5\n' .. net:__tostring());
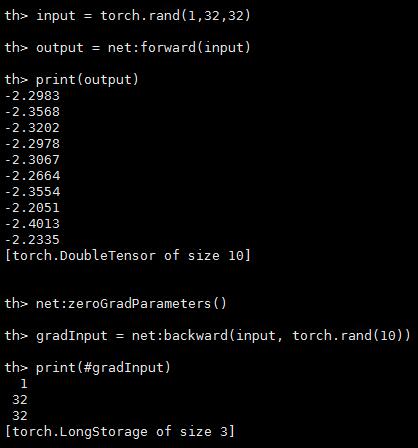
input = torch.rand(1,32,32) -- pass a random tensor as input to the network
output = net:forward(input)
print(output)
net:zeroGradParameters() -- zero the internal gradient buffers of the network (will come to this later)
gradInput = net:backward(input, torch.rand(10))
print(#gradInput)
损失函数(loss function)
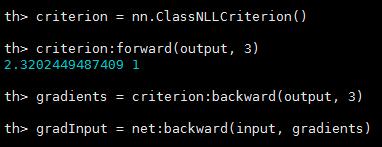
criterion = nn.ClassNLLCriterion() -- a negative log-likelihood criterion for multi-class classification
criterion:forward(output, 3) -- let's say the groundtruth was class number: 3
gradients = criterion:backward(output, 3)
gradInput = net:backward(input, gradients)
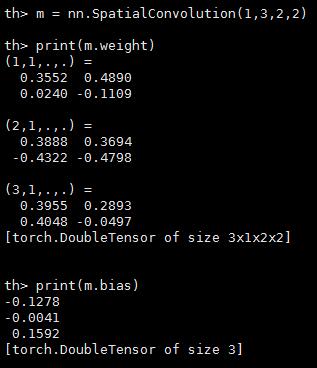
查看学习到的权值(weights)和偏差(bias),其中,权值weights的跟新策略为weight = weight + learningRate * gradWeight
m = nn.SpatialConvolution(1,3,2,2) -- learn 3 2x2 kernels
print(m.weight) -- initially, the weights are randomly initialized
print(m.bias) -- The operation in a convolution layer is: output = convolution(input,weight) + bias
训练神经网络(cifar-10)
cifar-10是加拿大研究院开源的一个数据集,包含10类目标,大小为32*32*3
整体流程分为下面几步
<1>导入数据,并且做归一化处理(减均值,除标准差)
<2>定义网络结构
<3>定义损失函数
<4>训练网络
<5>测试训练结果
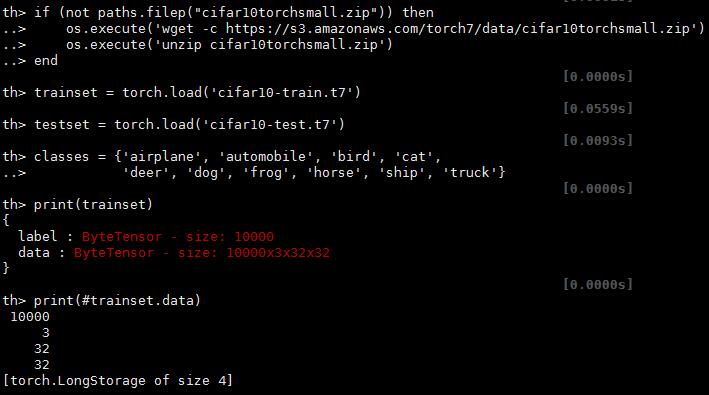
<1>下载数据,归一化处理
require 'paths'
if (not paths.filep("cifar10torchsmall.zip")) then
os.execute('wget -c https://s3.amazonaws.com/torch7/data/cifar10torchsmall.zip')
os.execute('unzip cifar10torchsmall.zip')
end
trainset = torch.load('cifar10-train.t7')
testset = torch.load('cifar10-test.t7')
classes = {'airplane', 'automobile', 'bird', 'cat',
'deer', 'dog', 'frog', 'horse', 'ship', 'truck'}
print(trainset)
print(#trainset.data)
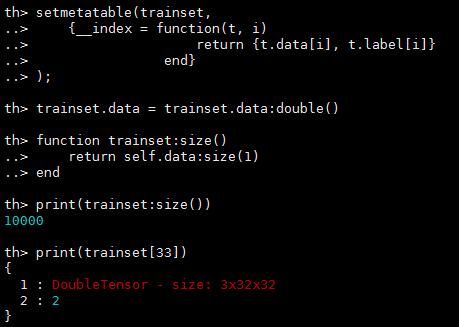
定义一个可以返回图片和标签的函数
setmetatable(trainset,
{__index = function(t, i)
return {t.data[i], t.label[i]}
end}
);
trainset.data = trainset.data:double() -- convert the data from a ByteTensor to a DoubleTensor.
function trainset:size()
return self.data:size(1)
end
print(trainset:size())
print(trainset[33]) -- load sample number 33.
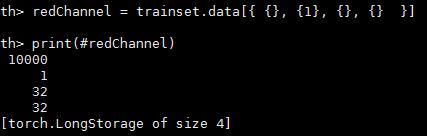
获取图片数据的红色通道
redChannel = trainset.data[{ {}, {1}, {}, {} }] -- this picks {all images, 1st channel, all vertical pixels, all horizontal pixels}
print(#redChannel)
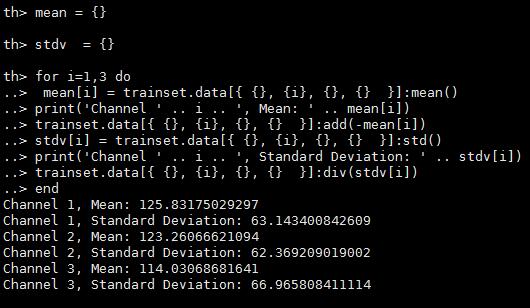
减均值和归一化操作
mean = {} -- store the mean, to normalize the test set in the future
stdv = {} -- store the standard-deviation for the future
for i=1,3 do -- over each image channel
mean[i] = trainset.data[{ {}, {i}, {}, {} }]:mean() -- mean estimation
print('Channel ' .. i .. ', Mean: ' .. mean[i])
trainset.data[{ {}, {i}, {}, {} }]:add(-mean[i]) -- mean subtraction
stdv[i] = trainset.data[{ {}, {i}, {}, {} }]:std() -- std estimation
print('Channel ' .. i .. ', Standard Deviation: ' .. stdv[i])
trainset.data[{ {}, {i}, {}, {} }]:div(stdv[i]) -- std scaling
end
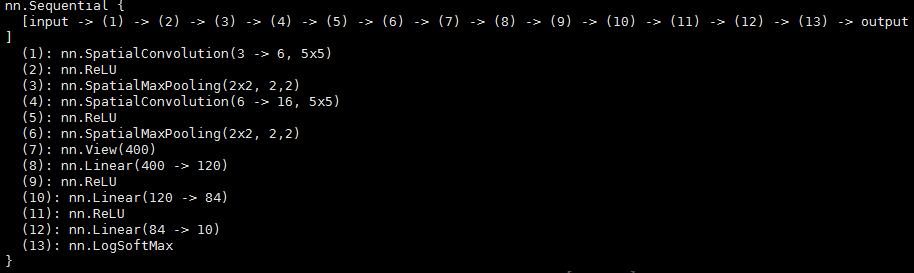
<2>定义一个神经网络,这里使用的还是lenet5
net = nn.Sequential() net:add(nn.SpatialConvolution(3, 6, 5, 5)) -- 3 input image channels, 6 output channels, 5x5 convolution kernel
net:add(nn.ReLU()) -- non-linearity
net:add(nn.SpatialMaxPooling(2,2,2,2)) -- A max-pooling operation that looks at 2x2 windows and finds the max.
net:add(nn.SpatialConvolution(6, 16, 5, 5))
net:add(nn.ReLU()) -- non-linearity
net:add(nn.SpatialMaxPooling(2,2,2,2))
net:add(nn.View(16*5*5)) -- reshapes from a 3D tensor of 16x5x5 into 1D tensor of 16*5*5 net:add(nn.Linear(16*5*5, 120)) -- fully connected layer (matrix multiplication between input and weights)
net:add(nn.ReLU()) -- non-linearity
net:add(nn.Linear(120, 84))
net:add(nn.ReLU()) -- non-linearity
net:add(nn.Linear(84, 10)) -- 10 is the number of outputs of the network (in this case, 10 digits) net:add(nn.LogSoftMax()) -- converts the output to a log-probability. Useful for classification problems
<3>定义损失函数
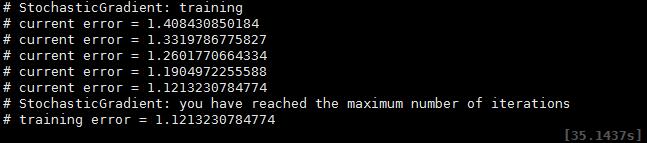
criterion = nn.ClassNLLCriterion()<4>训练神经网络(cpu训练7700)
trainer = nn.StochasticGradient(net, criterion)
trainer.learningRate = 0.001
trainer.maxIteration = 5 -- just do 5 epochs of training.
trainer:train(trainset)
<5>测试网络训练,输出准确性
测试集的减均值和归一化处理
testset.data = testset.data:double() -- convert from Byte tensor to Double tensor
for i=1,3 do -- over each image channel
testset.data[{ {}, {i}, {}, {} }]:add(-mean[i]) -- mean subtraction
testset.data[{ {}, {i}, {}, {} }]:div(stdv[i]) -- std scaling
end
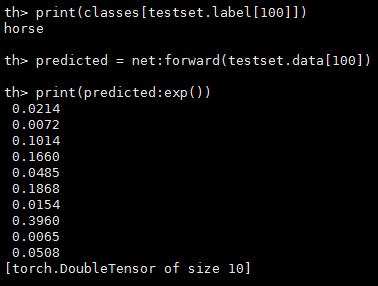
随便测试一下第100张图片是否分类正确,并且输出分数
print(classes[testset.label[100]])
predicted = net:forward(testset.data[100])
-- the output of the network is Log-Probabilities. To convert them to probabilities, you have to take e^x
print(predicted:exp())
输出测试集上的准确性
correct = 0
for i=1,10000 do
local groundtruth = testset.label[i]
local prediction = net:forward(testset.data[i])
local confidences, indices = torch.sort(prediction, true) -- true means sort in descending order
if groundtruth == indices[1] then
correct = correct + 1
end
end
print(correct, 100*correct/10000 .. ' % ')
输出测试集上的准确性和类别
class_performance = {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
for i=1,10000 do
local groundtruth = testset.label[i]
local prediction = net:forward(testset.data[i])
local confidences, indices = torch.sort(prediction, true) -- true means sort in descending order
if groundtruth == indices[1] then
class_performance[groundtruth] = class_performance[groundtruth] + 1
end
end
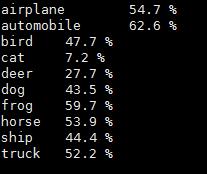
for i=1,#classes do
print(classes[i], 100*class_performance[i]/1000 .. ' %')
end
<6>使用cuda进行训练,大大加速训练过程(TitanX),可以看到速度提高了22.88倍
require 'cunn';
net = net:cuda()
criterion = criterion:cuda()
trainset.data = trainset.data:cuda()
trainset.label = trainset.label:cuda()
trainer = nn.StochasticGradient(net, criterion)
trainer.learningRate = 0.001
trainer.maxIteration = 5 -- just do 5 epochs of training.
trainer:train(trainset)
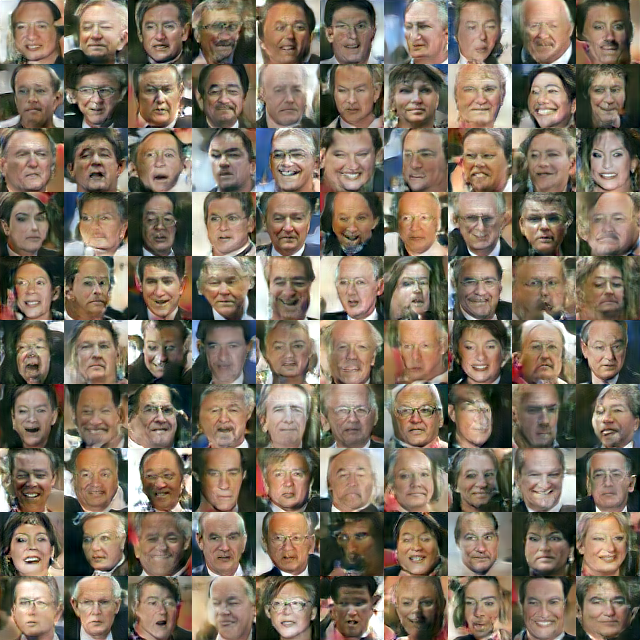
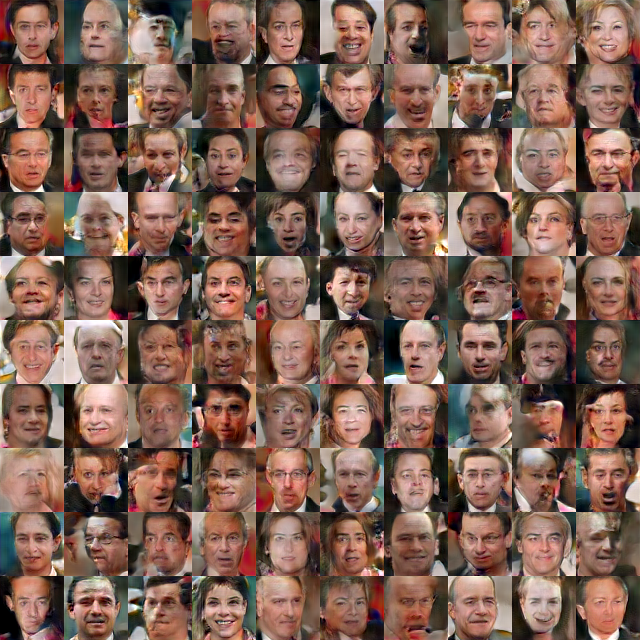
(3)对抗生成网络torch-gan
git clone https://github.com/skaae/torch-gan.git
th train_lfw.lua -g 0 --K 10
然后就可以静静的等待结果了。
reference:
https://github.com/soumith/cvpr2015/blob/master/Deep%20Learning%20with%20Torch.ipynb
































 848
848











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








